1998 OPEL FRONTERA oil temperature
[x] Cancel search: oil temperaturePage 2070 of 6000
6E–177 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
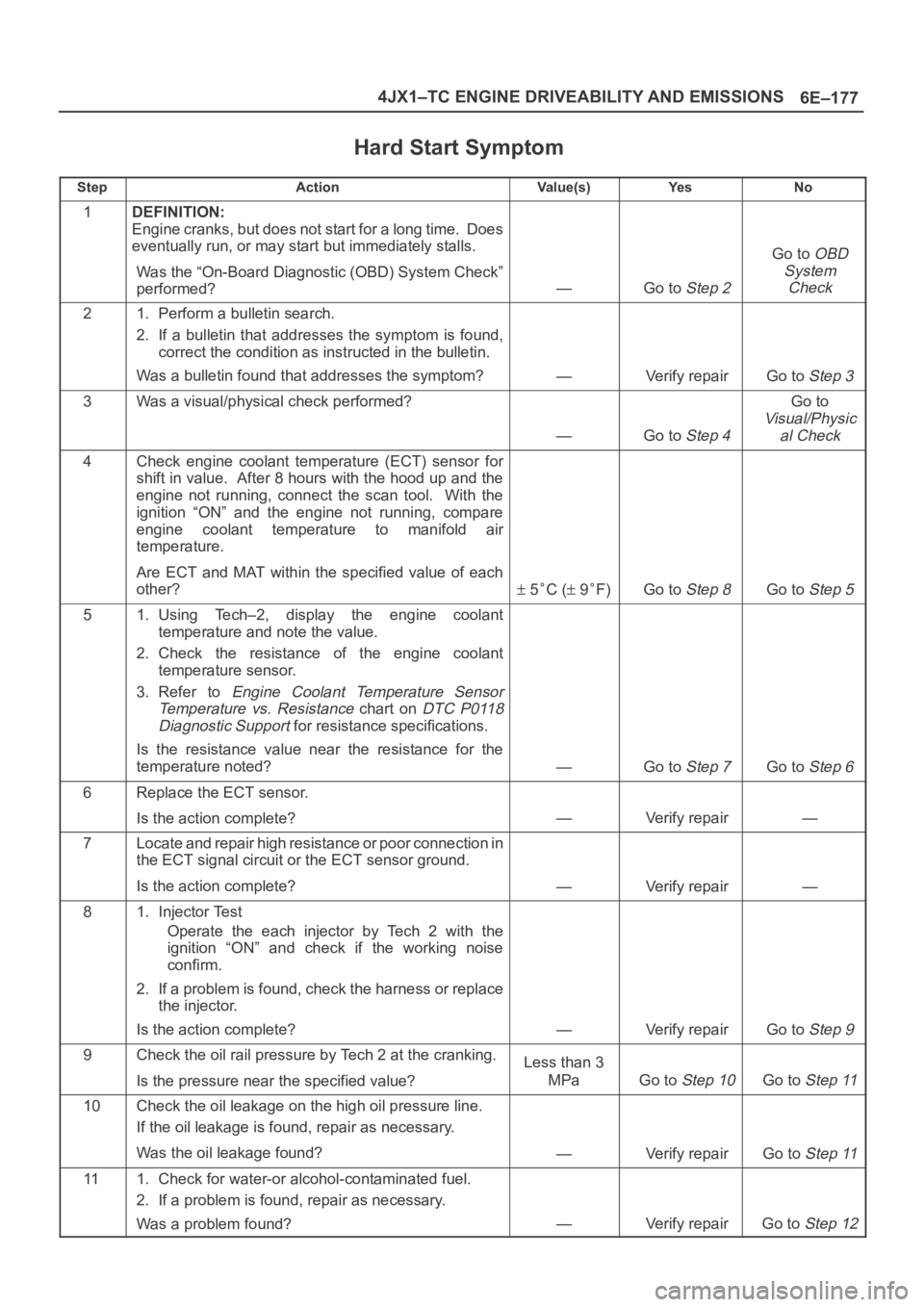
Hard Start Symptom
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1DEFINITION:
Engine cranks, but does not start for a long time. Does
eventually run, or may start but immediately stalls.
Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom?
—Verify repairGo to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to
Visual/Physic
al Check
4Check engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor for
shift in value. After 8 hours with the hood up and the
engine not running, connect the scan tool. With the
ignition “ON” and the engine not running, compare
engine coolant temperature to manifold air
temperature.
Are ECT and MAT within the specified value of each
other?
5C ( 9F)Go to Step 8Go to Step 5
51. Using Tech–2, display the engine coolant
temperature and note the value.
2. Check the resistance of the engine coolant
temperature sensor.
3. Refer to
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
Temperature vs. Resistance
chart on DTC P0118
Diagnostic Support
for resistance specifications.
Is the resistance value near the resistance for the
temperature noted?
—Go to Step 7Go to Step 6
6Replace the ECT sensor.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
7Locate and repair high resistance or poor connection in
the ECT signal circuit or the ECT sensor ground.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
81. Injector Test
Operate the each injector by Tech 2 with the
ignition “ON” and check if the working noise
confirm.
2. If a problem is found, check the harness or replace
the injector.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repairGo to Step 9
9Check the oil rail pressure by Tech 2 at the cranking.
Is the pressure near the specified value?Less than 3
MPa
Go to Step 10Go to Step 11
10Check the oil leakage on the high oil pressure line.
If the oil leakage is found, repair as necessary.
Was the oil leakage found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 11
111. Check for water-or alcohol-contaminated fuel.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 12
Page 2098 of 6000
6E–205 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
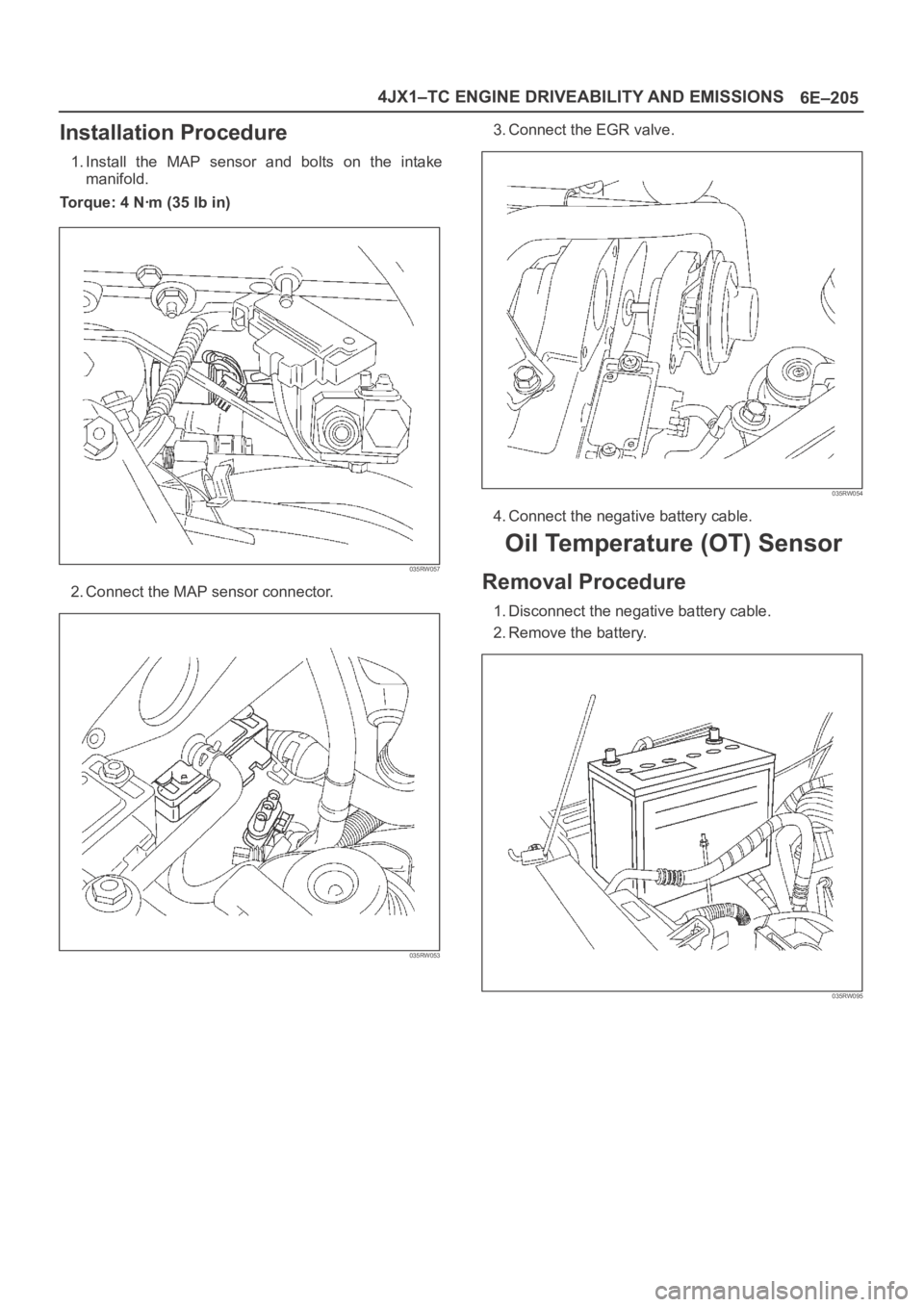
Installation Procedure
1. Install the MAP sensor and bolts on the intake
manifold.
Torque: 4 Nꞏm (35 lb in)
035RW057
2. Connect the MAP sensor connector.
035RW053
3. Connect the EGR valve.
035RW054
4. Connect the negative battery cable.
Oil Temperature (OT) Sensor
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the battery.
035RW095
Page 2119 of 6000

6E–226
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
0018
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure. The MAP sensor
signal voltage to the ECM varies from below 2 volts at idle
(high vacuum) to above 4 volts.
The MAP sensor is used to determine the following:
Boost pressure for injector control.
Barometric pressure (BARO).
If the ECM detects a voltage that is lower than the
possible range of the MAP sensor, DTC P0107 will be set.
A signal voltage higher than the possible range of the
sensor will set DTC P0108. An intermittent low or high
voltage will set DTC P1107 or DTC P1106, respectively.
The ECM can detect a shifted MAP sensor. The ECM
compares the MAP sensor signal to a calculated MAP
based on throttle position and various engine load factors.
If the ECM detects a MAP signal that varies excessively
above or below the calculated value, DTC P0106 will set.
Engine Control Module (ECM)
The engine control module (ECM) is located in the engine
room.
The ECM constantly observes the information from
various sensors. The ECM controls the systems that
affect vehicle performance. The ECM performs the
diagnostic function of the system. It can recognize
operational problems, alert the driver through the MIL
(Service Engine Soon lamp), and store diagnostic trouble
codes (DTCs). DTCs identify the problem areas to aid the
technician in making repairs.
ECM Function
The ECM supplies 5, 12 and 110 volts to power various
sensors or switches. The power is supplied through
resistances in the ECM which are so high in value that a
test light will not light when connected to the circuit. In
some cases, even an ordinary shop voltmeter will not give
an accurate reading because its resistance is too low.
Therefore, a digital voltmeter with at least 10 megohms
input impedance is required to ensure accurate voltage
readings. The ECM controls output circuits such as theinjectors, glow relays, etc., by controlling the ground or
the power feed circuit through transistors or through
either of the following two devices:
Output Driver Module (ODM)
Quad Driver Module (QDM)
ECM Components
The ECM is designed to maintain exhaust emission levels
to government mandated standards while providing
excellent driveability and fuel efficiency. The ECM
monitors numerous engine and vehicle functions via
electronic sensors such as the crankshaft position (CKP)
sensor, and vehicle speed sensor (VSS). The ECM also
controls certain engine operations through the following:
Fuel injector control
Rail pressure control
ECM Voltage Description
The ECM supplies a buffered voltage to various switches
and sensors. It can do this because resistance in the
ECM is so high in value that a test light may not illuminate
when connected to the circuit. An ordinary shop
voltmeter may not give an accurate reading because the
voltmeter input impedance is too low. Use a 10-megohm
input impedance digital voltmeter to assure accurate
voltage readings.
The input/output devices in the ECM include
analog-to-digital converters, signal buffers, counters,
and special drivers. The ECM controls most components
with electronic switches which complete a ground circuit
when turned “ON.” These switches are arranged in
groups of 4 and 7, called either a surface-mounted quad
driver module (QDM), which can independently control up
to 4 output terminals, or QDMs which can independently
control up to 7 outputs. Not all outputs are always used.
ECM Input/Outputs
Inputs – Operating Conditions Read
Air Conditioning “ON” or “OFF”
Engine Coolant Temperature
Crankshaft Position
Electronic Ignition
Manifold Absolute Pressure
Battery Voltage
Intake Throttle Position
Vehicle Speed
Fuel Temperature
Oil Temperature
Intake Air Temperature
EGR boost pressure
Oil rail pressure
Camshaft Position
Accelerator position
Outputs – Systems Controlled
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
Injector Control
QWS
Page 2121 of 6000

6E–228
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
General Description (Air Induction)
Air Induction System
The air induction system filters contaminants from the
outside air, and directs the progress of the air as it is
drawn into the engine. A remote-mounted air cleaner
prevents dirt and debris in the air from entering the
engine. The air duct assembly routes filtered air to the
throttle body. Air enters the engine by to following steps:
1. Through the throttle body.
2. Into the intake manifold.
3. Through the cylinder head intake ports.
4. Into the cylinders.
General Description (Fuel Metering)
Deceleration Mode
The ECM reduces the amount of fuel injected when it
detects a decrease in the Accelerator position.
Fuel Injector
Fuel injector comprises the solenoid, hydraulic line, and
fuel line. Fuel injection is controlled by the continuity time
signal and continuity start timing signal from ECM to the
solenoid
ECM determines the running conditions of engine by
input signals such as engine speed. Accelerator throttle
valve opening, and engine coolant temperature, thereby
to send the solenoid the best suited signal to the engine
status. When current is carried to the solenoid, the
armature opens the poppet valve to alow high pressure oil
to run into the injector. Under the pressure of the oil, the
piston and plunger are depressed to compress the fuel in
the combustion chamber of the plunger. Specifically, the
pressure of the fuel compressed is increased by a piston
top/ plunger bottom area ratio over the pressure of high
pressure oil, thereby lifting the fuel nozzle end needle for
injecting fuel.
Fuel Metering System Components
The fuel metering system is made up of the following
parts:
The fuel injectors.
The intake throttle body.
The Accelerator position (AP) sensor
The ECM.
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor.
The camshaft position (CMP) sensor.
Basic System Operation
Fuel is supplied through fuel filter to the fuel pump.
The fuel pump is installed to the oil pump, and fuel is
forced, through the fuel pump outlet, pipe and cylinder
head inside, into the fuel injector.
An orifice is provided at the rear fuel outlet of cylinder
head to control the pressure of oil.The injector is controlled by ECM which gives
opening/closing commands to the solenoid installed on
the top of the injector. Opening/closing operation of the
pressurized engine oil circuit of the injector controls fuel
injection quantity, fuel injection timing, etc.
A/C Clutch Diagnosis
A/C Request Signal
This signal tells the ECM when the A/C mode is selected
at the A/C control head. The ECM uses this to adjust the
idle speed.
Refer to
A/C Clutch Circuit Diagnosis for A/C wiring
diagrams and diagnosis for A/C electrical system.
General Description Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) System
EGR Purpose
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system is use to
reduce emission levels of oxides of nitrogen (NOx). NOx
emission levels are caused by a high combustion
temperature. The EGR system lowers the NOx emission
levels by decreasing the combustion temperature.
The ECM uses information from the following sensors to
control EGR valve boost pressure.
ECT
ITP
Engine Speed
AP sensor
Page 2152 of 6000
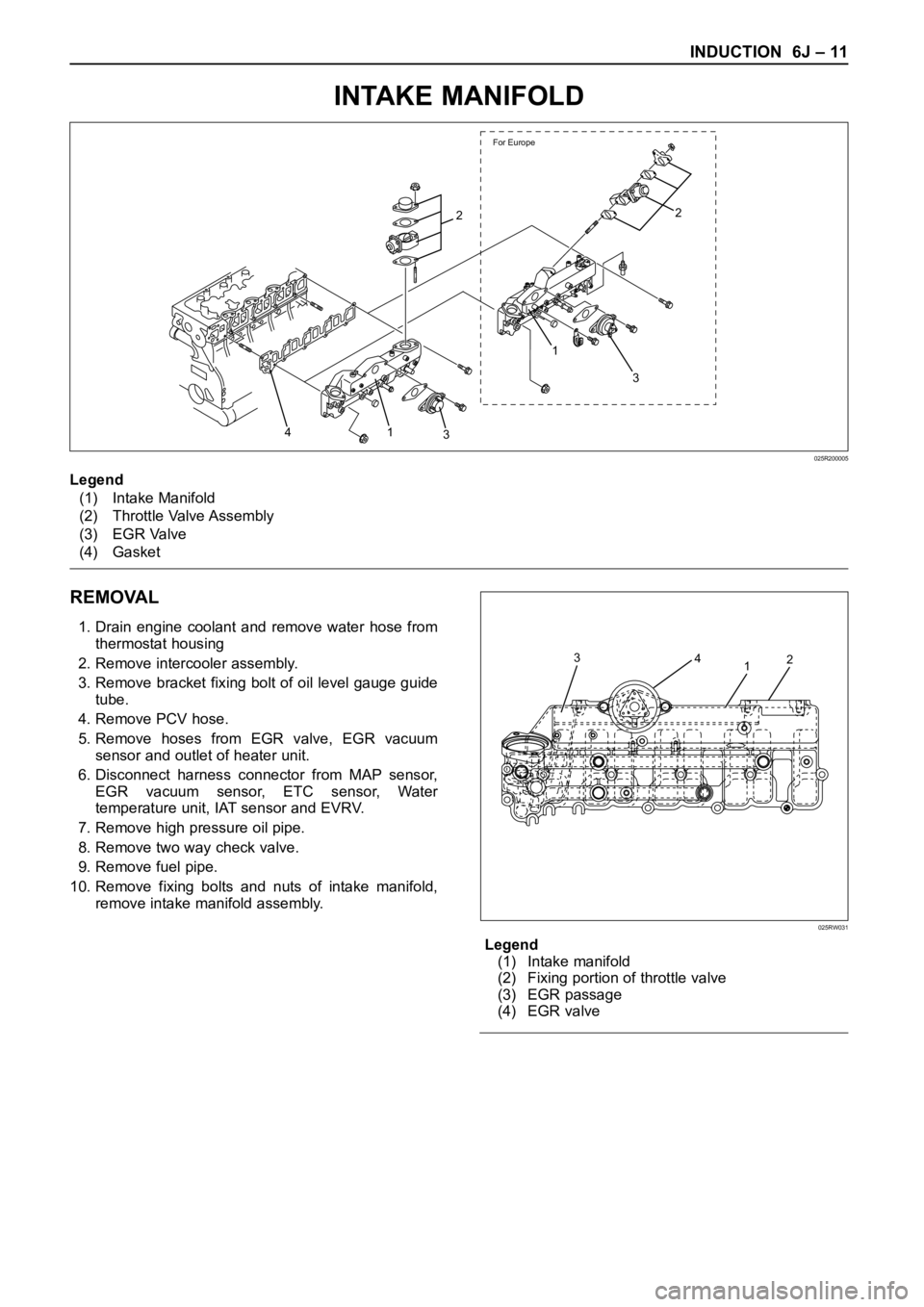
INDUCTION 6J – 11
INTAKE MANIFOLD
REMOVAL
1. Drain engine coolant and remove water hose from
thermostat housing
2. Remove intercooler assembly.
3. Remove bracket fixing bolt of oil level gauge guide
tube.
4. Remove PCV hose.
5. Remove hoses from EGR valve, EGR vacuum
sensor and outlet of heater unit.
6. Disconnect harness connector from MAP sensor,
EGR vacuum sensor, ETC sensor, Water
temperature unit, IAT sensor and EVRV.
7. Remove high pressure oil pipe.
8. Remove two way check valve.
9. Remove fuel pipe.
10. Remove fixing bolts and nuts of intake manifold,
remove intake manifold assembly.
Legend
(1) Intake manifold
(2) Fixing portion of throttle valve
(3) EGR passage
(4) EGR valve
For Europe
2
1
3
3 1 42
Legend
(1) Intake Manifold
(2) Throttle Valve Assembly
(3) EGR Valve
(4) Gasket
025R200005
3124
025RW031
Page 2153 of 6000

6J – 12 INDUCTION
INSPECTION AND RAPAIR
1. Visually check for cracks/clogs inside intake
manifold.
2. If foreign material is observed, it should be taken
out, and if there are some cracks on the intake
manifold, it must be replaced.
INSTALLATION
1. Install the intake manifold assembly, tighten bolts
and to the specified torque.
Torque: 20 Nꞏm (2.0 kgꞏm / 14.5 lb ft) for bolt
Torque: 20 Nꞏm (2.0 kgꞏm / 14.5 lb ft) for nut
2. Install fuel pipe.
Torque: 4 Nꞏm (0.4 kgꞏm / 2.9 lb ft) for M16 nut
(Apply engine oil)
Torque: 13 Nꞏm (1.3 kgꞏm / 9.4 lb ft) for M10 cap nut
Torque: 14 Nꞏm (1.4 kgꞏm / 10 lb ft) for M10
(Apply engine oil)
3. Install two way check valve.
Torque: 20 Nꞏm (2.0 kgꞏm / 14.5 lb ft)
4. Fill with about 300 cc of engine oil from the high
pressure oil pipe installation port of the oil rail using
an oil filler.
If assembled without filling the oil rail with oil, the
time for engine starting will be longer.
5. Install high pressure oil pipe, then tighten sleeve nut
to the specified torque.
Torque: 29 Nꞏm (3.0 kgꞏm / 21.7 lb ft)
6. Reconnect harness connector to MAP sensor, EGR
vacuum sensor, ETC sensor, Water thermo unit,
IAT sensor and EVRV sensor.
7. Install hoses to EGR valve, EGR vacuum sensor
and Water outlet of heater.
8. Connect PCV hose.
9. Install oil level gauge guide and fix it.
10. Install intercooler assembly.
Refer to “Intercooler” in this manual.
11. Install water hose to thermostat housing and fill with
engine coolant.
Model of Turbocharger IHI RHF5
Turbine Maximum Speed 180,000 rpm
Maximum Inlet Gas Temperature 800 °C (1472 °F)
Vibration Peak (G) criteria Maximum 4 (G) at Turbine Rotor Speed 140,000 rpm
Tolerance Limit of Compressor Blade Height Less then 0.5 mm (0.0197 in)
MAIN DATA AND SPECIFICATIONS
Page 2155 of 6000
7A–1 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
TRANSMISSION
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
CONTENTS
Service Precaution 7A–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Construction 7A–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Range Reference Chart 7A–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Normal Operation Of 1998 4L30–E
Transmission 7A–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnosis 7A–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Driver Information 7A–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Diagnosis Procedure 7A–8. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Preliminary Inspection Chart 7A–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Checking Transmission Fluid Level and
Condition 7A–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Test Driving 7A–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Mechanical / Hydraulic Diagnosis Check Trans
Indicator Chart 7A–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Mechanical / Hydraulic Diagnosis Symptoms
Index 7A–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Stall Test 7A–23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Line Pressure Test 7A–23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Shift Speed Chart 7A–24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Lockup Speed Chart 7A–26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Changing Transmission Fluid 7A–27. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Selector Lever 7A–27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspection 7A–27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 7A–28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Mode Switch 7A–29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 7A–29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmission (With Transfer Case) 7A–31. . . . . . . .
Transmission And Associated Parts 7A–31. . . . . .
Removal 7A–31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–33. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Solenoid (Main Case Valve Body) 7A–36. . . . . . . . .
Removal 7A–36. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–36. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Solenoid (Adapter Case Valve Body) 7A–37. . . . . . .
Removal 7A–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Valve Body Assembly (Main Case) 7A–38. . . . . . . .
Removal 7A–38. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–38. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Valve Body Assembly (Adapter Case) 7A–40. . . . . .
Removal 7A–40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) 7A–40. . . . . . . . . Removal 7A–40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Speed Sensor (Extension Housing) 7A–41. . . . . . . .
Removal 7A–41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmission Oil Temperature Sensor
(Adapter Case) 7A–41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 7A–41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Front Oil Seal (Converter Housing) 7A–42. . . . . . . .
Removal 7A–42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rear Oil Seal (Extension Housing) 7A–43. . . . . . . . .
Removal 7A–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 7A–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmission (4L30–E) 7A–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembly 7A–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reassembly 7A–47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Converter Housing And Oil Pump Assembly 7A–57
Disassembled View 7A–57. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembly 7A–57. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspection And Repair 7A–57. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reassembly 7A–57. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Oil Pump 7A–58. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembled View 7A–58. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembly 7A–58. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspection And Repair 7A–58. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reassembly 7A–58. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Main Case Valve Body 7A–59. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembled View 7A–59. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembly 7A–59. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspection And Repair 7A–60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reassembly 7A–60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Adapter Case Valve Body 7A–61. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembled View 7A–61. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembly 7A–61. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspection And Repair 7A–61. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reassembly 7A–61. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Third Clutch And Sprag Unit 7A–63. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembled View 7A–63. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembly 7A–63. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspection And Repair 7A–64. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reassembly 7A–64. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Third Clutch 7A–65. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 2159 of 6000

7A–5 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Normal Operation Of 1998 4L30–E
Tr a n s m i s s i o n
Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
Application Conditions:
The TCC is normally applied in 2nd, 3rd and 4th gears
only when all of the following conditions exist:
— The engine coolant temperature is above 70
C
(158
F).
— The brake pedal is released.
— The shift pattern requests TCC apply.
Moreover, TCC is always applied in 2nd, 3rd and 4th
gears when the transmission oil temperature is above
135
C (275F).
This mode should be canceled at 125
C (257F).
ATF Warning Lamp
The ATF warning lamp will be constantly on (not flashing)
if the transmission oil temperature is above 140
C
(284
F).
The ATF warning lamp goes off again when the
transmission oil temperature is below 130
C (266F).
Special Shift Pattern When The Engine Is
Cold:
A special shift pattern is activated when the engine
coolant temperature is below 70
C (158F). (3–4 shifts,
for example, are delayed for small throttle openings and
will occur a few MPH higher.)
Diagnosis
Introduction
The systematic troubleshooting information covered by
this Section offers a practical and systematic approach to
diagnosing 4L30–E transmission, using information that
can be obtained from road tests, electrical diagnosis, oil
pressure checks or noise evaluation.
The key to correcting a complaint is to make use of all of
the available symptoms and logically letting them direct
you to the cause.
When dealing with automatic transmission complaints, it
is best to gather as many symptoms as possible before
making the decision to remove the transmission from the
vehicle.
Frequently, the correction of the complaint does not
require removal of the transmission from the vehicle.
Driver Information
To analyze the problem fill out a complete description of
the owner’s complaint.
Please draw a circle around the right information and
complete the following form. (The next page is an
example of a completed form). You can draw a circle
around many numbers if you are not sure.