1998 OPEL FRONTERA display
[x] Cancel search: displayPage 3442 of 6000

SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM9J–5
1. Energy Reserve — The SDM maintains 24–Volt Loop
Reserve (24VLR) energy supply to provide
deployment energy when ignition voltage is lost in a
frontal crash.
2. Frontal Crash Detection — The SDM monitors
vehicle velocity changes to detect frontal crashes
which are severe enough to warrant deployment.
3. Air Bag Deployment — When a frontal crash of
sufficient force is detected, the SDM will cause
enough current to flow through the air bag assembly
to deploy the air bag.
4. Malfunction Detection — The SDM performs
diagnostic monitoring of SRS electrical components
and sets a diagnostic trouble code when a
malfunction is detected.
5. Frontal Crash Recording — The SDM records
information regarding SRS status during frontal
crash.
6. Malfunction Diagnosis — The SDM displays SRS
diagnostic trouble codes and system status
information through the use of a scan tool.
7. Driver Notification — The SDM warns the vehicle
driver of SRS malfunctions by controlling the “Air
Bag” warning lamp.
The SDM is connected to the SRS wiring harness by a
24–pin connector. This harness connector uses a
shorting clip across certain terminals in the contact area.
This shorting clip connects the “AIR BAG” warning lamp
to ground when the SDM harness connector is
disconnected or CPA (Connector Position Assurance) is
not inserted even if completely connected. This will
cause the “AIR BAG” warning lamp to come “ON” steady
whenever the ignition switch is at the ON or START
positions with the SDM disconnected.
827RW044
Legend
(1) SDM
(2) SRS Harness
(3) Connector Position Assurance
“Air Bag” Warning Lamp
Ignition voltage is applied to the “AIR BAG” warning lamp
when the ignition switch is at the ON or START positions.
The SDM controls the lamp by providing ground with a
lamp driver. The “AIR BAG” warning lamp is used in the
SRS to do the following:
1. Verify lamp and SDM operation by turn on 3.5
seconds and then turns “OFF” when the ignition
switch is first turned “ON”.
2. Warn the vehicle driver of SRS electrical system
malfunctions which could potentially affect the
operation of the SRS. These malfunctions could
result in nondeployment in case of a frontal crash or
deployment for conditions less severe than intended.
The “AIR BAG ” warning lamp is the key to driver
notification of SRS malfunctions. For proper lamp
operation, refer to the “SRS Diagnostic System Check” in
this section.
821RW037
SRS Coil Assembly
The SRS coil assembly consists of two current carrying
coils. This is attached to the steering column and allow
rotation of the steering wheel while maintaining
continuous contact of the driver deployment loop to the
driver air bag assembly.
There is a shorting clip on the yellow 2–pin connector near
the base of steering column which connects the SRS coil
to the SRS wiring harness.
The shorting clip shorts to the SRS coil and driver air bag
assembly when the yellow 2–pin connector is
disconnected. The circuit to the driver air bag assembly is
shorted in this way to help prevent unwanted deployment
of the air bag when servicing the steering column or other
SRS components.
Page 3465 of 6000
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM 9J–28
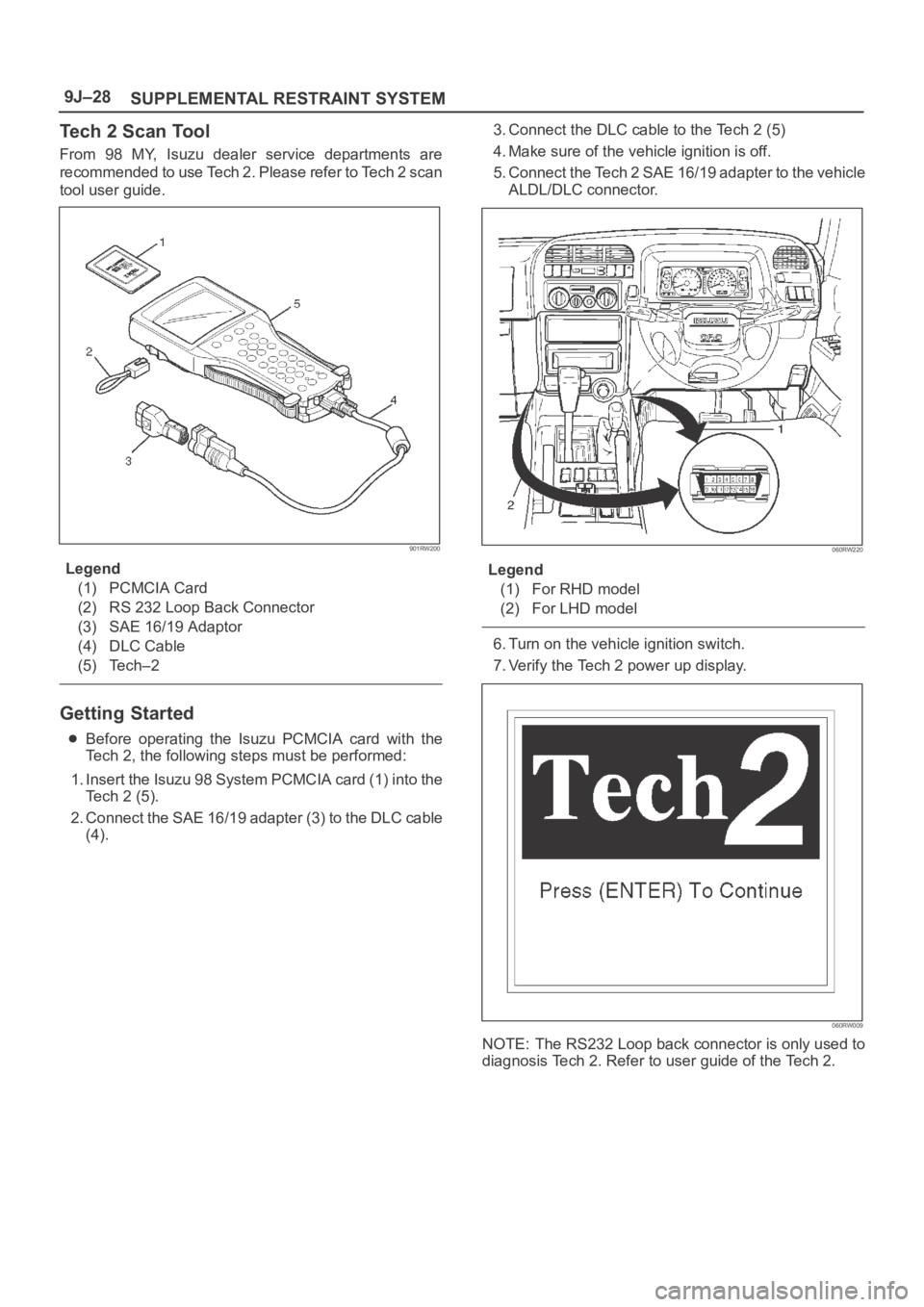
Tech 2 Scan Tool
From 98 MY, Isuzu dealer service departments are
recommended to use Tech 2. Please refer to Tech 2 scan
tool user guide.
901RW200
Legend
(1) PCMCIA Card
(2) RS 232 Loop Back Connector
(3) SAE 16/19 Adaptor
(4) DLC Cable
(5) Tech–2
Getting Started
Before operating the Isuzu PCMCIA card with the
Tech 2, the following steps must be performed:
1. Insert the Isuzu 98 System PCMCIA card (1) into the
Tech 2 (5).
2. Connect the SAE 16/19 adapter (3) to the DLC cable
(4).3. Connect the DLC cable to the Tech 2 (5)
4. Make sure of the vehicle ignition is off.
5. Connect the Tech 2 SAE 16/19 adapter to the vehicle
ALDL/DLC connector.
060RW220
Legend
(1) For RHD model
(2) For LHD model
6. Turn on the vehicle ignition switch.
7. Verify the Tech 2 power up display.
060RW009
NOTE: The RS232 Loop back connector is only used to
diagnosis Tech 2. Refer to user guide of the Tech 2.
Page 3466 of 6000
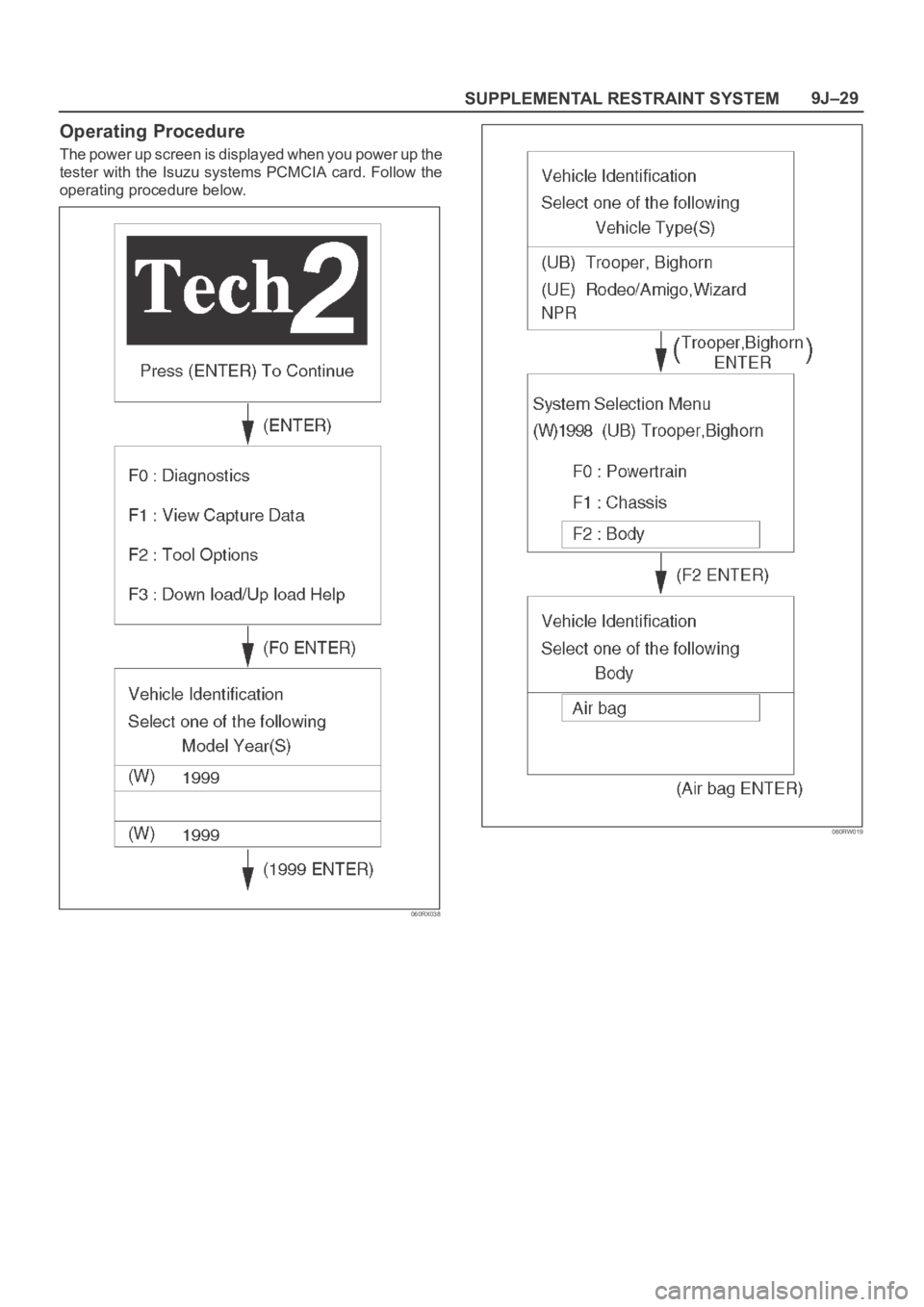
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM9J–29
Operating Procedure
The power up screen is displayed when you power up the
tester with the Isuzu systems PCMCIA card. Follow the
operating procedure below.
060RX038
060RW019
Page 3489 of 6000

RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM 9J1–2
Diagnostic Information
CAUTION: When fasteners are removed, always
reinstall them at the same location from which they
were removed. if a fastener needs to be replaced, use
the correct part number fastener for that application.
if the correct part number fastener is not available, a
fastener of equal size and strength (or stronger) may
be used. fasteners that are not reused, and those
requiring thread locking compound will be called
out. the correct torque value must be used when
installing fasteners that require it. if the above
conditions are not followed, parts or system damage
could result.
Diagnostic Procedures
WARNING: TO AVOID DEPLOYMENT WHEN
TROUBLESHOOTING THE SRS, DO NOT USE
ELECTRICAL TEST EQUIPMENT SUCH AS A
BATTERY–POWERED OR AC–POWERED
VOLTMETER, OHMMETER, ETC., OR ANY TYPE OF
ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT OTHER THAN THAT
SPECIFIED IN THIS MANUAL. DO NOT USE A NON
POWERED, PROBE–TYPE TESTER.
INSTRUCTIONS IN THIS MANUAL MUST BE
FOLLOWED CAREFULLY, OTHERWISE PERSONAL
INJURY MAY RESULT.
The diagnostic procedures used in this section are
designed to aid in finding and repairing SRS problems.
Outlined below are the steps to find and repair SRS
problems quickly and effectively. Failure to carefully
follow these procedures may result in extended
diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis and incorrect parts
replacement.
1.Perform The “SRS Diagnostic System Check”.
The “SRS Diagnostic System Check” should always
be the starting point of any SRS diagnostics. The
“SRS Diagnostic System Check” checks for proper
“AIR BAG” warning lamp operation and checks for
SRS trouble codes using both “Flash Code” and
“Scan Tool” Methods.
2.Refer To The Proper Diagnostic Chart As Directed
By The “SRS Diagnostic System Check”.
The “SRS Diagnostic System Check” will lead you to
the correct chart to diagnose any SRS problems.
Bypassing these procedures may result in extended
diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis and incorrect
parts replacement.
3.Repeat The “SRS Diagnostic System Check”
After Any Repair Or Diagnostic Procedures Have
Been Performed.
Preforming the “SRS Diagnostic System Check” after
all repair or diagnostic procedures will assure that the
repair has been made correctly and that no other
conditions exist.
Diagnostic Codes
The Sensing and Diagnostic Module (SDM) maintains a
history record of all diagnostic codes that have beendetected since the SRS codes were last cleared during
service.
1. Active Codes — Faults that are presently detected
this ignition cycle. Active codes are stored in RAM
(Random Access Memory).
2. History Codes — All faults detected since the last
time the history fault memory was cleared. History
codes are stored in EEPROM. (Electronically
Erasable Programmable Read only Memory)
How To Read Trouble Codes
All codes (Active and history) can be read (or cleared) by
using a scan tool or equivalent.
If a PDT is not available, have the vehicle serviced by
ISUZU dealer.
How To Clear Trouble Codes
Trouble codes can only be cleared by using a Scan Tool.
If a “scan tool” is not available then inform the owner of the
stored codes and suggest that the codes are cleared
upon the next visit to an Isuzu dealership.
Scan Tool Diagnostics
A scan tool can be used to read current and history codes
and to clear all history codes after a repair is complete.
The scan tool must be updated to communicate with the
SRS through a memory card or a manufacturer’s update
before it can be used for SRS diagnostics. To use the
scan tool, connect it to the DLC connector and turn the
ignition switch “ON”. Then follow the manufacturer’s
directions for communication with the SRS. The scan tool
reads serial data from the SDM “Serial Data” output
(terminal 24) to the DLC connector (terminal 9).
Basic Knowledge Required
Before using this section of the Service Manual, there is
some basic knowledge which will be required. Without
this knowledge, you will have trouble using the diagnostic
procedures in this section. Use care to prevent harm or
unwanted deployment. Read all cautions in the service
manual and on warning labels attached to SRS
components.
Basic Electrical Circuits
You should understand the basic theory of electricity
including series and parallel circuits, and understand the
voltage drops across series resistors. You should know
the meaning of voltage (volts), current (amps), and
resistance (ohms). You should understand what happens
in a circuit with an open or a shorted wire. You should be
able to read and understand a wiring diagram.
“Flash Code” Diagnostics
Flash code diagnostics can be used to read active codes
and to determine if history codes are present but cannot
be used to clear codes or read history codes. Flash code
diagnostics is enabled by grounding by terminal 4
shorting to terminal 13 of the DLC connector with the
ignition switch “ON”. Grounding terminal 4 of the DLC
connector pulls the “Diagnostics Request” input (Terminal
1) of the SDM low and signals the SDM to enter the flash
code diagnostic display mode.
Page 3490 of 6000

9J1–3
RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM
The SDM displays the trouble codes by flashing the
warning lamp. Each code that is displayed will consist of a
number of flashes which represents the tens digit, a 1.2
second pause, following by a number of flashes which
represents the ones digit of the code. Each code is
displayed one time before moving on to the next code.
After all of the codes have been displayed, the entire code
sequence will continually by repeated until ground is
removed from terminal 4 of the DLC connector.
Two special codes exist when reading in the flash code
mode (Flash Code 12 and Flash Code 13). “Flash Code
12“ will always be the first code displayed when the flash
code mode is enable Code 12 is not an indication of a SRS
problem but an indication that the flash code mode has
been enabled. If there are no active or history codes
present, the SDM will display code 12 until ground is
removed from the DLC connector at terminal 4. “flash
Code 13” will be displayed if history codes are present. To
read the history codes a scan tool must be used.
Page 3492 of 6000

9J1–5
RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM
diagnostic trouble codes in the order specified may result in extended diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis and
incorrect parts replacement.
SRS Diagnostic System Check
StepActionYe sNo
1Note the “Air Bag” warning lamp as ignition switch is turned “ON.”
Does the “AIR BAG” warning lamp turn on 3.5 seconds?
Go to Step 2Go to Step 3
2Note the “AIR BAG” warning lamp after it turn on 3.5 seconds.
Does the “AIR BAG” warning lamp go “OFF”?
Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
3Note the “AIR BAG” warning lamp as ignition switch is turned
“ON”.
Does the “AIR BAG” warning lamp come “ON” steady?
Go to Chart BGo to Chart C
41. Note the “AIR BAG” warning lamp as that ignition switch is
turned “ON.”
Ignition switch “OFF.”
2. Connect a scan tool to data link connector.
3. Follow direction given in the scan tool instruction manual.
Ignition switch “ON.”
4. Request the SRS diagnostic trouble code display, recode all
history diagnostic trouble code(s). specify as such, on repair
order
Is (are) diagnostic trouble code(s) displayed?Ignition switch
“OFF”
When DTC 71 is
set, go to DTC 71
Chart
For all other
history codes
refer to
“Diagnostic Aids”
For that specific
DTC
A history DTC
indicates the
malfunction has
been repaired or
is intermittent
SRS is functional
and free of
malfuncitons, no
further diagnosis
is required
If scan tool
indicated “NO
DATA
RECEIVED,”
refer to chassis
electrical section8
51. Ignition switch “OFF.”
2. Connect a scan tool to data link connector.
3. Follow directions as given in the scan tool instruction manual.
4. Ignition switch “ON.”
5. Request the SRS diagnostic trouble code display, Recode all
diagnostic trouble code(s), specifying as current or history on
repair order.
Is (are) diagnostic trouble code (s) displayed?Ignition switch
“OFF”
When DTC 53 is
set, go to DTC 53
chart
When DTC 51 is
set, go to DTC 51
chart
When DTC 19 is
set, go to DTC 19
chart
When DTC 25 is
set, go to DTC 25
chart
Diagnose
remaining current
DTCs from
lowest to highest
When only history
DTCs exist, refer
to “Diagnostics
Aids” for that
specific DTC
A history DTC
indicates the
malfunction has
been repaired or
is intermittent
If scan tool
indicates “No
Data Received,”
refer to chassis
electrical section8
Page 3494 of 6000

9J1–7
RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM
Chart A SDM Integrity Check
WARNING: DURING SERVICE PROCEDURES. BE VERY CAREFUL WHEN HANDLING A SENSING AND
DIAGNOSTIC MODULE (SDM). NEVER STRIKE OR JAR THE SDM. NEVER POWER UP THE SRS WHEN THE
S D M I S N O T R I G I D LY AT TA C H E D T O T H E V E H I C L E . A L L S D M A N D M O U N T ING BRACKET FASTENERS MUST
BE CAREFULLY TORQUED AND THE ARROW MUST BE POINTING TOWARD THE FRONT OF THE VEHICLE
TO ENSURE PROPER OPERATION OF THE SRS. THE SDM COULD BE ACTIVATED WHEN POWERED WHILE
NOT RIGIDLY ATTACHED TO THE VEHICLE WHICH COULD CAUSE DEPLOYMENT AND RESULT IN
PERSONAL INJURY.
Step
ActionYe sNo
11. This chart assumes that the “SRS Diagnostic System Check”
and either a symptom chart or a diagnostic trouble code chart
diagnosis have been performed. When all circuitry outside the
SDM has been found to operate properly, as indicated by the
appropriate diagnostic chart, and the symptom or DTC
remains current, the following
2. Diagnostic procedures must be performed to verify the need
for SDM replacement.
3. Ignition switch “OFF”.
4. Reconnect all SRS components, ensure all components are
properly mounted.
5. Ensure the ignition switch has been “OFF” for at least 15
seconds.
6. Note “AIR BAG” warning lamp as ignition switch is turned
“ON.”
Does warning lamp turn on 3.5 seconds then go “OFF”?
The symptom or
DTC is no longer
occurring
Clear SRS
diagnostic trouble
codes
Repeat “SRS
Diagnostic
System Check”
Go to Step 2
2Using a scan tool request diagnostic trouble code display
Is the same symptom or DTC occurring as was when the “SRS
Diagnostic System Check ” was first performed?
Go to Step 3
Ignition switch
“OFF”
Go to the
appropriate chart
for the indicated
malfunction
31. Clear “SRS Diagnostic Trouble Codes”.
2. Ignition switch “OFF” for at least two minutes.
3. Note “AIR BAG” warning lamp as ignition switch is turned
“ON.”
Does warning lamp turn on 3.5 seconds then go “OFF”?SRS is functional
and free of
malfunctions
No further
diagnosis is
required
Go to Step 4
Ignition switch
“OFF”
Replace SDM
Go to Step 4
4Reconnect all SRS components, ensure all components are
properly mounted.
Was this step finished?Repeat the “SRS
Diagnostic
System Check”
Go to Step 4
Page 3496 of 6000
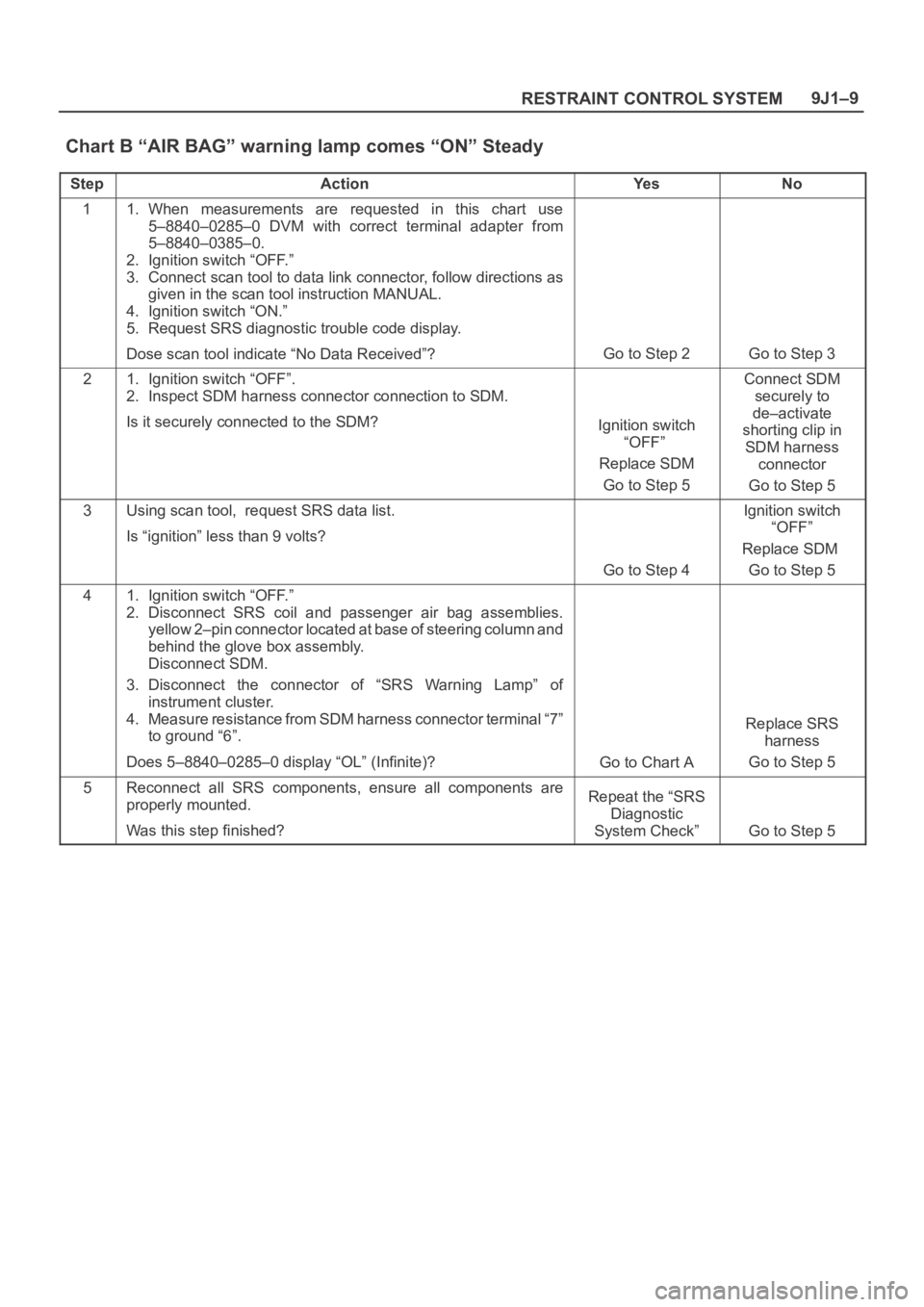
9J1–9
RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM
Chart B “AIR BAG” warning lamp comes “ON” Steady
StepActionYe sNo
11. When measurements are requested in this chart use
5–8840–0285–0 DVM with correct terminal adapter from
5–8840–0385–0.
2. Ignition switch “OFF.”
3. Connect scan tool to data link connector, follow directions as
given in the scan tool instruction MANUAL.
4. Ignition switch “ON.”
5. Request SRS diagnostic trouble code display.
Dose scan tool indicate “No Data Received”?
Go to Step 2Go to Step 3
21. Ignition switch “OFF”.
2. Inspect SDM harness connector connection to SDM.
Is it securely connected to the SDM?
Ignition switch
“OFF”
Replace SDM
Go to Step 5
Connect SDM
securely to
de–activate
shorting clip in
SDM harness
connector
Go to Step 5
3Using scan tool, request SRS data list.
Is “ignition” less than 9 volts?
Go to Step 4
Ignition switch
“OFF”
Replace SDM
Go to Step 5
41. Ignition switch “OFF.”
2. Disconnect SRS coil and passenger air bag assemblies.
yellow 2–pin connector located at base of steering column and
behind the glove box assembly.
Disconnect SDM.
3. Disconnect the connector of “SRS Warning Lamp” of
instrument cluster.
4. Measure resistance from SDM harness connector terminal “7”
to ground “6”.
Does 5–8840–0285–0 display “OL” (Infinite)?
Go to Chart A
Replace SRS
harness
Go to Step 5
5Reconnect all SRS components, ensure all components are
properly mounted.
Was this step finished?Repeat the “SRS
Diagnostic
System Check”
Go to Step 5