1998 OPEL FRONTERA seat
[x] Cancel search: seatPage 4907 of 6000
6E–250
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
DTC P1404 – EGR Closed Stuck
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition “ON,” engine “OFF”, review and record
Tech 2 Failure Records Data.
2. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
3. Using a Tech 2, monitor “DTC inf. for DTC P1404
until the DTC P1404 test runs. Note the result.
Does the Tech 2 indicates DTC P1404 failed this
ignition?
—Go to Step 3
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
31. Disconnect the EGR valve harness connector.
2. Inspect the EGR valve and connectors for damaged
pin or terminals.
Were there any damaged pins or terminals?
—Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
4Repair the damaged pin or terminal.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
51. Remove EGR valve from Engine.
2. Inspect EGR valve whether there is any excessive
carbon deposit on EGR shaft.
3. Inspect any foreign material inside of EGR valve.
Was excessive carbon deposit on EGR valve shaft
or/and foreign material in EGR valve ?
—Go to Step 6Go to Step 7
61. Clean up EGR valve shaft and inside of EGR valve.
2. Remove foreign material from EGR valve.
3. Visually inspect damage of pintle and seat whether
there is bent, leakage may occur.
Was there any severe damage which affects function?
3–6 ohmsGo to Step 8
Verify repair
Go to
Step 7
71. Reconnect.
2. Ignition “OFF”.
3. Install the Tech 2.
4. Run the engine at idle.
5. On the Tech 2, select F3:Misc. Test F5:EGR.
6. Use the “UP” arrow to increase the EGR from 0% to
40%.
Did EGR work properly?
——Go to Step 8
81. Reset the learned zero EGR valve position.
2. Repeat step 7.
Did EGR work properly?
—Verify repairGo to Step 9
9Replace the EGR valve.
Replace the EGR valve. Does DTC P1404 still fail
“specific DTC” test on the Tech 2?
—Go to Step 10Verify repair
10Replace the PCM.
IMPORTANT:The replacement PCM must be
programmed. Refer to
UBS 98model year Immobilizer
Workshop Manual.
Is the action complete?—Verify repair—
Page 4919 of 6000

6E–262
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Symptom Diagnosis
Preliminary Checks
Before using this section, perform the “On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System Check” and verify all of the
following items:
The powertrain control module (PCM) and malfunction
indicator lamp (MIL) (Service Engine Soon lamp) are
operating correctly.
There are no DTC(s) stored.
Tech 2 data is within normal operating range. Refer to
Typical Scan Data Values.
Verify the customer complaint and locate the correct
symptom in the table of contents. Perform the
procedure included in the symptom chart.
Visual/Physical Check
Several of the symptom procedures call for a careful
visual/physical check. This can lead to correcting a
problem without further checks and can save valuable
time.
This check should include the following items:
PCM grounds for cleanliness, tightness and proper
location.
Vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper
connections, as shown on the “Vehicle Emission
Control Information” label. Check thoroughly for any
type of leak or restriction.
Air intake ducts for collapsed or damaged areas.
Air leaks at throttle body mounting area, mass air flow
(MAF) sensor and intake manifold sealing surfaces.
Ignition wires for cracking, hardness, and carbon
tracking.
Wiring for proper connections, pinches and cuts.
Intermittents
IMPORTANT:An intermittent problem may or may not
turn on the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) or store a
DTC. DO NOT use the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
charts for intermittent problems. The fault must be
present to locate the problem.
Most intermittent problems are caused by faulty electrical
connections or wiring. Perform a careful visual/physical
check for the following conditions:
Poor mating of the connector halves or a terminal not
fully seated in the connector (backed out).
Improperly formed or damaged terminal.
All connector terminals in the problem circuit should be
carefully checked for proper contact tension.
Poor terminal-to-wire connection. This requires
removing the terminal from the connector body to
check.
Road test the vehicle with a J 39200 Digital Multimeter
connected to a suspected circuit. An abnormal voltage
when the malfunction occurs is a good indication that
there is a fault in the circuit being monitored.
Use Tech 2 to help detect intermittent conditions. Tech 2s
have several features that can be used to locate anintermittent condition. Use the following feature to find
intermittent faults:
Using Tech 2’s “Freeze Frame” buffer or “Failure
Records” buffer can aid in locating an intermittent
condition. Review and record the information in the
freeze frame or failure record associated with the
intermittent DTC being diagnosed. The vehicle can be
driven within the conditions that were present when the
DTC originally set.
To check for loss of diagnostic code memory, disconnect
the MAP sensor and idle the engine until the MIL (Service
Engine Soon lamp) comes on. DTC P0107 should be
stored and kept in memory when the ignition is turned
“OFF.” If not, the PCM is faulty. When this test is
completed, make sure that you clear the DTC P0107 from
memory.
An intermittent MIL (Service Engine Soon lamp) with no
stored DTC may be caused by the following:
Ignition coil shorted to ground and arcing at ignition
wires or plugs.
MIL (Service Engine Soon lamp) wire to PCM shorted
to ground.
Poor PCM grounds. Refer to the PCM wiring
diagrams.
Check for improper installation of electrical options such
as lights, cellular phones, etc. Route ignition coil wiring
away from the ignition coils. Check all wires from the
PCM to the ignition coil for poor connections.
Check for an open diode across the A/C compressor
clutch and check for other open diodes (refer to wiring
diagrams in
Electrical Diagnosis).
If problem has not been found, refer to
PCM Connector
Symptom
tables.
Page 4955 of 6000

6E–298
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
4. Remove the MAP sensor from the mounting bracket.
055RW002
Installation Procedure
1. Install the MAP sensor in the mounting bracket.
055RW002
2. Install the mounting bracket retaining bolt on the
common chamber.
3. Connect the MAP electrical connector.
055RW005
4. Connect the negative battery cable.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL)
Removal and Installation Procedure
Refer to Warning light bulb, indicator light valve,
illumination light bulb, A/T indicator light bulb in Meter and
Gauge.
Powertrain Control Module
(PCM)
Service Precaution
NOTE: To prevent possible electrostatic discharge
damage to the PCM, do not touch the connector pins or
soldered components on the circuit board.
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
Damage
Electronic components used in the control systems are
often designed to carry very low voltage. Electronic
components are susceptible to damage caused by
electrostatic discharge. Less than 100 volts of static
electricity can cause damage to some electronic
components. By comparison, it takes as much as 4,000
volts for a person to even feel the zap of a static
discharge.
There are several ways for a person to become statically
charged. The most common methods of charging are by
friction and by induction. An example of charging by
friction is a person sliding across a car seat.
Charging by induction occurs when a person with well
insulated shoes stands near a highly charged object and
momentarily touches ground. Charges of the same
polarity are drained off leaving the person highly charged
with the opposite polarity. Static charges can cause
Page 4956 of 6000

6E–299 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
damage, therefore, it is important to use care when
handling and testing electronic components.
NOTE: To prevent possible Electrostatic Discharge
damage, follow these guidelines:
Do not touch the control module connector pins or
soldered components on the control module circuit
board.
Do not open the replacement part package until the
part is ready to be installed.
Before removing the part from the package, ground
the package to a known good ground on the vehicle.
If the part has been handled while sliding across the
seat, or while sitting down from a standing position, or
while walking a distance, touch a known good ground
before installing the part.
NOTE: To prevent internal PCM damage, the ignition
must be in the “OFF” position in order to disconnect or
reconnect power to the PCM (for example: battery cable,
PCM pigtail, PCM fuse, jumper cables, etc.).
IMPORTANT:When replacing the production PCM
with a service PCM, it is important to transfer the
broadcast code and production PCM number to the
service PCM label. This will allow positive identification of
PCM parts throughout the service life of the vehicle. Do
not record this information on the metal PCM cover.
IMPORTANT:The ignition should always be in the
“OFF” position in order to install or remove the PCM
connectors.
Service of the PCM should normally consist of either re-
placement of the PCM or EEPROM programming. If the
diagnostic procedures call for the PCM to be replaced,
the PCM should be checked first to ensure it is the correct
part. If it is, remove the faulty PCM and install the new
service PCM.
The service PCM EEPROM will not be programmed.
DTC P0601 indicates the check sum error.
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Block the wheels.
3. Remove the front console assembly.
1. Remove the four screws.
TS23755
2. Remove the transfer shift lever knob by
unscrewing the knob.
3. Move the transmission gear selector out of the
park position.
4. Lift up sharply on the back edge of the assembly.
5. Disconnect the seat heater switch connectors (if
equipped).
6. Disconnect the POWER and WINTER switch
connectors.
7. Lift out the front console assembly.
TS23756
Page 4961 of 6000
6E–304
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
2. Install the air filter element in the air cleaner housing.
TS23794
3. Install the air cleaner lid on the MAF sensor and the air
cleaner housing.
TS23973
4. Tighten the clamp and secure the four latches
between the lid and the air cleaner housing.
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
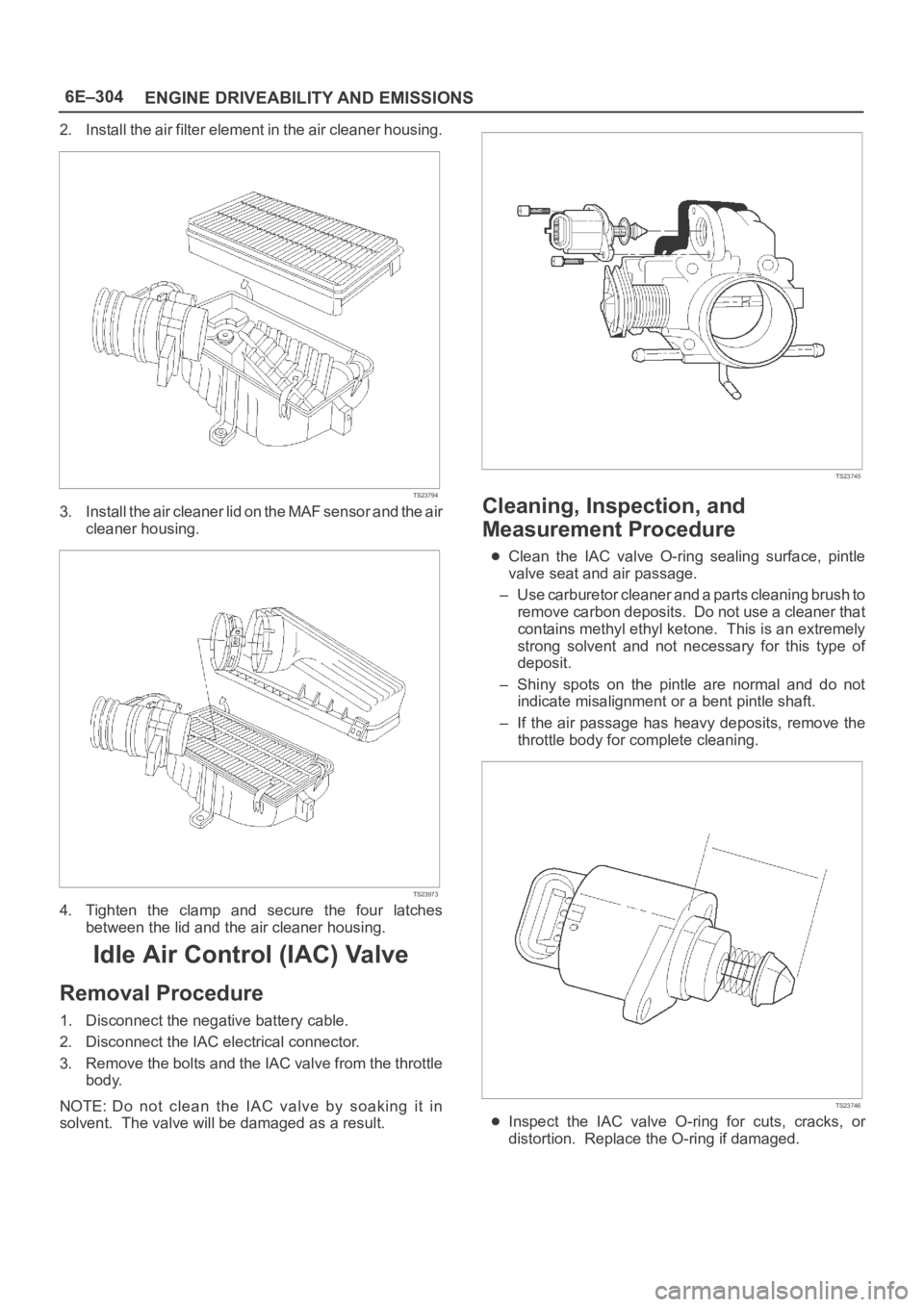
2. Disconnect the IAC electrical connector.
3. Remove the bolts and the IAC valve from the throttle
body.
NOTE: Do not clean the IAC valve by soaking it in
solvent. The valve will be damaged as a result.
TS23745
Cleaning, Inspection, and
Measurement Procedure
Clean the IAC valve O-ring sealing surface, pintle
valve seat and air passage.
– Use carburetor cleaner and a parts cleaning brush to
remove carbon deposits. Do not use a cleaner that
contains methyl ethyl ketone. This is an extremely
strong solvent and not necessary for this type of
deposit.
– Shiny spots on the pintle are normal and do not
indicate misalignment or a bent pintle shaft.
– If the air passage has heavy deposits, remove the
throttle body for complete cleaning.
TS23746
Inspect the IAC valve O-ring for cuts, cracks, or
distortion. Replace the O-ring if damaged.
Page 4982 of 6000

6E–325 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Spark Plug Gap Check
Check the gap of all spark plugs before installation.
Use a round wire feeler gauge to ensure an accurate
check.
Plugs installed with the wrong gap can cause poor
engine performance and excessive emissions.
Installation Procedure
NOTE: The plug must thread smoothly into the cylinder
head and be fully seated. Use a thread chaser if
necessary to clean the threads in the cylinder head.
Cross-threading or failure to fully seat the spark plug can
cause plug overheating, exhaust blow-by gas, or thread
damage. Do not overtighten the spark plugs. Over
tightening can cause aluminum threads to strip.
1. Install the spark plug in the engine. Use the
appropriate spark plug socket.
Tighten
Tighten the spark plug to 18 Nꞏm (13 lb ft.).
2. Install the ignition coil and spark plug boot over the
spark plug.
014RW108
3. Secure the ignition coil to the rocker cover with two
screws.
014RW091
4. Connect the electrical connector at the ignition coil.
5. Connect the negative battery cable.
Catalytic Converter
Removal and Installation Procedure
Refer to Engine Exhaust in Engine.
Air Conditioning Relay
Removal Procedure
1. Remove the fuse and relay box cover from under the
hood.
2. Consult the diagram on the cover to determine which
is the correct relay.
3. Insert a small screwdriver into the catch slot on the
forward side of the fuel pump relay.
The screwdriver blade will release the catch inside.
T321092
Page 4990 of 6000
6E–333 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
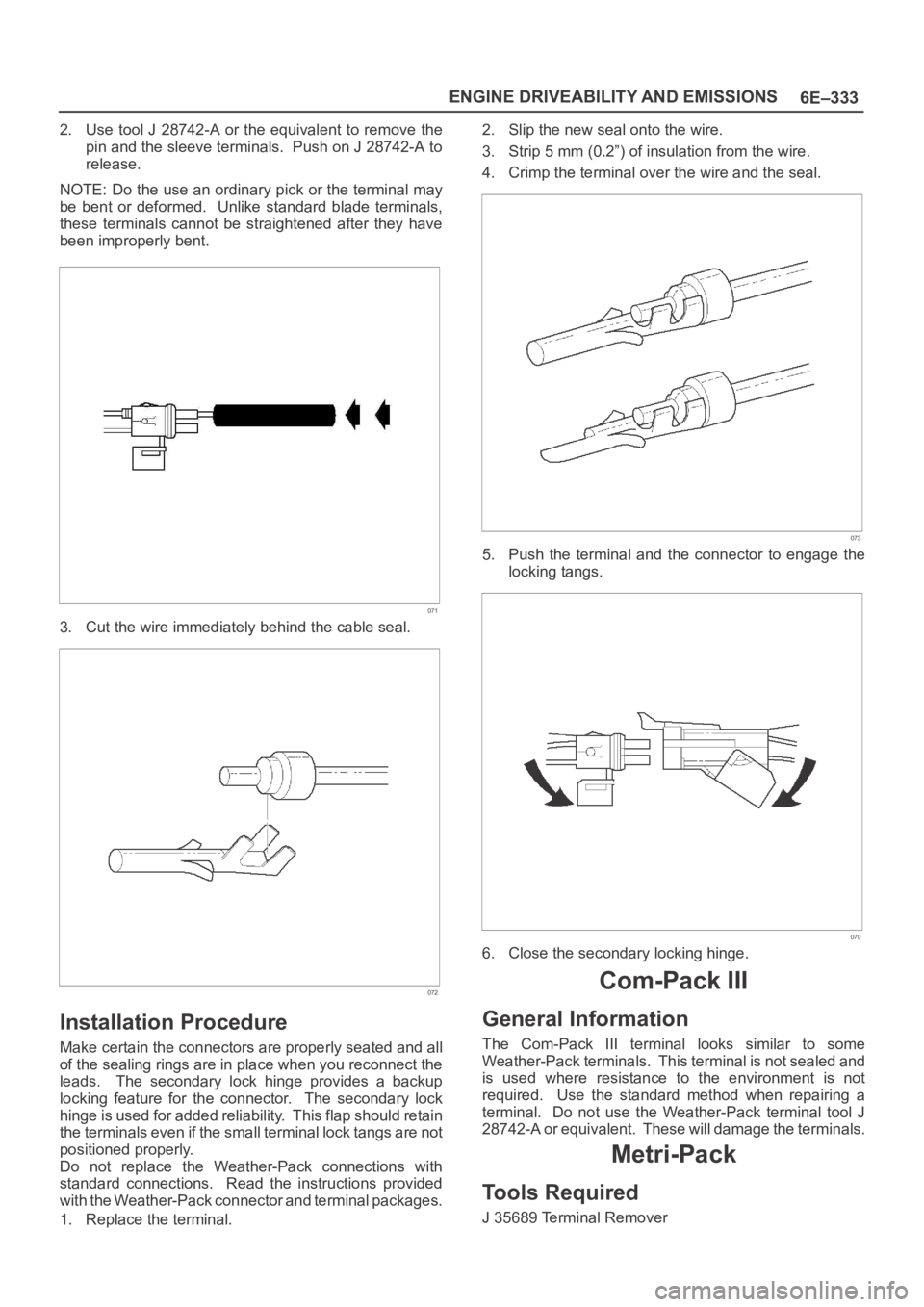
2. Use tool J 28742-A or the equivalent to remove the
pin and the sleeve terminals. Push on J 28742-A to
release.
NOTE: Do the use an ordinary pick or the terminal may
be bent or deformed. Unlike standard blade terminals,
these terminals cannot be straightened after they have
been improperly bent.
071
3. Cut the wire immediately behind the cable seal.
072
Installation Procedure
Make certain the connectors are properly seated and all
of the sealing rings are in place when you reconnect the
leads. The secondary lock hinge provides a backup
locking feature for the connector. The secondary lock
hinge is used for added reliability. This flap should retain
the terminals even if the small terminal lock tangs are not
positioned properly.
Do not replace the Weather-Pack connections with
standard connections. Read the instructions provided
with the Weather-Pack connector and terminal packages.
1. Replace the terminal.2. Slip the new seal onto the wire.
3. Strip 5 mm (0.2”) of insulation from the wire.
4. Crimp the terminal over the wire and the seal.
073
5. Push the terminal and the connector to engage the
locking tangs.
070
6. Close the secondary locking hinge.
Com-Pack III
General Information
The Com-Pack III terminal looks similar to some
Weather-Pack terminals. This terminal is not sealed and
is used where resistance to the environment is not
required. Use the standard method when repairing a
terminal. Do not use the Weather-Pack terminal tool J
28742-A or equivalent. These will damage the terminals.
Metri-Pack
Tools Required
J 35689 Terminal Remover
Page 4991 of 6000

6E–334
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Removal Procedure
S o m e c o n n e c t o r s u s e t e r m i n a l s c a l l e d M e t r i - P a c k S e r i e s
150. These may be used at the engine coolant
temperature (ECT) sensor.
1. Slide the seal (1) back on the wire.
2. Insert the J 35689 tool or equivalent (3) in order to
release the terminal locking tang (2).
060
3. Push the wire and the terminal out through the
connector. If you reuse the terminal, reshape the
locking tang.
Installation Procedure
Metri-Pack terminals are also referred to as “pull-to-seat”
terminals.
1. In order to install a terminal on a wire, the wire must be
inserted through the seal (2) and through the
connector (3).
2. The terminal (1) is then crimped onto the wire.
061
3. Then the terminal is pulled back into the connector to
seat it in place.