Page 978 of 1529
INTERIOR TRIM COMPONENTS
REPAIRS 76-3-13
11.Fit instrument pack to fascia and secure with
screws.
12.Position instrument cowl and connect
multiplugs to switches.
13.Fit cowl to clips on fascia and secure with
screws.
14.Fit fascia access panel.
+ INTERIOR TRIM COMPONENTS,
REPAIRS, Panel - fascia access - driver's
side.
15.Fit fascia lower closing panels and secure with
clips.
16.Fit fascia mats.
17.Fit 'A' post trim panels.
18.Fit centre console
lFor models with automatic gearbox:
+ INTERIOR TRIM COMPONENTS,
REPAIRS, Console - centre - automatic
models.
lFor models with manual gearbox:
+ INTERIOR TRIM COMPONENTS,
REPAIRS, Console - centre - manual
models.
19.Fit steering column nacelle.
+ STEERING, REPAIRS, Nacelle -
steering column.
20.Fit steering wheel.
+ STEERING, REPAIRS, Steering
wheel.
21.Fit radio cassette player.
+ IN CAR ENTERTAINMENT,
REPAIRS, Radio.
22.Connect battery.
Page 990 of 1529

SCREENS
REPAIRS 76-4-1
SCREENS REPAIRS
Glass/sealing rubber - tail door
$% 76.31.22
Remove
1.Remove spare wheel from rear door.
2.Remove centre high mounted stop lamp.
+ LIGHTING, REPAIRS, Lamp - stop -
centre high mounted (CHMSL).
3.Pull the rear wiper arm away from the glass.
4.Disconnect leads from rear window heater.
5.Ease glass sealing rubber from tail door flange
and with assistance, from inside push the glass
and sealing rubber out.
6.Remove sealing rubber from glass. Refit
1.Thoroughly clean the tail door glass mounting
flange.
2.Clean glass and fit sealing rubber. Ensure
sealing rubber is fully located onto glass.
3.Fit a draw cord into the outside groove of the
sealing rubber with cord ends situated on top
corner of bend at bottom of glass.
4.To aid assembly, lubricate the tail door glass
mounting flange with liquid soap.
5.Position the assembled glass and rubber to
outside of flange.
6.With assistance from second operator pushing
glass into door, hold one end of cord and pull
the other end carefully around the aperture,
easing the rubber seal over the flange.
7.Connect leads to rear window heater.
8.Fit centre high mounted stop lamp.
+ LIGHTING, REPAIRS, Lamp - stop -
centre high mounted (CHMSL).
9.Fit rear wiper onto glass.
10.Fit spare wheel.
Page 1001 of 1529
SEATS
76-5-4 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Description - electric seats
General
All markets use the same electric seat system. Electically operated lumbar support is optional. The system consists
of an electrical sub-system and a mechanical sub-system.
The electrical sub-system consists of the following components:
lBCU.
lSeat power relays.
lSeat switch packs.
lSeat fore/ aft motors.
lSeat cushion front up/ down motors.
lSeat cushion rear up/ down motors.
lSeat squab motor.
lLumbar pump.
lLumbar deflate solenoid.
The mechanical sub-system consist of the following components:
lGear wheels.
lRack and pinion assemblies.
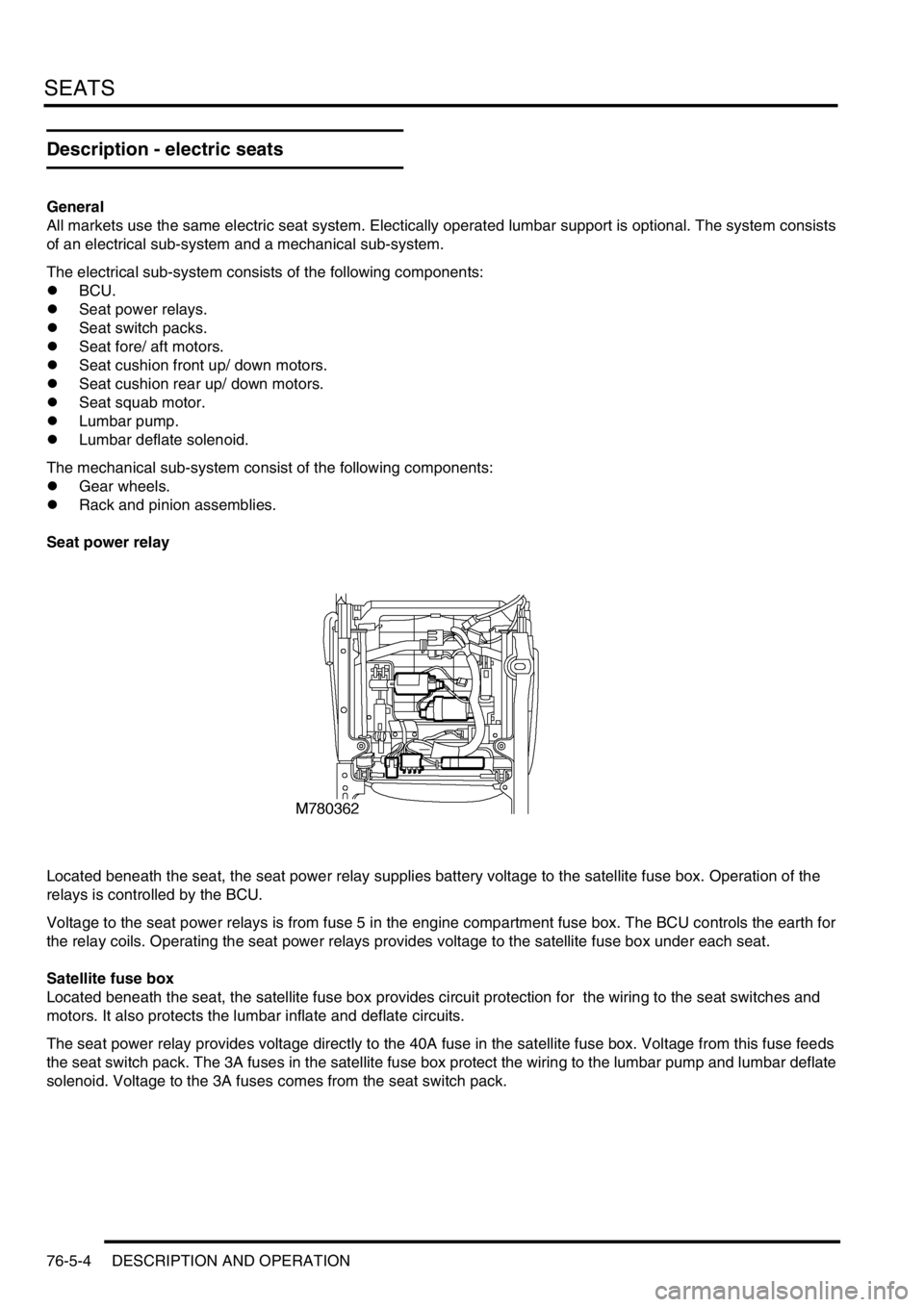
Seat power relay
Located beneath the seat, the seat power relay supplies battery voltage to the satellite fuse box. Operation of the
relays is controlled by the BCU.
Voltage to the seat power relays is from fuse 5 in the engine compartment fuse box. The BCU controls the earth for
the relay coils. Operating the seat power relays provides voltage to the satellite fuse box under each seat.
Satellite fuse box
Located beneath the seat, the satellite fuse box provides circuit protection for the wiring to the seat switches and
motors. It also protects the lumbar inflate and deflate circuits.
The seat power relay provides voltage directly to the 40A fuse in the satellite fuse box. Voltage from this fuse feeds
the seat switch pack. The 3A fuses in the satellite fuse box protect the wiring to the lumbar pump and lumbar deflate
solenoid. Voltage to the 3A fuses comes from the seat switch pack.
Page 1005 of 1529

SEATS
76-5-8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Operation - electric seats
Seat power relay enable line
The BCU provides the seat power relays with an earth supply to the relay coil that enables the relay operation. When
this seat power relay enable line is active, the seat power relay energises allowing seat operation.
In order for the seat power relay to be active the BCU must detect either of the following condition options:
lIgnition switch in position II.
lIgnition switch in position II or driver's door within 45 seconds of opening.
Seat fore/ aft movement
When the cushion switch is operated and the seat power relay enable line is operating, power and earth are supplied
to the motor in the seat, allowing the seat to move forward or backward depending on switch position. The motor
drives a gear wheel along a gear rack connected to the seat base. Sliding the cushion switch forward causes the motor
to drive the seat forward. Sliding the cushion switch rearward reverses polarity of the voltage at the seat motor, driving
the seat rearward.
Seat cushion front up/ down movement
When the cushion switch is operated and the seat power relay enable line is operating, power and earth are supplied
to the motor in the seat, allowing the front of the seat cushion to move upward or downward depending on switch
position. The motor drives a gear wheel along a gear rack connected to the seat base. Sliding the front of the cushion
switch upward causes the motor to drive the seat upward. Sliding the front of the cushion switch downward reverses
polarity of the voltage at the seat motor driving the seat downward.
Seat cushion rear up/ down movement
When the cushion switch is operated and the seat power relay enable line is operating, power and earth are supplied
to the motor in the seat, allowing the seat to move upwards or downwards depending on switch position. The motor
drives a gear wheel along a gear rack connected to the seat base. Sliding the rear of the cushion switch upward
causes the motor to drive the seat upward. Sliding the rear of the cushion switch downward reverses polarity of the
voltage at the seat motor driving the seat downward.
Squab fore/ aft movement
When the squab switch is operated and the seat power relay enable line is operating, power and earth is supplied to
the motor in the squab, allowing the squab to move forward or backward depending on switch position. The motor
drives a gear wheel along a rotary gear rack connected to the squab. Sliding the squab switch forward causes the
motor to drive the squab forward. Sliding the squab switch rearward reverses polarity of the voltage at the seat motor
driving the squab rearward.
Lumbar inflate/ deflate
Sliding the squab switch upwards when the seat power relay enable line is operating applies voltage to the lumbar
pump. The lumbar pump inflates the lumbar bladder, increasing lumbar support. The lumbar pump and the normally
closed lumbar deflate solenoid hold the air in the bladder. Sliding the squab switch downwards applies voltage to the
deflate solenoid, venting the air in the lumbar bladder to atmosphere, decreasing lumbar support.
Diagnostics
TestBook can only verify that the seat power relay line is enabled. It cannot determine the status of the system or any
of the components.
Page 1049 of 1529
SUNROOF
76-6-18 REPAIRS
Motor - sunroof
$% 76.84.07
This procedure is applicable to the motor of both
sunroofs.
Remove
1.Gain access to the sunroof motor:
lFor front sunroof motor, remove front
stowage pocket.
+ INTERIOR TRIM COMPONENTS,
REPAIRS, Stowage pocket - front.
lFor rear sunroof motor, remove headlining.
+ INTERIOR TRIM COMPONENTS,
REPAIRS, Headlining.
CAUTION: The sunroof must be fully closed
before removing the sunroof motor.
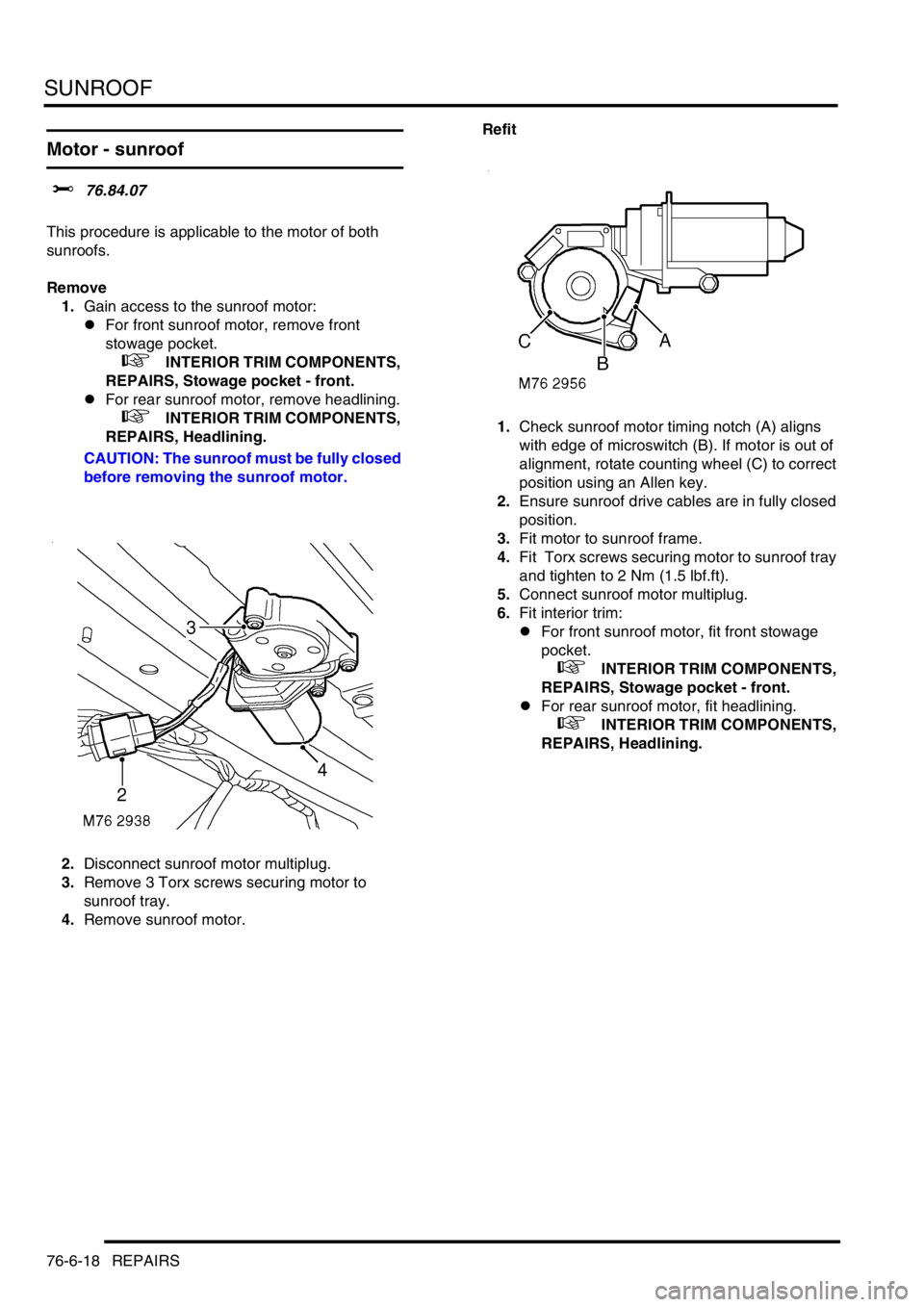
2.Disconnect sunroof motor multiplug.
3.Remove 3 Torx screws securing motor to
sunroof tray.
4.Remove sunroof motor. Refit
1.Check sunroof motor timing notch (A) aligns
with edge of microswitch (B). If motor is out of
alignment, rotate counting wheel (C) to correct
position using an Allen key.
2.Ensure sunroof drive cables are in fully closed
position.
3.Fit motor to sunroof frame.
4.Fit Torx screws securing motor to sunroof tray
and tighten to 2 Nm (1.5 lbf.ft).
5.Connect sunroof motor multiplug.
6.Fit interior trim:
lFor front sunroof motor, fit front stowage
pocket.
+ INTERIOR TRIM COMPONENTS,
REPAIRS, Stowage pocket - front.
lFor rear sunroof motor, fit headlining.
+ INTERIOR TRIM COMPONENTS,
REPAIRS, Headlining.
Page 1056 of 1529
CHASSIS AND BODY DIMENSIONS
BODY DIMENSIONS 77-1-5
BODY DIMENSIONS
Body Dimensions
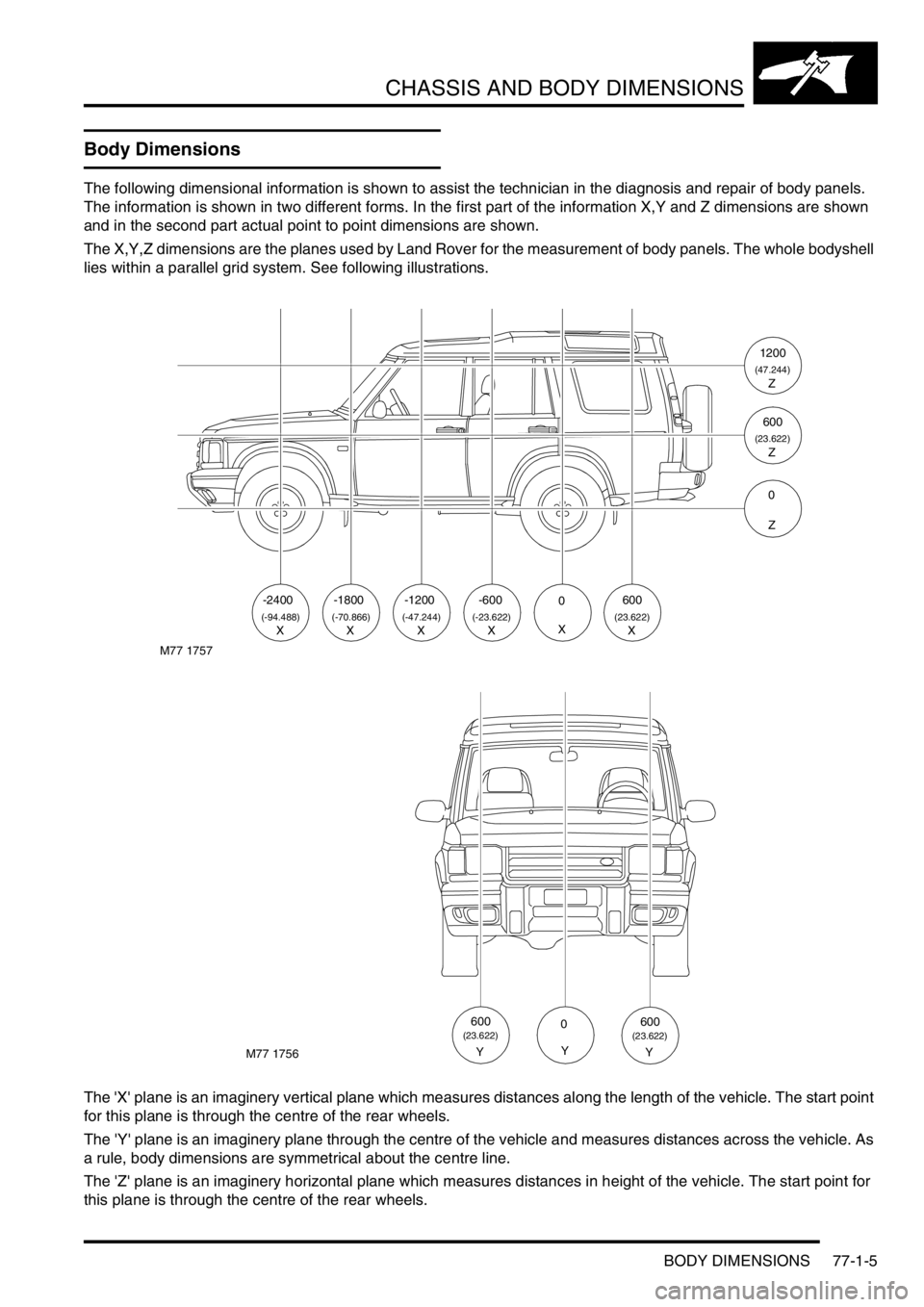
The following dimensional information is shown to assist the technician in the diagnosis and repair of body panels.
The information is shown in two different forms. In the first part of the information X,Y and Z dimensions are shown
and in the second part actual point to point dimensions are shown.
The X,Y,Z dimensions are the planes used by Land Rover for the measurement of body panels. The whole bodyshell
lies within a parallel grid system. See following illustrations.
The 'X' plane is an imaginery vertical plane which measures distances along the length of the vehicle. The start point
for this plane is through the centre of the rear wheels.
The 'Y' plane is an imaginery plane through the centre of the vehicle and measures distances across the vehicle. As
a rule, body dimensions are symmetrical about the centre line.
The 'Z' plane is an imaginery horizontal plane which measures distances in height of the vehicle. The start point for
this plane is through the centre of the rear wheels.
M77 1757
-2400
(-94.488)X
-1800
(-70.866)
-1200-6000600
(-47.244)(-23.622)(23.622)XXXXX
1200
(47.244)Z
600
(23.622)Z
0
Z
M77 1756
0
Y
600(23.622)
Y
600(23.622)
Y
Page 1062 of 1529
CHASSIS AND BODY DIMENSIONS
BODY DIMENSIONS 77-1-11
Internal information
I.D Description Length
A Distance between seat belt anchorage top fixing and
seat belt reel lower fixing1814.5 (71.437)
B Distance between seat belt anchorage lower fixings on
wheel arch inner1430.2 (56.307)
M77 1760
A
B
Page 1073 of 1529
PANEL REPAIRS
77-2-6 REPLACEMENT PANELS
'D'-post assembly
1'D' post outer assembly
2'D' post closing assembly3Wheelarch rear outer assembly
4Bodyside inner rear assembly