1998 OPEL FRONTERA transmission
[x] Cancel search: transmissionPage 4916 of 6000

6E–259 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1640 Driver-1-Input High Voltage
Circuit Description
Output driver modules (ODMs) are used by the
powertrain control module (PCM) to turn “ON” many of
the current-driven devices that are needed to control
various engine and transmission functions. Each ODM is
capable of controlling up to 7 separate outputs by
applying ground to the device which the PCM is
commanding “ON.”
Unlike the Quad Driver Modules (QDMs) used in prior
model years, ODMs have the capability of diagnosing
each output circuit individually. DTC P1640 set indicates
an improper voltage level has been detected on an ODM
output.
Since A/C is an option, No A/C will cause the air
conditioning clutch relay output to always fault. If a fault is
seen on the air conditioning clutch relay output, it will not
be logged as a fault until the A/C request input interrupts a
high voltage, indicating that A/C has been installed.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Ignition “ON.”
Engine running.
No DTC 1618.
Ignition voltage is above 13.2 volts for 4 seconds.
Output voltage does not equal ignition voltage when
output is “OFF” or output voltage is not less than 1 volt
when output is “ON.”
Above conditions occur for at least 1 second.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will not illuminate the malfunction indicator
lamp (MIL).
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Failure Records only. This
information will not be stored as Freeze Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P1640 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at PCM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage, If the harness appears to be OK, disconnect
the PCM, turn the ignition “ON” and observe a
voltmeter connected to the suspect driver circuit at the
PCM harness connector while moving connectors and
wiring harnesses relates to the MIL. A change in
voltage will indicate the location of the fault.
Poor connection at component – Examine for
damaged connectors, unplugged connector, or
damaged terminals at the following locations:
Instrument cluster harness, canister purge solenoid,
A/C clutch relay. An open ignition feed circuit at any of
these components will cause DTC P1640 to be set.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
The following PCM pins are controlled by output driver
modules (ODMs):
A13 – “Check Engine Lamp”
A14 – SVS (”Check Trans”)
B14 – A/C Clutch
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
6. The Tech 2 Driver Module Status indicates the PCM
pin that is affected.
11. The Tech 2 may indicate “short circuit” even when
the problem is an open circuit. The cause of an
open circuit may be in the component itself-lamp,
purge, solenoid, or A/C compressor relay.
13.A short to ground on the ignition side of the
component will blow the fuse. Since the fuse was
checked in Step 4, a short to ground would be
between the affected component and the PCM.
Page 4922 of 6000
6E–265 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
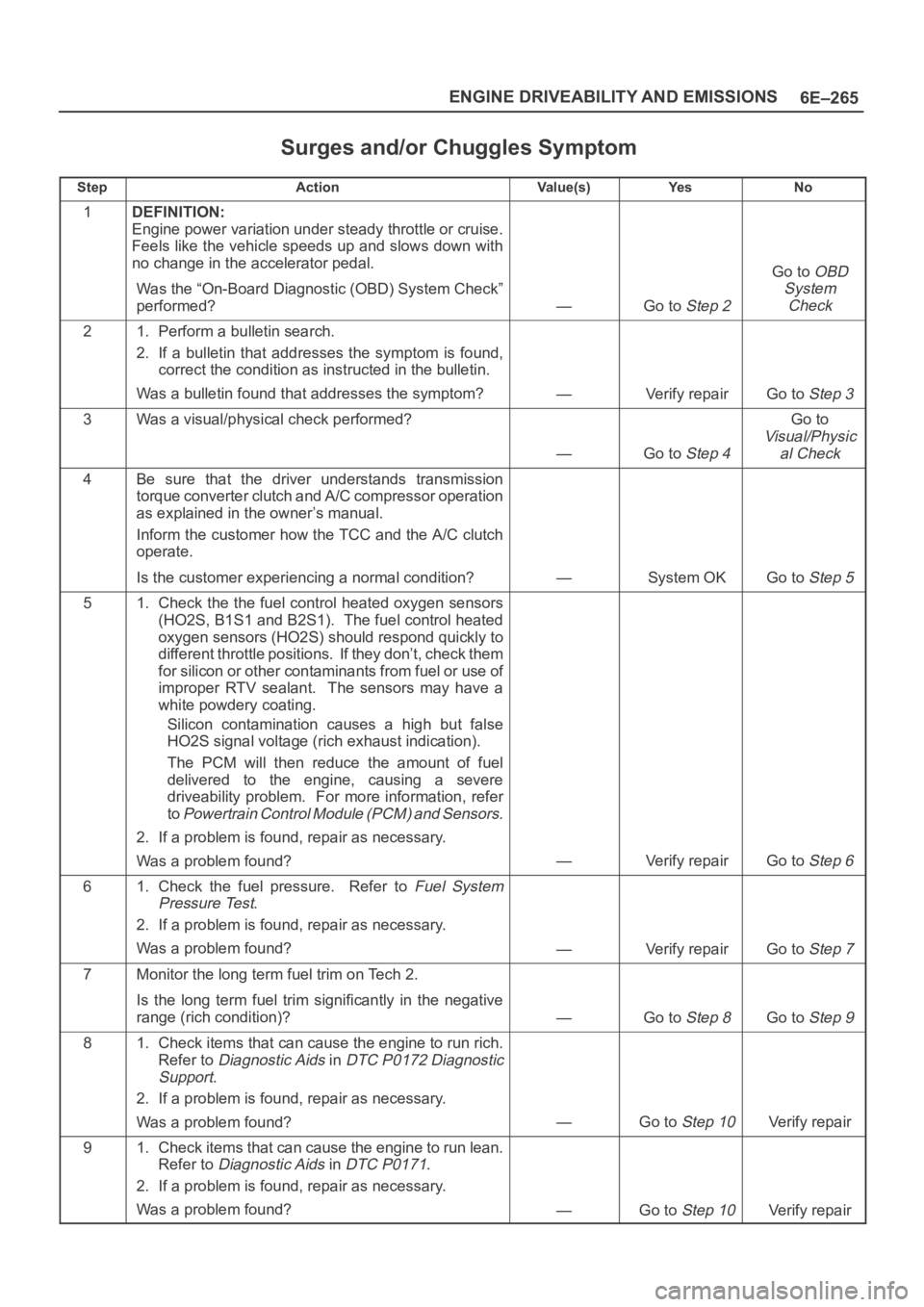
Surges and/or Chuggles Symptom
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1DEFINITION:
Engine power variation under steady throttle or cruise.
Feels like the vehicle speeds up and slows down with
no change in the accelerator pedal.
Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom?
—Verify repairGo to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to
Visual/Physic
al Check
4Be sure that the driver understands transmission
torque converter clutch and A/C compressor operation
as explained in the owner’s manual.
Inform the customer how the TCC and the A/C clutch
operate.
Is the customer experiencing a normal condition?
—System OKGo to Step 5
51. Check the the fuel control heated oxygen sensors
(HO2S, B1S1 and B2S1). The fuel control heated
oxygen sensors (HO2S) should respond quickly to
different throttle positions. If they don’t, check them
for silicon or other contaminants from fuel or use of
improper RTV sealant. The sensors may have a
white powdery coating.
Silicon contamination causes a high but false
HO2S signal voltage (rich exhaust indication).
The PCM will then reduce the amount of fuel
delivered to the engine, causing a severe
driveability problem. For more information, refer
to
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) and Sensors.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 6
61. Check the fuel pressure. Refer to Fuel System
Pressure Test
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 7
7Monitor the long term fuel trim on Tech 2.
Is the long term fuel trim significantly in the negative
range (rich condition)?
—Go to Step 8Go to Step 9
81. Check items that can cause the engine to run rich.
Refer to
Diagnostic Aids in DTC P0172 Diagnostic
Support
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Go to Step 10Verify repair
91. Check items that can cause the engine to run lean.
Refer to
Diagnostic Aids in DTC P0171.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Go to Step 10Verify repair
Page 4926 of 6000

6E–269 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Lack of Power, Sluggish or Spongy Symptom
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
111. Check the PCM grounds for the cleanliness,
tightness and proper locations. Refer to the PCM
wiring diagrams in
Electrical Diagnosis.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 12
121. Check the exhaust system for possible restriction:
Inspect the exhaust system for damaged or
collapsed pipes.
Inspect the muffler for heat distress or possible
internal failure.
Check for a possible plugged three-way
catalytic converter by checking the exhaust
system back pressure. Refer to
Restricted
Exhaust System Check
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 13
131. Check the torque converter clutch (TCC) for proper
operation. Refer to
4L30-E Transmission
Diagnosis
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 14
141. Check for an engine mechanical problem. Check
for low compression, incorrect or worn camshaft,
loose timing belt, etc. Refer to
Engine Mechanical.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 15
151. Review all diagnostic procedures within this table.
2. If all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
Visual/physical inspection
Te c h 2 d a t a
Freeze Frame data/Failure Records buffer
All electrical connections within a suspected
circuit and/or system.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repair
Contact
Te c h n i c a l
Assistance
Page 4927 of 6000
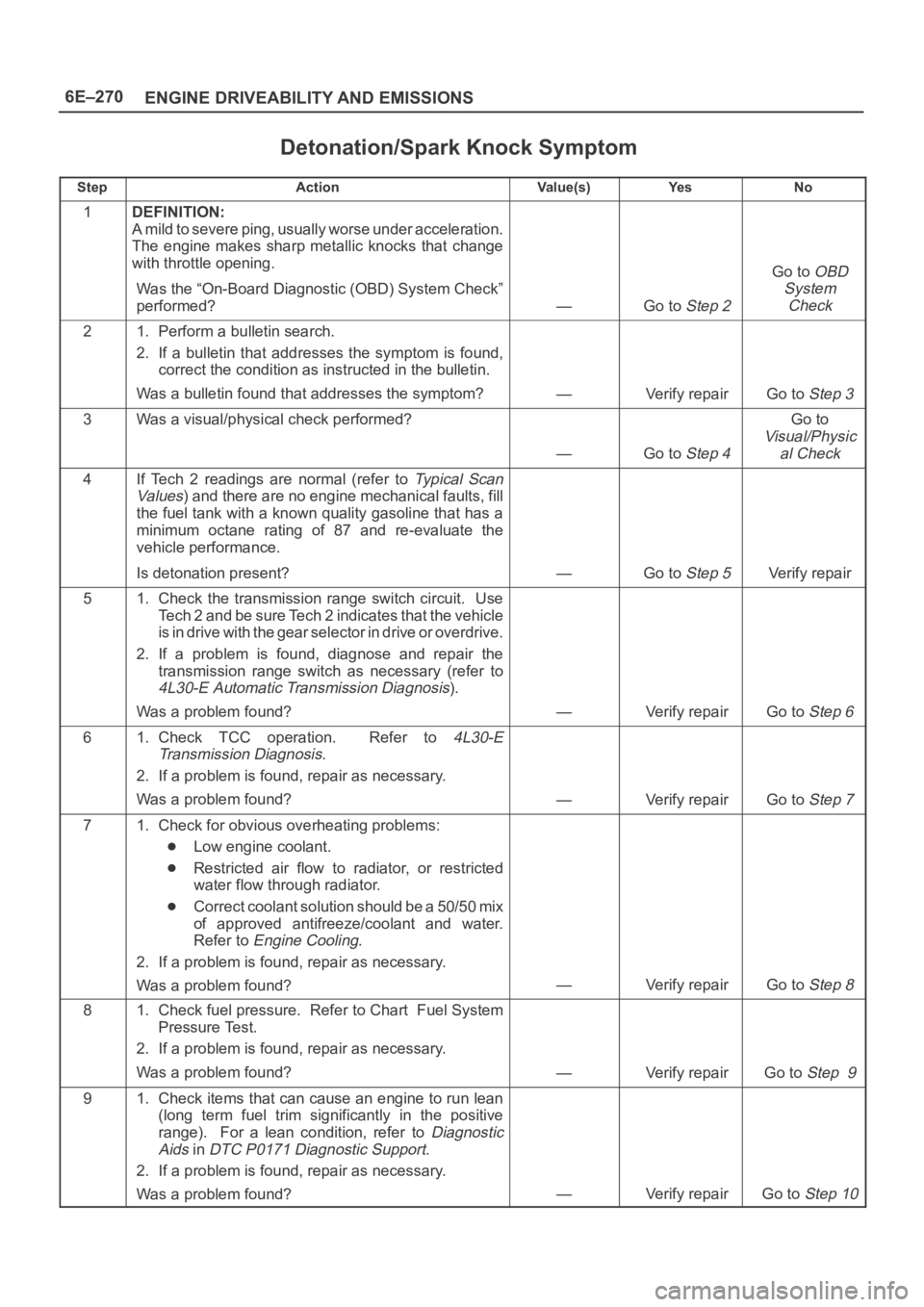
6E–270
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Detonation/Spark Knock Symptom
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1DEFINITION:
A mild to severe ping, usually worse under acceleration.
The engine makes sharp metallic knocks that change
with throttle opening.
Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom?
—Verify repairGo to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to
Visual/Physic
al Check
4If Tech 2 readings are normal (refer to Ty p i c a l S c a n
Va lu es
) and there are no engine mechanical faults, fill
the fuel tank with a known quality gasoline that has a
minimum octane rating of 87 and re-evaluate the
vehicle performance.
Is detonation present?
—Go to Step 5Verify repair
51. Check the transmission range switch circuit. Use
Tech 2 and be sure Tech 2 indicates that the vehicle
is in drive with the gear selector in drive or overdrive.
2. If a problem is found, diagnose and repair the
transmission range switch as necessary (refer to
4L30-E Automatic Transmission Diagnosis).
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 6
61. Check TCC operation. Refer to 4L30-E
Transmission Diagnosis
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 7
71. Check for obvious overheating problems:
Low engine coolant.
Restricted air flow to radiator, or restricted
water flow through radiator.
Correct coolant solution should be a 50/50 mix
of approved antifreeze/coolant and water.
Refer to
Engine Cooling.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
81. Check fuel pressure. Refer to Chart Fuel System
Pressure Test.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 9
91. Check items that can cause an engine to run lean
(long term fuel trim significantly in the positive
range). For a lean condition, refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
in DTC P0171 Diagnostic Support.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 10
Page 4931 of 6000
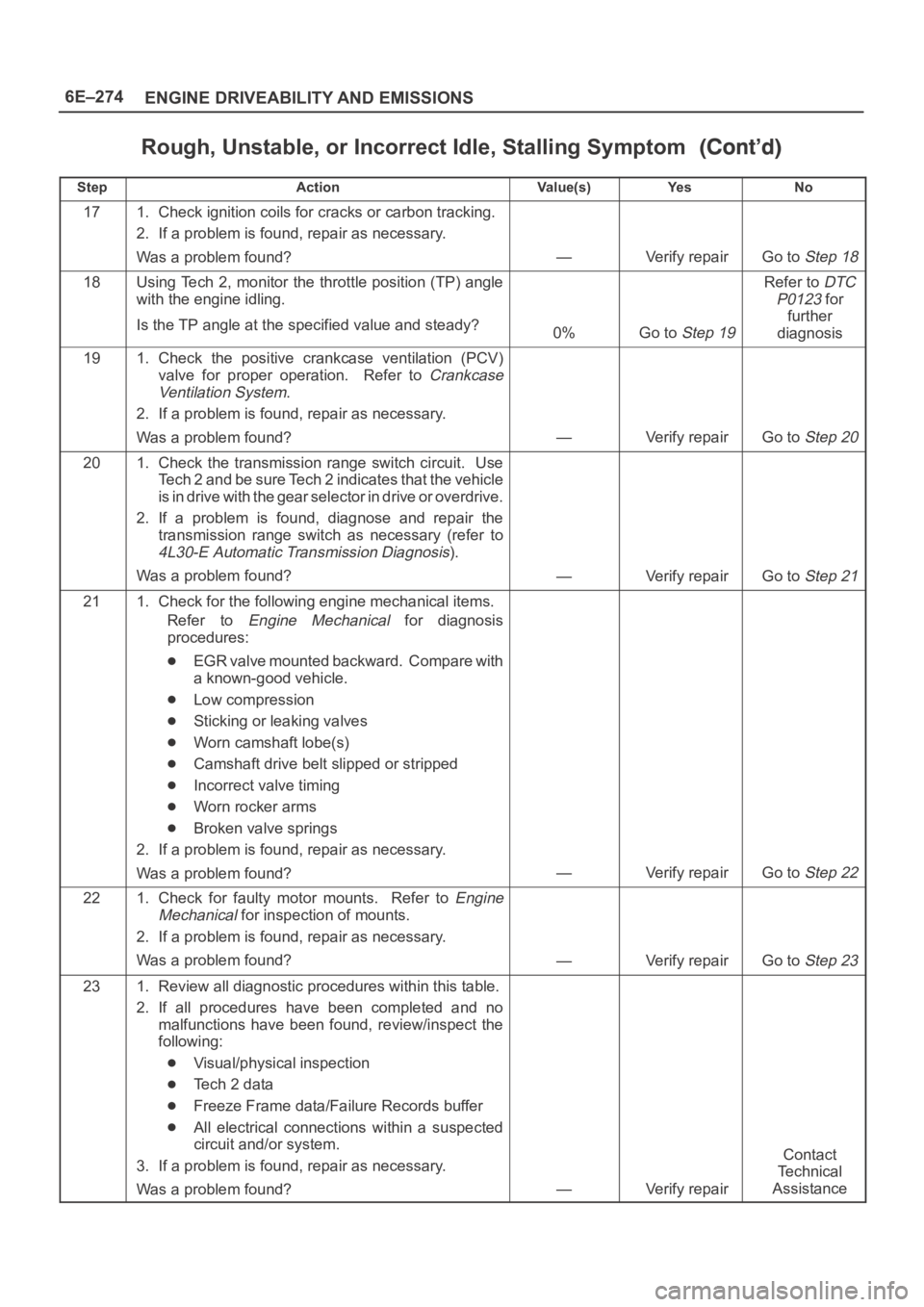
6E–274
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle, Stalling Symptom
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
171. Check ignition coils for cracks or carbon tracking.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 18
18Using Tech 2, monitor the throttle position (TP) angle
with the engine idling.
Is the TP angle at the specified value and steady?
0%Go to Step 19
Refer to DTC
P0123
for
further
diagnosis
191. Check the positive crankcase ventilation (PCV)
valve for proper operation. Refer to
Crankcase
Ventilation System
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 20
201. Check the transmission range switch circuit. Use
Tech 2 and be sure Tech 2 indicates that the vehicle
is in drive with the gear selector in drive or overdrive.
2. If a problem is found, diagnose and repair the
transmission range switch as necessary (refer to
4L30-E Automatic Transmission Diagnosis).
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 21
211. Check for the following engine mechanical items.
Refer to
Engine Mechanical for diagnosis
procedures:
EGR valve mounted backward. Compare with
a known-good vehicle.
Low compression
Sticking or leaking valves
Worn camshaft lobe(s)
Camshaft drive belt slipped or stripped
Incorrect valve timing
Worn rocker arms
Broken valve springs
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 22
221. Check for faulty motor mounts. Refer to Engine
Mechanical
for inspection of mounts.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 23
231. Review all diagnostic procedures within this table.
2. If all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
Visual/physical inspection
Te c h 2 d a t a
Freeze Frame data/Failure Records buffer
All electrical connections within a suspected
circuit and/or system.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repair
Contact
Te c h n i c a l
Assistance
Page 4933 of 6000
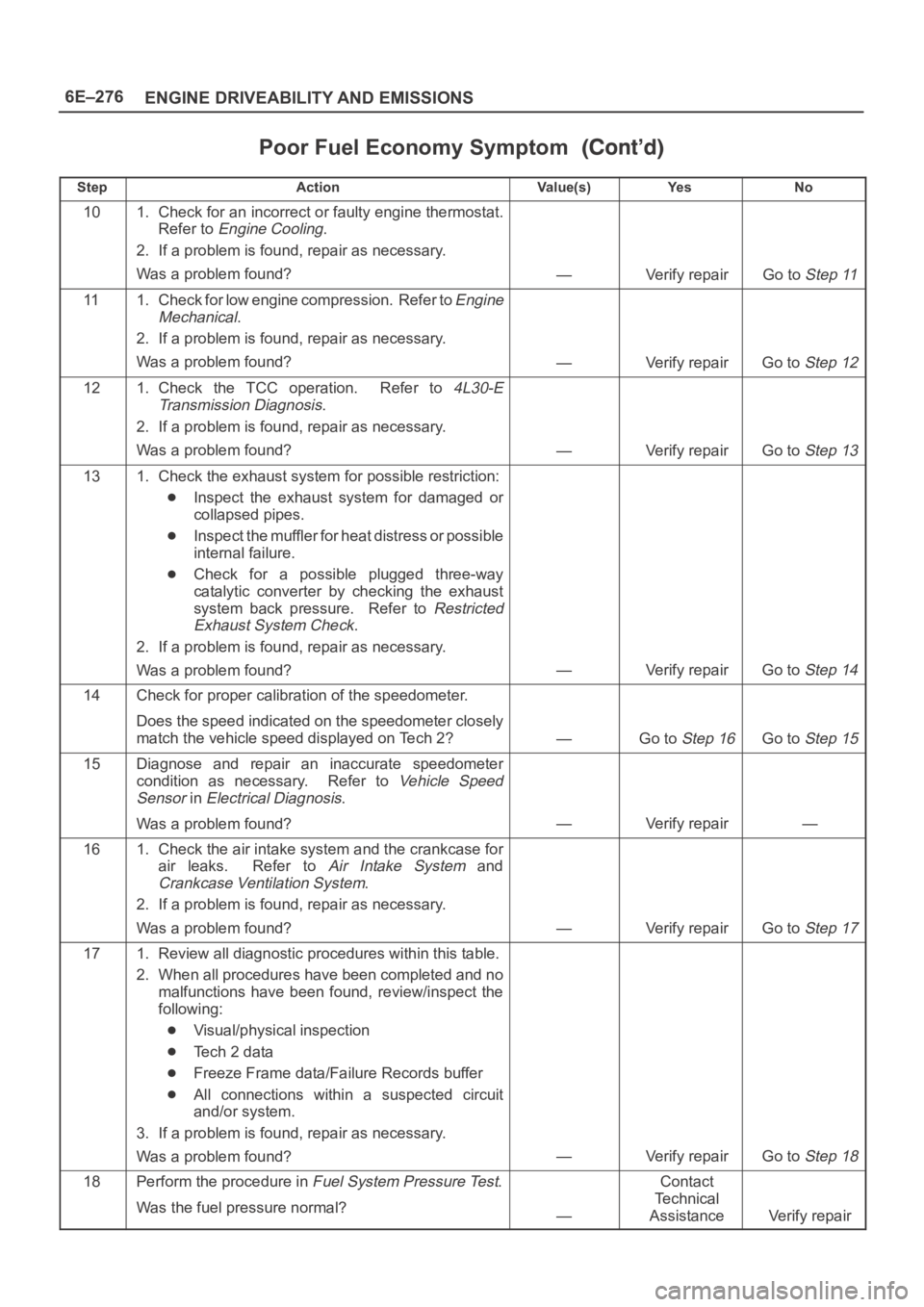
6E–276
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Poor Fuel Economy Symptom
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
101. Check for an incorrect or faulty engine thermostat.
Refer to
Engine Cooling.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 11
111. Check for low engine compression. Refer to Engine
Mechanical
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 12
121. Check the TCC operation. Refer to 4L30-E
Transmission Diagnosis
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 13
131. Check the exhaust system for possible restriction:
Inspect the exhaust system for damaged or
collapsed pipes.
Inspect the muffler for heat distress or possible
internal failure.
Check for a possible plugged three-way
catalytic converter by checking the exhaust
system back pressure. Refer to
Restricted
Exhaust System Check
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 14
14Check for proper calibration of the speedometer.
Does the speed indicated on the speedometer closely
match the vehicle speed displayed on Tech 2?
—Go to Step 16Go to Step 15
15Diagnose and repair an inaccurate speedometer
condition as necessary. Refer to
Vehicle Speed
Sensor
in Electrical Diagnosis.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repair—
161. Check the air intake system and the crankcase for
air leaks. Refer to
Air Intake System and
Crankcase Ventilation System.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 17
171. Review all diagnostic procedures within this table.
2. When all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
Visual/physical inspection
Te c h 2 d a t a
Freeze Frame data/Failure Records buffer
All connections within a suspected circuit
and/or system.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 18
18Perform the procedure in Fuel System Pressure Test.
Was the fuel pressure normal?
—
Contact
Te c h n i c a l
Assistance
Verify repair
Page 4941 of 6000
6E–284
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Cuts Out, Misses Symptom
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
171. Check ignition coils for cracks or carbon tracking.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 18
18Using Tech 2, monitor the TP angle with the engine
idling.
Is the TP angle at the specified value and steady?
0%Go to Step 19
Refer to DTC
P0123
for
further
diagnosis
191. Check the PCV valve for proper operation. Refer to
Crankcase Ventilation System.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 20
201. Check the transmission range switch circuit. Use
Tech 2 and be sure Tech 2 indicates that the vehicle
is in drive with the gear selector in drive or overdrive.
2. If a problem is found, diagnose and repair the
transmission range switch as necessary (refer to
4L30-E Automatic Transmission Diagnosis).
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 21
211. Check the following engine mechanical items.
Refer to
Engine Mechanical for diagnosis
procedures:
Low compression
Sticking or leaking valves
Worn camshaft lobe(s)
Camshaft drive belt slipped or stripped
Incorrect valve timing
Worn rocker arms
Broken valve springs
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 22
221. Check for faulty motor mounts. Refer to Engine
Mechanical
for inspection of mounts.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 23
231. Review all diagnostic procedures within this table.
2. If all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
Visual/physical inspection
Te c h 2 d a t a
Freeze Frame data/Failure Records butter
All electrical connections within a suspected
circuit and/or system
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repair
Contact
Te c h n i c a l
Assistance
Page 4945 of 6000

6E–288
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Default Matrix Table
Service Procedure Default Strategy
A referral strategy has been established to assist the
technician with additional information when the cause of
the failure cannot be determined. If no problem is found
after performing diagnostics, then refer to the default
matrix table for further diagnostic information.
Default Matrix Table
Strategy Based Diagnostic Charts
Initial DiagnosisDefault Section(s)
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
CheckVehicle does not enter diagnostics.Chassis Electrical
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
CheckVehicle enters diagnostics and
communicates with Tech 2. MIL is
“ON” in diagnostics. Engine does not
start and run.Ignition System Check
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
CheckEngine starts and runs, no PCM
codes set. Customer complains of
vibration.—
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
CheckEngine starts and runs, no PCM
codes set. Customer complains of
harsh or soft shift, poor performance,
delayed or no engagement into drive
or reverse, transmission fluid leak,
transmission noise or vibration, or
improper TCC operation.Automatic Transmission
PCM Power and Ground CheckOn-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check.Chassis Electrical
PCM Power and Ground CheckOn-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check. PCM power and ground
circuits OK. Data link voltage
incorrect.Chassis Electrical
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
CheckEngine starts and runs, no PCM
codes set. Customer complains of
harsh or soft shift, poor performance,
delayed or no engagement into drive
or reverse, transmission fluid leak,
transmission noise or vibration, or
improper TCC operation.Automatic Transmission
SymptomsInitial DiagnosisDefault Section(s)
Intermittents1. On-board Diagnostic (OBD)
system check.
2. Careful visual/physical
inspections.Chassis Electrical
Hard Starts1. OBD system check.
2. Sensors (ECT, MAP, MAF, TP) ;
MAP output chart.
3. Fuel system electrical test, fuel
system diagnosis.
4. Ignition system.
5. IAC system check.Engine Mechanical, Ignition
System Check, Exhaust System
Diagnosis
Surges and/or Chuggles1. OBD system check.
2. Heated oxygen sensors.
3. Fuel system diagnosis.
4. Ignition system.Calibration ID “Broadcast
Code”/Service Bulletins, Ignition
System Check, Generator
Output, Exhaust System
Diagnosis, 4L30-E System Test