1998 OPEL FRONTERA ignition
[x] Cancel search: ignitionPage 2317 of 6000

7A1–72
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
DTC P1860 TCC Solenoid Electrical
StepActionYe sNo
11. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine “on”, turn the ignition switch “on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record “Failure
Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the“Clear Info”
function is used.
3. Record the DTC “Failure Records”.
Go to Step 2Go to Step 3
2Using the J39200 DVOM, back probe between PCM connector
terminals J2–D2 and J2–C8.
Is the voltage 0 ?
Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
31. Apply brake pedal and select transmission range “D”.
2. Do a test drive, and increase the vehicle speed to TCC “on” at
4th.
Does the scan tool display DTC P1860 at TCC “ON”?
Go to Step 9
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
41. Turn the ignition “off”.
2. Disconnect the J2 (WHITE) PCM connector.
3. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
PCM connector terminals J2–D2 and J2–C8.
Is the resistance within 18 – 20 ohms?
Go to Step 6Go to Step 7
5The wiring harness between PCM connector terminal J2–D2 and
transmission adapter case connector terminal M6–4(A) is shorted
to voltage.
Was a problem found and corrected?
Go to Step 18Go to Step 19
6Intermittent condition.
Check the wiring harness and terminals between PCM connector
J2 and transmission adapter case connector M–6.
Was a problem found and corrected?
Go to Step 18Go to Step 19
71. Disconnect the transmission 16–way connector H–53.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminal H53–8 and ground.
Is the resistance within 18 – 20 ohms?
Go to Step 15Go to Step 8
81. Disconnect the transmission adapter case connector M–6.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminal M6–4(A) and ground.
Is the resistance within 18 – 20 ohms?
Go to Step 16Go to Step 17
91. Turn the ignition “off”.
2. Disconnect the J2 (WHITE) PCM connector.
3. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals J2–D2 and J2–C8.
Is the resistance within 18 – 20 ohms?
Go to Step 18Go to Step 10
101. Disconnect the transmission 16–way connector H–53.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminal H53–8 and ground.
Is the resistance within 18–20 ohms?
Go to Step 12Go to Step 11
111. Disconnect the transmission adapter case connector M–6.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminal M6–4(A) and ground.
Is the resistance within 18–20 ohms?
Go to Step 13Go to Step 14
Page 2650 of 6000
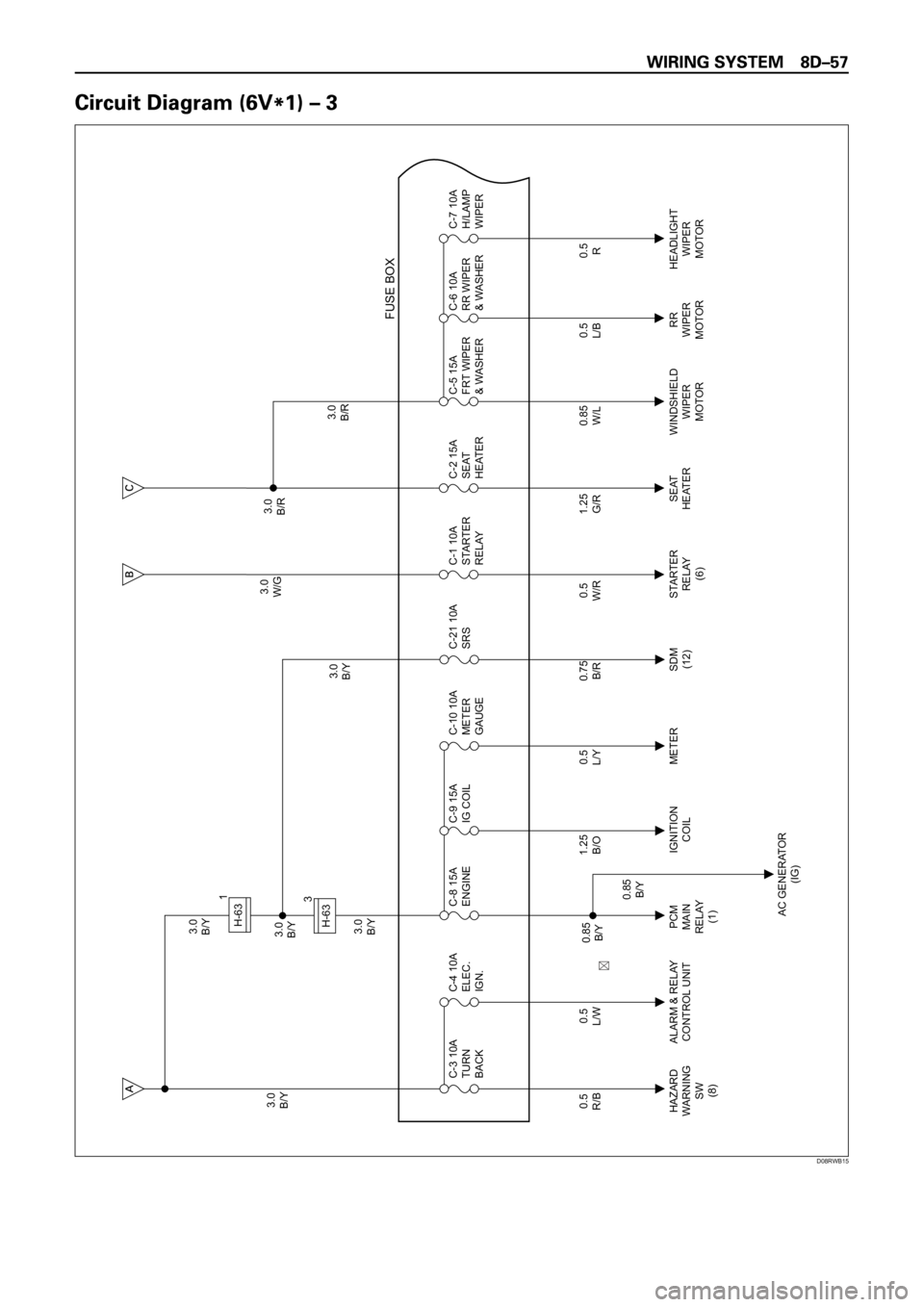
3.0
B/Y3.0
B/Y
3.0
B/Y3.0
B/Y3.0
W/G3.0
B/R
3.0
B/R 3.0
B/Y
0.5
R/B
HAZARD
WARNING
SW
(8)PCM
MAIN
RELAY
(1)IGNITION
COILMETER STARTER
RELAY
(6)SEAT
HEATERWINDSHIELD
WIPER
MOTORRR
WIPER
MOTORHEADLIGHT
WIPER
MOTOR
AC GENERATOR
(IG) ALARM & RELAY
CONTROL UNIT C-3 10A
TURN
BACK
0.5
L/WC-4 10A
ELEC.
IGN.
0.5
L/YC-10 10A
METER
GAUGE
0.5
W/RC-1 10A
STARTER
RELAY
0.85
W/LC-5 15A
FRT WIPER
& WASHERC-6 10A
RR WIPER
& WASHERC-7 10A
H/LAMP
WIPER
FUSE BOX
1.25
B/OC-9 15A
IG COIL C-8 15A
ENGINE
0.5
L/B
0.85
B/Y
0.85
B/Y
0.5
R
0.75
B/R
SDM
(12)C-21 10A
SRS
1.25
G/RC-2 15A
SEAT
HEATER
H-631
3
H-63
��
D08RWB15
Page 2677 of 6000
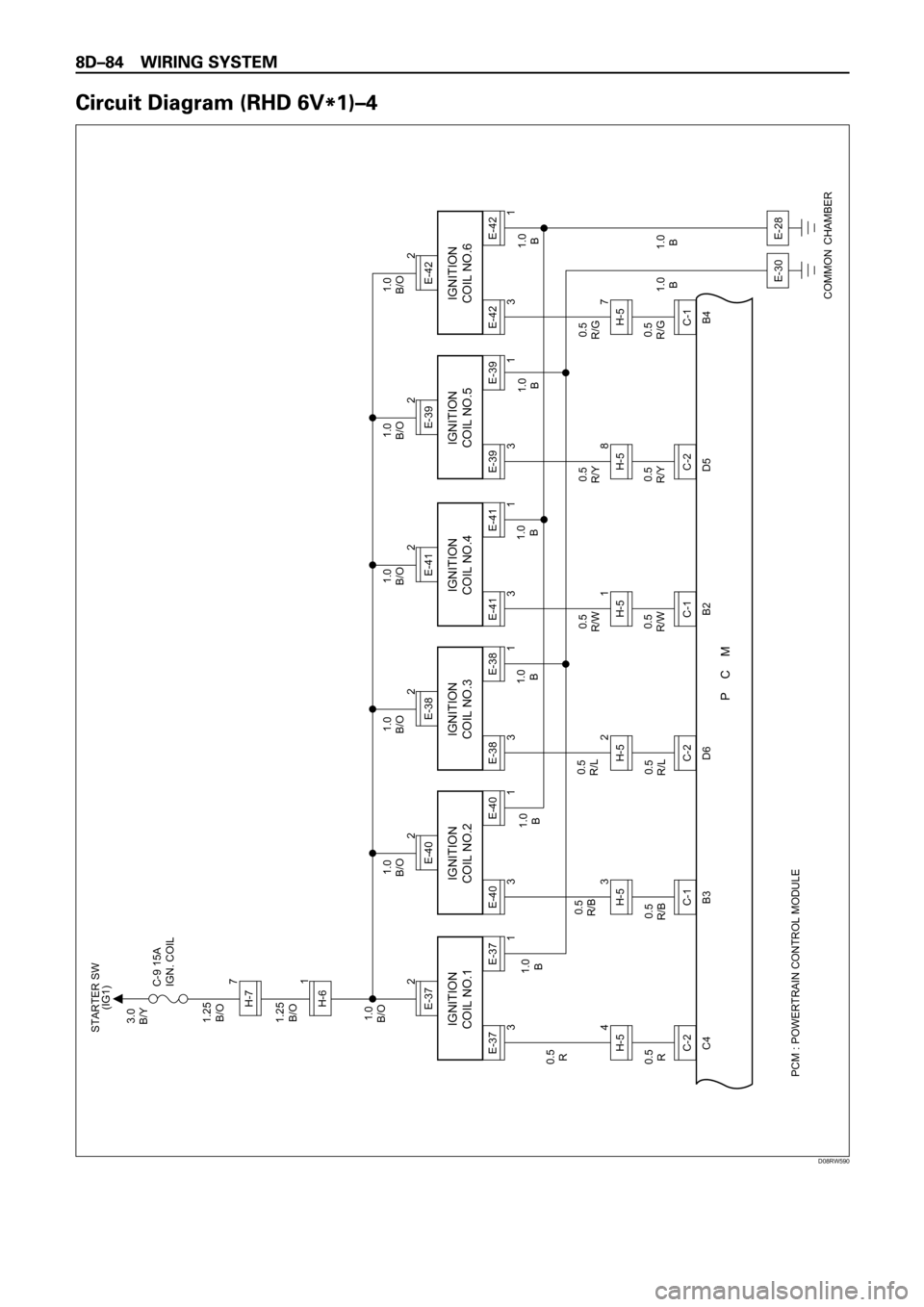
PCM : POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
1.0
B/O
1.0
B/O1.0
B/O1.0
B/O1.0
B/O1.0
B/O3.0
B/Y
1.25
B/O
1.25
B/OC-9 15A
IGN. COILSTARTER SW
(IG1)
2
E-371H-6H-77
0.5
R 0.5
R1.0
B
C-2E-3714
1.0
B
COMMON
E-30
1.0
B
CHAMBERE-28 3
E-37
1
H-54
2
E-40
0.5
R/B0.5
R/B1.0
BC-1E-4014
3
E-40
1
H-53
2
E-38
0.5
R/L0.5
R/L1.0
BC-2E-3814
3
E-38
1
H-52
2
E-41
0.5
R/W1.0
BC-1E-4114
3
E-41
1
H-51
2
E-39
0.5
R/Y1.0
BC-2E-3914
3
E-39
1
H-58
2
E-42
0.5
R/G
0.5
R/W0.5
R/Y0.5
R/G1.0
B
C-1E-4214
3
E-42
1
H-57
P C M
C4 B3 D6 B2 D5 B4
IGNITION
COIL NO.1
IGNITION
COIL NO.2
IGNITION
COIL NO.3
IGNITION
COIL NO.4
IGNITION
COIL NO.5
IGNITION
COIL NO.6
D08RW590
Page 2692 of 6000

PCM : POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
1.0
B/O
1.0
B/O1.0
B/O1.0
B/O1.0
B/O1.0
B/O3.0
B/Y
1.25
B/O
1.25
B/OC-9 15A
IGN. COILSTARTER SW
(IG1)
2
E-371H-6H-816
0.5
R 0.5
R1.0
B
C-2E-3714
1.0
B
COMMON
E-30
1.0
B
CHAMBERE-28 3
E-37
1
H-54
2
E-40
0.5
R/B0.5
R/B1.0
BC-1E-4014
3
E-40
1
H-53
2
E-38
0.5
R/L0.5
R/L1.0
BC-2E-3814
3
E-38
1
H-52
2
E-41
0.5
R/W1.0
BC-1E-4114
3
E-41
1
H-51
2
E-39
0.5
R/Y1.0
BC-2E-3914
3
E-39
1
H-58
2
E-42
0.5
R/G
0.5
R/W0.5
R/Y0.5
R/G1.0
B
C-1E-4214
3
E-42
1
H-57
P C M
C4 B3 D6 B2 D5 B4
IGNITION
COIL NO.1
IGNITION
COIL NO.2
IGNITION
COIL NO.3
IGNITION
COIL NO.4
IGNITION
COIL NO.5
IGNITION
COIL NO.6
D08RW905
Page 3358 of 6000
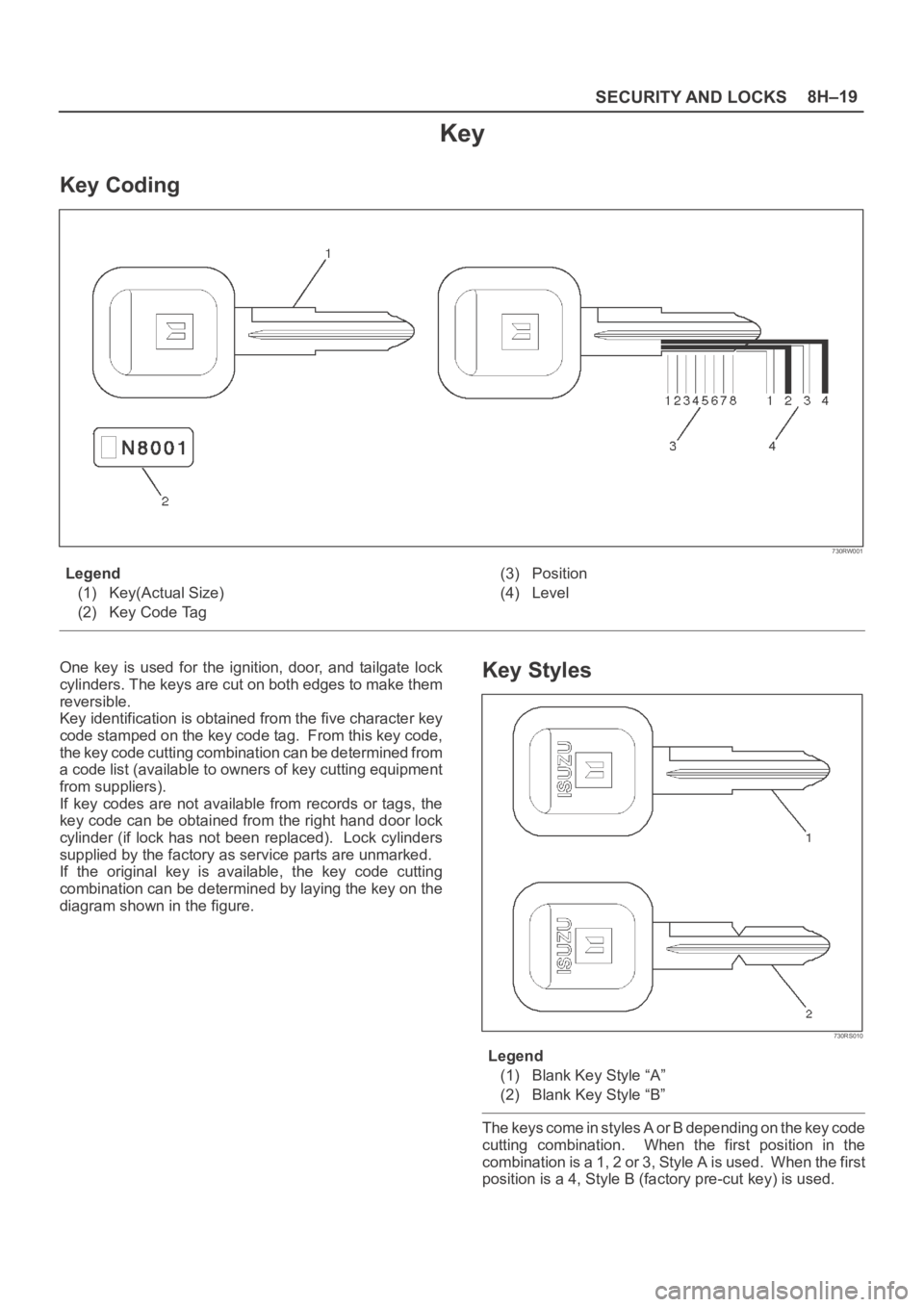
SECURITY AND LOCKS8H–19
Key
Key Coding
730RW001
Legend
(1) Key(Actual Size)
(2) Key Code Tag(3) Position
(4) Level
One key is used for the ignition, door, and tailgate lock
cylinders. The keys are cut on both edges to make them
reversible.
Key identification is obtained from the five character key
code stamped on the key code tag. From this key code,
the key code cutting combination can be determined from
a code list (available to owners of key cutting equipment
from suppliers).
If key codes are not available from records or tags, the
key code can be obtained from the right hand door lock
cylinder (if lock has not been replaced). Lock cylinders
supplied by the factory as service parts are unmarked.
If the original key is available, the key code cutting
combination can be determined by laying the key on the
diagram shown in the figure.Key Styles
730RS010
Legend
(1) Blank Key Style “A”
(2) Blank Key Style “B”
The keys come in styles A or B depending on the key code
cutting combination. When the first position in the
combination is a 1, 2 or 3, Style A is used. When the first
position is a 4, Style B (factory pre-cut key) is used.
Page 3442 of 6000

SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM9J–5
1. Energy Reserve — The SDM maintains 24–Volt Loop
Reserve (24VLR) energy supply to provide
deployment energy when ignition voltage is lost in a
frontal crash.
2. Frontal Crash Detection — The SDM monitors
vehicle velocity changes to detect frontal crashes
which are severe enough to warrant deployment.
3. Air Bag Deployment — When a frontal crash of
sufficient force is detected, the SDM will cause
enough current to flow through the air bag assembly
to deploy the air bag.
4. Malfunction Detection — The SDM performs
diagnostic monitoring of SRS electrical components
and sets a diagnostic trouble code when a
malfunction is detected.
5. Frontal Crash Recording — The SDM records
information regarding SRS status during frontal
crash.
6. Malfunction Diagnosis — The SDM displays SRS
diagnostic trouble codes and system status
information through the use of a scan tool.
7. Driver Notification — The SDM warns the vehicle
driver of SRS malfunctions by controlling the “Air
Bag” warning lamp.
The SDM is connected to the SRS wiring harness by a
24–pin connector. This harness connector uses a
shorting clip across certain terminals in the contact area.
This shorting clip connects the “AIR BAG” warning lamp
to ground when the SDM harness connector is
disconnected or CPA (Connector Position Assurance) is
not inserted even if completely connected. This will
cause the “AIR BAG” warning lamp to come “ON” steady
whenever the ignition switch is at the ON or START
positions with the SDM disconnected.
827RW044
Legend
(1) SDM
(2) SRS Harness
(3) Connector Position Assurance
“Air Bag” Warning Lamp
Ignition voltage is applied to the “AIR BAG” warning lamp
when the ignition switch is at the ON or START positions.
The SDM controls the lamp by providing ground with a
lamp driver. The “AIR BAG” warning lamp is used in the
SRS to do the following:
1. Verify lamp and SDM operation by turn on 3.5
seconds and then turns “OFF” when the ignition
switch is first turned “ON”.
2. Warn the vehicle driver of SRS electrical system
malfunctions which could potentially affect the
operation of the SRS. These malfunctions could
result in nondeployment in case of a frontal crash or
deployment for conditions less severe than intended.
The “AIR BAG ” warning lamp is the key to driver
notification of SRS malfunctions. For proper lamp
operation, refer to the “SRS Diagnostic System Check” in
this section.
821RW037
SRS Coil Assembly
The SRS coil assembly consists of two current carrying
coils. This is attached to the steering column and allow
rotation of the steering wheel while maintaining
continuous contact of the driver deployment loop to the
driver air bag assembly.
There is a shorting clip on the yellow 2–pin connector near
the base of steering column which connects the SRS coil
to the SRS wiring harness.
The shorting clip shorts to the SRS coil and driver air bag
assembly when the yellow 2–pin connector is
disconnected. The circuit to the driver air bag assembly is
shorted in this way to help prevent unwanted deployment
of the air bag when servicing the steering column or other
SRS components.
Page 3443 of 6000
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM 9J–6
825RS017
Air Bag Assemblies
The air bag assembly consist of an inflatable air bag
assembly and an inflator (a canister of gas–generating
material and an initiating device). When the vehicle is in a
frontal crash of sufficient force.
The SDM causes current flow through the deployment
loops. Current passing through the inflator ignites the
material in the air bag assembly. The gas produced from
this reaction rapidly inflates the air bag assembly.
There is a shorting clip on the driver air bag assembly
connector which connects the SRS coil assembly. The
shorting clip shorts across the driver air bag assembly
circuits when driver air bag assembly connector is
disconnected.
The circuit to the driver air bag assembly is shorted in this
way to help prevent unwanted deployment of the air bag
when servicing the driver air bag assembly, the steering
column or other SRS components.
827RS008There is a shorting clip on the passenger air bag
assembly connector which connects to the SRS harness.The shorting clip shorts across the passenger air bag
assembly circuit when the passenger air bag assembly
connector is disconnected. The circuit to the passenger
air bag assembly is shorted in this way to help prevent
unwanted deployment of the air bag when servicing the
passenger air bag assembly, the instrument panel or
other SRS components.
827RS001
Seat Belt with Pretensioner (If so
equipped)
The seat belt comprises a seat belt and a cylinder (a
cylinder filled with powder and an ignition device). In
cases of frontal collision which cause a shock exceeding
a specified level, the controller lets current flow to the
inflation circuit. The current ignites the cylinder of the seat
belt, producing gas. The gas helps tighten the seat belt to
restrain firmly the driver’s upper half in his seat.
760RW033
Page 3444 of 6000

SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM9J–7
Steering Column
The steering column absorbs energy and is designed to
compress in a frontal crash to decrease the chance of
injury to the driver.
431RW019
Knee Bolster
The knee bolsters are used to absorb energy to protect
knees and control the forward movement of the vehicle’s
front seat occupants during a frontal crash, by limiting leg
movement.
740RT015
Definitions
Air Bag
An inflatable cloth cushion designed to deploy in certain
frontal crashes. It supplements the protection offered by
the seat belts by distributing the impact load more evenly
over the vehicle occupant’s head and torso.
Asynchronous
Performed in a nonperiodic fashion, (i.e., no defined time
or interval).B+
Battery voltage, (B+) The voltage available at the battery
at the time of the indicated measurement. With the key
“ON” and the engine not running, the system voltage will
likely be between 12 and 12.5 volts. At idle, the voltage
may be 14 to 16 volts. The voltage could be as low as 10
volts during engine cranking.
Bulb Check
The SDM will cause the “AIR BAG” warning lamp to turn
on 3.5 seconds and then go “OFF” whenever the ignition
switch transitions to the ON position from any other
ignition switch position and no malfunctions are detected.
“Continuous Monitoring”
Tests performed by the SDM on the SRS every 100
milliseconds while “Ignition 1” voltage is in the normal
operating voltage range at the SDM.
Data Link Connector (DLC)
Formerly “DLC” a connector which allows communication
with an external computer, such as a scan tool.
Datum Line
A base line parallel to the plane of the underbody or frame
from which all vertical measurements originate.
Deploy
To inflate the air bag.
Deployment Loops
The circuits which supply current to the air bag
assemblies to deploy the air bag.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
Formerly “Code”, a numerical designator used by the
SDM to indicate specific SRS malfunctions.
Driver Current Source
An output of the SDM which applies current into the driver
air bag assembly circuit during the “Initiator Assembly
Resistance Test”.
Driver Air Bag Assembly
An assembly located in the steering wheel hub consisting
of an inflatable bag, an inflator and an initiator.
EEPROM
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory.
Memory which retains its contents when power is
removed from the SDM.
Ignition Cycle
The voltage at the SDM “Ignition 1” inputs, with ignition
switch “ON”, is within the normal operating voltage range
for at least ten seconds before turning ignition switch
“OFF”.
Ignition 1
A battery voltage (B+) circuit which is only powered with
the ignition switch in the ON, or START positions.
Initiator
The electrical component inside the air bag assembly
which, when sufficient current flows, sets off the chemical
reaction that inflates the air bag.
“Initiator Assembly Resistance Test”
Tests performed once each ignition cycle when no
malfunctions are detected during “Turn–ON” or
“Continuous Monitoring”. This test checks for the correct
SDM configuration for the vehicle, shorts to “Ignition 1” in