1999 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 1230 of 1529
AIR CONDITIONING
REPAIRS 82-41
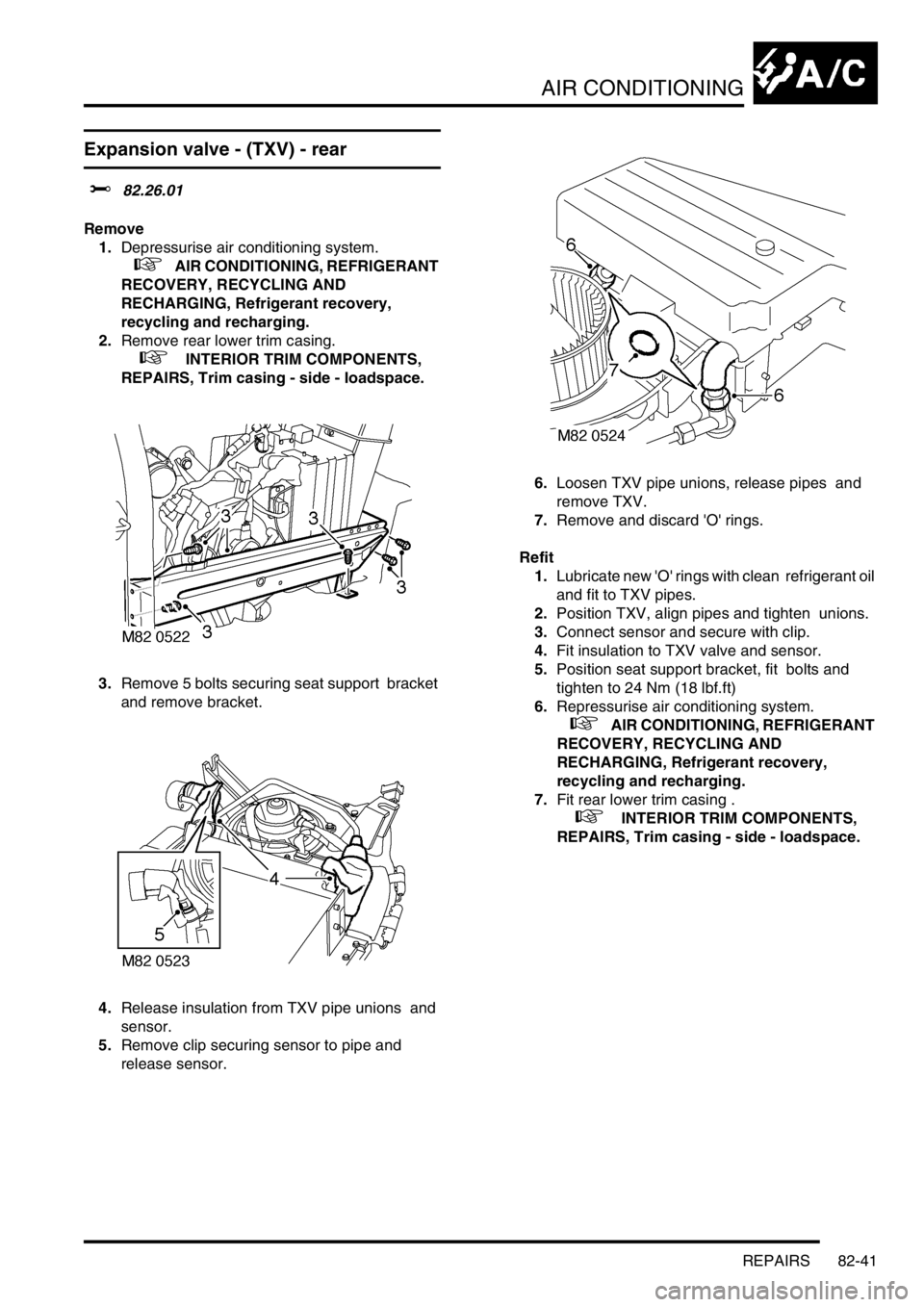
Expansion valve - (TXV) - rear
$% 82.26.01
Remove
1.Depressurise air conditioning system.
+ AIR CONDITIONING, REFRIGERANT
RECOVERY, RECYCLING AND
RECHARGING, Refrigerant recovery,
recycling and recharging.
2.Remove rear lower trim casing.
+ INTERIOR TRIM COMPONENTS,
REPAIRS, Trim casing - side - loadspace.
3.Remove 5 bolts securing seat support bracket
and remove bracket.
4.Release insulation from TXV pipe unions and
sensor.
5.Remove clip securing sensor to pipe and
release sensor. 6.Loosen TXV pipe unions, release pipes and
remove TXV.
7.Remove and discard 'O' rings.
Refit
1.Lubricate new 'O' rings with clean refrigerant oil
and fit to TXV pipes.
2.Position TXV, align pipes and tighten unions.
3.Connect sensor and secure with clip.
4.Fit insulation to TXV valve and sensor.
5.Position seat support bracket, fit bolts and
tighten to 24 Nm (18 lbf.ft)
6.Repressurise air conditioning system.
+ AIR CONDITIONING, REFRIGERANT
RECOVERY, RECYCLING AND
RECHARGING, Refrigerant recovery,
recycling and recharging.
7.Fit rear lower trim casing .
+ INTERIOR TRIM COMPONENTS,
REPAIRS, Trim casing - side - loadspace.
Page 1288 of 1529

BODY CONTROL UNIT
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-3-1
BODY CONTROL UNIT DESCRIPTION AND OPERAT ION
Description
General
The Body Control Unit (BCU) is located behind the passenger glovebox and is connected to the main harness by four
connectors on its bottom edge and an additional connector located on the side of the BCU casing. Mounting the BCU
behind the fascia makes it reasonably inaccessible for intruders to disable the anti-theft system.
The BCU uses solid-state microprocessor control to perform logical operations and timing functions for a variety of
the vehicle's electrically operated systems, these include:
lDoor locking.
lAnti-theft alarm and immobilisation system.
lExterior lighting including direction indicators and hazard warning lamps.
lCourtesy lighting.
lWipers and washers.
lElectric windows and sunroof.
lHeated windows.
The BCU also communicates with several other electronically controlled systems such as the EAT ECU and SLABS
ECU and also has a datalink between the Intelligent Driver Module (IDM) and the instrument pack. The datalink is a
low speed bus capable of transmitting and receiving messages at a data rate of 10,400 bits per second. Additional
inputs and outputs to peripheral devices are included which are necessary for determining vehicle status for particular
logical operations e.g. crank, ignition key inserted, fuel flap enable etc.
The BCU receives its power supply from the engine compartment fuse box, and is protected by a 10 A fuse.
The BCU communicates with the IDM to provide the control signals to perform power switching operations in
conjunction with dedicated relays.
IDM
The IDM is integrated into the passenger compartment fuse box, which is mounted behind the fascia below the
steering column. There are no harnesses between the fuse box and the IDM. The IDM performs the power switching
operations for several of the vehicle's electrical systems.
The IDM communicates with the BCU and the instrument pack via a serial interface. If the BCU or the IDM is replaced,
the communications link between the two units has to be re-established. This can be done either by switching on the
ignition and leaving it on for five minutes, or by using TestBook. The vehicle immobilisation will remain active until the
communications link between the BCU and IDM has been re-established.
Transit mode
To prevent excessive battery drain during transit to overseas markets, the vehicle is placed in a transit mode. The
following functions are disabled when the vehicle is in transit mode:
lVolumetric sensors.
lPassive immobilisation.
lImmobilisation of the vehicle by use of door lock.
lIgnition key interlock.
lElectric seat enable time-out with driver's door open.
Page 1289 of 1529

BODY CONTROL UNIT
86-3-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Power supply
Battery supply to the BCU and the IDM is provided through a 10 A fuse located in the engine compartment fuse box.
The BCU unit receives an ignition switched power supply (ignition switch position II) input via a 10 A fuse in the
passenger compartment fuse box.
The BCU receives a signal when the ignition switch is turned to the crank position, it then supplies an earth path to
the starter relay coil, to enable the crank operation by supplying power through the starter relay contacts to the starter
motor.
Battery voltage is monitored and BCU operation will function normally between 8 and 18 volts. Between 5.7 and 8
volts the BCU is in the 'under volts' state. The status of the battery is used to determine which outputs may be driven.
If a voltage supply above 18 volts is experienced, outputs will not normally be driven except for those functions which
are required during cranking (robust immobilisation, antenna coil, crank enable relay and feed to gear position switch
contacts W, X, Y, Z). In the over voltage state the vehicle can be driven, but all other functions are disabled and
outputs are switched off (power windows, heated screen, direction indicators etc.).
All functions are disabled on power up until communications between the BCU and IDM have been established. If
communications cannot be established, operation will commence with degraded functionality.
Battery supply to the IDM is provided through the inertia switch and a 10 A fuse in the engine compartment fuse box.
If the inertia switch contacts are closed battery voltage is available at the IDM; if the inertia switch contacts are open
there is no battery supply to the IDM. The supply condition of the IDM is signalled to the BCU via the serial bus. If the
inertia switch is operated (contacts open) the change in state is detected by the BCU which unlocks the doors if the
ignition switch is in position II and the alarm is not set.
The BCU is earthed through a hard-wire connection.
Inputs and outputs
The BCU and IDM process inputs and provide the necessary outputs for control and operation of the vehicle's 'body'
systems.
BCU inputs
The BCU processes signals received from the following components:
lDoor latch switches.
lDriver's door key lock/ unlock switches.
lBonnet activated security system.
lVolumetric sensors.
lCentral Door Locking (CDL) switches.
lRemote transmitter (via receiver unit).
lInertia fuel cut-off switch.
lIgnition switch.
lFuel flap release switch.
The input voltages (V
in) for BCU digital signals are defined as follows:
lLogic 1 when V
in ≥ 6V.
lLogic 0 when V
in ≤ 2V.
BCU input voltages between 2 and 6 volts are indeterminate and cannot be guaranteed.
Analogue input voltages are measured as a ratio with respect to battery voltage.
Page 1304 of 1529

BODY CONTROL UNIT
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-3-17
The existence of an intermediate state causes a fault code to be detected by the BCU. To reduce the chances of the
fault condition occurring while changing selector lever position, the inputs are debounced and only considered valid
when they have existed for at least 33 ms.
Transmission neutral selector
The transmission neutral sensor provides an earth signal to the BCU when the transfer box is in neutral. The earth
signal causes the BCU to operate an audible warning when the transfer box is in neutral with the ignition switched on.
+ TRANSFER BOX - LT230SE, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Self levelling suspension and ABS
The BCU communicates with the SLABS ECU for several functions:
lAn output is provided from the SLABS ECU to the BCU to provide the logic conditions for issuing the SLS audible
warning.
lThe BCU receives an input from the SLABS ECU relating to the raise/ lower command from the remote handset.
+ REAR SUSPENSION, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - SLS.
Hill descent control
The BCU provides an output signal to the SLABS ECU for automatic transmission in neutral for HDC control. The
BCU checks the status of the ignition and 'gearbox state' inputs and provides a 'Neutral selected' output. If the ignition
is on and 'gearbox state' is Neutral, the 'Neutral selected' output is on, otherwise 'Neutral selected' is off.
+ BRAKES, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Heated screens
The Heated Front Screen (HFS) is fitted for some market destinations and is operated from a non-latching switch
located on the instrument pack cowl. The BCU will only allow the heated front screen to operate when the engine is
running and controls the time-out period for switching the circuit off.
The heated front screen operation can also be controlled from the Automatic Temperature Control (ATC) ECU on
vehicles fitted with air conditioning.
The heated rear window will only function when the engine is running, and is operated by a non-latching switch on the
instrument pack cowl. The heated rear window can also be operated by the ATC ECU on vehicles fitted with air
conditioning.
Interior courtesy lamps
The BCU controls the operation of the interior courtesy lamps. The courtesy lamps are situated in the front, mid and
rear areas of the headlining.
Fuel flap actuator
The BCU provides an earth path to the fuel flap release solenoid to allow the fuel filler flap to be opened. This is only
allowed if the alarm system is not set and all other conditions have been satisfied. The fuel flap release switch is
located in the fascia switch pack on vehicles up to 2003 model year or in the instrument pack binacle on vehicles from
2003 model year. The switch receives a voltage supply from the passenger compartment fuse box.
Page 1306 of 1529

BODY CONTROL UNIT
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-3-19
Operation
For IDM inputs which are also inputs for BCU functions, the delay before the BCU recognises the change in input
status is less than 250 ms. The BCU uses a debounce algorithm to ignore changes in input having a duration less
than 100 ms with the exception of automatic gearbox W, X, Y, Z inputs, which have a debounce period of 33 ms.
Transit mode
To prevent excessive battery drain during transit to overseas markets, the vehicle is placed in a transit mode.
To exit the transit mode, simultaneously hold down the heated rear window switch and the rear fog lamp switch, turn
the ignition switch from 0 to II and, after a minimum of 2 seconds, release the switches.
Transit mode can be entered using TestBook. When TestBook communicates with the BCU for diagnostics related to
BCU operation, it first checks that the vehicle is not in transit mode.
Anti-theft system
The BCU uses the driver's door key lock and unlock switches to activate and deactivate the security system. The
driver's door lock is also used for entering the EKA.
+ ALARM SYSTEM AND HORN, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Immobilisation
For immobilisation, the BCU disables the starter motor relay. When the engine is cranking, the ECM looks for a coded
signal from the BCU. If the signal is not received within one second of cranking, the fuel supply to the engine is
stopped and the injectors are disabled. This also prevents unburnt fuel from entering the catalyst.
If the BCU is disconnected, the engine starter motor will remain isolated by the starter motor relay and the ECM will
remain immobilised. The main wiring for the system is contained within the main harness which is relatively
inaccessible, so preventing intruders from disabling the system by cutting the wires for the immobilisation system.
Once the immobiliser has been activated, destruction of the trigger device or the wiring to it will not disarm the system.
The RF transmitter communicates to the BCU via the RF receiver using a 70 bit code. Pressing the unlock button on
the transmitter will re-mobilise the vehicle. The RF transponder is integrated into the metal key assembly, inserting
the key into the ignition switch will induce a signal in the exciter coil to re-mobilise the vehicle.
Anti-theft alarm
The alarm system provides a warning of unauthorised access to the vehicle and includes perimetric and volumetric
monitoring under the control of the BCU.
The perimetric protection system detects opening of all doors, tail door and bonnet and will also detect the operation
of the ignition key switch. The following conditions must be satisfied before the BCU will operate all of the functions
of perimetric protection:
lAll doors and hinged panels are in the closed position.
lIgnition key out of the ignition switch.
lInertia switch is not tripped.
If all conditions are not satisfied the BCU will enter a mislock condition.
The volumetric sensor uses two ultrasonic sensors mounted in the headlining to detect movement within the vehicle.
The alarm will trigger when the sensor signals the BCU for 200 ms or greater. Within a single setting period the alarm
system will allow a maximum of 10 triggers as a result of any combination of sensor inputs. It is possible to lock the
vehicle without enabling the volumetric alarm by using the key. The same conditions needed to satisfy enabling of the
perimetric protection system is also needed to enable volumetric protection.
When the alarm system is set the BCU checks the status of all the inputs from the door and bonnet switches to ensure
the integrity of the vehicle before setting the alarm system into operational mode. In some markets, when the alarm
is set the BCU sends a signal to the IDM which will cause the direction indicators to flash three times for a duration of
3 seconds.
If the sensors are triggered the BCU will activate an alarm sounder to provide an audible warning of a theft attempt.
The activation period of the alarm sounder is 25 to 30 seconds. The duty cycle of the alarm sounder is 50:50 ± 10%.
Page 1307 of 1529

BODY CONTROL UNIT
86-3-20 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
In some markets, when the alarm is triggered the BCU also activates the direction indicators, in phase with the audible
warning, to provide an optical warning of a theft attempt. The activation period of the optical alarm is 25 to 30 seconds.
The duty cycle of the optical warning is 50:50 ± 10%.
The alarm system relies upon the vehicle battery for power. However, the BCU remembers the status of the security
system if it loses battery supply. If the security system was in a set condition when battery supply was lost the BCU
will trigger the alarm and initiate a visual warning by flashing the hazard lamps when the battery voltage is restored.
On vehicles with a BBUS fitted, the BBUS will sound if the battery is disconnected while the alarm system is set.
Door switches
The BCU uses the door latch switches to indicate if a door is open or closed. The BCU provides power to all door latch
switches; the switches are in the 'normally open' condition when the doors are shut. When a door is opened, the door
switch contacts are closed and the circuit is earthed, signalling a change in state to the BCU. All doors except the
driver's doors are connected in parallel, so the BCU will recognise a passenger door has been opened but will not be
able to distinguish which one. The driver's door has a dedicated signal line which enables the BCU to detect if the
driver's door has been opened or closed.
Door lock actuators
The CDL system has the facility to enable superlocking. All door lock actuators are controlled by the BCU via the IDM.
The driver's door is controlled separately from all other doors, enabling functions like single point entry and key
access.
Driver's door key lock and unlock switches
The BCU uses the driver's door key lock and unlock switches to activate and deactivate the security system. The
driver's door lock is also used for entering the EKA code.
Two separate switches are incorporated into the key lock assembly of the driver's door. The switches are normally
open and the BCU provides a separate power supply to each. The BCU is signalled when a circuit is earthed enabling
it to determine the direction in which the lock has been turned.
Bonnet switch
The bonnet switch is powered from the BCU and is used as a logical input for operation of the security system. The
switch is normally open with the bonnet closed, when the bonnet is opened the switch contacts close to complete a
circuit to earth and signal the change in state to the BCU.
Key-in sensor
When the ignition key is inserted into the lock barrel the key-in sensor contacts close and supply a signal to the BCU.
The BCU monitors the ignition switch for a change in state and triggers the alarm if it receives an ignition signal before
it receives an alarm disarm signal.
Another feed to the ignition switch is provided by the BCU to provide switch illumination.
A key-in warning can be enabled or disabled. When the key-in warning is enabled, an audible warning is generated
if the ignition key is in and the driver's door is opened.
Passive coil
The passive coil is located around the ignition key barrel. When the BCU detects that the ignition key has been turned
to the crank position, the vehicle's immobilisation system is activated and a signal is sent to the passive coil at a
frequency of 125 kHz. The magnetic field generated in the coil is induced in the remote transmitter to trigger a re-
mobilisation signal.
BBUS/ alarm sounder/ vehicle horn
The BBUS is an audible warning device which operates under the control of the BCU if the anti-theft system is
activated or the vehicle battery is disconnected. The unit contains its own internal battery power source which is
charged via a feed from the passenger compartment fuse box. The BBUS will not sound if the battery is disconnected
while the security system has not been set.
Some markets utilise an alarm sounder which operates independently or in conjunction with the vehicle horn if the
anti-theft system is triggered.
Page 1326 of 1529

ALARM SYSTEM AND HORN
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-4-3
1Theft deterrent LED
2Receiver
3Volumetric sensors
4Central door locking switch
5Body Control Unit (BCU)
6Bonnet activated alarm switch
7Vehicle horn
8Alarm sounder
9Fuel cut off switch
10Fuel flap release switch
11Door latch switches, drivers door key lock/
unlock switches
12Battery Backed Up Sounder (BBUS)
13Passive remobilisation exciter coil
Page 1327 of 1529
ALARM SYSTEM AND HORN
86-4-4 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
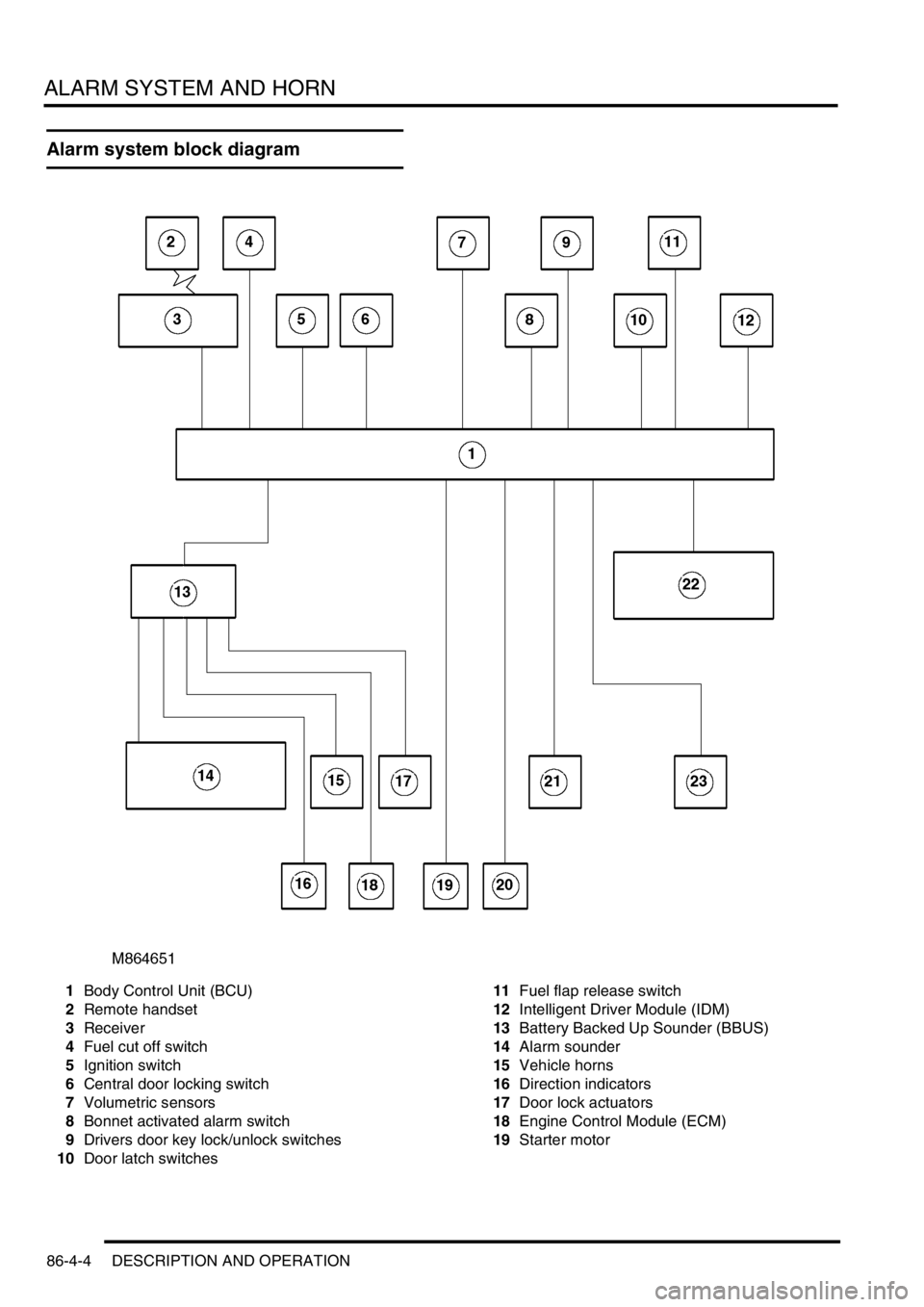
Alarm system block diagram
1Body Control Unit (BCU)
2Remote handset
3Receiver
4Fuel cut off switch
5Ignition switch
6Central door locking switch
7Volumetric sensors
8Bonnet activated alarm switch
9Drivers door key lock/unlock switches
10Door latch switches 11Fuel flap release switch
12Intelligent Driver Module (IDM)
13Battery Backed Up Sounder (BBUS)
14Alarm sounder
15Vehicle horns
16Direction indicators
17Door lock actuators
18Engine Control Module (ECM)
19Starter motor