1998 OPEL FRONTERA air filter
[x] Cancel search: air filterPage 1368 of 6000

6E–251 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1508 IAC System Low RPM
T321115
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) controls engine
idle speed by adjusting the position of the idle air control
(IAC) motor pintle. The IAC is a bi-directional stepper
motor driven by two coils. The PCM applies current to the
IAC coils in steps (counts) to extend the IAC pintle into a
passage in the throttle body to decrease air flow. The
PCM reverses the current to retract the pintle, increasing
air flow. This method allows highly accurate control of idle
speed and quick response to changes in engine load. If
the PCM detects a condition where too low of an idle
speed is present and the PCM is unable to adjust idle
speed by increasing the IAC counts, DTC P1508 will set,
indicating a problem with the idle control system.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
No Tech 2 test is being run.
None of these DTCs are set: TP sensor, VSS, ECT,
EGR, fuel system, MAF, MAP, IAT, canister purge,
injector control or ignition control.
Barometric pressure is above 75 kPa.
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) is above 50C
(120
F).
Engine speed is more than 100-200 RPM lower than
desired idle, based upon coolant temperature.
The engine has been running for at least 125 seconds.
Vehicle speed is less than 1 mph.
Canister purge duty cycle is above 10%.
Ignition voltage is between 9.5 volts and 16.7 volts.
The throttle is closed.
Engine speed is lower than desired idle.
All of the above conditions are met for 10 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P1508 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at PCM or IAC motor – Inspect
harness connectors for backed-out terminals,
improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or
damaged terminals, and poor terminal-to-wire
connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring for damage.
Restricted air intake system – Check for a possible
collapsed air intake duct, restricted air filter element,
or foreign objects blocking the air intake system.
Throttle body – Check for objects blocking the IAC
passage or throttle bore, excessive deposits in the IAC
Page 1370 of 6000
6E–253 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
DTC P1508 – IAC System Low RPM
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
5Visually/physically inspect for following conditions:
Restricted air intake system. Check for a possible
collapsed air intake duct, restricted air filter
element, or foreign objects blocking the air intake
system.
T h r o t t l e b o d y. C h e c k f o r o b j e c t s b l o c k i n g t h e I A C
passage or throttle bore, excessive deposits in
the IAC passage and on the IAC pintle, and
excessive deposits in the throttle bore and on the
throttle plate.
Do any of the above require a repair?
—
Refer to
appropriate
section for
on-vehicle
service
Go to Step 6
61. Check for a poor connection at the IAC harness
connector.
2. If a problem is found, replace faulty terminals as
necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 7
7Replace the IAC valve.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
8Replace the PCM.
IMPORTANT:The replacement PCM must be
programmed. Refer to
UBS 98model year Immobilizer
Workshop Manual.
Is the action complete?—Verify repair—
Page 1385 of 6000
6E–268
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Lack of Power, Sluggish or Spongy Symptom
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1DEFINITION:
Engine delivers less than expected power. Little or no
increase in speed when accelerator pedal is pushed
down part-way.
Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom?
—Verify repairGo to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to
Visual/Physic
al Check
41. Remove and check the air filter element for dirt or
restrictions. Refer to
Air Intake System in
ON-Vehicle Service.
2. Replace the air filter element if necessary.
Was a repair required?
—Verify repairGo to Step 5
51. Check for low fuel pressure. Refer to Fuel System
Pressure Test
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 6
61. Check for water- or alcohol-contaminated fuel.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 7
71. Using Tech 2, monitor the knock sensor (KS)
system for excessive spark retard activity. Refer to
Knock Sensor (KS) System.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
81. Check for proper ignition voltage output with spark
tester J 26792 (ST-125). Refer to
Electronic Ignition
System
for procedure.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 9
91. Remove the spark plugs and check for wet plugs,
cracks, wear, improper gap, burned electrodes, or
heavy deposits. Refer to
Electronic Ignition
System
.
NOTE: If spark plugs are gas or oil fouled, the cause of
the fouling must be determined before replacing the
spark plugs.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 10
101. Check the ignition coils for cracks or carbon
tracking.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 11
Page 1390 of 6000
6E–273 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle, Stalling Symptom
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
101. Visually/physically inspect for the following
conditions:
Restricted air intake system. Check for a
possible collapsed air intake duct, restricted
air filter element, or foreign objects blocking
the air intake system.
Throttle body. Check for objects blocking the
IAC passage or throttle bore, excessive
deposits in the IAC passage and on the IAC
pintle, and excessive deposits in the throttle
bore and on the throttle plate.
Large vacuum leak. Check for a condition that
causes a large vacuum leak, such as an
incorrectly installed or faulty crankcase
ventilation valve or a disconnected brake
booster hose.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
11Check the injector connections. If any of the injectors
are connected to an incorrect cylinder, correct as
necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 12
121. Perform the “Injector Coil/Balance Test” in Fuel
Metering System
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 13
131. Check for fuel in the pressure regulator vacuum
hose.
2. If fuel is present, replace the fuel pressure regulator
assembly. Refer to
Fuel Metering System.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 14
141. Check for proper ignition voltage output with spark
tester J 26792 (ST-125). Refer to
Electronic Ignition
System
for the procedure.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 15
151. Remove spark plugs. Check for wet plugs, cracks,
wear, improper gap, burned electrodes, or heavy
deposits. Refer to
Electronic Ignition System.
NOTE: If spark plugs are gas or oil fouled, the cause of
the fouling must be determined before replacing the
spark plugs.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 16
161. Check for a loose ignition coil ground.
Refer to
Electrical Ignition System.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 17
Page 1392 of 6000
6E–275 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Poor Fuel Economy Symptom
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1DEFINITION:
Fuel economy, as measured by an actual road test, is
noticeably lower than expected. Also, economy is
noticeably lower than it was on this vehicle at one time,
as previously shown by an actual road test.
(Non-standard tires will cause odometer readings to be
incorrect, and that may cause fuel economy to appear
poor when it is actually normal.)
Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom?
—Verify repairGo to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to
Visual/Physic
al Check
4Check owner’s driving habits.
Is the A/C “ON” full time (defroster mode “ON”)?
Are tires at the correct pressure?
Are excessively heavy loads being carried?
Is acceleration too much, too often?
Was a problem found?
—Go to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Review the items in Step 4 with the customer and
advise as necessary.
Is the action complete?
—System OK—
61. Visually/physically check: Vacuum hoses for splits,
kinks, and improper connections and routing as
shown on the “Vehicle Emission Control
Information” label.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 7
71. Remove and check the air filter element for dirt or for
restrictions. Refer to
Air Intake System.
2. Replace the air filter element if necessary.
Was a repair required?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
81. Remove spark plugs and check for wet plugs,
cracks, wear, improper gap, burned electrodes, or
heavy deposits. Refer to
Spark Plug Replacement.
NOTE: If spark plugs are gas or oil fouled, the cause of
the fouling must be determined before replacing the
spark plugs.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 9
91. Check for low engine coolant level. Refer to Engine
Cooling
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 10
Page 1400 of 6000
6E–283 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Cuts Out, Misses Symptom
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
101. Visually/physically inspect for the following
conditions:
Restricted air intake system. Check for a
possible collapsed air intake duct, restricted
air filter element, or foreign objects blocking
the air intake system.
Throttle body. Check for objects blocking the
IAC passage or throttle bore, excessive
deposits in the IAC passage and on the IAC
pintle, and excessive deposits in the throttle
bore and on the throttle plate.
Large vacuum leak. Check for a condition that
causes a large vacuum leak, such as an
incorrectly installed or faulty PCV valve or
brake booster hose disconnected .
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
11Check the injector connections. If any of the injectors
are connected to an incorrect cylinder, correct as
necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 12
121. Perform the “Injector Coil/Balance Test” in Fuel
Metering System
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 13
131. Check for fuel in the pressure regulator vacuum
hose.
2. If fuel is present, replace the fuel pressure regulator
assembly. Refer to
Fuel Metering System.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 14
141. Check for proper ignition voltage output with spark
tester J 26792 (ST-125). Refer to
Electronic Ignition
System
for the procedure.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 15
151. Remove spark plugs. Check for wet plugs, cracks,
wear, improper gap, burned electrodes, or heavy
deposits. Refer to
Electronic Ignition System.
NOTE: If spark plugs are gas or oil fouled, the cause of
the fouling must be determined before replacing the
spark plugs.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 16
161. Check for a loose ignition coil ground.
Refer to
Electronic Ignition System.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 17
Page 1420 of 6000
6E–303 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
4. Check the transfer case oil level. Add fluid if
necessary.
5. Connect the negative battery cable.
Air Cleaner/Air Filter
Removal Procedure
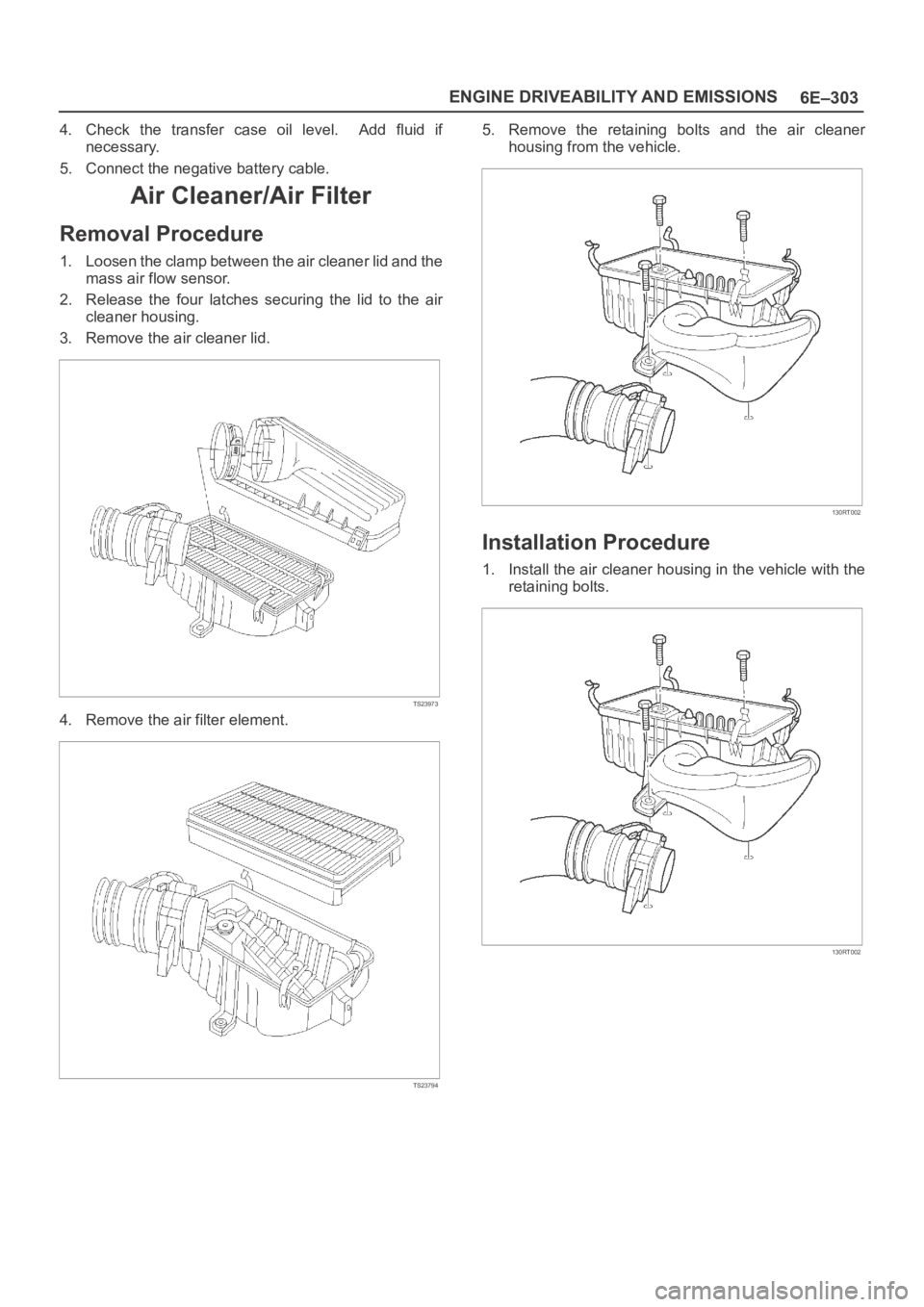
1. Loosen the clamp between the air cleaner lid and the
mass air flow sensor.
2. Release the four latches securing the lid to the air
cleaner housing.
3. Remove the air cleaner lid.
TS23973
4. Remove the air filter element.
TS23794
5. Remove the retaining bolts and the air cleaner
housing from the vehicle.
130RT002
Installation Procedure
1. Install the air cleaner housing in the vehicle with the
retaining bolts.
130RT002
Page 1421 of 6000
6E–304
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
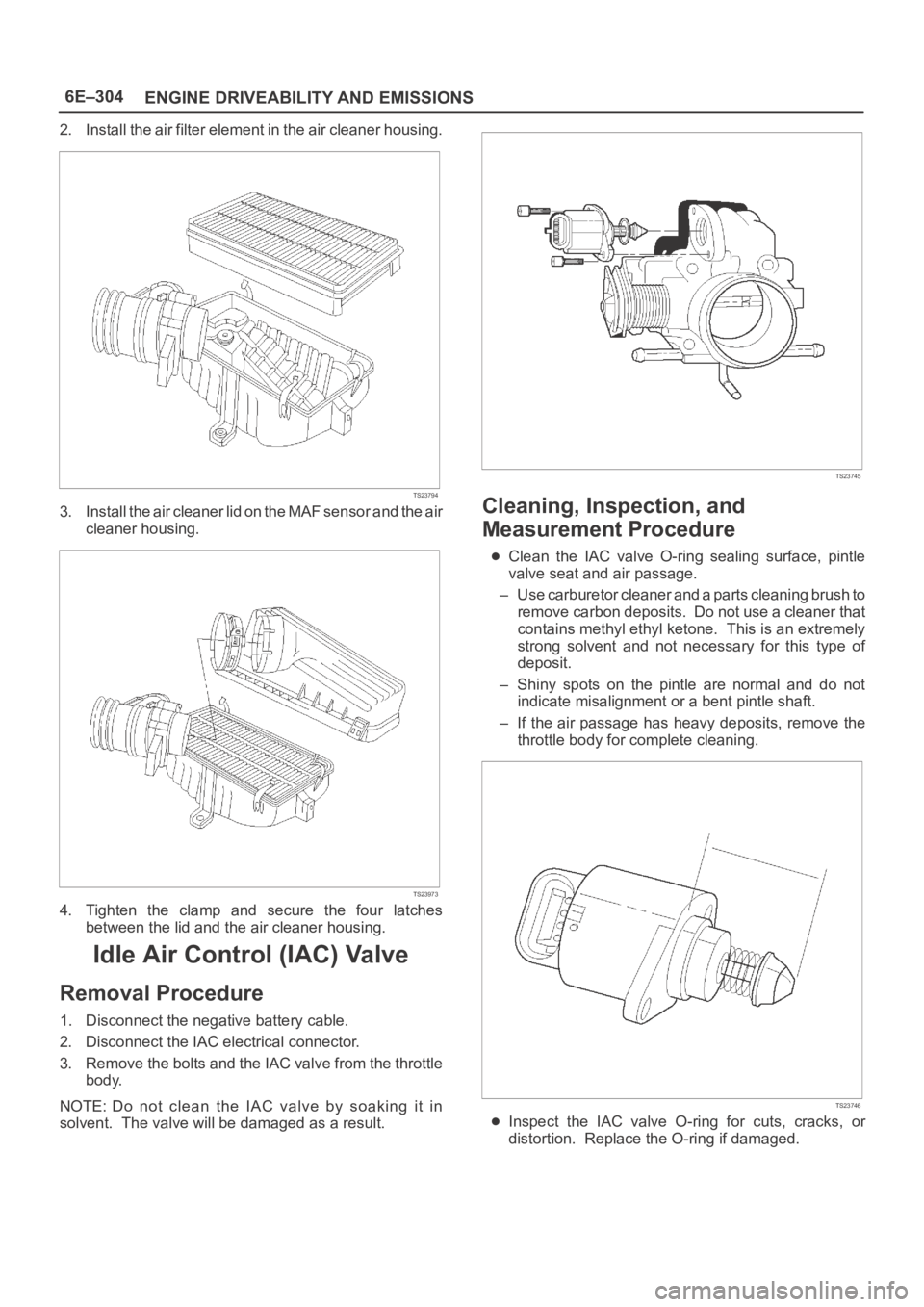
2. Install the air filter element in the air cleaner housing.
TS23794
3. Install the air cleaner lid on the MAF sensor and the air
cleaner housing.
TS23973
4. Tighten the clamp and secure the four latches
between the lid and the air cleaner housing.
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the IAC electrical connector.
3. Remove the bolts and the IAC valve from the throttle
body.
NOTE: Do not clean the IAC valve by soaking it in
solvent. The valve will be damaged as a result.
TS23745
Cleaning, Inspection, and
Measurement Procedure
Clean the IAC valve O-ring sealing surface, pintle
valve seat and air passage.
– Use carburetor cleaner and a parts cleaning brush to
remove carbon deposits. Do not use a cleaner that
contains methyl ethyl ketone. This is an extremely
strong solvent and not necessary for this type of
deposit.
– Shiny spots on the pintle are normal and do not
indicate misalignment or a bent pintle shaft.
– If the air passage has heavy deposits, remove the
throttle body for complete cleaning.
TS23746
Inspect the IAC valve O-ring for cuts, cracks, or
distortion. Replace the O-ring if damaged.