1998 OPEL FRONTERA overheating
[x] Cancel search: overheatingPage 4603 of 6000
6B–10
ENGINE COOLING
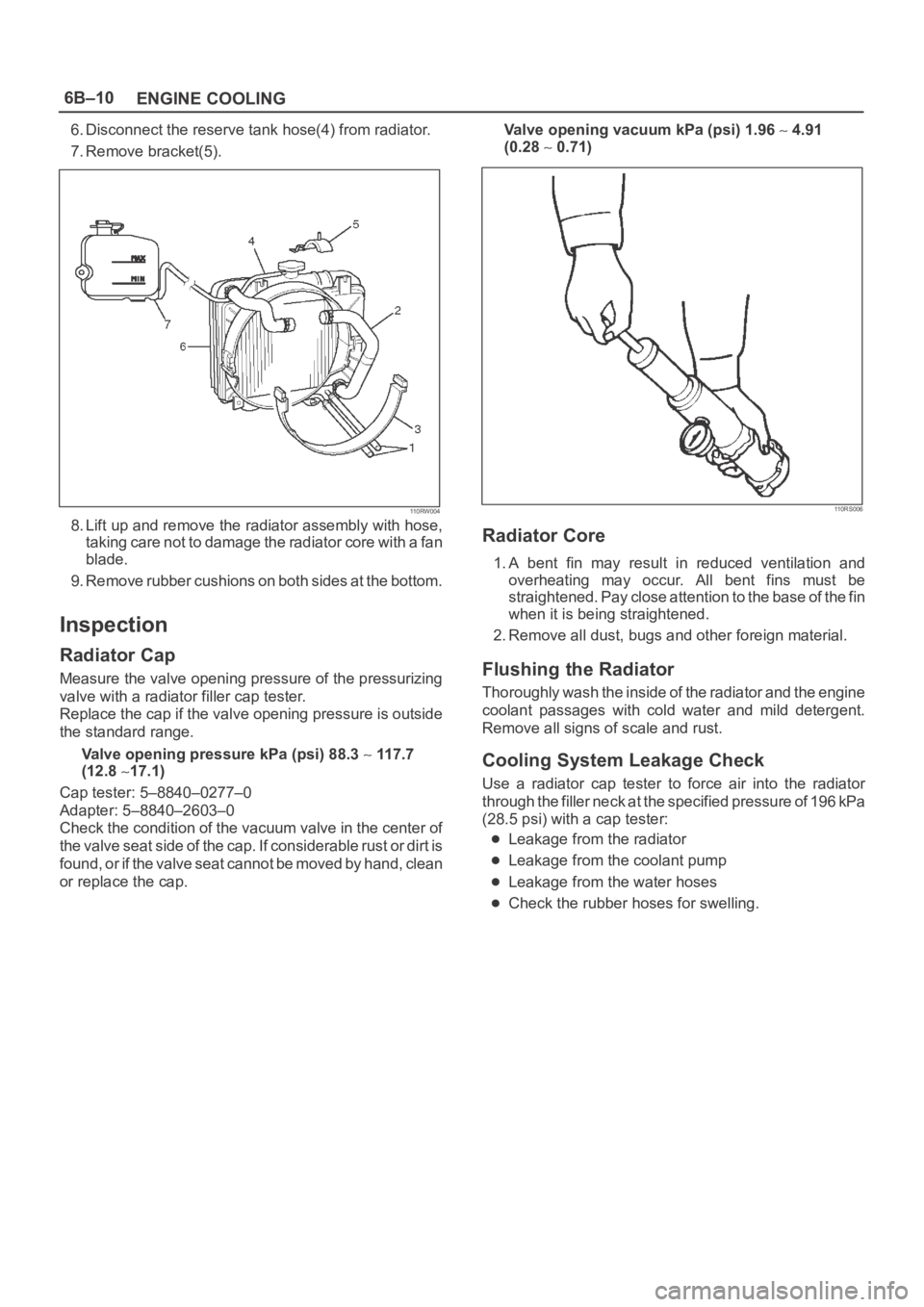
6. Disconnect the reserve tank hose(4) from radiator.
7. Remove bracket(5).
110RW004
8. Lift up and remove the radiator assembly with hose,
taking care not to damage the radiator core with a fan
blade.
9. Remove rubber cushions on both sides at the bottom.
Inspection
Radiator Cap
Measure the valve opening pressure of the pressurizing
valve with a radiator filler cap tester.
Replace the cap if the valve opening pressure is outside
the standard range.
Valve opening pressure kPa (psi) 88.3
117.7
(12.8
17.1)
Cap tester: 5–8840–0277–0
Adapter: 5–8840–2603–0
Check the condition of the vacuum valve in the center of
the valve seat side of the cap. If considerable rust or dirt is
found, or if the valve seat cannot be moved by hand, clean
or replace the cap.Valve opening vacuum kPa (psi) 1.96
4.91
(0.28
0.71)
110RS006
Radiator Core
1. A bent fin may result in reduced ventilation and
overheating may occur. All bent fins must be
straightened. Pay close attention to the base of the fin
when it is being straightened.
2. Remove all dust, bugs and other foreign material.
Flushing the Radiator
Thoroughly wash the inside of the radiator and the engine
coolant passages with cold water and mild detergent.
Remove all signs of scale and rust.
Cooling System Leakage Check
Use a radiator cap tester to force air into the radiator
through the filler neck at the specified pressure of 196 kPa
(28.5 psi) with a cap tester:
Leakage from the radiator
Leakage from the coolant pump
Leakage from the water hoses
Check the rubber hoses for swelling.
Page 4695 of 6000

6E–38
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
General Service Information
OBD Serviceablity Issues
The list of non-vehicle faults that could affect the
performance of the OBD system has been compiled.
These non-vehicle faults vary from environmental
conditions to the quality of fuel used.
The illumination of the MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) due to
a non-vehicle fault could lead to misdiagnosis of the
vehicle, increased warranty expense and customer
dissatisfaction. The following list of non-vehicle faults
does not include every possible fault and may not apply
equally to all product lines.
Fuel Quality
Using fuel with the wrong octane rating for your vehicle
may cause driveability problems. Many of the major fuel
companies advertise that using “premium” gasoline will
improve the performance of your vehicle. Most premium
fuels use alcohol to increase the octane rating of the fuel.
Although alcohol-enhanced fuels may raise the octane
rating, the fuel’s ability to turn into vapor in cold
temperatures deteriorates. This may affect the starting
ability and cold driveability of the engine.
Low fuel levels can lead to fuel starvation, lean engine
operation, and eventually engine misfire.
Non-OEM Parts
All of the OBD diagnostics have been calibrated to run
with OEM parts. Something as simple as a
high-performance exhaust system that affects exhaust
system back pressure could potentially interfere with the
operation of the EGR valve and thereby turn on the MIL
(“Check Engine” lamp). Small leaks in the exhaust
system near the post catalyst oxygen sensor can also
cause the MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) to turn on.
Aftermarket electronics, such as cellular phones,
stereos, and anti-theft devices, may radiate EMI into the
control system if they are improperly installed. This may
cause a false sensor reading and turn on the MIL (“Check
Engine” lamp).
Environment
Temporary environmental conditions, such as localized
flooding, will have an effect on the vehicle ignition system.
If the ignition system is rain-soaked, it can temporarily
cause engine misfire and turn on the MIL (“Check Engine”
lamp).
Poor Vehicle Maintenance
The sensitivity of OBD diagnostics will cause the MIL
(“Check Engine” lamp) to turn on if the vehicle is not
maintained properly. Restricted air filters, fuel filters, and
crankcase deposits due to lack of oil changes or improper
oil viscosity can trigger actual vehicle faults that were not
previously monitored prior to OBD. Poor vehicle
maintenance can not be classified as a “non-vehicle
fault”, but with the sensitivity of OBD diagnostics, vehicle
maintenance schedules must be more closely followed.Related System Faults
Many of the OBD system diagnostics will not run if the
PCM detects a fault on a related system or component.
One example would be that if the PCM detected a Misfire
fault, the diagnostics on the catalytic converter would be
suspended until Misfire fault was repaired. If the Misfire
fault was severe enough, the catalytic converter could be
damaged due to overheating and would never set a
Catalyst DTC until the Misfire fault was repaired and the
Catalyst diagnostic was allowed to run to completion. If
this happens, the customer may have to make two trips to
the dealership in order to repair the vehicle.
Maintenance Schedule
Refer to the Maintenance Schedule.
Visual / Physical Engine Compartment
Inspection
Perform a careful visual and physical engine
compartment inspection when performing any diagnostic
procedure or diagnosing the cause of an emission test
failure. This can often lead to repairing a problem without
further steps. Use the following guidelines when
performing a visual/physical inspection:
Inspect all vacuum hoses for punches, cuts,
disconnects, and correct routing.
Inspect hoses that are difficult to see behind other
components.
Inspect all wires in the engine compartment for proper
connections, burned or chafed spots, pinched wires,
contact with sharp edges or contact with hot exhaust
manifolds or pipes.
Basic Knowledge of Tools Required
NOTE: Lack of basic knowledge of this powertrain when
performing diagnostic procedures could result in an
incorrect diagnosis or damage to powertrain
components. Do not attempt to diagnose a powertrain
problem without this basic knowledge.
A basic understanding of hand tools is necessary to effec-
tively use this section of the Service Manual.
Serial Data Communications
Class II Serial Data Communications
This vehicle utilizes the “Class II” communication system.
Each bit of information can have one of two lengths: long
or short. This allows vehicle wiring to be reduced by
transmitting and receiving multiple signals over a single
wire. The messages carried on Class II data streams are
also prioritized. If two messages attempt to establish
communications on the data line at the same time, only
the message with higher priority will continue. The device
with the lower priority message must wait. The most
significant result of this regulation is that it provides Tech 2
manufacturers with the capability to access data from any
make or model vehicle that is sold.
Page 4927 of 6000
6E–270
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Detonation/Spark Knock Symptom
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1DEFINITION:
A mild to severe ping, usually worse under acceleration.
The engine makes sharp metallic knocks that change
with throttle opening.
Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom?
—Verify repairGo to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to
Visual/Physic
al Check
4If Tech 2 readings are normal (refer to Ty p i c a l S c a n
Va lu es
) and there are no engine mechanical faults, fill
the fuel tank with a known quality gasoline that has a
minimum octane rating of 87 and re-evaluate the
vehicle performance.
Is detonation present?
—Go to Step 5Verify repair
51. Check the transmission range switch circuit. Use
Tech 2 and be sure Tech 2 indicates that the vehicle
is in drive with the gear selector in drive or overdrive.
2. If a problem is found, diagnose and repair the
transmission range switch as necessary (refer to
4L30-E Automatic Transmission Diagnosis).
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 6
61. Check TCC operation. Refer to 4L30-E
Transmission Diagnosis
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 7
71. Check for obvious overheating problems:
Low engine coolant.
Restricted air flow to radiator, or restricted
water flow through radiator.
Correct coolant solution should be a 50/50 mix
of approved antifreeze/coolant and water.
Refer to
Engine Cooling.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
81. Check fuel pressure. Refer to Chart Fuel System
Pressure Test.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 9
91. Check items that can cause an engine to run lean
(long term fuel trim significantly in the positive
range). For a lean condition, refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
in DTC P0171 Diagnostic Support.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 10
Page 4982 of 6000

6E–325 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Spark Plug Gap Check
Check the gap of all spark plugs before installation.
Use a round wire feeler gauge to ensure an accurate
check.
Plugs installed with the wrong gap can cause poor
engine performance and excessive emissions.
Installation Procedure
NOTE: The plug must thread smoothly into the cylinder
head and be fully seated. Use a thread chaser if
necessary to clean the threads in the cylinder head.
Cross-threading or failure to fully seat the spark plug can
cause plug overheating, exhaust blow-by gas, or thread
damage. Do not overtighten the spark plugs. Over
tightening can cause aluminum threads to strip.
1. Install the spark plug in the engine. Use the
appropriate spark plug socket.
Tighten
Tighten the spark plug to 18 Nꞏm (13 lb ft.).
2. Install the ignition coil and spark plug boot over the
spark plug.
014RW108
3. Secure the ignition coil to the rocker cover with two
screws.
014RW091
4. Connect the electrical connector at the ignition coil.
5. Connect the negative battery cable.
Catalytic Converter
Removal and Installation Procedure
Refer to Engine Exhaust in Engine.
Air Conditioning Relay
Removal Procedure
1. Remove the fuse and relay box cover from under the
hood.
2. Consult the diagram on the cover to determine which
is the correct relay.
3. Insert a small screwdriver into the catch slot on the
forward side of the fuel pump relay.
The screwdriver blade will release the catch inside.
T321092
Page 5007 of 6000

6E–350
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
to the intake manifold through an orifice with a PCM
controlled pintle. During operation, the PCM controls
pintle position by monitoring the pintle position feedback
signal. The feedback signal can be monitored with Tech 2
as “Actual EGR Pos.” “Actual EGR Pos.” should always
be near the commanded EGR position (”Desired EGR
Pos.”). If a problem with the EGR system will not allow the
PCM to control the pintle position properly, DTC P1406
will set. The PCM also tests for EGR flow. If incorrect flow
is detected, DTC P0401 will set. If DTCs P0401 and/or
P1406 are set, refer to the DTC charts.
The linear EGR valve is usually activated under the
following conditions:
Warm engine operation.
Above-idle speed.
Too much EGR flow at idle, cruise or cold operation may
cause any of the following conditions to occur:
Engine stalls after a cold start.
Engine stalls at idle after deceleration.
Vehicle surges during cruise.
Rough idle.
Too little or no EGR flow may allow combustion
temperatures to get too high. This could cause:
Spark knock (detonation).
Engine overheating.
Emission test failure.
DTC P0401 (EGR flow test).
Poor fuel economy.
0017
EGR Pintle Position Sensor
The PCM monitors the EGR valve pintle position input to
endure that the valve responds properly to commands
from the PCM and to detect a fault if the pintle position
sensor and control circuits are open or shorted. If the
PCM detects a pintle position signal voltage outside the
normal range of the pintle position sensor, or a signal
voltage that is not within a tolerance considered
acceptable for proper EGR system operation, the PCM
will set DTC P1406.
General Description (Positive
Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) System)
Crankcase Ventilation System Purpose
The crankcase ventilation system is use to consume
crankcase vapors in the combustion process instead of
venting them to the atmosphere. Fresh air from the
throttle body is supplied to the crankcase and mixed with
blow-by gases. This mixture is then passed through the
positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) valve into the
common chamber.
Crankcase Ventilation System Operation
The primary control is through the positive crankcase
v e n t i l a t i o n ( P C V ) v a l v e . T h e PCV valve meters the flow at
a rate that depends on the intake vacuum. The PCV valve
restricts the flow when the inlet vacuum is highest. In
addition, the PCV valve can seal the common chamber
off in case of sudden high pressure in the crankcase.
028RV002
While the engine is running, exhaust fuses and small
amounts of the fuel/air mixture escape past the piston
Page 5014 of 6000
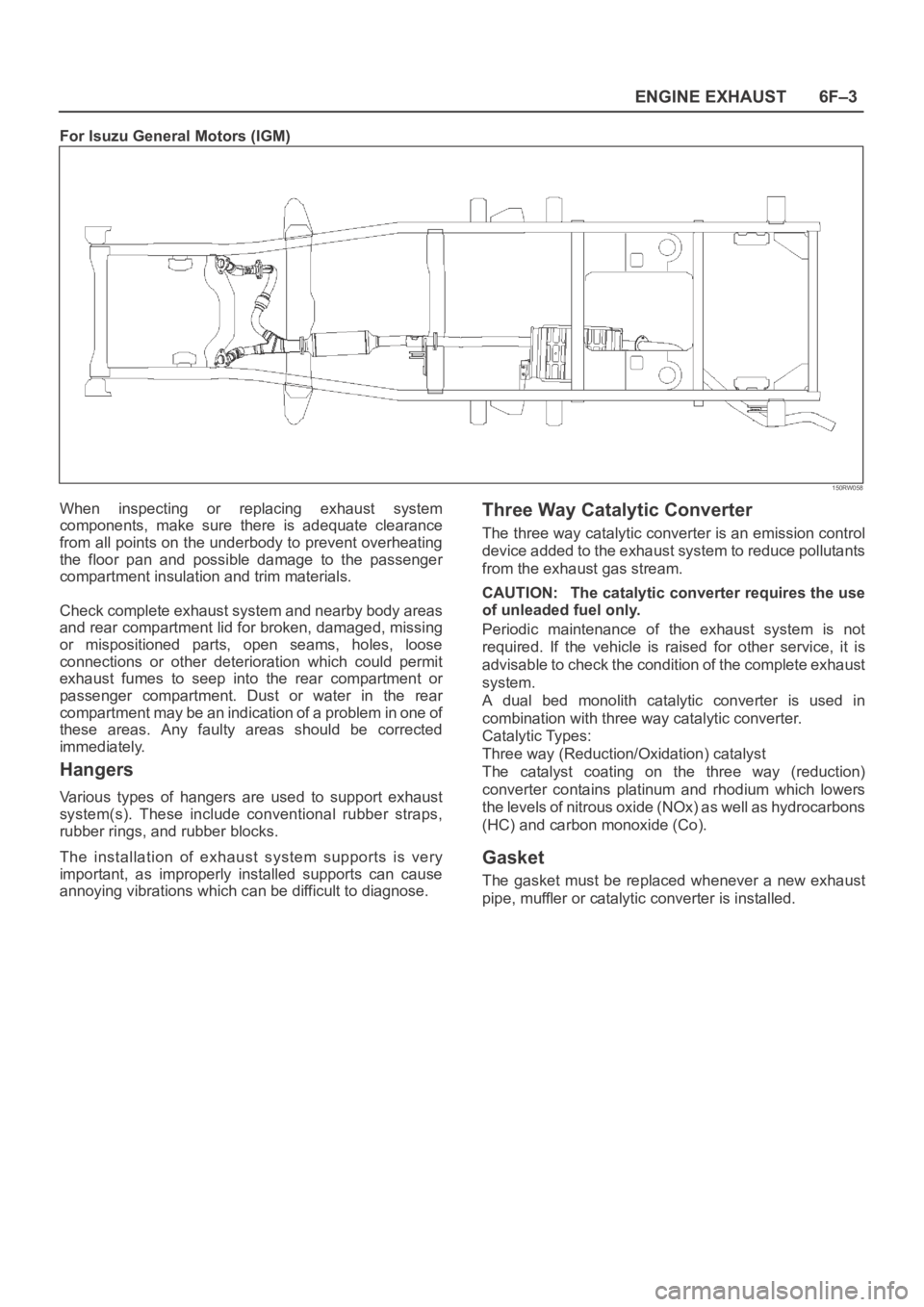
6F–3 ENGINE EXHAUST
For Isuzu General Motors (IGM)
150RW058
When inspecting or replacing exhaust system
components, make sure there is adequate clearance
from all points on the underbody to prevent overheating
the floor pan and possible damage to the passenger
compartment insulation and trim materials.
Check complete exhaust system and nearby body areas
and rear compartment lid for broken, damaged, missing
or mispositioned parts, open seams, holes, loose
connections or other deterioration which could permit
exhaust fumes to seep into the rear compartment or
passenger compartment. Dust or water in the rear
compartment may be an indication of a problem in one of
these areas. Any faulty areas should be corrected
immediately.
Hangers
Various types of hangers are used to support exhaust
system(s). These include conventional rubber straps,
rubber rings, and rubber blocks.
The installation of exhaust system supports is very
important, as improperly installed supports can cause
annoying vibrations which can be difficult to diagnose.
Three Way Catalytic Converter
The three way catalytic converter is an emission control
device added to the exhaust system to reduce pollutants
from the exhaust gas stream.
CAUTION: The catalytic converter requires the use
of unleaded fuel only.
Periodic maintenance of the exhaust system is not
required. If the vehicle is raised for other service, it is
advisable to check the condition of the complete exhaust
system.
A dual bed monolith catalytic converter is used in
combination with three way catalytic converter.
Catalytic Types:
Three way (Reduction/Oxidation) catalyst
The catalyst coating on the three way (reduction)
converter contains platinum and rhodium which lowers
the levels of nitrous oxide (NOx) as well as hydrocarbons
(HC) and carbon monoxide (Co).
Gasket
The gasket must be replaced whenever a new exhaust
pipe, muffler or catalytic converter is installed.
Page 5374 of 6000

ENGINE COOLING 6B – 5
ENGINE COOLANT CHANGE
PROCEDURE
1. To change engine coolant, make sure that the
engine is cool.
WARNING:
When the coolant is heated to a high temperature,
be sure not to loosen or remove the radiator cap.
Otherwise you might get scalded by hot vapor or
boiling water. To open the radiator cap, put a piece
of thick cloth on the cap and loosen the cap slowly
to reduce the pressure once the coolant has
become cooler.
2. Open radiator cap and drain the cooling system by
loosening the drain valve on the radiator and on the
cylinder body.
NOTE: For best results it is suggested that the engine
cooling system be flushed at least once a year. It is
advisable to flush the interior of the cooling system
including the radiator before using anti-freeze
(ethylene-glycol based).
Replace damaged rubber hoses as the engine anti-
freeze coolant is liable to leak out even minor cracks.
Isuzu recommends using Isuzu genuine anti-freeze
(ethylene-glycol based) or equivalent, for the cooling
system and not add any inhibitors or additives.
CAUTION:
A failure to correctly fill the engine cooling system
in changing or topping off coolant may sometimes
cause the coolant to overflow from the filler neck
even before the engine and radiator are completely
full.
If the engine runs under this condition, shortage of
coolant may possibly result in engine overheating.
To avoid such trouble, the following precautions
should be taken in filling the system.
3. To refill engine coolant, pour coolant up to filler neck
using a filling hose which is smaller in outside
diameter than the filler neck. Otherwise air between
the filler neck and the filling hose will block entry,
preventing the system from completely filling up.
4. Keep a filling rate of 9 liter/min. or less. Filling over
this maximum rate may force air inside the engine
and radiator.
And also, the coolant overflow will increase, making
it difficult to determine whether or not the system is
completely full.
5. After filling the system full, pull out the filling hose
and check to see if air trapped in the system is
dislodged and the coolant level goes down. Should
the coolant level go down, repeat topping-off until
there is no more drop in the coolant level.
6. Directly after filling the radiator, fill the reservoir to
the maximum level.
7. Install and tighten radiator cap and start the engine.
After idling for 2 to 3 minutes, stop the engine and
reopen radiator cap. If the water level is lower,
replenish.WARNING:
When the coolant is heated to a high temperature,
be sure not to loosen or remove the radiator cap.
Otherwise you might get scalded by hot vapor or
boiling water. To open the radiator cap, put a piece
of thick cloth on the cap and loosen the cap slowly
to reduce the pressure once the coolant has
become cooler.
8. After tightening radiator cap, warm up the engine at
about 2,000 rpm.
Set heater adjustment to the highest temperature
position, and let the coolant circulate also into
heater water system.
9. Check to see the thermostat has opened by the
needle position of a water thermometer, conduct a
5-minute idle again and stop the engine.
10. When the engine has been cooled, check filler neck
for water level and replenish if required. Should
extreme shortage of coolant be found, check the
coolant system and reservoir tank hose for leakage.
11. Fill the coolant into the reservoir tank up to “MAX”
line.
Page 5378 of 6000

ENGINE COOLING 6B – 9
RADIATOR
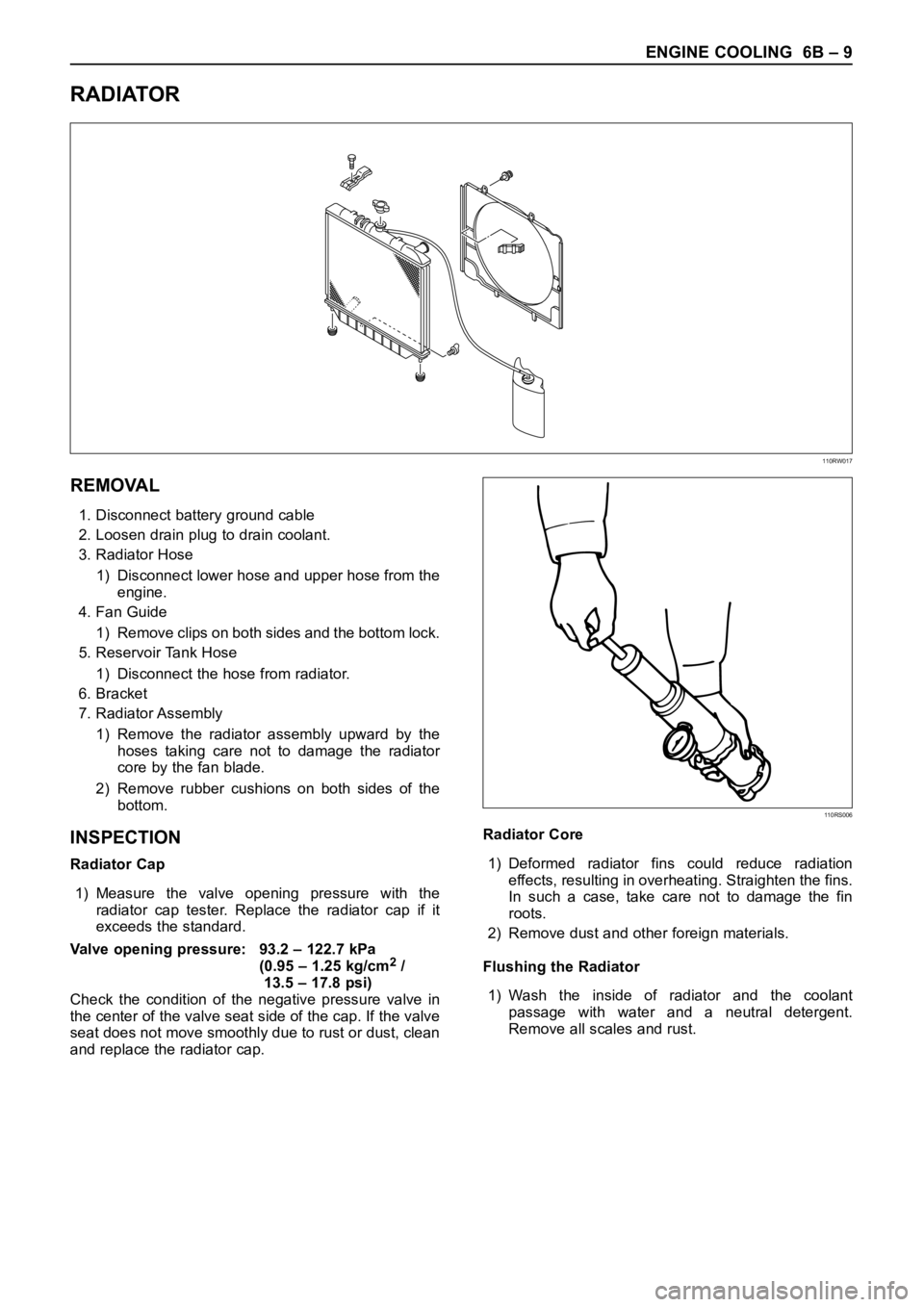
REMOVAL
1. Disconnect battery ground cable
2. Loosen drain plug to drain coolant.
3. Radiator Hose
1) Disconnect lower hose and upper hose from the
engine.
4. Fan Guide
1) Remove clips on both sides and the bottom lock.
5. Reservoir Tank Hose
1) Disconnect the hose from radiator.
6. Bracket
7. Radiator Assembly
1) Remove the radiator assembly upward by the
hoses taking care not to damage the radiator
core by the fan blade.
2) Remove rubber cushions on both sides of the
bottom.
INSPECTION
Radiator Cap
1) Measure the valve opening pressure with the
radiator cap tester. Replace the radiator cap if it
exceeds the standard.
Valve opening pressure: 93.2 – 122.7 kPa
(0.95 – 1.25 kg/cm
2/
13.5 – 17.8 psi)
Check the condition of the negative pressure valve in
the center of the valve seat side of the cap. If the valve
seat does not move smoothly due to rust or dust, clean
and replace the radiator cap.Radiator Core
1) Deformed radiator fins could reduce radiation
effects, resulting in overheating. Straighten the fins.
In such a case, take care not to damage the fin
roots.
2) Remove dust and other foreign materials.
Flushing the Radiator
1) Wash the inside of radiator and the coolant
passage with water and a neutral detergent.
Remove all scales and rust.
110RW017
110RS006