1998 OPEL FRONTERA battery
[x] Cancel search: batteryPage 2288 of 6000
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–43
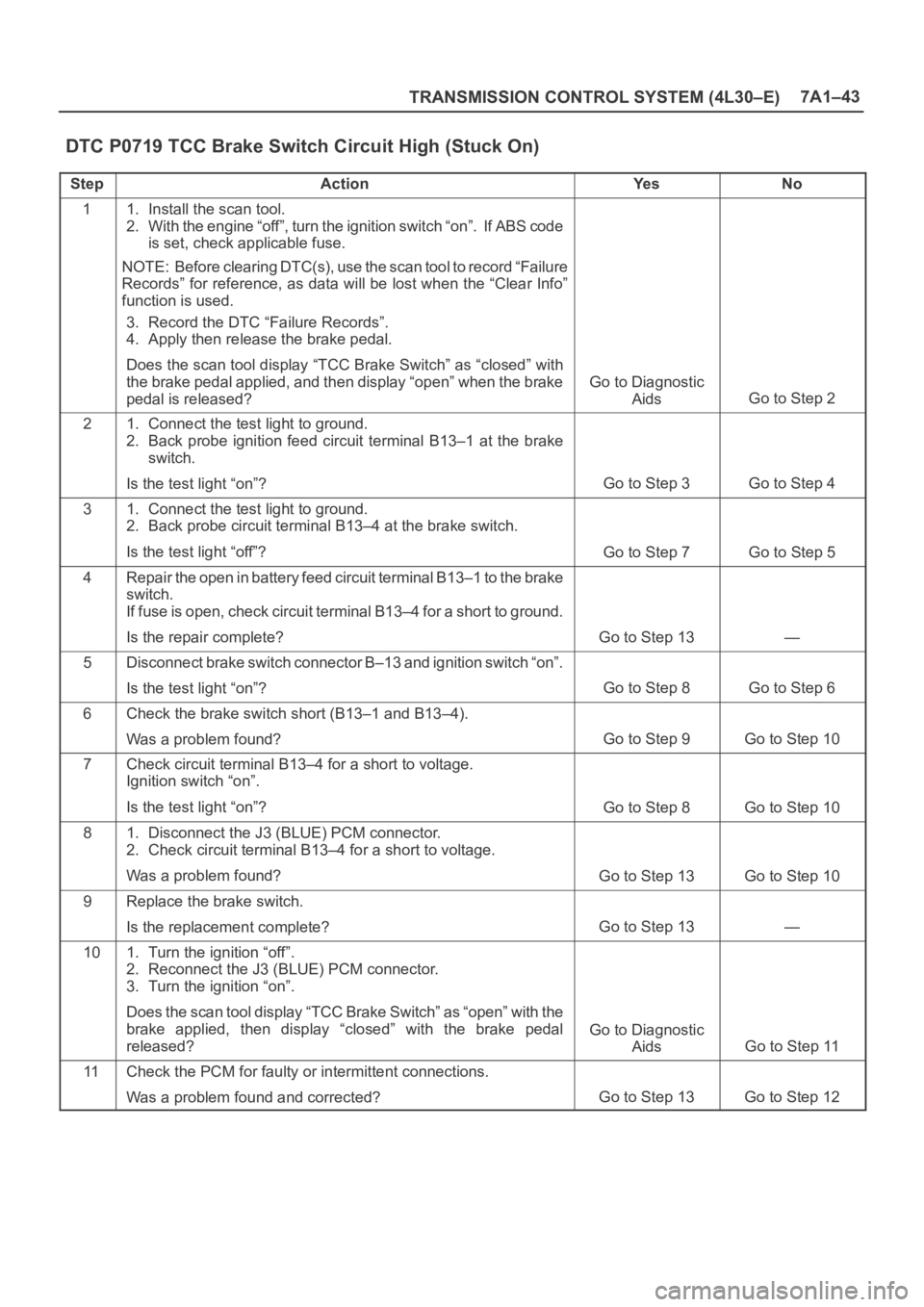
DTC P0719 TCC Brake Switch Circuit High (Stuck On)
StepActionYe sNo
11. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine “off”, turn the ignition switch “on”. If ABS code
is set, check applicable fuse.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record “Failure
Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the “Clear Info”
function is used.
3. Record the DTC “Failure Records”.
4. Apply then release the brake pedal.
Does the scan tool display “TCC Brake Switch” as “closed” with
the brake pedal applied, and then display “open” when the brake
pedal is released?
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
Go to Step 2
21. Connect the test light to ground.
2. Back probe ignition feed circuit terminal B13–1 at the brake
switch.
Is the test light “on”?
Go to Step 3Go to Step 4
31. Connect the test light to ground.
2. Back probe circuit terminal B13–4 at the brake switch.
Is the test light “off”?
Go to Step 7Go to Step 5
4Repair the open in battery feed circuit terminal B13–1 to the brake
switch.
If fuse is open, check circuit terminal B13–4 for a short to ground.
Is the repair complete?
Go to Step 13—
5Disconnect brake switch connector B–13 and ignition switch “on”.
Is the test light “on”?
Go to Step 8Go to Step 6
6Check the brake switch short (B13–1 and B13–4).
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 9Go to Step 10
7Check circuit terminal B13–4 for a short to voltage.
Ignition switch “on”.
Is the test light “on”?
Go to Step 8Go to Step 10
81. Disconnect the J3 (BLUE) PCM connector.
2. Check circuit terminal B13–4 for a short to voltage.
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 13Go to Step 10
9Replace the brake switch.
Is the replacement complete?
Go to Step 13—
101. Turn the ignition “off”.
2. Reconnect the J3 (BLUE) PCM connector.
3. Turn the ignition “on”.
Does the scan tool display “TCC Brake Switch” as “open” with the
brake applied, then display “closed” with the brake pedal
released?
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
Go to Step 11
11Check the PCM for faulty or intermittent connections.
Was a problem found and corrected?
Go to Step 13Go to Step 12
Page 2299 of 6000

7A1–54
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
DTC P0748 Pressure Control Solenoid (PCS) (Force Motor) Circuit Electrical
D07RW008
Circuit Description
The PCS is a PCM–controlled device used to regulate
transmission line pressure. The PCM compares TPS
voltage, engine rpm, and other inputs to determine the
line pressure appropriate for a given load. The PCM will
regulate the pressure by applying a varying amperage to
the PCS. The applied amperage can vary from 0.1 to 1
amp, and is monitored by the PCM.
This DTC detects a continuous open or short to ground in
the PCS circuit or the PCS. This is a type “C” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
Battery voltage is between 10 and 16 volts.
The PCM detects that the different between
commanded and actual current is 200 milliampere
(mA) for over 1 second.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
Maximum line pressure.
The PCM will illuminate the CHECK TRANS Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC/CHECK
TRANS Lamp
The PCM will turn “off” the CHECK TRANS Lamp
after three consecutive ignition cycles without a
failure reported.
The DTC can be cleared from PCM history by using a
scan tool.
The DTC will be cleared from memory when the
vehicle has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a
failure reported.
The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled “off”
long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connection at the
PCM and at the transmission 5–way connector. Look
for possible bent, backed out, deformed or damaged
terminals. Check for weak terminal tension as well.
Also check for a chafed wire that could short to bare
m e t a l o r o t h e r w i r i n g . I n s p e c t f o r a b r o k e n w i r e i n s i d e
the insulation.
When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
2. This test checks the ability of the PCM to command
the PCS.
3. This test checks the PCS and internal wiring harness
for incorrect resistance.
Page 2301 of 6000

7A1–56
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
DTC P0753 Shift Solenoid A Electrical
D07RW009
Circuit Description
The shift solenoid A is a simple on/off solenoid
located in the main case valve body. The solenoid is
the normally closed type. In second or third gear, the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) energizes the
solenoid to open a fluid inlet port. When the port is
open, fluid pressure actuates the shift valve.
The solenoid is activated by current. This current is
produced by applying a voltage to one side (the High
side) and a ground to the other side (Low side).
The High Side Driver (HSD) is a circuit of the PCM
that acts as a switch between the solenoids and the
supply voltage. The High side of the solenoid is
permanently supplied with voltage, except in
BACKUP MODE or when ignition is off the HSD is
turned off.
This DTC detects a continuous open or short to ground in
the shift solenoid A circuit or the shift solenoid A. This is a
type “C” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
Ignition is “on”, Engine “run”.
Battery voltage is between 10 and 16 volts.
The PCM commands the solenoid “on” and the
voltage remains high (B+) or the PCM commands the
solenoid “off” and the voltage remains low (zero
volts).
All conditions met for 0.33 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
Maximum line pressure.
Immediate landing to 4th gear.
Inhibit TCC engagement.
The PCM will illuminate the CHECK TRANS Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The MIL/DTC
The PCM will turn off the CHECK TRANS Lamp after
three consecutive ignition cycles without a failure
reported.
The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
The DTC will be cleared from history when the vehicle
has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a failure
reported.
The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled “off”
long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connection at the
PCM and at the transmission 16–way connector.
Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed or
damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal tension
as we ll. A lso ch eck fo r a ch af e d w ire th at cou l d s ho r t
to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for a broken wire
inside the insulation.
Page 2304 of 6000

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–59
DTC P0758 Shift Solenoid B Electrical
D07RW009
Circuit Description
The shift solenoid B is a simple on/off solenoid
located in the main case valve body. It is normally
open. When the port is open, fluid pressure actuates
the shift valve. In first or second gear, the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) energizes the solenoid to
close a fluid inlet port.
The solenoid is activated by current. This current is
procuded by applying a voltage to one side (the High
side) and a ground to the other side (Low side).
The High Side Driver (HSD) is a circuit of the PCM
that acts as a switch between the solenoids and the
supply voltage. The High side of the solenoid is
permanently supplied with voltage. In BACKUP
MODE or when the ignition is off, the HSD is turned
off.
This DTC detects a continuous open or short to ground in
the shift solenoid B circuit or shift solenoid B. This is a
type “C” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
Ignition is “on”, Engine “run”.
Battery voltage is between 10 and 16 volts.
The PCM commands the solenoid “on” and the
voltage remains high (B+)or the PCM commands the
solenoid “off” and the voltage remains low (zero
volts).
All conditions met for 0.33 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
Fixed to 4th gear.
Maximum line pressure.
Inhibit TCC engagement.
The PCM will illuminate the CHECK TRANS Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The MIL/DTC
The PCM will turn off the CHECK TRANS Lamp after
three consecutive ignition cycles without a failure
reported.
The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
The DTC will be cleared from history when the vehicle
has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a failure
reported.
The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled “off”
long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the PCM and at the transmission 16–way connector.
Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed or
damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal tension
as we ll. A lso ch eck fo r a ch af e d w ire th at cou l d s ho r t
to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for a broken wire
inside the insulation.
Page 2312 of 6000
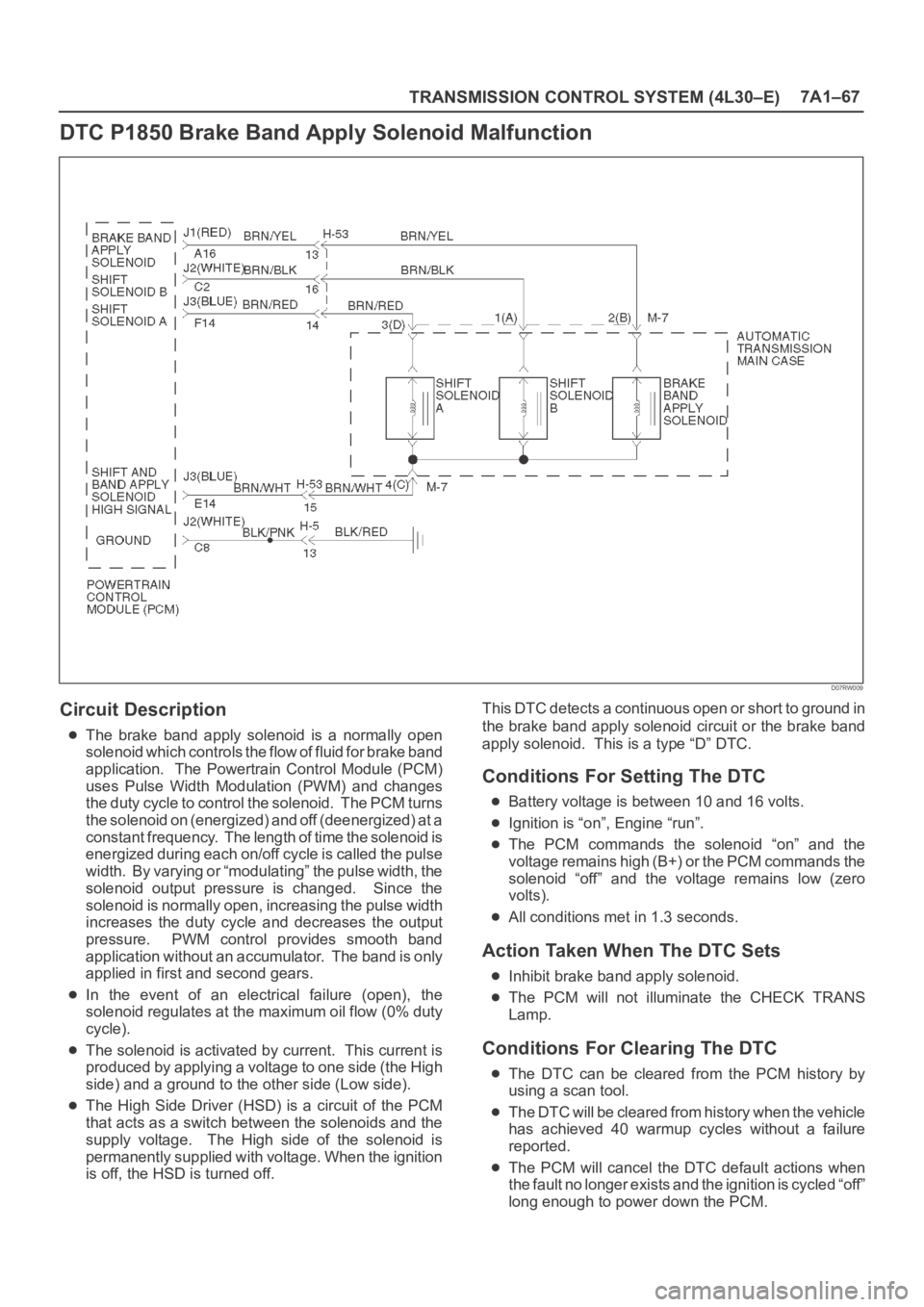
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–67
DTC P1850 Brake Band Apply Solenoid Malfunction
D07RW009
Circuit Description
The brake band apply solenoid is a normally open
solenoid which controls the flow of fluid for brake band
application. The Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
uses Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) and changes
the duty cycle to control the solenoid. The PCM turns
the solenoid on (energized) and off (deenergized) at a
constant frequency. The length of time the solenoid is
energized during each on/off cycle is called the pulse
width. By varying or “modulating” the pulse width, the
solenoid output pressure is changed. Since the
solenoid is normally open, increasing the pulse width
increases the duty cycle and decreases the output
pressure. PWM control provides smooth band
application without an accumulator. The band is only
applied in first and second gears.
In the event of an electrical failure (open), the
solenoid regulates at the maximum oil flow (0% duty
cycle).
The solenoid is activated by current. This current is
produced by applying a voltage to one side (the High
side) and a ground to the other side (Low side).
The High Side Driver (HSD) is a circuit of the PCM
that acts as a switch between the solenoids and the
supply voltage. The High side of the solenoid is
permanently supplied with voltage. When the ignition
is off, the HSD is turned off.This DTC detects a continuous open or short to ground in
the brake band apply solenoid circuit or the brake band
apply solenoid. This is a type “D” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
Battery voltage is between 10 and 16 volts.
Ignition is “on”, Engine “run”.
The PCM commands the solenoid “on” and the
voltage remains high (B+) or the PCM commands the
solenoid “off” and the voltage remains low (zero
volts).
All conditions met in 1.3 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
Inhibit brake band apply solenoid.
The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
The DTC will be cleared from history when the vehicle
has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a failure
reported.
The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled “off”
long enough to power down the PCM.
Page 2316 of 6000

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–71
DTC P1860 TCC Solenoid Electrical
D07RW010
Circuit Description
The PCM allows current to flow through the solenoid coil
according to the duty cycle (percentage of “on” and “off”
time). This current flow through the solenoid coil creates
a magnetic field that magnetizes the solid core. The
magnetized core attracts the check ball to seat against
spring pressure. This blocks the exhaust for the TCC
signal fluid and allows 2–3 drive fluid to feed to TCC signal
circuit. The TCC signal fluid pressure acts on the TCC
regulator valve to regulate line pressure and to apply fluid
pressure to the torque converter clutch shift valve. When
the TCC shift valve is in the apply position, regulated
apply fluid pressure is directed through the TCC valve to
apply the torque converter clutch. The TCC solenoid is
used in conjunction with the TCC solenoid to regulate fluid
to the torque converter. The TCC solenoid is attached to
the valve body within the transmission.
This DTC detects a continuous open or short to ground or
ignition in the TCC circuit or the TCC solenoid. This is a
type “D” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
Battery voltage is between 10 and 16 volts.
No shift solenoid A DTC P0753.
No shift solenoid B DTC P0758.
Ignition is “on”, Engine “run”.
The PCM commands the solenoid “on” and the
voltage remains low (zero volts).
The PCM commands the solenoid “off” and the
voltage remains high (B+).
All conditions met for 0.25 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
Inhibit TCC engagement.
The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The MIL/DTC
The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
The DTC will be cleared from history when the vehicle
has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a failure
reported.
The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled “off”
long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the PCM and at the transmission 16–way connector.
Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed or
damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal tension
as we ll. A lso ch eck fo r a ch af e d w ire th at cou l d s ho r t
to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for a broken wire
inside the insulation.
When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
3. This test checks for voltage to the solenoid.
4. This test checks the ability of the PCM and wiring to
control the ignition circuit.
9. This test checks the resistance of the TCC solenoid
and the internal wiring harness.
Page 2324 of 6000
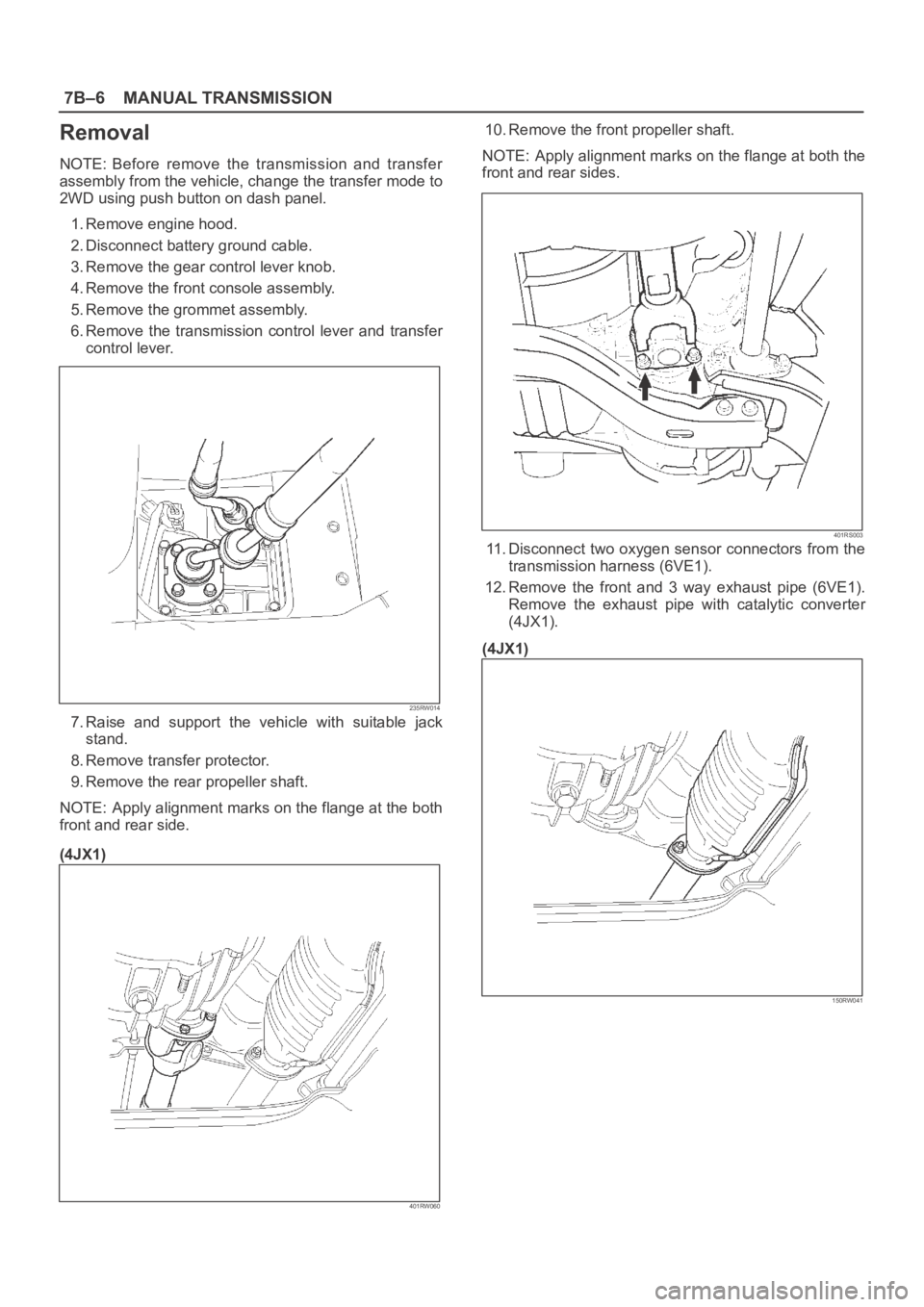
7B–6MANUAL TRANSMISSION
Removal
NOTE: Before remove the transmission and transfer
assembly from the vehicle, change the transfer mode to
2WD using push button on dash panel.
1. Remove engine hood.
2. Disconnect battery ground cable.
3. Remove the gear control lever knob.
4. Remove the front console assembly.
5. Remove the grommet assembly.
6. Remove the transmission control lever and transfer
control lever.
235RW014
7. Raise and support the vehicle with suitable jack
stand.
8. Remove transfer protector.
9. Remove the rear propeller shaft.
NOTE: Apply alignment marks on the flange at the both
front and rear side.
(4JX1)
401RW060
10. Remove the front propeller shaft.
NOTE: Apply alignment marks on the flange at both the
front and rear sides.
401RS003
11. Disconnect two oxygen sensor connectors from the
transmission harness (6VE1).
12.Remove the front and 3 way exhaust pipe (6VE1).
Remove the exhaust pipe with catalytic converter
(4JX1).
(4JX1)
150RW041
Page 2334 of 6000
7B–16MANUAL TRANSMISSION
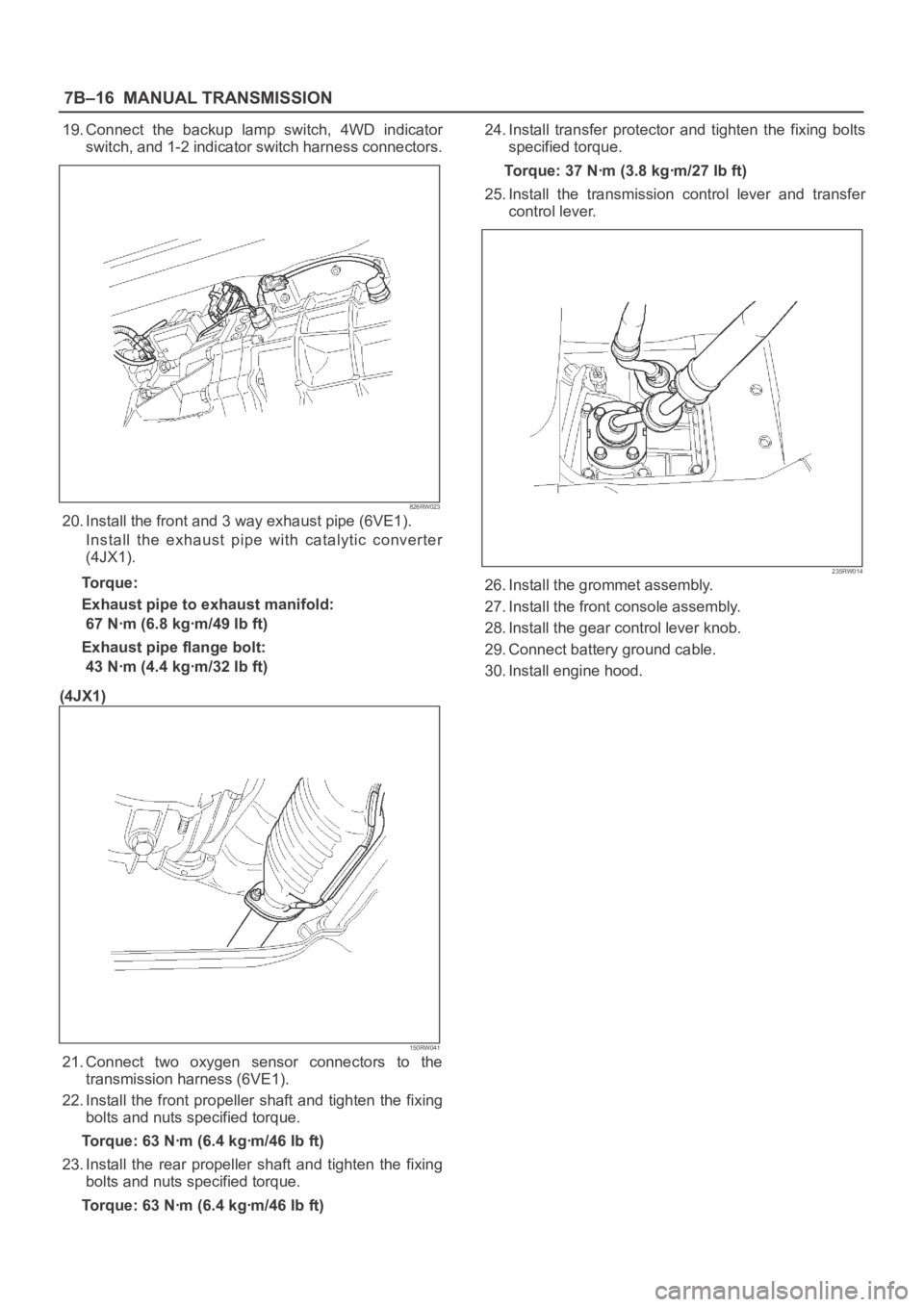
19. Connect the backup lamp switch, 4WD indicator
switch, and 1-2 indicator switch harness connectors.
826RW023
20. Install the front and 3 way exhaust pipe (6VE1).
Install the exhaust pipe with catalytic converter
(4JX1).
Torque:
Exhaust pipe to exhaust manifold:
67 Nꞏm (6.8 kgꞏm/49 Ib ft)
Exhaust pipe flange bolt:
43 Nꞏm (4.4 kgꞏm/32 Ib ft)
(4JX1)
150RW041
21. Connect two oxygen sensor connectors to the
transmission harness (6VE1).
22. Install the front propeller shaft and tighten the fixing
bolts and nuts specified torque.
Torque: 63 Nꞏm (6.4 kgꞏm/46 Ib ft)
23. Install the rear propeller shaft and tighten the fixing
bolts and nuts specified torque.
Torque: 63 Nꞏm (6.4 kgꞏm/46 Ib ft)24. Install transfer protector and tighten the fixing bolts
specified torque.
Torque: 37 Nꞏm (3.8 kgꞏm/27 Ib ft)
25. Install the transmission control lever and transfer
control lever.
235RW014
26. Install the grommet assembly.
27. Install the front console assembly.
28. Install the gear control lever knob.
29. Connect battery ground cable.
30. Install engine hood.