1999 DODGE RAM Fuel pressure
[x] Cancel search: Fuel pressurePage 1395 of 1691

See appropriate DTC P0505: IAC MOTOR CIRCUIT in SELF-
DIAGNOSTICS - JEEP, TRUCKS & RWD VANS article.
IGNITION SYSTEM
NOTE: For basic ignition checks, see TEST NS-SEL: NO START TEST
SELECTION in SELF-DIAGNOSTICS - JEEP, TRUCKS & RWD VANS
article.
EMISSION SYSTEMS & SUB-SYSTEMS
NOTE: To locate emission components, refer to emission control
information label in engine compartment.
AIR INJECTION
No Air Supply (Ram Pickup 5.9L & 8.0L)
1) Start engine, and increase engine speed to 1500 RPM. Check
air supply at rubber hoses. If air supply increases with RPM, air pump
operation is okay.
2) If air pump is okay, check for leakage at hoses and
fittings. Repair or replace hoses as necessary.
3) If hoses are okay, check pressure relief valve for
leakage. If air is expelled through pressure relief valve at idle,
replace relief valve.
4) If relief valve is okay on 5.9L, test is complete. On 8.
0L, check inlet air filter. Repair air filter if plugged. If air
filter is okay, test is complete.
CRANKCASE VENTILATION (CCV)
8.0L
1) CCV system does NOT use a PCV valve. System consists of a
fixed orifice (Gray color) that is calibrated to a specific flow rate.\
The fixed orifice (located on intake manifold) is connected by a tube
to right valve cover.
2) A similar orifice is used on left cylinder head, but is
Black in color and cannot be interchanged with Gray orifice. Ensure
orifice, tubes and fittings are clean and in good condition. No
further information is available from manufacturer.
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR)
EGR Valve
See TEST NTC-2: CHECKING EGR SYSTEM in SELF-DIAGNOSTICS -
JEEP, TRUCKS & RWD VANS article.
FUEL EVAPORATION
EVAP Canister
EVAP canister is located in engine compartment. Canister has
no moving parts. Check for loose, missing, cracked or broken
connections and parts. Repair or replace as necessary. No liquid
should be in canister.
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (LDP)
LDP
See appropriate DTC P1494: LEAK DETECTION PUMP SWITCH OR
MECHANICAL FAULT test in SELF-DIAGNOSTICS - JEEP, TRUCKS & RWD VANS
Page 1455 of 1691

Check the following:
* Check secondary ignition system
* Check engine vacuum
* Check fuel pressure
* Check Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor calibration
* Check Throttle Position (TP) sensor calibration
* Check Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) calibration
* Check minimum idle airflow
* Check Idle Air Control (IAC) motor operation
* Check engine mechanical condition
* Check evaporative system
* Check EGR system
* Check coolant temperature sensor and connector
* Check Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor calibration
STARTS BUT STALLS
Check the following:
* Check secondary ignition system
* Check PCM power and ground circuits
* Check fuel pressure
* Check Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor calibration
* Check Throttle Position (TP) sensor calibration
* Check Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) calibration
* Check minimum idle airflow
* Check Idle Air Control (IAC) motor operation
HESITATION OR STUMBLE
Check the following:
* Check secondary ignition system
* Check PCM power and ground circuits
* Check engine vacuum
* Check fuel pressure
* Check Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor calibration
* Check Throttle Position (TP) sensor calibration
* Check Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) calibration
* Check minimum idle airflow
* Check oxygen sensor switching
* Check oxygen sensor heater
* Check Idle Air Control (IAC) motor operation
* Check engine mechanical condition
* Check evaporative system
* Check EGR system
* Check Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor calibration
* Check Park/Neutral Position (PNP) switch.
SURGING
Check the following:
* Check secondary ignition system
* Check PCM power and ground circuits
* Check engine vacuum
* Check fuel pressure
* Check Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor calibration
* Check Throttle Position (TP) sensor calibration
* Check Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) calibration
* Check minimum idle airflow
Page 1456 of 1691

* Check oxygen sensor switching
* Check Idle Air Control (IAC) motor operation
* Check evaporative system.
LACK OF POWER
Check the following:
* Check secondary ignition system
* Check PCM power and ground circuits
* Check fuel pressure
* Check Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor calibration
* Check Throttle Position (TP) sensor calibration
* Check Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) calibration
* Check minimum idle airflow
* Check oxygen sensor switching
* Check Idle Air Control (IAC) motor operation
* Check EGR system.
KNOCKING
Check the following:
* Check secondary ignition system
* Check PCM power and ground circuits
* Check fuel pressure
* Check Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor calibration
* Check Throttle Position (TP) sensor calibration
* Check Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) calibration
* Check minimum idle airflow
* Check oxygen sensor switching
* Check Idle Air Control (IAC) motor operation
* Check evaporative system.
ENGINE MISFIRE
Check the following:
* Check secondary ignition system
* Check PCM power and ground circuits
* Check fuel pressure
* Check minimum idle airflow
* Check oxygen sensor switching
* Check Idle Air Control (IAC) motor operation
* Check EGR system.
BACKFIRE
Check the following:
* Check secondary ignition system
* Check PCM power and ground circuits
* Check fuel pressure
* Check Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) calibration
* Check minimum idle airflow
* Check oxygen sensor switching
* Check EGR system.
ROUGH OR ERRATIC IDLE
Check the following:
Page 1457 of 1691

* Check secondary ignition system
* Check PCM power and ground circuits
* Check engine vacuum
* Check fuel pressure
* Check Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor calibration
* Check Throttle Position (TP) sensor calibration
* Check Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) calibration
* Check minimum idle airflow
* Check oxygen sensor switching
* Check oxygen sensor heater
* Check Idle Air Control (IAC) motor operation
* Check engine mechanical condition
* Check evaporative system
* Check EGR system
* Check Intake Air Temperature (IAT) motor operation
* Check Park/Neutral Position (PNP) switch.
POOR FUEL ECONOMY
Check the following:
* Check secondary ignition system
* Check PCM power and ground circuits
* Check engine vacuum
* Check fuel pressure
* Check Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor calibration
* Check Throttle Position (TP) sensor calibration
* Check Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) calibration
* Check minimum idle airflow
* Check oxygen sensor switching
* Check oxygen sensor heater
* Check Idle Air Control (IAC) motor operation
* Check engine mechanical condition
* Check evaporative system
* Check EGR system
* Check Intake Air Temperature (IAT) motor operation
* Check Park/Neutral Position (PNP) switch.
INTERMITTENTS
INTERMITTENT PROBLEM DIAGNOSIS
Intermittent fault testing requires duplicating circuit or
component failure to identify the problem. These procedures may lead
to PCM setting a Diagnostic Trouble Code (FTC) which may help in
diagnosis.
If problem vehicle does not produce FTC, monitor voltage or
resistance values using a DVOM while attempting to reproduce
conditions causing intermittent fault. A status change on DVOM
indicates a fault has been located.
Use a DVOM to pinpoint faults. When monitoring voltage,
ensure ignition switch is in ON position or engine is running. Ensure
ignition switch is in OFF position or negative battery cable is
disconnected when monitoring circuit resistance. Status changes on
DVOM during test procedures indicate area of fault.
TEST PROCEDURES
Intermittent Simulation
To reproduce the conditions creating an intermittent fault,
use the following methods:
Page 1460 of 1691
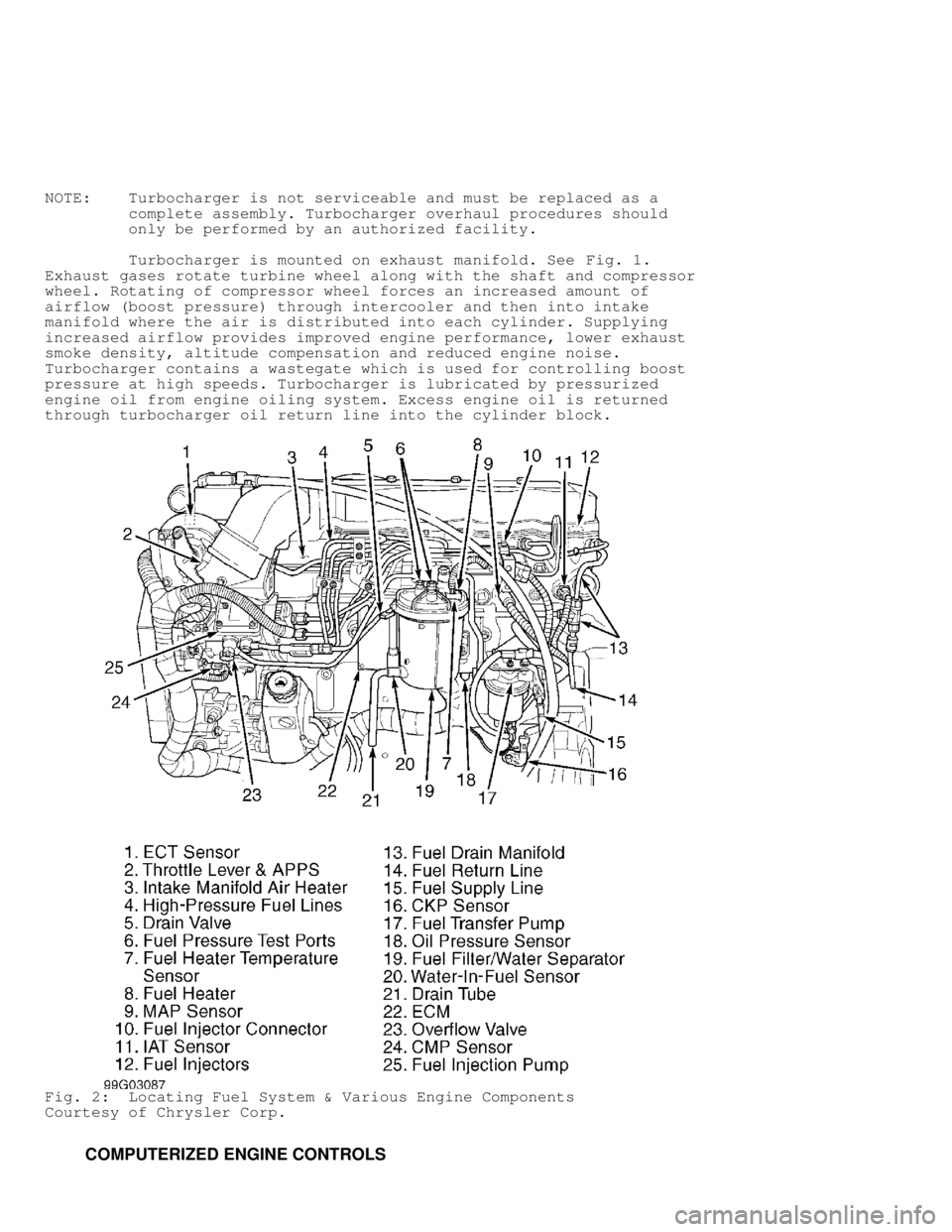
NOTE: Turbocharger is not serviceable and must be replaced as a
complete assembly. Turbocharger overhaul procedures should
only be performed by an authorized facility.
Turbocharger is mounted on exhaust manifold. See Fig. 1.
Exhaust gases rotate turbine wheel along with the shaft and compressor
wheel. Rotating of compressor wheel forces an increased amount of
airflow (boost pressure) through intercooler and then into intake
manifold where the air is distributed into each cylinder. Supplying
increased airflow provides improved engine performance, lower exhaust
smoke density, altitude compensation and reduced engine noise.
Turbocharger contains a wastegate which is used for controlling boost
pressure at high speeds. Turbocharger is lubricated by pressurized
engine oil from engine oiling system. Excess engine oil is returned
through turbocharger oil return line into the cylinder block.
Fig. 2: Locating Fuel System & Various Engine Components
Courtesy of Chrysler Corp.
COMPUTERIZED ENGINE CONTROLS
Page 1463 of 1691

thermostat housing. See Fig. 2.
Fuel Injection Pump Control Module (FPCM)
Fuel Pump Control Module (FPCM) controls fuel pump using
inputs from Engine Control Module (ECM). FPCM is integral to top of
fuel pump. ECM and FPCM are interconnected together for fuel injection
control.
Fuel Temperature Sensors
There are 2 fuel temperature sensors. One sensor is located
inside injection pump, and will set FTC under high temperature
conditions. Engine Control Module (ECM) will lower engine power if FTC\
is set. Other sensor is an integral part of fuel heater. See FUEL
HEATER.
Intake Manifold Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
Intake manifold air temperature sensor is a variable
thermistor sensor located on top of intake manifold, behind intake
manifold air heater. See Fig. 4. Intake manifold air temperature
sensor delivers an input signal to Engine Control Module (ECM) to
indicate intake manifold air temperature. ECM uses input signal for
controlling intake manifold air heater, fuel control and timing.
Fig. 4: Locating Intake Manifold Air Temperature Sensor & MAP Sensor
Courtesy of Chrysler Corp.
Manifold Air Pressure (MAP) Sensor (Boost Pressure)
Manifold Air Pressure (MAP) sensor, located at rear of intake\
Page 1464 of 1691

manifold, sends input signal to Engine Control Module (ECM). ECM uses
input signal for controlling fuel control, timing and engine
protection. ECM will lower engine power if boost is too high.
Oil Pressure Sensor
Oil pressure sensor signal is input to Engine Control Module
(ECM). ECM converts signal to pressure value. Value is sent on CCD Bus\
to instrument panel gauge/light. Oil pressure sensor is located on
side of engine block, below ECM. See Fig. 2.
Power Take Off (PTO)
This input is used on vehicles equipped with a Power Take Off
(PTO) unit. When PTO is engaged, Engine Control Module (ECM) will
disable some OBD-II functions.
Water-In-Fuel (WIF) Sensor
WIF sensor is located in bottom of fuel filter/water
separator. See Fig. 2. WIF sensor delivers input signal to Engine
Control Module (ECM) when water exists in the fuel filter/water
separator. As water level increases, resistance across WIF sensor
decreases. ECM compares decrease in resistance to a high water
standard value. When resistance is 30,000-40,000 ohms, ECM will turn
on WATER-IN-FUEL warning light. WATER-IN-FUEL warning light is located
on instrument panel, just below tachometer. ECM monitors input signal
when ignition switch is in the ON position and continues to monitor
input signal until intake manifold air heater post-heat cycle is
complete.
PCM INPUT SIGNALS
A/C Switch
When A/C switch is in ON position, an input signal is
delivered from A/C switch to Engine Control Module (ECM) to indicate
that A/C operation has been requested. Once A/C operation has been
requested, an A/C request signal is delivered to ECM from A/C high-
pressure switch and A/C low-pressure switch. The A/C request signal
indicates evaporator pressure is within proper range for A/C
operation. ECM uses A/C request signal to cycle A/C compressor clutch
by using an A/C clutch relay. A/C clutch relay may also be referred to
as A/C compressor clutch relay. If A/C high-pressure switch or A/C
low-pressure switch opens, A/C request signal will not be delivered to
the ECM. ECM will then open ground circuit for A/C clutch relay and
A/C compressor clutch will be disengaged.
The A/C clutch relay is located in power distribution center
at driver's side front corner of engine compartment, near the battery.
The A/C high-pressure switch is located on discharge line, near A/C
compressor. The A/C low-pressure switch is located on top of
accumulator.
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor (APPS) Output From ECM
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor (APPS) is mounted on top
left of engine. See Fig. 2. Sensor provides DC voltage input signal to
Engine Control Module (ECM) to indicate throttle position. On previous\
engines, there were linkages between accelerator pedal, throttle
position sensor and injection pump. On this engine, no linkage exists
between accelerator pedal and injection pump. APPS signal is sent on
CCD Bus circuit from ECM to PCM.
Automatic Shutdown (ASD) Relay
A 12-volt input signal is delivered from ASD relay to Engine
Control Module (ECM) when ASD relay is energized. If ECM does not
receive a 12-volt input signal when ASD relay is energized, a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (FTC) will be stored in ECM. ASD relay is
Page 1466 of 1691

Transmission speed sensor may also be referred to as
transmission output shaft speed sensor. Transmission speed sensor is
located on overdrive case at rear of transmission. Transmission speed
sensor delivers input signal to Powertrain Control Module (PCM) to
indicate transmission output shaft speed.
Overdrive Switch (A/T Models)
Transmission overdrive switch may be referred to as
overdrive/override switch, OD switch or overdrive off switch.
Transmission overdrive switch is located on end of gearshift lever.
When vehicle operator depresses transmission overdrive switch, an
input signal is delivered to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The
PCM uses input signal for controlling transmission overdrive shifts by
use of transmission overdrive solenoid on transmission valve body.
Transmission overdrive switch is normally in the ON position, allowing
transmission overdrive operation. If transmission overdrive switch is
depressed once, switch is in OFF position, allowing no transmission
overdrive upshift. If transmission overdrive switch is depressed
again, switch returns to the ON position, allowing transmission
overdrive operation.
Park/Neutral Switch (A/T Models)
Park/neutral switch delivers input signal to Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) to indicate if transmission is in Park, Neutral
or Drive. PCM uses input signal for controlling cruise control system,
transmission torque converter clutch operation and transmission
overdrive solenoid. When park/neutral switch is in Park or Neutral,
switch also provides a ground circuit for the engine starting system.
Park/neutral switch is located on the driver's side of transmission,
near shift linkage.
Transmission Governor Pressure Sensor (A/T Models)
Transmission governor pressure sensor delivers input signal
to Powertrain Control Module (PCM) to indicate transmission governor
pressure. PCM uses input signal for controlling governor pressure by
use of governor pressure solenoid on transmission valve body.
Transmission Temperature Sensor (A/T Models)
Transmission temperature sensor monitors transmission fluid
temperature and delivers input signal to Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). PCM uses input signal for controlling transmission torque
converter clutch operation, transmission overdrive shifts and governor
pressure. Transmission temperature sensor is located on transmission
valve body, incorporated into governor pressure sensor.
PCM prevents torque converter clutch engagement and
transmission overdrive operation when transmission fluid temperature
is less than 50
�F (10�C). If transmission fluid temperature is more
than 260�F (126�C), PCM forces a 4-3 downshift and engages torque
converter clutch until transmission fluid cools down. Once
transmission fluid cools to less than 230
�F (110�C), PCM allows a 3-4
shift again.
Vehicle Speed & Distance
Vehicle speed sensor is no longer used. The vehicle speed and
distance traveled are determined by rear wheel speed sensor. Rear
wheel speed sensor is mounted on top of rear axle housing, above the
ring gear. Rear wheel speed sensor delivers an input signal to
Controller Anti-Lock Brake (CAB) to indicate vehicle speed and
distance traveled. The CAB then delivers input signal to Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) to indicate vehicle speed and distance traveled.
PCM uses input signal for controlling control cruise control system
and fuel system. The CAB is mounted on top of the hydraulic control
unit. Hydraulic control unit contains the pump assembly that