1998 OPEL FRONTERA Gas
[x] Cancel search: GasPage 741 of 6000

4D1–20
TRANSFER CASE (STANDARD TYPE)
Removal
1. Remove the speedometer sensor.
2. Remove the plate.
3. Remove the speedometer driven gear bushing and
driven gear.
NOTE: Apply a reference mark to the driven gear bushing
before removal.
4. Remove the front companion flange and the rear
companion flange, using the flange companion holder
5–8840–0133–0 (J–8614–11) to remove the end
nuts.
262RW067
NOTE: Use a universal puller to remove the rear
companion flange.
5. Disconnect the transfer breather hose from the
control box.
6. Remove the control box assembly.
7. Remove the transfer rear cover assembly from the
transfer case assembly.
Installation
1. Apply the recommended liquid gasket (LOCTITE
17430) or its equivalent to the transfer rear cover
fitting faces.
220RS017
2. Install the transfer rear cover assembly to the transfer
case assembly.
3. Perform the following steps before fitting the transfer
rear case:
1. Shift the high–low shift rod to the 4H side.
2. Turn the select rod counterclockwise so that the
select block projection may enter into the
2WD–4WD shift block.
3. The cut–away portion of the select rod head (9)
should align with that of the rear case hole’s
stopper (10).
230RW004
4. Tighten the transfer rear case bolts to the specified
torque.
Torque: 37 Nꞏm (3.8kgꞏm/27 lb ft)
Page 749 of 6000
4D1–28
TRANSFER CASE (STANDARD TYPE)
Inspection and Repair
Refer to “TRANSFER CASE ASSEMBLY” in this section
for inspection and repair.
Reassembly
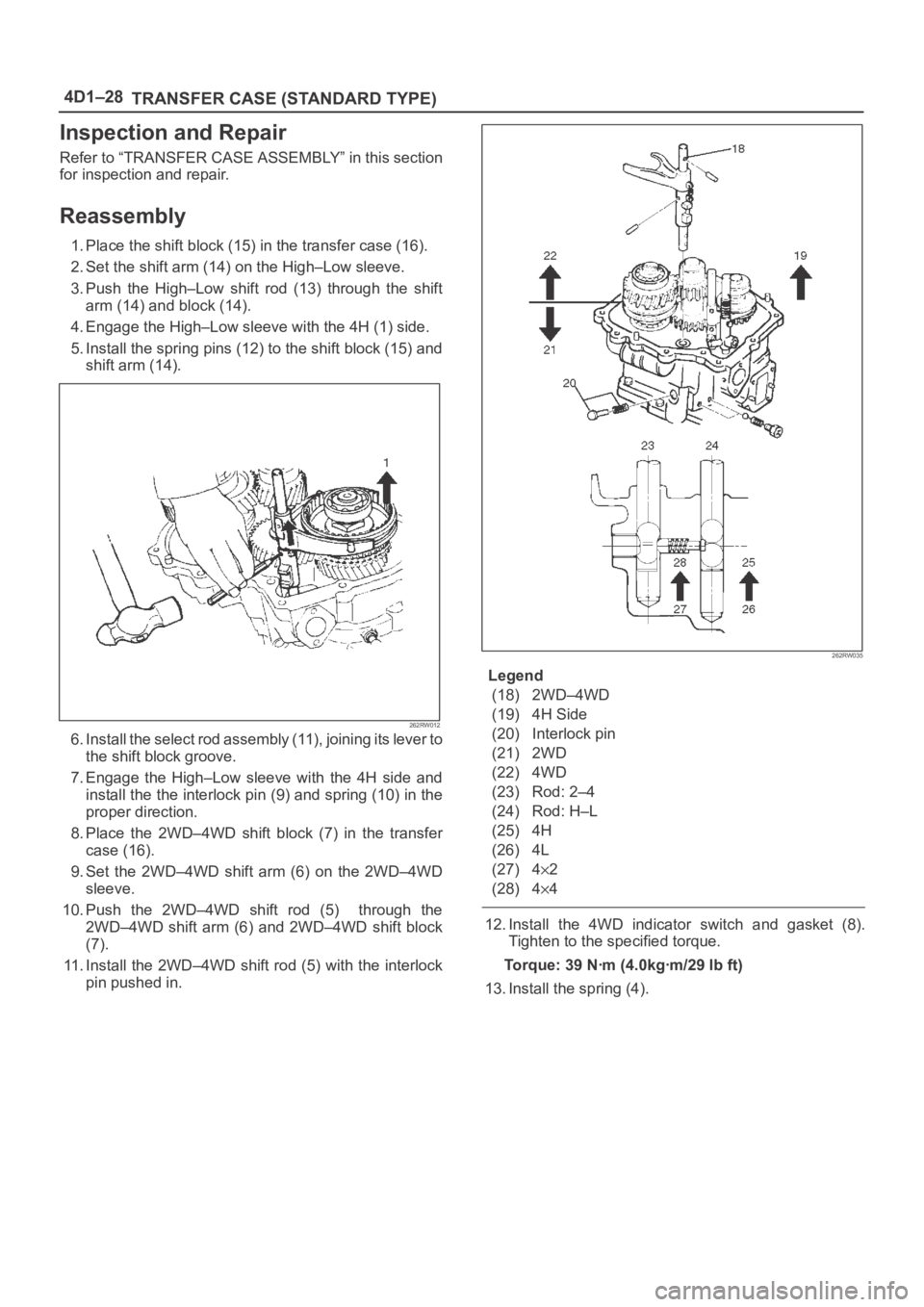
1. Place the shift block (15) in the transfer case (16).
2. Set the shift arm (14) on the High–Low sleeve.
3. Push the High–Low shift rod (13) through the shift
arm (14) and block (14).
4. Engage the High–Low sleeve with the 4H (1) side.
5. Install the spring pins (12) to the shift block (15) and
shift arm (14).
262RW012
6 . I n s t a l l t h e s e l e c t r o d a s s e m b l y ( 11 ) , j o i n i n g i t s l e v e r t o
the shift block groove.
7. Engage the High–Low sleeve with the 4H side and
install the the interlock pin (9) and spring (10) in the
proper direction.
8. Place the 2WD–4WD shift block (7) in the transfer
case (16).
9. Set the 2WD–4WD shift arm (6) on the 2WD–4WD
sleeve.
10. Push the 2WD–4WD shift rod (5) through the
2WD–4WD shift arm (6) and 2WD–4WD shift block
(7).
11. Install the 2WD–4WD shift rod (5) with the interlock
pin pushed in.
262RW035
Legend
(18) 2WD–4WD
(19) 4H Side
(20) Interlock pin
(21) 2WD
(22) 4WD
(23) Rod: 2–4
(24) Rod: H–L
(25) 4H
(26) 4L
(27) 4
2
(28) 4
4
12. Install the 4WD indicator switch and gasket (8).
Tighten to the specified torque.
Torque: 39 Nꞏm (4.0kgꞏm/29 lb ft)
13. Install the spring (4).
Page 777 of 6000

4D2–10
TRANSFER CASE (TOD)
6. Remove the offset lever set bolt on the right side.
261RW015
7. Remove the offset lever lock spring pin.
NOTE: When removing the spring pin, note the recess
position of the pin.
261RW016
8. Remove the offset lever.
261RW017
9. Remove the sixteen bolts and detach the transfer
cover assembly from the transfer case assembly.
NOTE: When removing the transfer cover assembly, be
careful not to damage the oil seal.
Reassembly
1. Apply liquid gasket (Loctite 598 or equivalent)
uniformly to the mating face that contacts the transfer
case.
261RW023
Page 961 of 6000

6A–5
ENGINE MECHANICAL
4. Engine Lacks Compression
Condition
Possible causeCorrection
Engine lacks compressionSpark plug loosely fitted or spark
plug gasket defectiveTighten to specified torque or replace
gasket
Valve timing incorrectAdjust
Cylinder head gasket defectiveReplace gasket
Valve incorrectly seatedLap valve
Valve stem seizedReplace valve and valve guide
Valve spring weakened or brokenReplace
Cylinder or piston rings wornOverhaul engine
Piston ring seizedOverhaul engine.
Engine Compression Test Procedure
1. Start and run the engine until the engine reaches
normal operating temperature.
2. Turn the engine off.
3. Remove all the spark plugs.
4. Remove ignition coil fuse (15A) and disable the
ignition system.
5. Remove the fuel pump relay from the relay and fuse
box.
6. Engage the starter and check that the cranking speed
is approximately 300 rpm.7. Install cylinder compression gauge into spark plug
hole.
8. With the throttle valve opened fully, keep the starter
engaged until the compression gage needle reaches
the maximum level. Note the reading.
9. Repeat the test with each cylinder.
If the compression pressure obtained falls below the
limit, engine overhaul is necessary.
Limit; 1000 kPa (145 psi)
Page 962 of 6000

6A–6
ENGINE MECHANICAL
Rough Engine Idling or Engine Stalling
ConditionPossible causeCorrection
Trouble in fuel injection systemIdle air control valve defectiveReplace
Throttle shutting off incompleteCorrect or replace
Throttle position sensor circuit open
or shortedCorrect or replace
Fuel injector circuits open or shortedCorrect or replace
Fuel injectors damagedReplace
Fuel pump relay defectiveReplace
Mass Airflow Sensor circuit open or
poor connectionsCorrect or replace
Mass Airflow Sensor defectiveReplace
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
circuit open or poor connectionsCorrect or replace
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
defectiveReplace
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
circuit open or poor connectionsCorrect or replace
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
defectiveReplace
Intake Air Temperature sensor circuit
open or poor connectionsCorrect or replace
Intake Air Temperature sensor
defectiveReplace
Knock Sensor (KS) cable broken or
poor connectionsCorrect or replace
KS defectiveReplace
KS Module circuits open or groundCorrect or replace
KS Module defectiveReplace
Vehicle Speed Sensor circuit open or
shortedCorrect or replace
Vehicle Speed Sensor defectiveReplace
Trouble in emission control systemPowertrain Control Module defectiveReplace
Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve
circuit open or poor connectionsCorrect or replace
Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve
faultyReplace
Canister purge valve circuit open or
poor connectionsCorrect or replace
Canister purge valve defectiveReplace
Evaporative Emission Canister
Purge control valve defectiveReplace
Trouble in ignition systemRefer to “Hard Start”
Page 967 of 6000

6A–11
ENGINE MECHANICAL
Condition CorrectionPossible cause
Engine overheatingLevel of Engine Coolant too lowReplenish
Fan clutch defectiveReplace
Incorrect fan installedReplace
Thermostat defectiveReplace
Engine Coolant pump defectiveCorrect or replace
Radiator cloggedClean or replace
Radiator filler cap defectiveReplace
Level of oil in engine crankcase too
low or wrong engine oilChange or replenish
Resistance in exhaust system
increasedClean exhaust system or replace
defective parts
Throttle Position Sensor adjustment
incorrectReplace with Throttle Valve ASM
Throttle Position Sensor circuit open
or shortedCorrect or replace
Cylinder head gasket damagedReplace
Engine overcoolingThermostat defectiveReplace (Use a thermostat set to
open at 82
C (180F))
Engine lacks compression————Refer to Hard Start
OthersTire inflation pressure abnormalAdjust to recommended pressures
Brake dragAdjust
Clutch slippingAdjust or replace
Level of oil in engine crankcase too
highCorrect level of engine oil
Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve
defectiveReplace
Engine Noisy
Abnormal engine noise often consists of various noises
originating in rotating parts, sliding parts and othermoving parts of the engine. It is, therefore, advisable to
locate the source of noise systematically.
Condition
Possible causeCorrection
Noise from crank journals or from
crank bearings
(Faulty crank journals and crankOil clearance increased due to worn
crank journals or crank bearingsReplace crank bearings and
crankshaft or regrind crankshaft and
install the undersize bearing
yj
bearings usually make dull noise that
becomes more evident when
accelerating)Crankshaft out of roundReplace crank bearings and
crankshaft or regrind crankshaft and
install the undersize bearing
Crank bearing seizedCrank bearing seized. Replace crank
bearings and crankshaft or regrind
crankshaft and install the undersize
bearing
Troubleshooting Procedure
Short out each spark plug in sequence using insulated
spark plug wire removers. Locate cylinder with defectivebearing by listening for abnormal noise that stops when
spark plug is shorted out.
Page 970 of 6000

6A–14
ENGINE MECHANICAL
Condition CorrectionPossible cause
Trouble in emission control systemHeated Oxygen Sensor circuit openCorrect or replace
Heated Oxygen Sensor defectiveReplace
Signal vacuum hose loosely fitted or
defectiveCorrect or replace
EGR Valve circuit open or shortedCorrect or replace
Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve
defectiveReplace
ECT Sensor circuit open or shortedCorrect or replace
Canister Purge Valve circuit open or
shortedCorrect or replace
Canister Purge Valve defectiveReplace
ECT Sensor defectiveReplace
Positive Crankcase Ventilation
(PCV) valve and hose cloggedCorrect or replace
Evaporator systemRefer to Section 6E
Trouble in ignition system————Refer to “Engine Lacks Power”
Trouble in cylinder head partsCarbon deposits in combustion
chamberRemove carbon
Carbon deposit on valve, valve seat
and valve guideRemove carbon
Engine Oil Consumption Excessive
ConditionPossible causeCorrection
Oil leakingOil pan drain plug looseRetighten or replace gasket
Crankcase fixing bolts loosenedRetighten
Oil pan setting bolts loosenedRetighten
Oil pan gasket brokenReplace gasket
Front cover retaining bolts loose or
gasket brokenRetighten or replace gasket
Head cover fixing bolts loose or
gasket brokenRetighten or replace gasket
Oil cooler adapter crackedReplace
Oil cooler center bolt looseRetighten
Oil cooler O–ring brokenReplace
Oil cooler piping loose or brokenRetighten or replace
Oil filter adapter crackedReplace
Oil filter attaching bolt loose or rubber
gasket brokenRetighten or replace oil filter
Oil cooler brokenReplace
Crankshaft front or rear oil seal
defectiveReplace oil seal
Oil pressure unit loose or brokenRetighten or replace
Blow–by gas hose brokenReplace hose
Positive Crankcase Ventilation Valve
cloggedClean
Engine/Transmission coupling failedReplace oil seal
Page 971 of 6000

6A–15
ENGINE MECHANICAL
Condition CorrectionPossible cause
Oil leaking into combustion
chambers due topoor seal in valve
Valve stem oil seal defectiveReplace
chambers due to oor seal in valve
systemValve stem or valve guide wornReplace valve and valve guide
Oil leaking into combustion
chambers due to poor seal in cylinder
t
Cylinders and pistons worn
excessivelyReplace cylinder body assembly and
pistons
partsPiston ring gaps incorrectly
positionedCorrect
Piston rings set with wrong side upCorrect
Piston ring stickingReplace cylinder body assembly and
pistons
Piston ring and ring groove wornReplace pistons and others
Return ports in oil rings cloggedClean piston and replace rings
Positive Crankcase Ventilation
System malfunctioningPositive Crankcase Ventilation Valve
cloggedClean
OthersImproper oil viscosityUse oil of recommended S.A.E.
viscosity
Continuous high speed driving
and/or severe usage such as trailer
towingContinuous high speed operation
and/or severe usage will normally
cause increased oil consumption
Fuel Consumption Excessive
ConditionPossible causeCorrection
Trouble in fuel systemMixture too rich or too lean due to
trouble in fuel injection systemRefer to “Abnormal Combustion”
Fuel cut function does not workRefer to “Abnormal Combustion”
Trouble in ignition systemMisfiring or abnormal combustion
due to trouble in ignition systemRefer to “Hard Start” or “Abnormal
Combustion”
OthersEngine idle speed too highReset Idle Air Control Valve
Returning of accelerator control
sluggishCorrect
Fuel system leakageCorrect or replace
Clutch slippingCorrect
Brake dragCorrect
Selection of transmission gear
incorrectCaution operator of incorrect gear
selection
Excessive Exhaust Gas
Recirculation flow due to trouble in
Exhaust Gas Recirculation systemRefer to “Abnormal Combustion”