2000 MITSUBISHI MONTERO oil pressure
[x] Cancel search: oil pressurePage 56 of 1839

11A-2
ENGINE <6G7>
CONTENTS
GENERAL INFORMATION 3..................
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 3.................
SEALANT 4..................................
SPECIAL TOOLS 4..........................
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE 6.....................
Drive Belt Tension Check and Adjustment 6......
Auto-tensioner Check 6.........................
Ignition Timing Check 6........................
Idle Speed Check 7............................
Idle Mixture Check 8...........................Compression Pressure Check 9.................
Intake Manifold Vacuum Check 10...............
Lash Adjuster Check 10........................
OIL PAN AND OIL SCREEN 13..............
TIMING BELT 15............................
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL 23.................
CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL 25...................
CYLINDER HEAD GASKET 27...............
ENGINE ASSEMBLY 30.....................
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 88 of 1839

11B-1
ENGINE <4D5>
CONTENTS
GENERAL INFORMATION 2..................
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 3.................
SEALANTS 3................................
SPECIAL TOOLS 4..........................
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE 5.....................
Drive Belt Tension Check and Adjustment 5......
Auto-tensioner check 7.........................
Valve Clearance Check and Adjustment 8........
Injection Timing Check and Adjustment 9........
Idle Speed Check and Adjustment 12............
Idle-up Mechanism Check and
Adjustment-For A/C 12.........................Compression Pressure Check 13................
Timing Belt Tension Adjustment 14..............
Timing Belt B Tension Adjustment 15............
OIL PAN AND OIL SCREEN 17..............
TIMING BELT AND TIMING BELT B 19......
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL 25.................
CAMSHAFT AND CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL 27..
CYLINDER HEAD GASKET 30...............
ENGINE ASSEMBLY 34.....................
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 90 of 1839

ENGINE <4D5> -Service Specifications/Sealants11B-3
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS
ItemsStandard valueLimit
A/C compressor drive beltVibration frequency Hz157 - 176–
(When inspection)Tension N260 - 325–
Deflection mm
A/C compressor drive beltVibration frequency Hz157 - 176–
(When adjustment)Tension N260 - 325–
Deflection mm
A/C compressor drive beltVibration frequency Hz192 - 208–
(When replacement)Tension N390 - 450–
Deflection mm
Valve clearance (at hot) mm0.25-
Injection timing (Value indicated on dial gauge mm)9_ATDC (1±0.03)-
Idle speed r/min750±100-
Compression pressure kPa (at engine speed of 280 r/min)3,040Min. 2,256
Compression pressure difference of all cylinder (at engine speed of 280
r/min) kPa-Max. 294
Timing belt tension mm4-5
Timing belt B tension mm4-5
SEALANTS
ItemsSpecified sealantRemarks
Oil panMITSUBISHI GENUINE PART
MD970389 or equivalentSemi-drying sealant
Semi-circular packing and rocker
cover gasket seal, and cylinder head
seal3M ATD Part No. 8660 or equivalent
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 142 of 1839

11C-1
ENGINE <4M4>
CONTENTS
GENERAL INFORMATION 2..................
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 2.................
SEALANTS AND ADHESIVES 3..............
SPECIAL TOOLS 3..........................
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE 5.....................
Drive Belt Tension Check and Adjustment 5......
Valve Clearance Check and Adjustment 8........
Injection Timing Check and Adjustment 9........
Idle Speed Check 12...........................Compression Pressure Check 12................
OIL PAN 14.................................
VACUUM PUMP 16..........................
TIMING CHAIN 17...........................
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL 21.................
CAMSHAFT 23..............................
CYLINDER HEAD GASKET 27...............
ENGINE ASSEMBLY 33.....................
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 154 of 1839

ENGINE <4M4> -On-vehicle Service11C-13
8. If there is a cylinder which compression or compression
difference is outside the limit, pour a small amount of
engine oil through the glow plug hole, and repeat the
operations in steps 6 - 7.
(1) If the compression increases after the oil is added,
the cause of the malfunction is a worn or damaged
piston ring and /or cylinder inner surface.
(2) If the compression does not rise after the oil is added,
the cause is a burnt or defective valve seat, or pressure
is leaking from the gasket.
9. Connect the fuel cut solenoid valve connector.
10. Install the glow plugs.
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 202 of 1839

12-1
ENGINE
LUBRICATION
CONTENTS
GENERAL INFORMATION 2..................
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 3.................
SEALANT 3..................................
LUBRICANTS 3..............................
SPECIAL TOOLS 3..........................ON-VEHICLE SERVICE 4.....................
Engine Oil Check 4............................
Engine Oil Replacement 4......................
Oil Filter Replacement 5........................
Oil Pressure Check 6..........................
ENGINE OIL COOLER 9.....................
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 217 of 1839

GDI -General Information13A-3
GENERAL INFORMATION
The Gasoline Direct Injection System consists
of sensors which detect the engine conditions,
the engine-ECU
which controls the system based on
signals from these sensors, and actuators
which operate under the control of the
engine-ECU
carries out activities such as fuel injection
control, idle speed control and ignition timing
control. In addition, the engine-ECU
engine-A/T-ECU is equipped with several
diagnosis modes which simplify troubleshooting
when a problem develops.
FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
The injector drive times and injector timing are
controlled so that the optimum air/fuel mixture
is supplied to the engine to correspond to the
continually-changing engine operation condi-
tions.
A single injector for each cylinder is mounted
at the cylinder head. The fuel is sent under
pressure from the fuel tank to the fuel pressure
regulator (low pressure) by the fuel pump (low
pressure). The pressure is regulated by the
fuel pressure regulator (low pressure) and the
fuel regulated is then sent to the fuel pump
(high pressure). The fuel under increased
pressure generated by the fuel pump (high
pressure) is then regulated by the fuel pressure
regulator (high pressure) and is then distributed
to each of the injectors via the delivery pipes.Fuel injection is normally carried out once for
each cylinder for every two rotations of the
crankshaft. The firing order is 1-2-3-4-5-6. This
is called sequential fuel injection.
When the engine is cold or under a severe
load, the “open-loop” control keeps the air/fuel
ratio at a richer than usual level to maintain
driveability. When the engine is under low or
medium loads, the air/fuel ratio becomes leaner
to reduce fuel consumption. When the engine
is running at medium or high loads after having
warmed up, the “closed-loop” control uses the
signal from the oxygen sensor to keep the
air/fuel ratio at the optimum theoretical level.
THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CONTROL
This system controls throttle valve opening
angle electronically. The engine-ECU
or engine-A/T-ECU determines how
deeply the accelerator pedal is depressed by
means of the accelerator position sensor (APS).
Then the engine-ECU
throttle valve opening angle to the throttle valve
controller. The throttle valve control servo
operates the throttle valve so that it reaches
the target opening angle.
IDLE SPEED CONTROL
This system maintains engine idle speed at
a predetermined condition by controlling the
air flow that passes through the throttle valve
according to engine idling condition and engine
loads at idling.
The engine-ECU
operates the throttle valve control servoso that engine speed is maintained within a
map value. The map value is predetermined
according to engine coolant temperature and
air-conditioning load.
IGNITION TIMING CONTROL
The power transistor located in the ignition
primary circuit turns ON and OFF to control
the primary current flow to the ignition coil. This
controls the ignition timing in order to provide
the optimum ignition timing with respect to the
engine operating conditions. The ignition timingis determined by the engine-ECU
engine-A/T-ECU from the engine speed,
intake air volume, engine coolant temperature,
atmospheric pressure and injection timing
(intake stroke or compression stroke).
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 227 of 1839
GDI -Troubleshooting
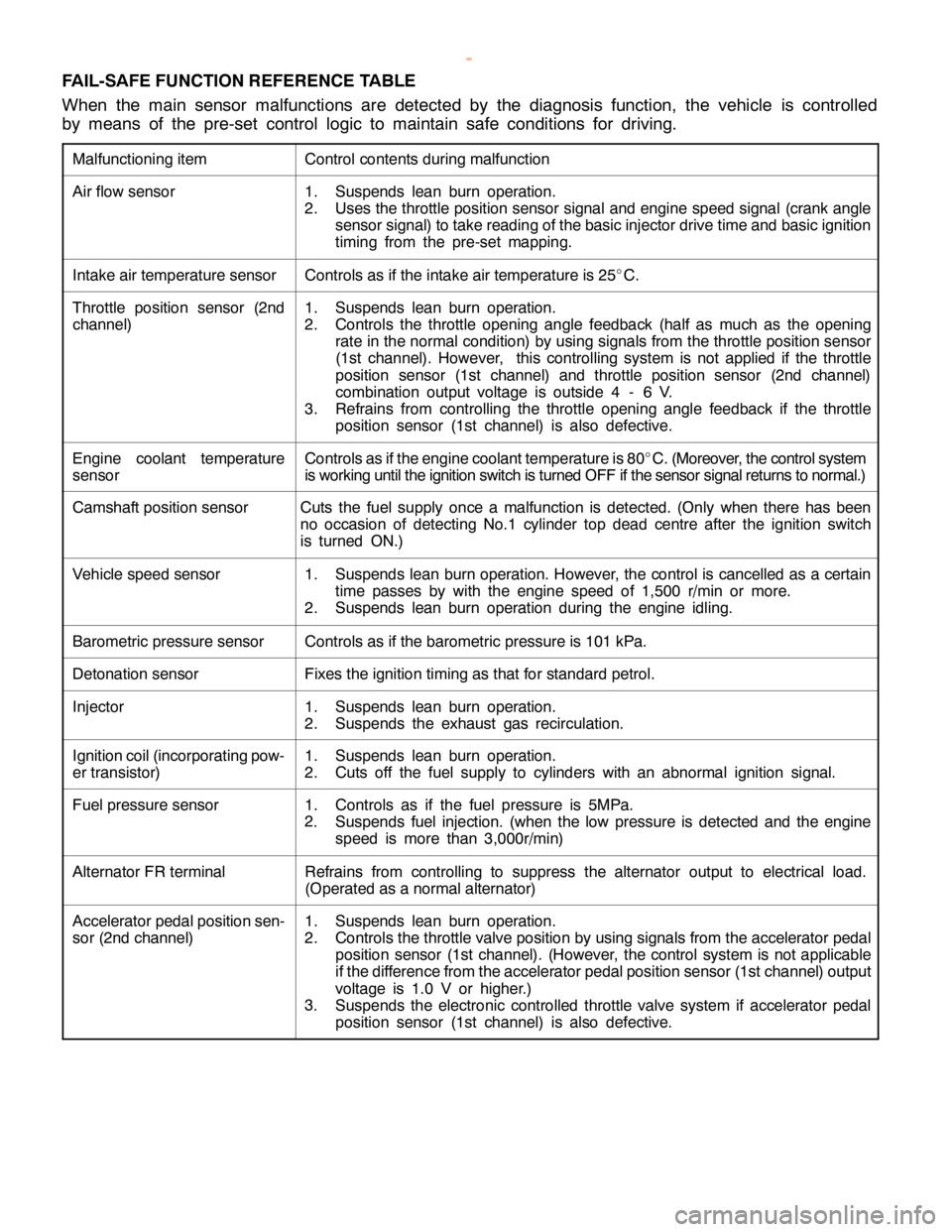
FAIL-SAFE FUNCTION REFERENCE TABLE
When the main sensor malfunctions are detected by the diagnosis function, the vehicle is controlled
by means of the pre-set control logic to maintain safe conditions for driving.
Malfunctioning itemControl contents during malfunction
Air flow sensor1. Suspends lean burn operation.
2. Uses the throttle position sensor signal and engine speed signal (crank angle
sensor signal) to take reading of the basic injector drive time and basic ignition
timing from the pre-set mapping.
Intake air temperature sensorControls as if the intake air temperature is 25_
C.
Throttle position sensor (2nd
channel)1. Suspends lean burn operation.
2. Controls the throttle opening angle feedback (half as much as the opening
rate in the normal condition) by using signals from the throttle position sensor
(1st channel). However, this controlling system is not applied if the throttle
position sensor (1st channel) and throttle position sensor (2nd channel)
combination output voltage is outside 4 - 6 V.
3. Refrains from controlling the throttle opening angle feedback if the throttle
position sensor (1st channel) is also defective.
Engine coolant temperature
sensorControls as if the engine coolant temperature is 80_
C. (Moreover, the control system
is working until the ignition switch is turned OFF if the sensor signal returns to normal.)
Camshaft position sensorCuts the fuel supply once a malfunction is detected. (Only when there has been
no occasion of detecting No.1 cylinder top dead centre after the ignition switch
is turned ON.)
Vehicle speed sensor1. Suspends lean burn operation. However, the control is cancelled as a certain
time passes by with the engine speed of 1,500 r/min or more.
2. Suspends lean burn operation during the engine idling.
Barometric pressure sensorControls as if the barometric pressure is 101 kPa.
Detonation sensorFixes the ignition timing as that for standard petrol.
Injector1. Suspends lean burn operation.
2. Suspends the exhaust gas recirculation.
Ignition coil (incorporating pow-
er transistor)1. Suspends lean burn operation.
2. Cuts off the fuel supply to cylinders with an abnormal ignition signal.
Fuel pressure sensor1. Controls as if the fuel pressure is 5MPa.
2
. Suspends fuel injection. (when the low pressure is detected and the engine
speed is more than 3,000r/min)
Alternator FR terminalRefrains from controlling to suppress the alternator output to electrical load.
(Operated as a normal alternator)
Accelerator pedal position sen-
sor (2nd channel)1. Suspends lean burn operation.
2. Controls the throttle valve position by using signals from the accelerator pedal
position sensor (1st channel). (However, the control system is not applicable
if the difference from the accelerator pedal position sensor (1st channel) output
voltage is 1.0 V or higher.)
3
. Suspends the electronic controlled throttle valve system if accelerator pedal
position sensor (1st channel) is also defective.
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk