Page 3971 of 6000
4A2A–2
DIFFERENTIAL (REAR 220mm)
General Description
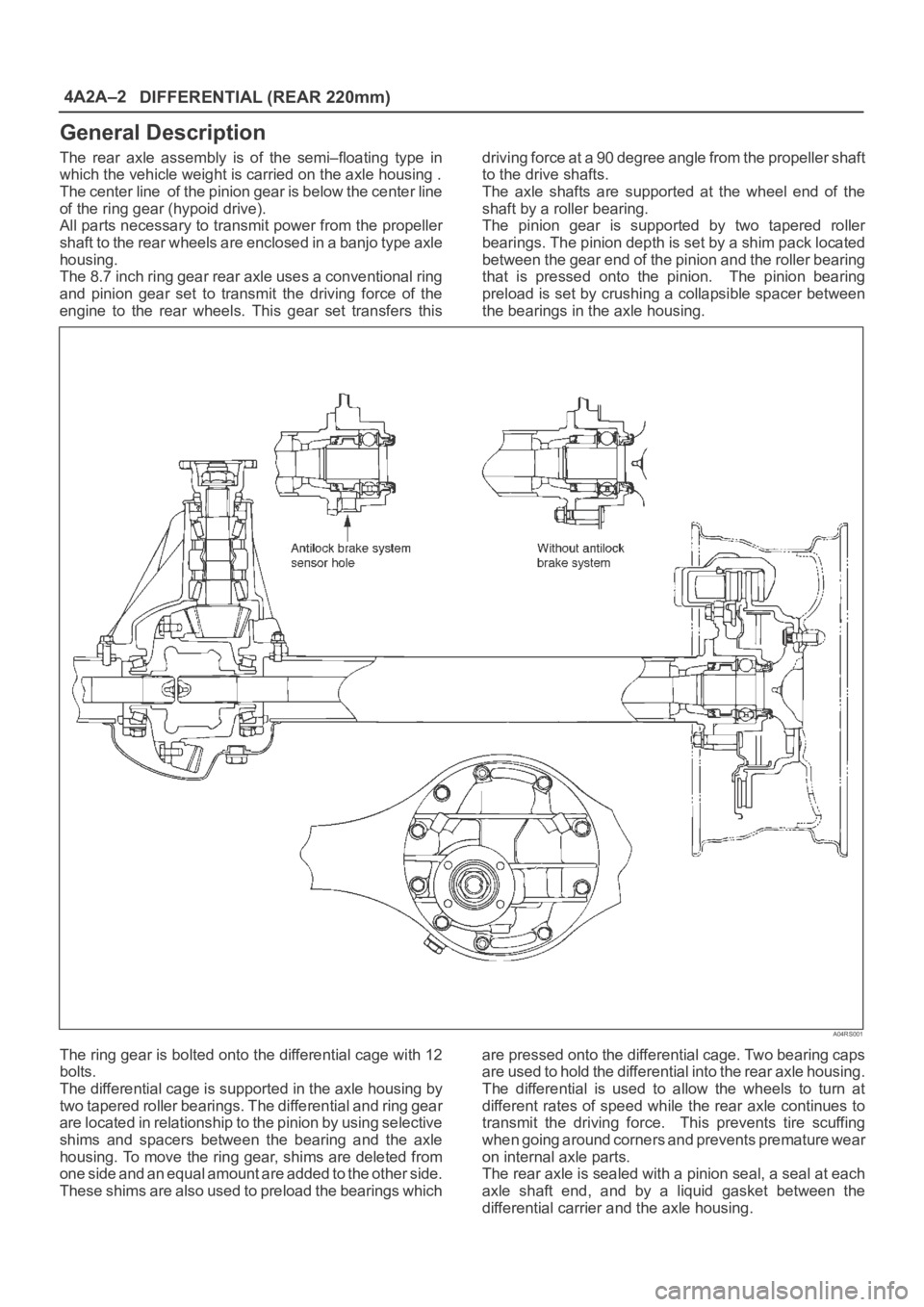
The rear axle assembly is of the semi–floating type in
which the vehicle weight is carried on the axle housing .
The center line of the pinion gear is below the center line
of the ring gear (hypoid drive).
All parts necessary to transmit power from the propeller
shaft to the rear wheels are enclosed in a banjo type axle
housing.
The 8.7 inch ring gear rear axle uses a conventional ring
and pinion gear set to transmit the driving force of the
engine to the rear wheels. This gear set transfers thisdriving force at a 90 degree angle from the propeller shaft
to the drive shafts.
The axle shafts are supported at the wheel end of the
shaft by a roller bearing.
The pinion gear is supported by two tapered roller
bearings. The pinion depth is set by a shim pack located
between the gear end of the pinion and the roller bearing
that is pressed onto the pinion. The pinion bearing
preload is set by crushing a collapsible spacer between
the bearings in the axle housing.
A04RS001
The ring gear is bolted onto the differential cage with 12
bolts.
The differential cage is supported in the axle housing by
two tapered roller bearings. The differential and ring gear
are located in relationship to the pinion by using selective
shims and spacers between the bearing and the axle
housing. To move the ring gear, shims are deleted from
one side and an equal amount are added to the other side.
These shims are also used to preload the bearings whichare pressed onto the differential cage. Two bearing caps
are used to hold the differential into the rear axle housing.
The differential is used to allow the wheels to turn at
different rates of speed while the rear axle continues to
transmit the driving force. This prevents tire scuffing
when going around corners and prevents premature wear
on internal axle parts.
The rear axle is sealed with a pinion seal, a seal at each
axle shaft end, and by a liquid gasket between the
differential carrier and the axle housing.
Page 4010 of 6000
DIFFERENTIAL (REAR 244mm)
4A2B–3
General Description
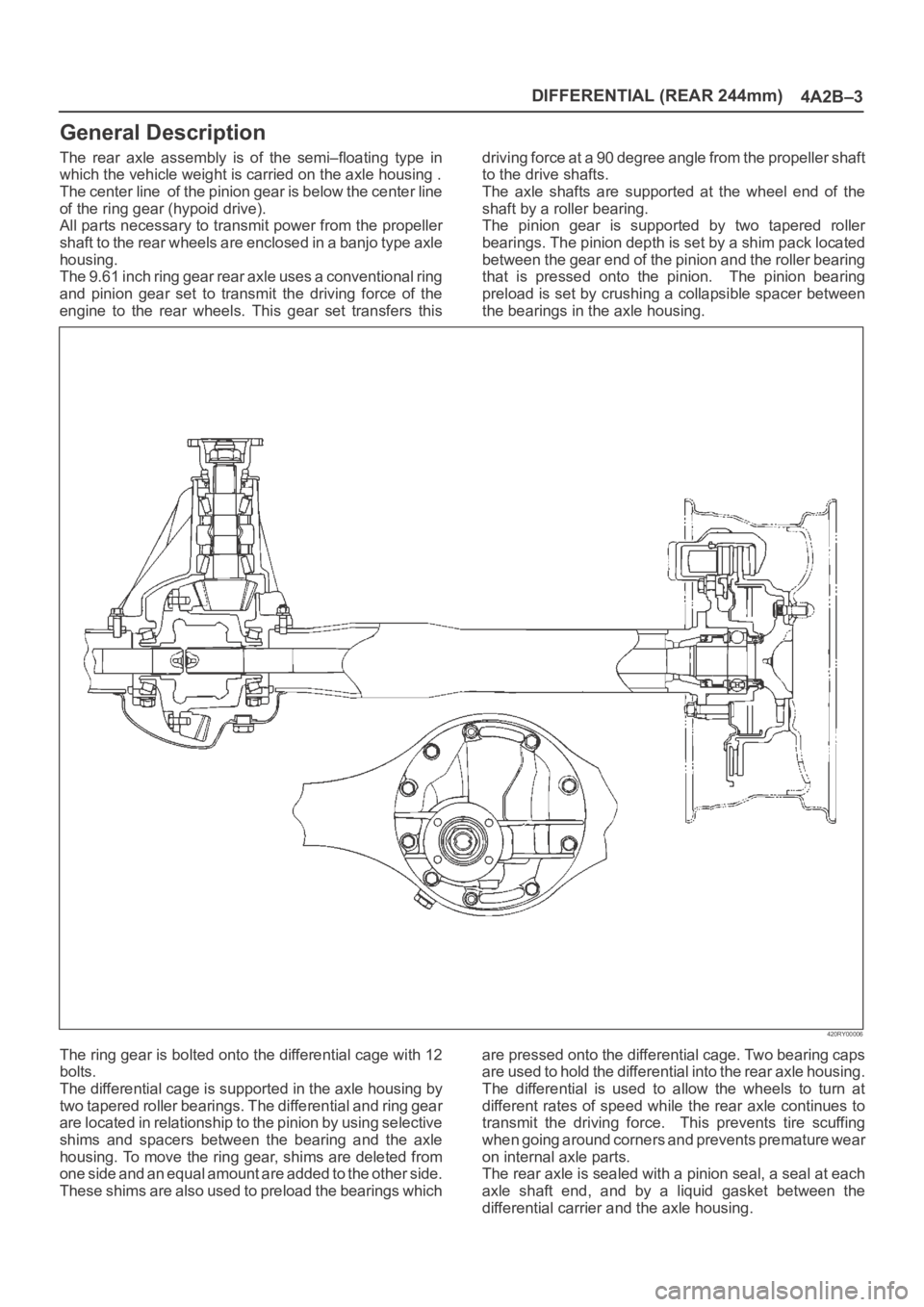
The rear axle assembly is of the semi–floating type in
which the vehicle weight is carried on the axle housing .
The center line of the pinion gear is below the center line
of the ring gear (hypoid drive).
All parts necessary to transmit power from the propeller
shaft to the rear wheels are enclosed in a banjo type axle
housing.
The 9.61 inch ring gear rear axle uses a conventional ring
and pinion gear set to transmit the driving force of the
engine to the rear wheels. This gear set transfers thisdriving force at a 90 degree angle from the propeller shaft
to the drive shafts.
The axle shafts are supported at the wheel end of the
shaft by a roller bearing.
The pinion gear is supported by two tapered roller
bearings. The pinion depth is set by a shim pack located
between the gear end of the pinion and the roller bearing
that is pressed onto the pinion. The pinion bearing
preload is set by crushing a collapsible spacer between
the bearings in the axle housing.
420RY00006
The ring gear is bolted onto the differential cage with 12
bolts.
The differential cage is supported in the axle housing by
two tapered roller bearings. The differential and ring gear
are located in relationship to the pinion by using selective
shims and spacers between the bearing and the axle
housing. To move the ring gear, shims are deleted from
one side and an equal amount are added to the other side.
These shims are also used to preload the bearings whichare pressed onto the differential cage. Two bearing caps
are used to hold the differential into the rear axle housing.
The differential is used to allow the wheels to turn at
different rates of speed while the rear axle continues to
transmit the driving force. This prevents tire scuffing
when going around corners and prevents premature wear
on internal axle parts.
The rear axle is sealed with a pinion seal, a seal at each
axle shaft end, and by a liquid gasket between the
differential carrier and the axle housing.
Page 4058 of 6000
4B1–13 DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (SHIFT ON THE FLY)
Parts Location (LHD / Gasoline Engine Model)
D08RW854
Legend
(1) I–12
(2) I–9
(3) H–7, H–8, H–24, H–25
(4) Fuse Box
(5) C–16
(6) C–94
(7) H–5
(8) M–11, M–12(9) M–22
(10) M–23
(11) M–24
(12) H–10
(13) M–26
(14) Relay & Fuse Box
(15) H–12, H–16
(16) E–30
Page 4060 of 6000
4B1–15 DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (SHIFT ON THE FLY)
Parts Location (RHD / Gasoline Engine Model)
D08RW853
Legend
(1) I–9
(2) I–12
(3) H–7, H–9
(4) C–16
(5) H–5
(6) C–94
(7) M–26
(8) M–11, M–12(9) M–22
(10) M–23
(11) M–24
(12) H–10
(13) H–12
(14) Relay & Fuse Box
(15) E–30
(16) H–15, H–16, H–25, H–26, H–27
(17) Fuse Box
Page 4063 of 6000
4B1–18
DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (SHIFT ON THE FLY)
Wiring Diagram (LHD / Gasoline Engine Model)
D08RW843
Page 4066 of 6000
4B1–21 DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (SHIFT ON THE FLY)
Wiring Diagram (RHD / Gasoline Engine Model)
D08RW638
Page 4090 of 6000
4B2–7 DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (TOD)
Check Lamp
Inform the following items.
Bulb check
Fail (fail alarm)
Trouble code
Diesel/gasoline MAP
821RW078
TOD ECU
This control unit is mounted to the front right hand seat via
a special bracket.
F07RW029
Page 4094 of 6000

4B2–11 DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (TOD)
The CHECK lamp also has the following functions.
D-G MAP recognition and display (The control unit
displays what type of vehicle, diesel or gasoline
vehicle, it recognizes.)
1. Short-circuit the self-diagnostic connector.
2. Turn on the starter switch. (Displays with respect to
the self-diagnosis begin to appear.)
NOTE: Do not start the engine.
3. Shift the transfer lever to the neutral position between
HIGH and 4L.
4. After all the conditions in 1 through 3 above are met,
set the throttle to the WOT (wide open throttle)
position (i.e., full open position). The display of the
self-diagnosis is temporarily suspended, and the
CHECK lamp begins to display that MAP is
recognized by the TPS (throttle position sensor)
according to the current conditions.NOTE: If the TPS has failed, this function might not work.
1. When the control unit recognizes the vehicle as
gasoline type, the CHECK lamp is turned on for five
seconds and this mode is repeated at an interval of
0.3 second.
2. When the control unit recognizes the vehicle as
diesel type, the CHECK lamp is turned off for five
seconds and this mode is repeated at an interval of
0.3 seconds.
3. Upon completion of step 4, the system resumes the
self-diagnosis. (The self-diagnosis is executed
from the beginning.)
5. Turn off the starter switch once. When above
conditions are met again in the future, the TPS MAP
control can be started.
C04RW010
If the accelerator wide–open–throttle(WOT) timing check
lamp is on, the subsequent timing will display immediately
after the WOT timing check lamp turns off. If the WOT
timing check lamp is off, the subsequent lamp timing will
display immediately.