1998 SSANGYONG MUSSO transmission oil
[x] Cancel search: transmission oilPage 1033 of 1463
5A-56 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
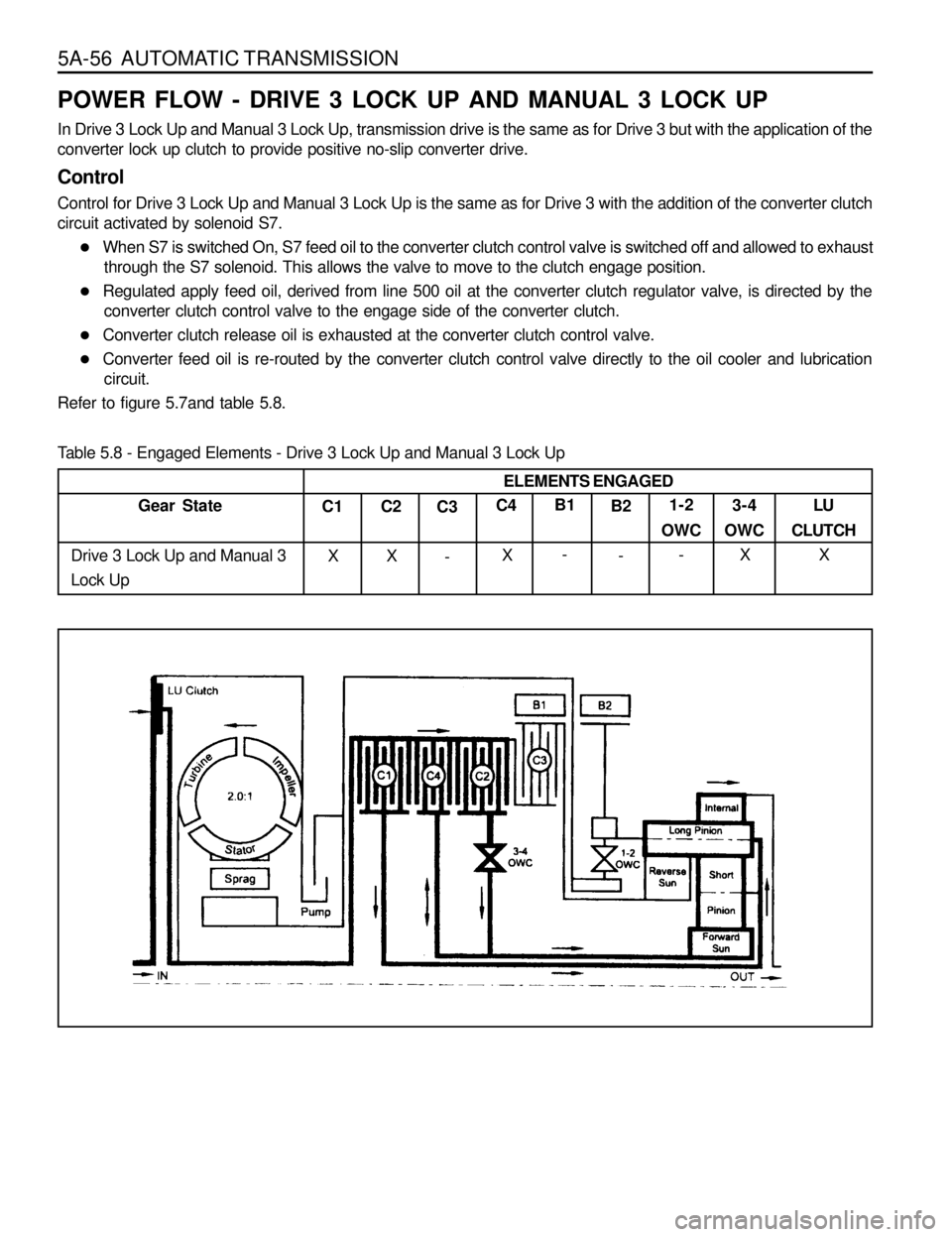
POWER FLOW - DRIVE 3 LOCK UP AND MANUAL 3 LOCK UP
In Drive 3 Lock Up and Manual 3 Lock Up, transmission drive is the same as for Drive 3 but with the application of the
converter lock up clutch to provide positive no-slip converter drive.
Control
Control for Drive 3 Lock Up and Manual 3 Lock Up is the same as for Drive 3 with the addition of the converter clutch
circuit activated by solenoid S7.
lWhen S7 is switched On, S7 feed oil to the converter clutch control valve is switched off and allowed to exhaust
through the S7 solenoid. This allows the valve to move to the clutch engage position.
lRegulated apply feed oil, derived from line 500 oil at the converter clutch regulator valve, is directed by the
converter clutch control valve to the engage side of the converter clutch.
lConverter clutch release oil is exhausted at the converter clutch control valve.
lConverter feed oil is re-routed by the converter clutch control valve directly to the oil cooler and lubrication
circuit.
Refer to figure 5.7and table 5.8.
Table 5.8 - Engaged Elements - Drive 3 Lock Up and Manual 3 Lock Up
Gear State
Drive 3 Lock Up and Manual 3
Lock UpC1
XC2
XC3
-C4
XB1
-B2
-1-2
OWC
-3-4
OWC
XLU
CLUTCH
X ELEMENTS ENGAGED
Page 1034 of 1463
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-57
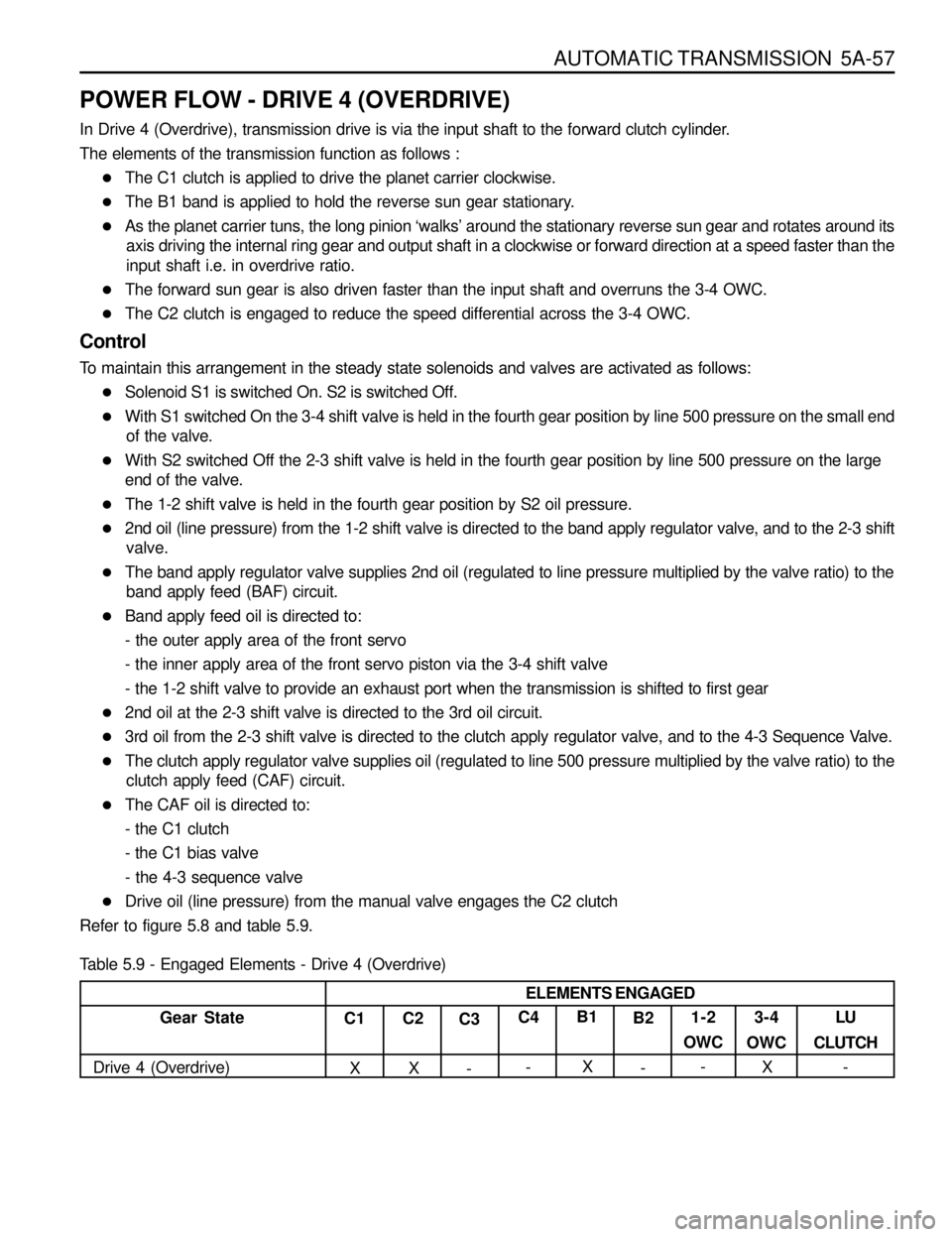
POWER FLOW - DRIVE 4 (OVERDRIVE)
In Drive 4 (Overdrive), transmission drive is via the input shaft to the forward clutch cylinder.
The elements of the transmission function as follows :
lThe C1 clutch is applied to drive the planet carrier clockwise.
lThe B1 band is applied to hold the reverse sun gear stationary.
lAs the planet carrier tuns, the long pinion ‘walks’ around the stationary reverse sun gear and rotates around its
axis driving the internal ring gear and output shaft in a clockwise or forward direction at a speed faster than the
input shaft i.e. in overdrive ratio.
lThe forward sun gear is also driven faster than the input shaft and overruns the 3-4 OWC.
lThe C2 clutch is engaged to reduce the speed differential across the 3-4 OWC.
Control
To maintain this arrangement in the steady state solenoids and valves are activated as follows:
lSolenoid S1 is switched On. S2 is switched Off.
lWith S1 switched On the 3-4 shift valve is held in the fourth gear position by line 500 pressure on the small end
of the valve.
lWith S2 switched Off the 2-3 shift valve is held in the fourth gear position by line 500 pressure on the large
end of the valve.
lThe 1-2 shift valve is held in the fourth gear position by S2 oil pressure.
l2nd oil (line pressure) from the 1-2 shift valve is directed to the band apply regulator valve, and to the 2-3 shift
valve.
lThe band apply regulator valve supplies 2nd oil (regulated to line pressure multiplied by the valve ratio) to the
band apply feed (BAF) circuit.
lBand apply feed oil is directed to:
- the outer apply area of the front servo
- the inner apply area of the front servo piston via the 3-4 shift valve
- the 1-2 shift valve to provide an exhaust port when the transmission is shifted to first gear
l2nd oil at the 2-3 shift valve is directed to the 3rd oil circuit.
l3rd oil from the 2-3 shift valve is directed to the clutch apply regulator valve, and to the 4-3 Sequence Valve.
lThe clutch apply regulator valve supplies oil (regulated to line 500 pressure multiplied by the valve ratio) to the
clutch apply feed (CAF) circuit.
lThe CAF oil is directed to:
- the C1 clutch
- the C1 bias valve
- the 4-3 sequence valve
lDrive oil (line pressure) from the manual valve engages the C2 clutch
Refer to figure 5.8 and table 5.9.
Table 5.9 - Engaged Elements - Drive 4 (Overdrive)
Gear State
Drive 4 (Overdrive)C1
XC2
XC3
-C4
-B1
XB2
-1-2
OWC
-3-4
OWC
XLU
CLUTCH
- ELEMENTS ENGAGED
Page 1036 of 1463
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-59
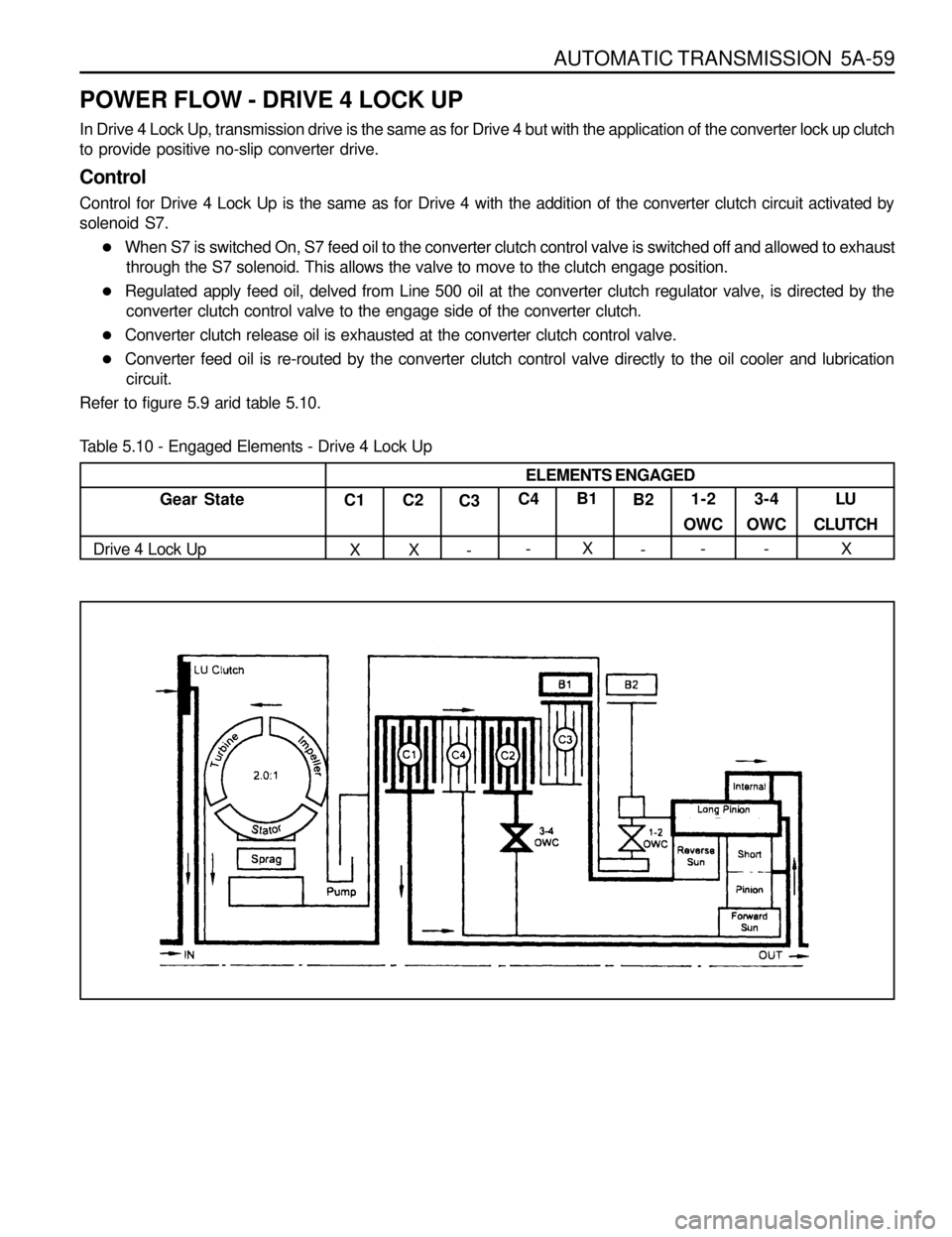
POWER FLOW - DRIVE 4 LOCK UP
In Drive 4 Lock Up, transmission drive is the same as for Drive 4 but with the application of the converter lock up clutch
to provide positive no-slip converter drive.
Control
Control for Drive 4 Lock Up is the same as for Drive 4 with the addition of the converter clutch circuit activated by
solenoid S7.
lWhen S7 is switched On, S7 feed oil to the converter clutch control valve is switched off and allowed to exhaust
through the S7 solenoid. This allows the valve to move to the clutch engage position.
lRegulated apply feed oil, delved from Line 500 oil at the converter clutch regulator valve, is directed by the
converter clutch control valve to the engage side of the converter clutch.
lConverter clutch release oil is exhausted at the converter clutch control valve.
lConverter feed oil is re-routed by the converter clutch control valve directly to the oil cooler and lubrication
circuit.
Refer to figure 5.9 arid table 5.10.
Table 5.10 - Engaged Elements - Drive 4 Lock Up
Gear State
Drive 4 Lock UpC1
XC2
XC3
-C4
-B1
XB2
-1-2
OWC
-3-4
OWC
-LU
CLUTCH
X ELEMENTS ENGAGED
Page 1037 of 1463
5A-60 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
DIAGNOSIS
DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
Recommended Test Equipment and Procedure
The test equipment is designed to be used with the control modules in all vehicles. The components used in the
transmission application are:
lMulti Function Tester, and
lAppropriate vehicle for testing.
Multi Function Tester (MFT)
The MFT is programmed with the special vehicle diagnostic software that allows selection of the unit under test.
The program allows the proper communication to the Transmission Control Unit (TCU).
It then requests information from the user via a menu system to select the required set up.
Examples are viewing codes, clearing error codes, and real-time operation. Set up and operation instructions are
detailed in the user manual.
This equipment can be used by trained personnel such as technicians and mechanics to diagnose electronic and
wiring problems relating to the vehicle transmission. Information that is available includes engine and road (shaft)
speed, transmission oil temperature, throttle position, solenoid/gear status and gear lever position. Current and
stored faults detected by the electronics are also available.
TCU Pin Description
The TCU pin descriptions are listed in table 6.1.1.
The wiring loom pins are shown in figure 6.1.1
Pin
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8Identification
Common Ground
Do not use
Mode Indicator Lamp -
‘Winter’
Gear Position ‘Park’
Lamp
Gear Position ‘Reverse’
Lamp
Gear Position ‘Neutral’
Lamp
Do not use
Engine Speed Input
Sensor (-Ve)Type
GND
-
OP
OP
OP
OP
-
IPDescription
Main power ground (or the module. Connects
directly to the battery negative terminal.
Indicates ‘WINTER’ mode shift schedule is se-
lected.
Drives the jewel in the instrument cluster to in-
dicate ‘PARK’ gear lever position.
Drives the jewel in the instrument cluster to in-
dicate ‘REVERSE’ gear lever position.
Drives the jewel in the instrument cluster to in-
dicate ‘NEUTRAL’ gear lever position.
Flywheel/Ring gear pulses to indicate engine
speed. 4WD
(Diesel)
O
O
l
l l l
l
4WD
(Gas)
O
O
O
l
l l l
l
l
Table 6.1.1 - TCU Pin Description
Page 1039 of 1463
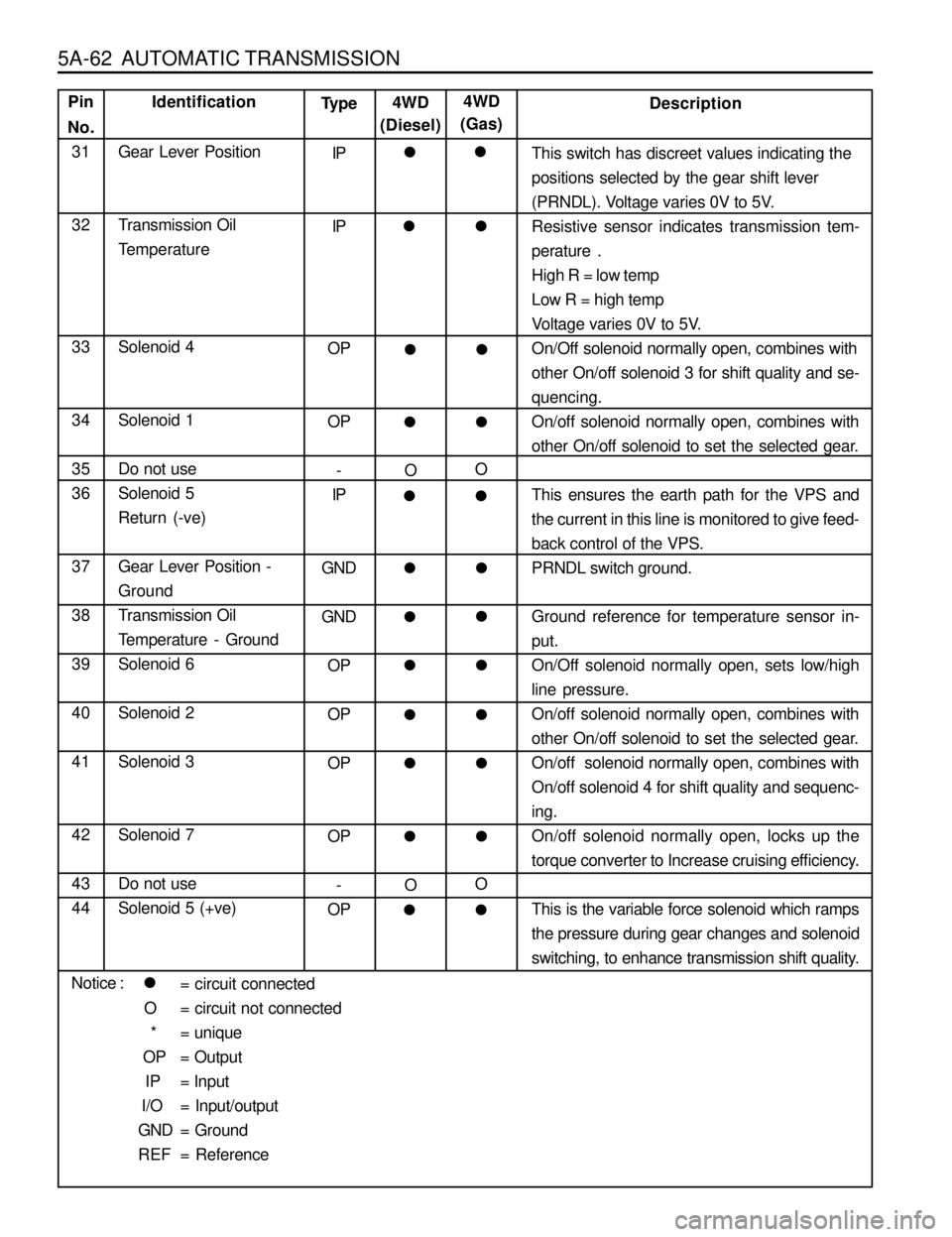
5A-62 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
Identification
Gear Lever Position
Transmission Oil
Temperature
Solenoid 4
Solenoid 1
Do not use
Solenoid 5
Return (-ve)
Gear Lever Position -
Ground
Transmission Oil
Temperature - Ground
Solenoid 6
Solenoid 2
Solenoid 3
Solenoid 7
Do not use
Solenoid 5 (+ve)Type
IP
IP
OP
OP
-
IP
GND
GND
OP
OP
OP
OP
-
OPDescription
This switch has discreet values indicating the
positions selected by the gear shift lever
(PRNDL). Voltage varies 0V to 5V.
Resistive sensor indicates transmission tem-
perature .
High R = low temp
Low R = high temp
Voltage varies 0V to 5V.
On/Off solenoid normally open, combines with
other On/off solenoid 3 for shift quality and se-
quencing.
On/off solenoid normally open, combines with
other On/off solenoid to set the selected gear.
This ensures the earth path for the VPS and
the current in this line is monitored to give feed-
back control of the VPS.
PRNDL switch ground.
Ground reference for temperature sensor in-
put.
On/Off solenoid normally open, sets low/high
line pressure.
On/off solenoid normally open, combines with
other On/off solenoid to set the selected gear.
On/off solenoid normally open, combines with
On/off solenoid 4 for shift quality and sequenc-
ing.
On/off solenoid normally open, locks up the
torque converter to Increase cruising efficiency.
This is the variable force solenoid which ramps
the pressure during gear changes and solenoid
switching, to enhance transmission shift quality. 4WD
(Diesel)
O
O
l
l
4WD
(Gas)
O
O
l
l
ll
ll
ll
ll
Pin
No.
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
ll
ll
ll
ll
ll
ll
l= circuit connected
O = circuit not connected
* = unique
OP = Output
IP = Input
I/O = Input/output
GND = Ground
REF = Reference Notice :
Page 1042 of 1463

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-65
If the gear lever is incorrectly adjusted, the transmission may shift gears on bumpy road surfaces.
6 Transmission Oil Temperature Sensing Fault
lAll shifts will be firm until the transmission has warmed up, because a high transmission oil temperature is
assumed.
If a fault is undetected, the temperature is likely to be evaluated as being lower than actual, resulting in softer shifts
with ‘end bump’ (very firm feel at the end of the shift).
7 Mode Setting Fault
lAll shifts will occur as if the mode is set to ‘NORMAL’.
lThe mode indicator will always be off indicating that ‘NORMAL’ mode is selected.
lThe mode indicator will not respond to changes in switch setting.
If a fault is undetected, the mode as indicated by the mode indicator is not likely to respond to the mode switch.
8 Battery Voltage Sensing Fault
If the battery voltage is low then shifts to first gear are inhibited.9 the battery voltage is high (>16.5V) then the
transmission goes into limp home (LHM) mode.
If a fault is undetected, the transmission is likely to incorrectly evaluate an ON/OFF solenoid fault resulting in limp
home mode (LHM) operation.
9 ON/OFF Solenoid Fault (Solenoids 1,2,3 and 4)
The transmission adopts its limp home mode (LHM) operation, described above. However, if solenoid 1 is faulty then
the fourth gear LHM strategy will be adopted independent of vehicle speed.
If a fault is undetected, the operation of the transmission is dependent on which solenoid is actually faulty. The
characteristics for different solenoid fault conditions are listed in table 6.1.2.
10 ON/OFF Solenoid Fault (Solenoids 6,7)
If solenoid 6 is found faulty it is always disabled resulting in high line pressure being applied continuously.
If solenoid 7 is found faulty it is disabled resulting in the transmission being locked always.
The transmission does not go into LHM.
11 Variable Pressure Solenoid Fault
The transmission adopts its LHM operation.
If a fault is undetected, the transmission shift feel is likely to be poor for all shifts.
12 Software Fault
The transmission adopts the third gear LHM strategy of operation, independent of vehicle speed. The operation of
the TCU under this condition is difficult to predict. Its operation may be erratic.
If a fault is undetected, the operation of the TCU is likely to be erratic.
13 Power Supply Fault
The transmission adopts the third gear LHM strategy of operation, independent of vehicle speed. If there is an
intermittent power supply connection, the TCU will power-up in fourth gear and then shift to the appropriate gear to
satisfy the conditions present. The power supply is not monitored for fault evaluation.
All faults except for solenoid faults can be recovered without having to turn the TCU off and back on. However, in
general the recovery requires that no faults are present for a period of time (approx. 3 or 30 seconds). Recovery from
a fault will not clear the fault from the keep alive memory
14 Transmission Sump Temperature Exceeding 135°C
lThe converter lockup clutch will be applied at lower speeds, causing a shudder through the vehicle.
lThe mode indicator will flash in some vehicles.
These faults can be due to the transmission oil overheating or due to an incorrect signal received from the temperature
sensor.
Page 1046 of 1463
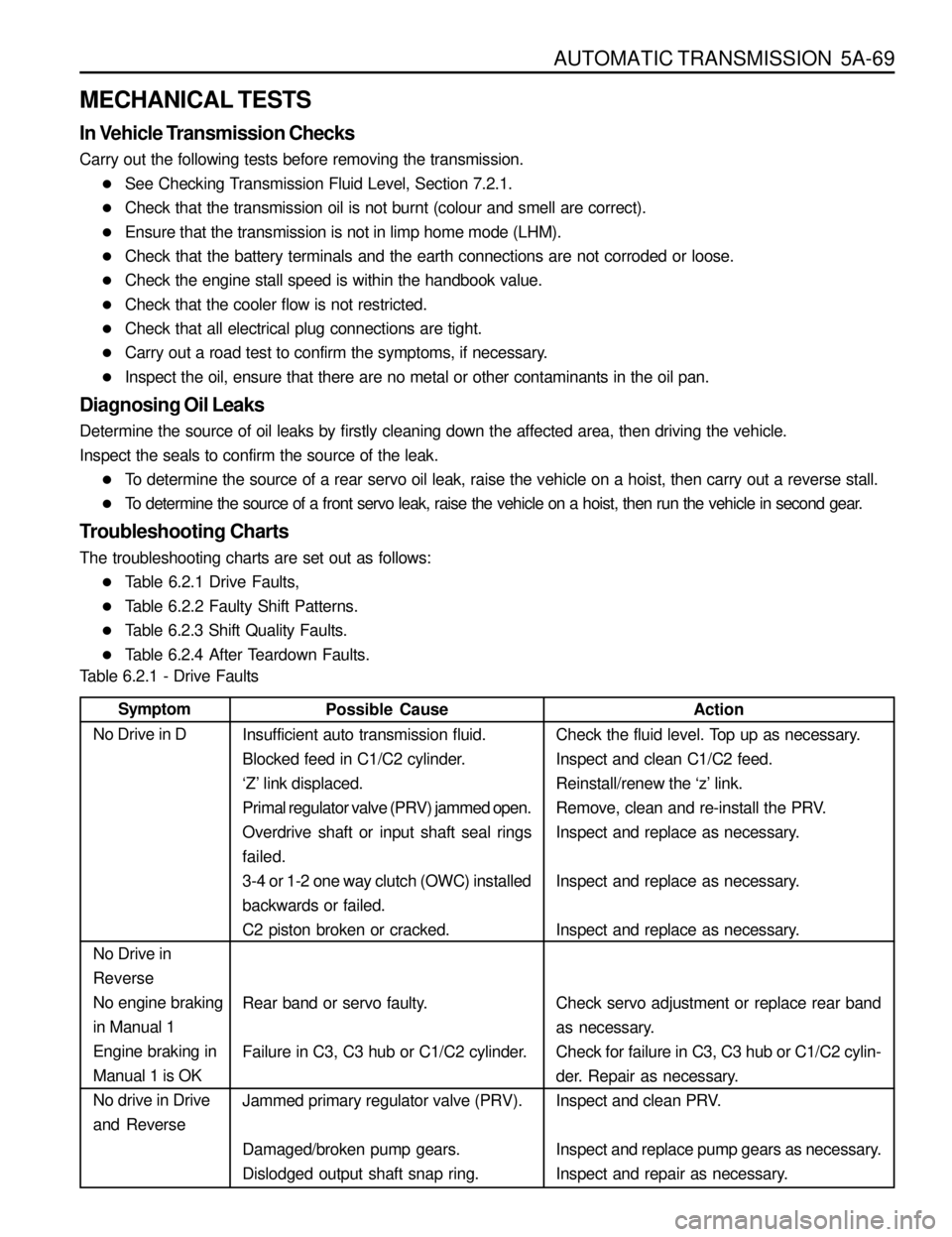
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-69
MECHANICAL TESTS
In Vehicle Transmission Checks
Carry out the following tests before removing the transmission.
lSee Checking Transmission Fluid Level, Section 7.2.1.
lCheck that the transmission oil is not burnt (colour and smell are correct).
lEnsure that the transmission is not in limp home mode (LHM).
lCheck that the battery terminals and the earth connections are not corroded or loose.
lCheck the engine stall speed is within the handbook value.
lCheck that the cooler flow is not restricted.
lCheck that all electrical plug connections are tight.
lCarry out a road test to confirm the symptoms, if necessary.
lInspect the oil, ensure that there are no metal or other contaminants in the oil pan.
Diagnosing Oil Leaks
Determine the source of oil leaks by firstly cleaning down the affected area, then driving the vehicle.
Inspect the seals to confirm the source of the leak.
lTo determine the source of a rear servo oil leak, raise the vehicle on a hoist, then carry out a reverse stall.
lTo determine the source of a front servo leak, raise the vehicle on a hoist, then run the vehicle in second gear.
Troubleshooting Charts
The troubleshooting charts are set out as follows:
lTable 6.2.1 Drive Faults,
lTable 6.2.2 Faulty Shift Patterns.
lTable 6.2.3 Shift Quality Faults.
lTable 6.2.4 After Teardown Faults.
Table 6.2.1 - Drive Faults
Action
Check the fluid level. Top up as necessary.
Inspect and clean C1/C2 feed.
Reinstall/renew the ‘z’ link.
Remove, clean and re-install the PRV.
Inspect and replace as necessary.
Inspect and replace as necessary.
Inspect and replace as necessary.
Check servo adjustment or replace rear band
as necessary.
Check for failure in C3, C3 hub or C1/C2 cylin-
der. Repair as necessary.
Inspect and clean PRV.
Inspect and replace pump gears as necessary.
Inspect and repair as necessary. Possible Cause
Insufficient auto transmission fluid.
Blocked feed in C1/C2 cylinder.
‘Z’ link displaced.
Primal regulator valve (PRV) jammed open.
Overdrive shaft or input shaft seal rings
failed.
3-4 or 1-2 one way clutch (OWC) installed
backwards or failed.
C2 piston broken or cracked.
Rear band or servo faulty.
Failure in C3, C3 hub or C1/C2 cylinder.
Jammed primary regulator valve (PRV).
Damaged/broken pump gears.
Dislodged output shaft snap ring.Symptom
No Drive in D
No Drive in
Reverse
No engine braking
in Manual 1
Engine braking in
Manual 1 is OK
No drive in Drive
and Reverse
Page 1051 of 1463
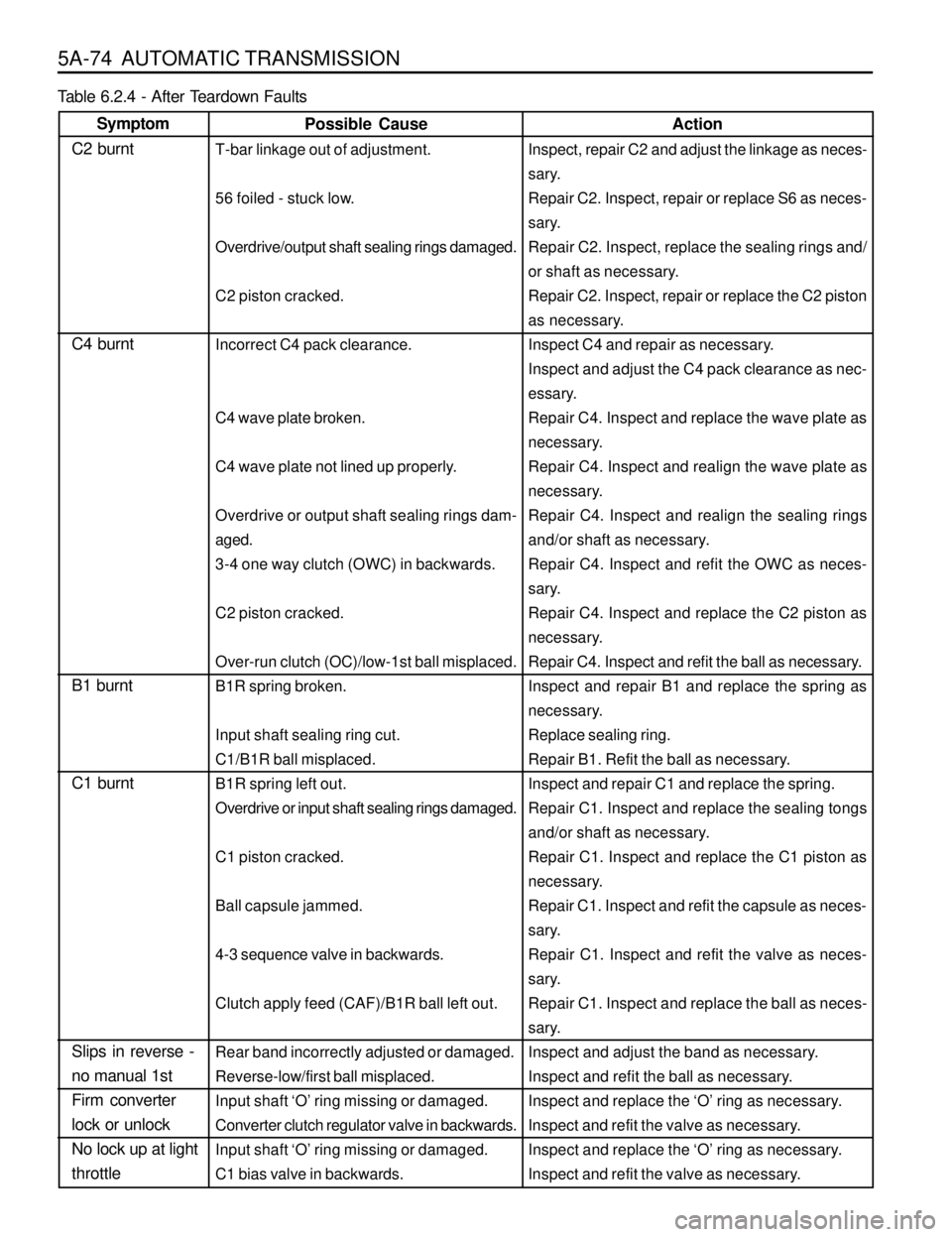
5A-74 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
Action
Inspect, repair C2 and adjust the linkage as neces-
sary.
Repair C2. Inspect, repair or replace S6 as neces-
sary.
Repair C2. Inspect, replace the sealing rings and/
or shaft as necessary.
Repair C2. Inspect, repair or replace the C2 piston
as necessary.
Inspect C4 and repair as necessary.
Inspect and adjust the C4 pack clearance as nec-
essary.
Repair C4. Inspect and replace the wave plate as
necessary.
Repair C4. Inspect and realign the wave plate as
necessary.
Repair C4. Inspect and realign the sealing rings
and/or shaft as necessary.
Repair C4. Inspect and refit the OWC as neces-
sary.
Repair C4. Inspect and replace the C2 piston as
necessary.
Repair C4. Inspect and refit the ball as necessary.
Inspect and repair B1 and replace the spring as
necessary.
Replace sealing ring.
Repair B1. Refit the ball as necessary.
Inspect and repair C1 and replace the spring.
Repair C1. Inspect and replace the sealing tongs
and/or shaft as necessary.
Repair C1. Inspect and replace the C1 piston as
necessary.
Repair C1. Inspect and refit the capsule as neces-
sary.
Repair C1. Inspect and refit the valve as neces-
sary.
Repair C1. Inspect and replace the ball as neces-
sary.
Inspect and adjust the band as necessary.
Inspect and refit the ball as necessary.
Inspect and replace the ‘O’ ring as necessary.
Inspect and refit the valve as necessary.
Inspect and replace the ‘O’ ring as necessary.
Inspect and refit the valve as necessary.
Possible Cause
T-bar linkage out of adjustment.
56 foiled - stuck low.
Overdrive/output shaft sealing rings damaged.
C2 piston cracked.
Incorrect C4 pack clearance.
C4 wave plate broken.
C4 wave plate not lined up properly.
Overdrive or output shaft sealing rings dam-
aged.
3-4 one way clutch (OWC) in backwards.
C2 piston cracked.
Over-run clutch (OC)/low-1st ball misplaced.
B1R spring broken.
Input shaft sealing ring cut.
C1/B1R ball misplaced.
B1R spring left out.
Overdrive or input shaft sealing rings damaged.
C1 piston cracked.
Ball capsule jammed.
4-3 sequence valve in backwards.
Clutch apply feed (CAF)/B1R ball left out.
Rear band incorrectly adjusted or damaged.
Reverse-low/first ball misplaced.
Input shaft ‘O’ ring missing or damaged.
Converter clutch regulator valve in backwards.
Input shaft ‘O’ ring missing or damaged.
C1 bias valve in backwards.
Symptom
C2 burnt
C4 burnt
B1 burnt
C1 burnt
Slips in reverse -
no manual 1st
Firm converter
lock or unlock
No lock up at light
throttle
Table 6.2.4 - After Teardown Faults