1998 OPEL FRONTERA transmission fluid
[x] Cancel search: transmission fluidPage 4784 of 6000
6E–127 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
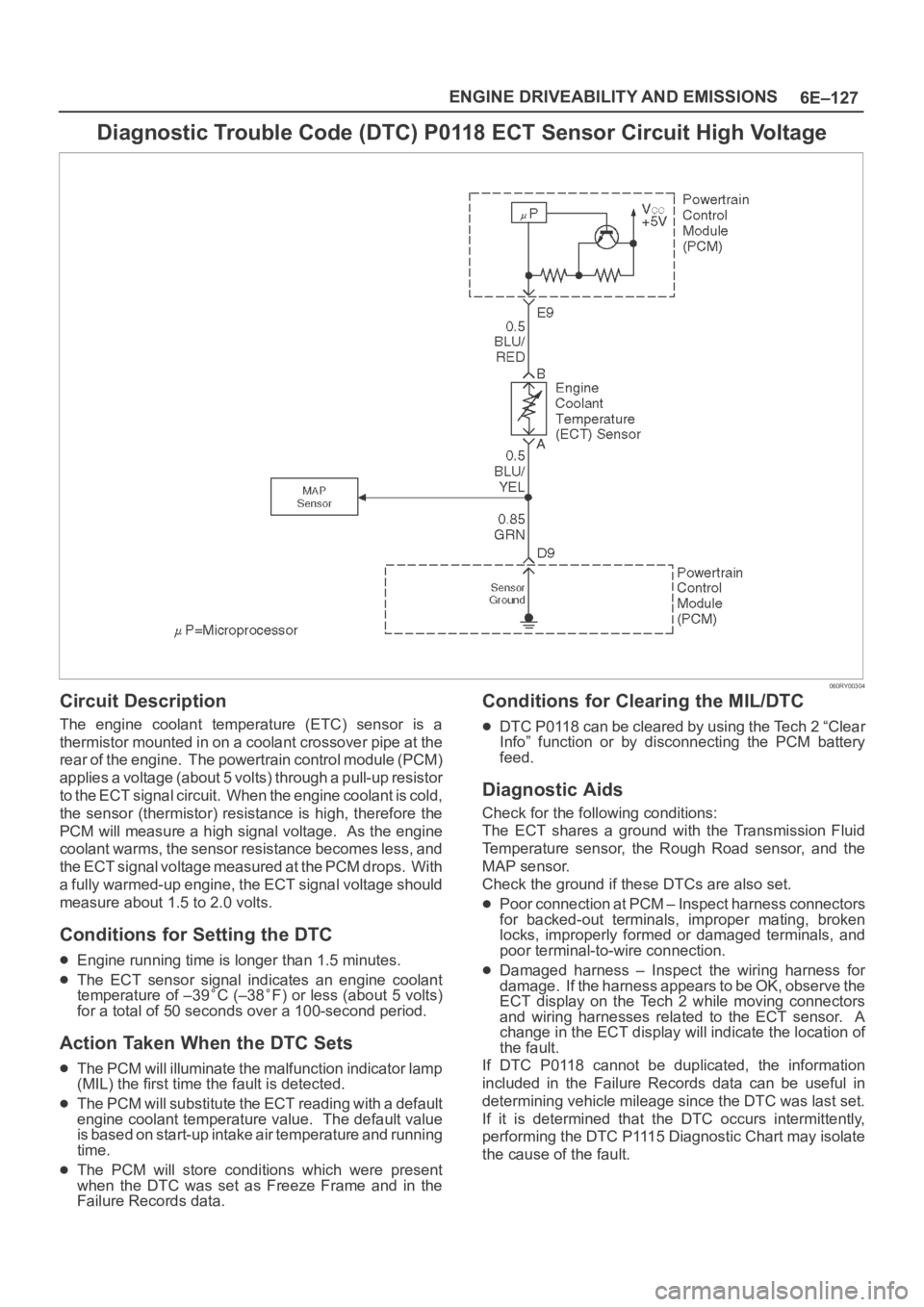
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0118 ECT Sensor Circuit High Voltage
060RY00304
Circuit Description
The engine coolant temperature (ETC) sensor is a
thermistor mounted in on a coolant crossover pipe at the
rear of the engine. The powertrain control module (PCM)
applies a voltage (about 5 volts) through a pull-up resistor
to the ECT signal circuit. When the engine coolant is cold,
the sensor (thermistor) resistance is high, therefore the
PCM will measure a high signal voltage. As the engine
coolant warms, the sensor resistance becomes less, and
the ECT signal voltage measured at the PCM drops. With
a fully warmed-up engine, the ECT signal voltage should
measure about 1.5 to 2.0 volts.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Engine running time is longer than 1.5 minutes.
The ECT sensor signal indicates an engine coolant
temperature of –39C (–38F) or less (about 5 volts)
for a total of 50 seconds over a 100-second period.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The PCM will substitute the ECT reading with a default
engine coolant temperature value. The default value
is based on start-up intake air temperature and running
time.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0118 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
The ECT shares a ground with the Transmission Fluid
Temperature sensor, the Rough Road sensor, and the
MAP sensor.
Check the ground if these DTCs are also set.
Poor connection at PCM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
ECT display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors
and wiring harnesses related to the ECT sensor. A
change in the ECT display will indicate the location of
the fault.
If DTC P0118 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
If it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently,
performing the DTC P1115 Diagnostic Chart may isolate
the cause of the fault.
Page 4945 of 6000

6E–288
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Default Matrix Table
Service Procedure Default Strategy
A referral strategy has been established to assist the
technician with additional information when the cause of
the failure cannot be determined. If no problem is found
after performing diagnostics, then refer to the default
matrix table for further diagnostic information.
Default Matrix Table
Strategy Based Diagnostic Charts
Initial DiagnosisDefault Section(s)
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
CheckVehicle does not enter diagnostics.Chassis Electrical
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
CheckVehicle enters diagnostics and
communicates with Tech 2. MIL is
“ON” in diagnostics. Engine does not
start and run.Ignition System Check
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
CheckEngine starts and runs, no PCM
codes set. Customer complains of
vibration.—
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
CheckEngine starts and runs, no PCM
codes set. Customer complains of
harsh or soft shift, poor performance,
delayed or no engagement into drive
or reverse, transmission fluid leak,
transmission noise or vibration, or
improper TCC operation.Automatic Transmission
PCM Power and Ground CheckOn-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check.Chassis Electrical
PCM Power and Ground CheckOn-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check. PCM power and ground
circuits OK. Data link voltage
incorrect.Chassis Electrical
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
CheckEngine starts and runs, no PCM
codes set. Customer complains of
harsh or soft shift, poor performance,
delayed or no engagement into drive
or reverse, transmission fluid leak,
transmission noise or vibration, or
improper TCC operation.Automatic Transmission
SymptomsInitial DiagnosisDefault Section(s)
Intermittents1. On-board Diagnostic (OBD)
system check.
2. Careful visual/physical
inspections.Chassis Electrical
Hard Starts1. OBD system check.
2. Sensors (ECT, MAP, MAF, TP) ;
MAP output chart.
3. Fuel system electrical test, fuel
system diagnosis.
4. Ignition system.
5. IAC system check.Engine Mechanical, Ignition
System Check, Exhaust System
Diagnosis
Surges and/or Chuggles1. OBD system check.
2. Heated oxygen sensors.
3. Fuel system diagnosis.
4. Ignition system.Calibration ID “Broadcast
Code”/Service Bulletins, Ignition
System Check, Generator
Output, Exhaust System
Diagnosis, 4L30-E System Test
Page 4997 of 6000

6E–340
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
the TP sensor is low. As the throttle valve opens, the
output increases so that at wide open throttle (WOT), the
output voltage should be above 4 volts.
The PCM calculates fuel delivery based on throttle valve
angle (driver demand). A broken or loose TP sensor may
cause intermittent bursts of fuel from an injector and
unstable idle because the PCM thinks the throttle is
moving. A hard failure in the TP sensor 5-volt reference
or signal circuits will set a DTC P0123. A hard failure with
the TP sensor ground circuit may set DTC P0123. Once
a DTC is set, the PCM will use an artificial default value
based on engine RPM and mass air flow for the throttle
position, and some vehicle performance will return. A
high idle may result when DTC P0123 is set. The PCM
can also detect a shifted TP sensor. The PCM monitors
throttle position and compares the actual TP sensor
reading to a predicted TP value calculated from engine
speed. If the PCM detects an out-of-range condition,
DTC P0121 will be set.
0021
Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT)
Sensor
The transmission fluid temperature sensor is a thermistor
which changes its resistance based on the temperature of
the transmission fluid. For a complete description of the
TFT sensor, refer to
4L30-E Automatic Transmission
Diagnosis
.
A failure in the TFT sensor or associated wiring will cause
DTC P0712 or DTC P0713 to set. In this case, engine
coolant temperature will be substituted for the TFT
sensor value and the transmission will operate normally.
Transmission Range Switch
IMPORTANT:The vehicle should not be driven with the
transmission range switch disconnected; idle quality will
be affected.
The four inputs from the transmission range switch
indicate to the PCM which position is selected by the
transmission selector lever. This information is used for
ignition timing, EVAP canister purge, EGR and IAC valve
operation.For more information on the transmission on the
transmission range switch, refer to
4L30-E Automatic
Transmission
.
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
The PCM determines the speed of the vehicle by
converting a plusing voltage signal from the vehicle speed
sensor (VSS) into miles per hour. The PCM uses this
signal to operate the cruise control, speedometer, and the
TCC and shift solenoids in the transmission. For more
information on the TCC and shift solenoids, refer to
4L30-E Automatic Transmission.
0008
Use of Circuit Testing Tools
Do not use a test light to diagnose the powertrain
electrical systems unless specifically instructed by the
diagnostic procedures. Use Connector Test Adapter Kit J
35616 whenever diagnostic procedures call for probing
connectors.
Aftermarket Electrical and Vacuum
Equipment
Aftermarket (add-on) electrical and vacuum equipment is
defined as any equipment which connects to the vehicle’s
electrical or vacuum systems that is installed on a vehicle
after it leaves the factory. No allowances have been
made in the vehicle design for this type of equipment.
NOTE: No add-on vacuum equipment should be added
to this vehicle.
NOTE: Add-on electrical equipment must only be
connected to the vehicle’s electrical system at the battery
(power and ground).
Add-on electrical equipment, even when installed to
these guidelines, may still cause the powertrain system to
malfunction. This may also include equipment not
connected to the vehicle electrical system such as
portable telephones and radios. Therefore, the first step
in diagnosing any powertrain problem is to eliminate all
aftermarket electrical equipment from the vehicle. After
Page 5406 of 6000

ENGINE ELECTRICAL 6D – 3
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
BATTERY CHARGING
Observe the following safety precautions when
charging the battery:
1. Never attempt to charge the battery when the fluid
level is below the lower level line on the side of the
battery. In this case, the battery must be replaced.
2. Pay close attention to the battery during the
charging procedure.
Battery charging should be discontinued or the rate
of charge reduced if the battery feels hot to the
touch.
Battery charging should be discontinued or the rate
of charge reduced if the battery begins to gas or
spew electrolyte from the vent holes.
3. In order to more easily view the hydrometer blue
dot or ring, it may be necessary to jiggle or tilt the
battery.
4. Battery temperature can have a great effect on
battery charging capacity.
5. The sealed battery used on this vehicle may be
either quick-charged or slow-charged in the same
manner as other batteries.
Whichever method you decide to use, be sure that
you completely charge the battery. Never partially
charge the battery.
JUMP STARTING
JUMP STARTING WITH AN AUXILIARY
(BOOSTER) BATTERY
CAUTION: Never push or tow the vehicle in an
attempt to start it. Serious damage to the emission
system as well as other vehicle parts will result.
Treat both the discharged battery and the booster
battery with great care when using jumper cables.
Carefully follow the jump starting procedure, being
careful at all times to avoid sparking.
WARNING: Failure to carefully follow the jump
starting procedure could result in the following:
1. Serious personal injury, particularly to your
eyes.
2. Property damage from a battery explosion,
battery acid, or an electrical fire.
3. Damage to the electronic components of one or
both vehicles.
Never expose the battery to an open flame or electrical
spark. Gas generated by the battery may catch fire or
explode. Remove any rings, watches, or other jewelry
before working around the battery. Protect your eyes by
wearing an approved set of goggles.
Never allow battery fluid to come in contact with your
eyes or skin.
Never allow battery fluid to come in contact with fabrics
or painted surfaces.
Battery fluid is a highly corrosive acid.Should battery fluid come in contact with your eyes,
skin, fabric, or a painted surface, immediately and
thoroughly rinse the affected area with clean tap water.
Never allow metal tools or jumper cables to come in
contact with the positive battery terminal, or any other
metal surface of the vehicle. This will protect against a
short circuit.
Always keep batteries out of the reach of young
children.
JUMP STARTING PROCEDURE
1. Set the vehicle parking brake.
If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic
transmission, place the selector lever in the “PARK”
position.
If the vehicle is equipped with a manual
transmission place the shift lever in the “NEUTRAL”
position.
Turn “OFF” the ignition.
Turn “OFF” all lights and any other accessory
requiring electrical power.
2. Look at the built-in hydrometer.
If the indication area of the built-in hydrometer is
completely clear, do not try to jump start.
3. Attach the end of one jumper cable to the positive
terminal of the booster battery.
Attach the other end of the same cable to the
positive terminal of the discharged battery.
Do not allow the vehicles to touch each other.
This will cause a ground connection, effectively
neutralizing the charging procedure.
Be sure that the booster battery has a 12 volt rating.
4. Attach one end of the remaining cable to the
negative terminal of the booster battery.
Attach the other end of the same cable to a solid
engine ground (such as the A/C compressor
bracket or the generator mounting bracket) of the
vehicle with the discharged battery.
This ground connection must be at least 450 mm
(18 in) from the battery of the vehicle whose battery
is being charged.
WARNING: Never attach the end of the jumper
cable directly to the negative terminal of the dead
battery.
5. Start the engine of the vehicle with the good battery.
Make sure that all unnecessary electrical
accessories have been turned “OFF”.
6. Start the engine of the vehicle with the dead battery.
7. To remove the jumper cables, follow the above
directions in the reverse order.
Be sure to first disconnect the negative cable from
the vehicle with the discharged battery.
Page 5485 of 6000
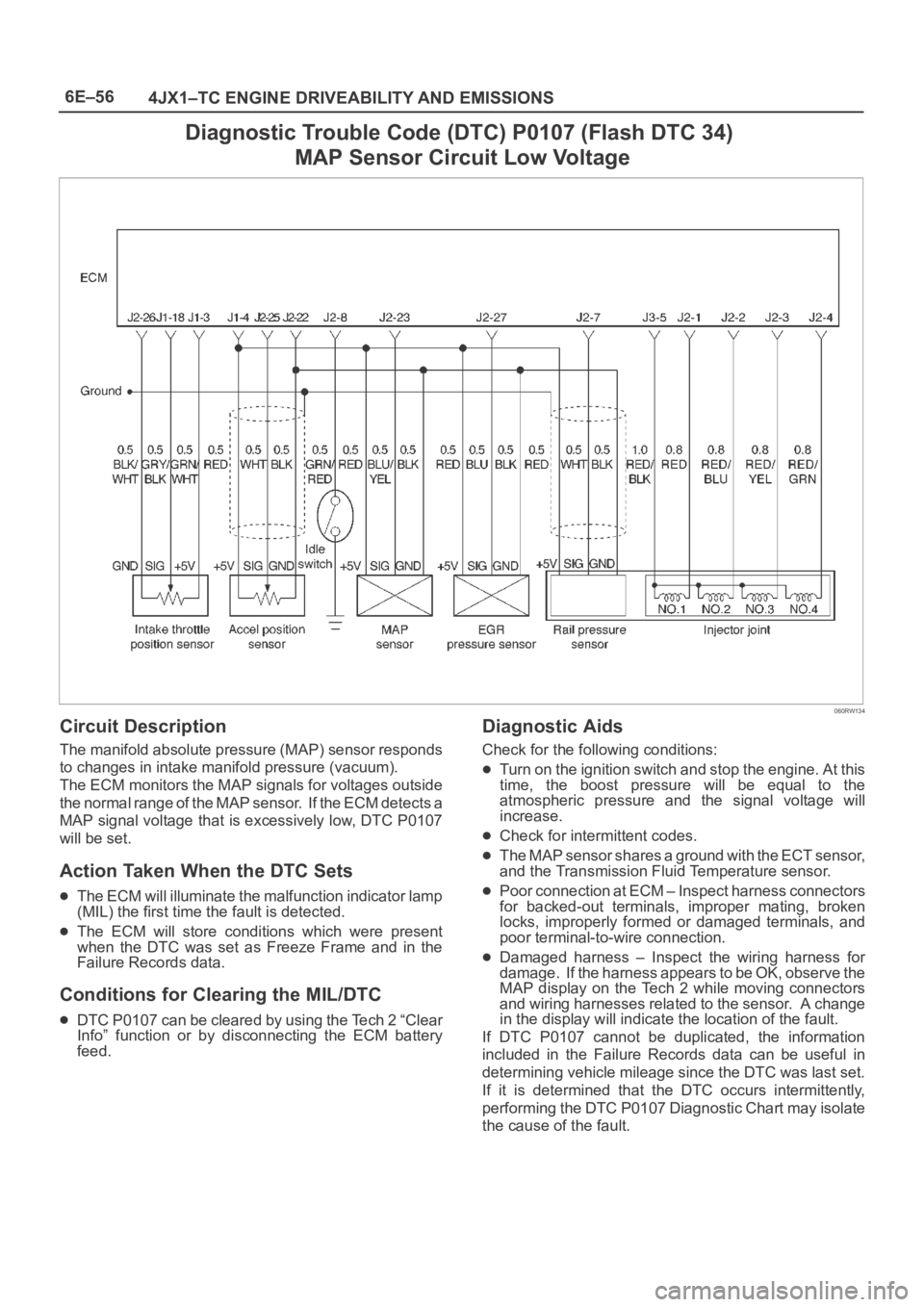
6E–56
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0107 (Flash DTC 34)
MAP Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
060RW134
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum).
The ECM monitors the MAP signals for voltages outside
the normal range of the MAP sensor. If the ECM detects a
MAP signal voltage that is excessively low, DTC P0107
will be set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0107 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Turn on the ignition switch and stop the engine. At this
time, the boost pressure will be equal to the
atmospheric pressure and the signal voltage will
increase.
Check for intermittent codes.
The MAP sensor shares a ground with the ECT sensor,
and the Transmission Fluid Temperature sensor.
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
MAP display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors
and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change
in the display will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC P0107 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
If it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently,
performing the DTC P0107 Diagnostic Chart may isolate
the cause of the fault.
Page 5628 of 6000
6E–199 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Default Matrix Table
Service Procedure Default Strategy
A referral strategy has been established to assist the
technician with additional information when the cause ofthe failure cannot be determined. If no problem is found
after performing diagnostics, then refer to the default
matrix table for further diagnostic information.
Default Matrix Table
Strategy Based Diagnostic ChartsInitial DiagnosisDefault Section(s)
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
CheckVehicle does not enter diagnostics.Chassis Electrical
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
CheckVehicle enters diagnostics and
communicates with the Tech 2. MIL is
“ON” in diagnostics. Engine does not
start and run.HEUI System Check
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
CheckEngine starts and runs, no ECM codes
set. Customer complains of vibration.—
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
CheckEngine starts and runs, no ECM codes
set. Customer complains of harsh or
soft shift, poor performance, delayed or
no engagement into drive or reverse,
transmission fluid leak, transmission
noise or vibration, or improper TCC
operation.Automatic Transmission
ECM Power and Ground CheckOn-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check.Chassis Electrical
ECM Power and Ground CheckOn-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check. ECM power and ground circuits
OK. Data link voltage incorrect.Chassis Electrical
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
CheckEngine starts and runs, no ECM codes
set. Customer complains of harsh or
soft shift, poor performance, delayed or
no engagement into drive or reverse,
transmission fluid leak, transmission
noise or vibration, or improper TCC
operation.Automatic Transmission
SymptomsInitial DiagnosisDefault Section(s)
Intermittents1. On-board diagnostic (OBD)
system check.
2. Careful visual/physical inspections.Chassis Electrical
Hard Starts1. OBD system check.
2. Sensors (ECT, MAP, EGR, AP) ;
output chart.
3. Fuel system electrical test, fuel
system diagnosis.
4. Injector system.Engine Mechanical, Injector
System Check, Exhaust System
Diagnosis
Surges and/or Chuggles1. OBD system check.
2. Fuel system diagnosis.
3. Injector system.Calibration ID “Broadcast”
/Service Bulletins, Ignition
System Check, Generator
Output, Exhaust System
Diagnosis
Lack of Power, Sluggish or Spongy1. OBD system check.
2. Fuel system diagnosis.
3. Injector system.Refer to Exhaust System in
Engine Exhaust, TCC
Operation, Calibration
ID/Service Bulletins
Page 5690 of 6000
7A–1 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
TRANSMISSION
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
CONTENTS
Service Precaution 7A–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Construction 7A–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Range Reference Chart 7A–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Normal Operation Of 2000 4L30–E
Transmission 7A–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnosis 7A–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Driver Information 7A–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Diagnosis Procedure 7A–8. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Preliminary Inspection Chart 7A–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Checking Transmission Fluid Level and
Condition 7A–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Test Driving 7A–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Mechanical / Hydraulic Diagnosis Check Trans
Indicator Chart 7A–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Mechanical / Hydraulic Diagnosis
Symptoms Index 7A–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Stall Test 7A–23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Line Pressure Test 7A–23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Shift Speed Chart (V6 3.2L 6VD1 Model) 7A–24. . .
Shift Speed Chart (V6 3.5L 6VE1 Model) 7A–26. .
Lockup Speed Chart (V6 3.2L 6VD1 Model) 7A–28
Lockup Speed Chart (V6 3.5L 6VE1 Model) 7A–28
Changing Transmission Fluid 7A–29. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Selector Lever 7A–29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspection 7A–29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 7A–30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Mode Switch 7A–31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 7A–31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmission (With Transfer Case) 7A–33. . . . . . . .
Transmission And Associated Parts 7A–33. . . . . .
Removal 7A–33. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–35. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Solenoid (Main Case Valve Body) 7A–39. . . . . . . . .
Removal 7A–39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Solenoid (Adapter Case Valve Body) 7A–40. . . . . . .
Removal 7A–40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Valve Body Assembly (Main Case) 7A–41. . . . . . . .
Removal 7A–41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Valve Body Assembly (Adapter Case) 7A–43. . . . . .
Removal 7A–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Installation 7A–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) 7A–43. . . . . . . . .
Removal 7A–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Speed Sensor (Extension Housing) 7A–44. . . . . . . .
Removal 7A–44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmission Oil Temperature Sensor
(Adapter Case) 7A–44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 7A–44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Front Oil Seal (Converter Housing) 7A–45. . . . . . . .
Removal 7A–45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rear Oil Seal (Extension Housing) 7A–46. . . . . . . . .
Removal 7A–46. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–46. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmission (4L30–E) 7A–46. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembly 7A–46. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reassembly 7A–50. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Converter Housing And Oil Pump Assembly 7A–60
Disassembled View 7A–60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembly 7A–60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspection And Repair 7A–60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reassembly 7A–60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Oil Pump 7A–61. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembled View 7A–61. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembly 7A–61. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspection And Repair 7A–61. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reassembly 7A–61. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Main Case Valve Body 7A–62. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembled View 7A–62. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembly 7A–62. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspection And Repair 7A–63. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reassembly 7A–63. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Adapter Case Valve Body 7A–64. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembled View 7A–64. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembly 7A–64. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspection And Repair 7A–64. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reassembly 7A–64. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Third Clutch And Sprag Unit 7A–65. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembled View 7A–65. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembly 7A–65. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspection And Repair 7A–66. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 5699 of 6000

7A–10
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Checking Transmission Fluid Level
and Condition
Checking fluid level and condition (color and odor) at
regular intervals will provide early diagnosis information
about the transmission. This information may be used to
correct a condition that, if not detected early, could result
in major transmission repairs.
IMPORTANT:When new, automatic transmission fluid
is red in color. As the vehicle is driven, the transmission
fluid will begin to look darker in color. The color may
eventually appear light brown.
A dark brown color with burnt odor may indicate
excessive fluid deterioration and signal a need for fluid
change.
Fluid Level
When adding or changing fluid, use only DEXRON –III.
Refer to Maintenance and Lubrication in General
Information section for maintenance information and
servicing interval.
CAUTION: DO NOT OVERFILL.
Overfilling will cause foaming, loss of fluid, abnor-
mal shifting and possible damage to the transmis-
sion.
1. Park the vehicle on level ground and apply the parking
brake firmly.
2. Check fluid level with engine running at idle.
NOTE: Be sure that transmission fluid temperature is
below 30
C (86F).
3. Move the selector lever through all gear ranges.
4. Move the selector lever to “Park”.
5. Let engine idle for 3 minutes and open the overfill
screw (1).
6. Add released transmission fluid until it flows out over
the overfill screw opening.
7. Let engine idle until a fluid temperature between 32
C
(90
F) and 57C (135F) is reached, then close the
overfill screw (1).
Torque: 38 N
m (3.9 kgꞏm/28 lb ft)
NOTE: To prevent fluid leaks, the overfill screw and oil
drain screws gasket must be replaced each time these
screws are removed.NOTE: Check transmission fluid temperature with scan
tool.
Minimum fluid level
57C (135F)
Maximum fluid level
32C (90F)
242RW003
CAUTION: Do not open overfill screw with engine
stopped.
CAUTION: DO NOT CHECK FLUID LEVEL UNDER
THESE CONDITIONS:
Immediately after driving at sustained highway
speeds.
In heavy city traffic during hot weather.
If vehicle is towing a trailer.
If the vehicle has been operated under these conditions,
shut the engine off and allow the vehicle to “cool” for thirty
(30) minutes. After the cool down period, restart the
vehicle and continue from step 2 above.