Page 1802 of 6000
ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A – 69
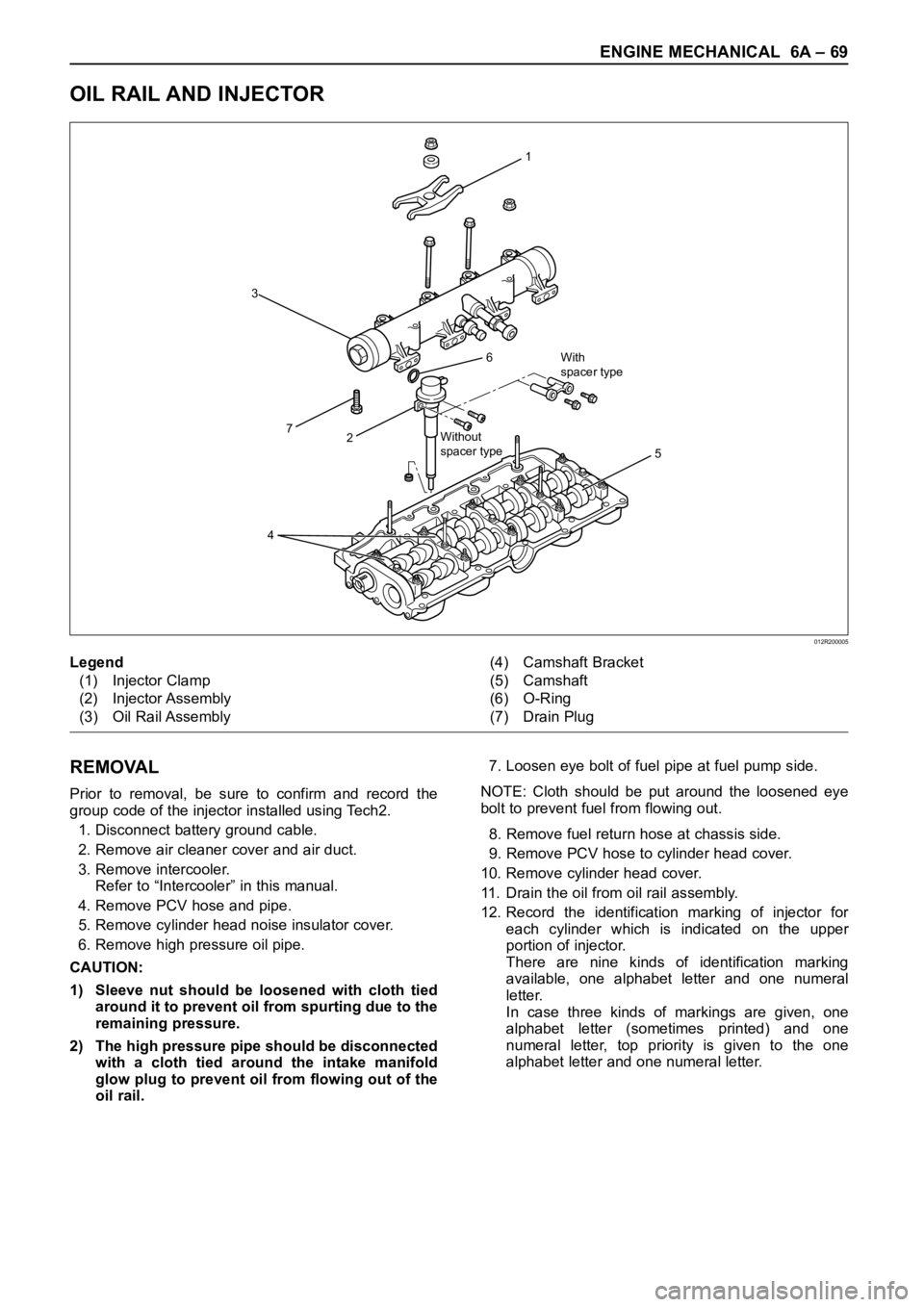
OIL RAIL AND INJECTOR
REMOVAL
Prior to removal, be sure to confirm and record the
group code of the injector installed using Tech2.
1. Disconnect battery ground cable.
2. Remove air cleaner cover and air duct.
3. Remove intercooler.
Refer to “Intercooler” in this manual.
4. Remove PCV hose and pipe.
5. Remove cylinder head noise insulator cover.
6. Remove high pressure oil pipe.
CAUTION:
1) Sleeve nut should be loosened with cloth tied
around it to prevent oil from spurting due to the
remaining pressure.
2) The high pressure pipe should be disconnected
with a cloth tied around the intake manifold
glow plug to prevent oil from flowing out of the
oil rail.7. Loosen eye bolt of fuel pipe at fuel pump side.
NOTE: Cloth should be put around the loosened eye
bolt to prevent fuel from flowing out.
8. Remove fuel return hose at chassis side.
9. Remove PCV hose to cylinder head cover.
10. Remove cylinder head cover.
11. Drain the oil from oil rail assembly.
12. Record the identification marking of injector for
each cylinder which is indicated on the upper
portion of injector.
There are nine kinds of identification marking
available, one alphabet letter and one numeral
letter.
In case three kinds of markings are given, one
alphabet letter (sometimes printed) and one
numeral letter, top priority is given to the one
alphabet letter and one numeral letter.
1
6
27
3
5
4
With
spacer type
Without
spacer type
012R200005
Legend
(1) Injector Clamp
(2) Injector Assembly
(3) Oil Rail Assembly(4) Camshaft Bracket
(5) Camshaft
(6) O-Ring
(7) Drain Plug
Page 1804 of 6000

ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A – 71
12. Immediately install high pressure oil pipe and
tighten to specified torque.
Torque: 80 Nꞏm (8.1 kgꞏm / 57.9 lb ft)
13. Install cylinder head noise insulator cover.
Refer to “Cylinder Head” in this manual.
14. Install intercooler assembly.
Refer to “Intercooler” in this manual.
15. Install air cleaner cover and air duct.
16. Use TECH2 to rewrite injector data to ECM.
For rewriting method refer to section “Data
Programming in Case of ECM Change” of 6E 4JX1
engine driveability and emissions in this manual.
NOTE:
1) On completion of servicing, bleed air from the
engine inside fuel passage by means of the priming
pump. (The priming pump should be operated more
times than in the case of conventional engines.)
2) As air is in the oil rail, it takes more time to start the
engine. Rough idling may occur while the air is
being bled completely after starting the engine, but
it does not indicate trouble.
The air will be bled and normal engine status will be
reached while the vehicle is driven for about 5 km
or engine is operated for about 5 minutes at 1500 to
2000 rpm.
3) The injector spare part will be provided for group
number B1, B2 and B3 only.
Page 1846 of 6000

ENGINE FUEL 6C – 1
ENGINE FUEL
CONTENTS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6C–1
On-Vehicle Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6C–7
Fuel Filter Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6C–7
Fuel Filter Cartridge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6C–7
Injector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6C–9
Fuel Pump Pipe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6C–13High Pressure Oil Pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6C–15
Fuel Tank . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6C–20
Fuel Gauge Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6C–21
Fuel Filler Cap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6C–21
To realize the compatibility between low exhaust
emission and high engine output, an HEUI
(Hydraulically actuated Electronically controlled Unit
Injector) system, has been introduced. This system is
comprised of a hydraulic system, fuel system, and
electronic control system, using a high-pressure oil
pump in place of the conventional fuel injection pump.
The oil pressurized by means of this pump and by
signals from the ECM (Electronic Control Module)
actuates the fuel injector provided for each cylinder.
Inside of the fuel injector, fuel pressure is increased due
to the high-pressure oil. The ECM detects the driving
state of the vehicle, forms, signals sent by engine and
other part sensors, which determines the optimum fuel
injection amount and timing, thus controlling the fuel
injectors. Thus high engine output, good fuel economy,
and low exhaust emission are realized.When working on the fuel system, there are several
things to keep in mind:
1) Any time the fuel system is being worked on,
disconnect the negative battery cable except for
those tests where battery voltage is required.
2) Always keep a dry chemical (Class B) fire
extinguisher near the work area.
3) Replace all pipes with the same pipe and fittings
that were removed.
Clean and inspect “O” rings. Replace where
required.
4) Always relieve the line pressure before servicing
any fuel system components.
5) Do not attempt repairs on the fuel system until you
have read the instructions and checked the pictures
relating to that repair.
6) After maintenance work, push priming pump and
send enough fuel to the fuel system before starting
the engine.
NOTE: In comparison with the conventional engine,
the capacity of fuel passage in the 4JX1 engine is
larger. It takes the priming pump more time to fill the
engine with fuel.
Page 1847 of 6000
6C – 2 ENGINE FUEL
FUEL FLOW
1
14 Except above region
89
10111
2
2
4
12
5 6
7
3
13
14 For Europe, Nicaragua,
Argentina, Philippin
11
4
Legend
(1) Fuel Filler Cap
(2) Fuel Tank
(3) Rollover Valve
(4) Fuel Supply Pipe
(5) Fuel Filter with Priming Pump
(6) Fuel Pump
(7) High Pressure Oil Pump(8) Cylinder Head
(9) Injector
(10) Orifice
(11) Fuel Return Pipe
(12) Fuel Tank Pressure Release Hose
(13) Intake Air Duct
(14) Fuel Tank Pressure Control Valve
040R200001
Page 1848 of 6000
ENGINE FUEL 6C – 3
FUEL PUMP
1
2
3 4
Legend
(1) High Pressure Oil Pump
(2) To Injector(3) From Fuel Tank
(4) Fuel Pump
140RW041
Page 1849 of 6000

6C – 4 ENGINE FUEL
HIGH PRESSURE OIL PUMP, OIL FLOW
P
33
32
31
30
1
2
3
4
56
8
97
10
11
12
13
14 23 29
25
28
27262415
16
17 18
19 20 21 22
Legend
(1) Camshaft
(2) Balance Shaft
(3) Crankshaft
(4) Oil Cooler and Oil Filter Assembly
(5) Oil Filter Relief Valve 98 Kpa (1 kg/cm
2/14.2 Psi)
(6) Oil Cooler Relief Valve 245 Kpa (2.5 kg/cm2/
36 Psi)
(7) First Oil Pump
(8) Main Oil Relief Valve 588 Kpa (6 kg/cm
2/ 85 Psi)
(9) To Oil Pan
(10) To Oil Pan
(11) Injector
(12) Oil Rail
(13) Sub Oil Filter Relief Valve 98 Kpa (1 kg/cm
2/
14.2 Psi)
(14) Sub Oil Filter
(15) Relief Valve 588 Kpa (6 kg/cm
2/ 85 Psi)
(16) Second Oil Pump(17) Oil Pan
(18) To Oil Pan
(19) Balance Shaft
(20) Cooling Jet Relief Valve 245 Kpa (2.5 kg/cm
2/
36 Psi)
(21) Cooling Jet
(22) To Oil Pan
(23) Two Way Check Valve
(24) Nipple Filter
(25) Edge Filter
(26) Edge Filter
(27) High Pressure Oil Pump Assembly
(28) To Oil Pan
(29) Pressure Control Valve
(30) To Oil Pan
(31) Turbocharger
(32) Oil Gallery
(33) Timing Gear Train
040RW018
Page 1850 of 6000
ENGINE FUEL 6C – 5
FUEL FILTER
Legend
(1) Priming Pump
(2) Fuel Filter Cartridge
A cartridge type fuel filter is used along with the piston
type fuel pump on the high pressure oil pump.
The fuel filter removes foreign material from the fuel
before it reaches the fuel pump.
A diaphragm type priming pump is installed at the top of
the fuel filter. It is used during the air bleeding
procedures.
INJECTOR ASSEMBLY
Legend
(1) Oil Passage
(2) Fuel Passage
1. Construction of Fuel Injector
The fuel injector is comprised of the solenoid
section, hydraulic line, and fuel line. Fuel injection is
controlled by the continuity time signal and
continuity start timing signal sent by the ECM
(Electronic Control Module) to the solenoid.
2. Working of Fuel Injector
1) The ECM detects the working of the engine from
its input signals, such as engine speed
accelerator throttle opening, and engine coolant
temperature, sending the optimal signals to the
solenoid.
1
2
041RW017
1
2
055RW018
Page 1851 of 6000
6C – 6 ENGINE FUEL
2) With the current carried to the solenoid, a
poppet valve is opened by means of an
armature to let high-pressure engine oil into the
injector.
3) Under the oil pressure, the piston and plunger
are depressed to compress the fuel. The
pressure of the compressed fuel is increased
over the pressure of high-pressure engine oil by
the ratio (about 7 : 1) of piston top to plunger
bottom.
4) The injection nozzle end needle is lifted under
the increased pressure of the fuel for fuel
injection.
5) With current stopped from the ECM, the poppet
valve is closed which holds up the high-pressure
engine oil and lets the oil used to compress fuel
out of the injector through its drain hole.