1998 PONTIAC BONNEVILLE service
[x] Cancel search: servicePage 271 of 395

How to Check and Add Oil
Check oil only when the engine is cold. Allow the
engine
to cool two to three hours after running.
If you remove the supercharger oil €ill plug while
the engine
is hot, pressure may cause hot oil to
blow out
of the oil fill hole. You may be burned.
Do not remove the plug until the engine cools.
1. Clean the area around the oil fill plug before
2. Remove the oil fill plug using a 3/16 inch
3. The oil level is correct when it just reaches the
bottom of the threads of the inspection hole.
4. Replace the oil plug with the O-ring in place.
Torque to
88 lb-in (10 N-m).
removing it.
Allen wrench.
Automatic Transaxle Fluid
When to Check and Change
A good time to check your automatic transaxle fluid
level is when the engine oil
is changed.
Change both the fluid and filter every
50,000 miles
(83 000 km) if the vehicle is mainly driven under one
or more of these conditions:
0 In heavy city traflic where the outside temperature
regularly reaches
90°F (32°C) or higher.
In hilly or mountainous terrain.
0 When doing frequent trailer towing.
Uses such as found in taxi, police or delivery service.
If you do not use your vehicle under any of these
conditions, the fluid and filter do not require changing.
See “Scheduled Maintenance Services” in the Index.
How to Check
Because this operation can be a little difficult, you may
choose to have
this done at your Pontiac dealership
Service Department.
If you do it yourself, be sure to follow all the instructions
here, or you could get
a false reading on the dipstick.
6-20
Page 281 of 395
-
NOTICE:
0
0
Using the wrong fluid can badly damage
brake system parts. For example, just a few
drops
of mineral-based oil, such as engine
oil, in your brake system can damage brake
system parts
so badly that they’ll have to be
replaced. Don’t let someone put in the
wrong kind
of fluid.
If you spill brake fluid on your vehicle’s
painted surfaces, the paint finish can be
damaged. Be careful not to spill brake fluid
on your vehicle. If you do, wash it off
immediately. See “Appearance Care” in
the Index.
Brake Wear
Your vehicle has front disc brakes and rear drum brakes.
Disc brake pads have built-in wear indicators
that
make a high-pitched warning sound when the brake
pads are worn and new pads are needed. The sound
may come
and go or be heard all the time your vehicle
is moving (except when
you are pushing on the brake
pedal
firmly).
A 3
,A CAUTION:
I I
The brake wear warning sound means that soon
your brakes won’t work well. That could lead to
an accident. When you hear the brake wear
warning sound, have your vehicle serviced.
I I
I NOTICE: I ~
Continuing to drive with worn-out brake pads
could result
in costly brake repair. I
6-30
Page 283 of 395

Battery
Every new Pontiac has an ACDelco Freedom@ battery.
You never have to add water to one of these. When it’s
time for a new battery, we recornend
an ACDelco
Freedom battery. Get one that has the replacement
number shown on the original battery’s label.
Bulb Replacement
For any bulb changing procedure not listed in this
section, contact your vehicle dealer’s service
department.
Halogen Bulbs
Vehicle Storage
If you’re not going to drive your vehicle for 25 days or more,
remove the black, negative (-) cable from the battery. This
will help keep your battery fiom running down.
I A CAUTION:
Batteries have acid that can burn you and gas
that can explode. You can be badly hurt if you
aren’t careful. See “Jump
Starting” in the Index
for tips on working around
a battery without
getting hurt.
1
Contact your dealer to learn how to prepare your vehicle
for longer storage periods.
Also, for your audio system, see “Theft-Deterrent
Feature”
in the Index.
A CAUTION:
Halogen bulbs have pressurized gas inside and
can burst if you drop or scratch the bulb. You or
others could be injured. Be sure to read and
follow the instructions on the bulb package.
If you go through a high pressure car wash, or it is very
humid, your headlamps may “fog up.”
This is normal.
The lenses should clear by themselves in time.
Headlamps
For the proper bulb type, see “Replacement Bulbs’’ in
the Index.
6-32
Page 292 of 395
For the proper windshield wiper blade replacement length and type, see “Normal Maintenance Replacement
Parts” in the Index.
Tires
Your new vehicle comes with high-quality tires made by
a leading tire manufacturer. If you ever have questions
about your tire warranty and where to obtain service, see
your Pontiac Warranty booklet for details.
Poorly maintained and improperly used tires
are dangerous.
0 Overloading your tires can cause
overheating as a result of too much friction.
You could have an airout and a serious
accident. See “Loading Your Vehicle” in
the Index.
CAUTION: (Continued)
0
a
0
Underinflated tires pose the same danger as
overloaded tires. The resulting accident
could cause serious injury. Check
all tires
frequently to maintain the recommended
pressure. Tire pressure should be checked when your tires are cold.
Overinflated tires are more likely to be
cut, punctured or broken
by a sudden
impact
-- such as when you hit a pothole.
Keep tires
at the recommended pressure.
Worn, old tires can cause accidents.
If your
tread
is badly worn, or if your tires have
been damaged, replace them.
Inflation -- Tire Pressure
The Tire-Loading Information label, which is on the
rear edge
of the driver’s door shows the correct inflation
pressures for your tires when they’re cold. “Cold”
means your vehicle has been sitting for at least three
hours or driven no more than
1 mile (1.6 km).
6-41
Page 294 of 395
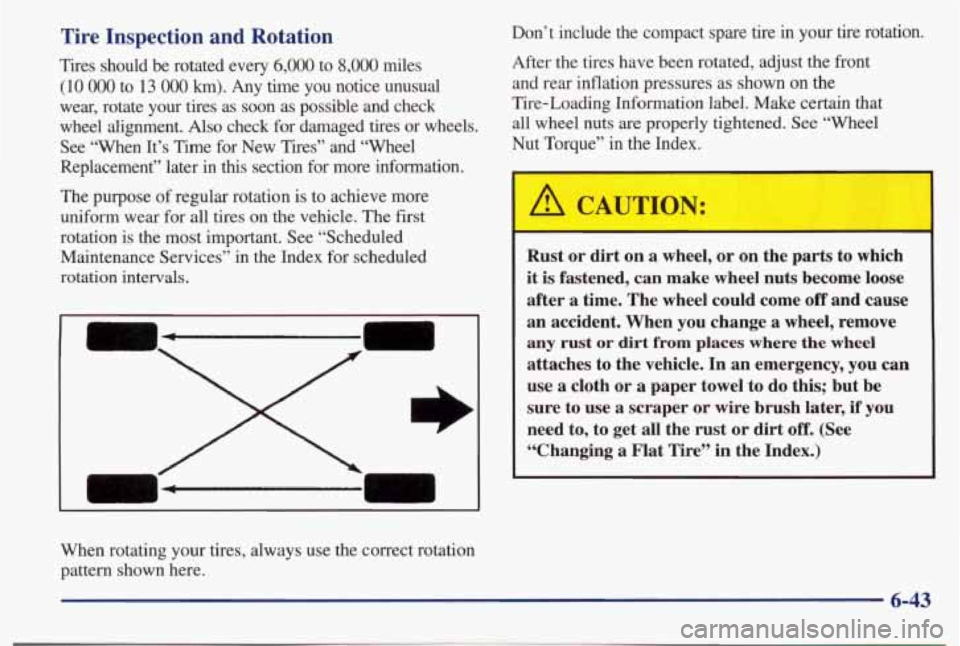
Tire Inspection and Rotation
Tires should be rotated every 6,000 to 8,000 miles
(10 OOO to 13 OOO km). Any time you notice unusual
wear, rotate your tires as soon as possible and check
wheel alignment.
Also check for damaged tires or wheels.
See “When It’s Time for New Tires” and “Wheel
Replacement” later in
this section for more information.
The purpose of regular rotation is to achieve more
uniform wear for all tires on the vehicle. The first
rotation is the most important. See “Scheduled Maintenance Services” in the Index for scheduled
rotation intervals.
m4
Don’t include the compact spare tire in your tire rotation.
After the tires have been rotated, adjust the front
and rear inflation pressures as shown
on the
Tire-Loading Information label. Make certain that all wheel nuts
are properly tightened. See “Wheel
Nut Torque” in the Index.
A CAUTION:
Rust or dirt on a wheel, or on the parts to which
it is fastened, can make wheel nuts become loose
after a time. The wheel could come
off and cause
an accident. When you change a wheel, remove
any rust or dirt from places where the wheel
attaches to the vehicle. In an emergency, you can
use a cloth or
a paper towel to do this; but be
sure to use a scraper or wire brush later,
if you
need to, to get all the rust or dirt
off. (See
“Changing a Flat Tire” in the Index.)
I
When rotating your tires, always use the correct rotation
pattern shown here.
6-43
Page 295 of 395

When It’s Time for New Tires
One way to tell when it’s
time for
new tires is to
check the treadwear
indicators, which will
appear when your tires have
only 1/16 inch
(1.6 mm) or
less of tread remaining.
You need a
new tire if any of the following statements
are true:
0 You can see the indicators at three or more places
0 You can see cord or fabric showing through the tire’s
The tread or sidewall is cracked, cut or snagged deep
around the tire.
rubber.
enough to show cord or fabric.
0 The tire has a bump, bulge or split.
0 The tire has a puncture, cut or other damage that
can’t be repaired well because of the size or location
of the damage.
Buying New Tires
To find out what kind and size of tires you need, look at
the Tire-Loading Information label.
The tires installed on
your vehicle when it was new had
a Tire Performance Criteria Specification
(TPC Spec)
number on each tire’s sidewall. When you get new tires,
get
ones with that same TPC Spec number. That way
your vehicle will continue to have tires that are designed
to give proper endurance, handling, speed rating,
traction, ride and other things during normal service on
your vehicle.
If your tires have an all-season tread
design,
the TPC number will be followed by an “MS”
(for mud and snow).
If
you ever replace your tires with those not having a
TPC Spec number, make sure they are the same size,
load range, speed rating and construction type (bias,
bias-belted or radial) as your original tires.
6-44
Page 297 of 395
Treadwear
The treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on
the wear rate
of the tire when tested under controlled
conditions on a specified government test course.
For example, a tire graded 150 would wear one
and a
half (1 1/2) times as well on the government course
as a tire graded 100. The relative performance of tires
depends upon the actual conditions
of their use,
however, and may depart significantly from the norm
due to variations
in driving habits, service practices
and differences in road characteristics and climate.
Traction -- A, B, C
The traction grades, from highest to lowest, are A, B,
and C, and they represent the tire’s ability to stop on
wet pavement as measured under controlled conditions
on specified government test surfaces of asphalt
and concrete.
A tire marked C may have poor
traction performance.
Warning: The traction grade assigned
to this tire is based
on braking (straight ahead) traction tests and does not
include cornering (turning) traction.
Temperature -- A, B, C
The temperature grades are A (the highest), B, and C,
representing the tire’s resistance to the generation of
heat and its ability to dissipate heat when tested under
controlled conditions on a specified indoor laboratory
test wheel. Sustained high temperature can cause the
material
of the tire to degenerate and reduce tire life, and
excessive temperature can lead to sudden
tire failure.
The grade
C corresponds to a level of performance
which
all passenger car tires must meet under the
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard
No. 109. Grades
B and A represent higher levels of performance on the
laboratory test wheel
than the minimum required by law.
Warning: The temperature grade for this tire is
established for a tire that is properly inflated and not
overloaded. Excessive speed, underinflation, or
excessive loading, either separately or in combination,
can cause heat buildup and possible tire failure.
6-46
Page 306 of 395

Finish Damage
Any stone chips, fractures or deep scratches in the finish
should be repaired right away. Bare metal will corrode
quickly and may develop into a major repair expense.
Minor chips and scratches can be repaired with touch-up materials available from your dealer or other service
outlets. Larger areas of finish damage can be corrected
in your dealer’s body and paint shop.
Underbody Maintenance
Chemicals used for ice and snow removal and dust
control can collect on the underbody.
If these are not
removed, accelerated corrosion (rust) can occur on the underbody parts such as fuel lines, frame, floor
pan and exhaust system even though they have
corrosion protection.
At least every spring, flush these materials from the
underbody with plain water. Clean
any areas where mud
and other debris can collect.
Dirt packed in closed areas
of the frame should be loosened before being flushed. Your dealer or
an underbody car washing system can do
this for
you.
Chemical Paint Spotting
Some weather and atmospheric conditions can create
a chemical fallout. Airborne pollutants can fall upon
and attack painted surfaces on your vehicle. This
damage can take two forms: blotchy, ringlet-shaped
discolorations, and small irregular dark spots etched
into the paint surface.
Although no defect in the paint job causes
this, Pontiac
will repair, at no charge to the owner, the surfaces of
new vehicles damaged by this fallout condition within
12 months or 12,000 miles
(20 000 km) of purchase,
whichever occurs first.
6-55