1998 OPEL FRONTERA fuse
[x] Cancel search: fusePage 4956 of 6000

6E–299 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
damage, therefore, it is important to use care when
handling and testing electronic components.
NOTE: To prevent possible Electrostatic Discharge
damage, follow these guidelines:
Do not touch the control module connector pins or
soldered components on the control module circuit
board.
Do not open the replacement part package until the
part is ready to be installed.
Before removing the part from the package, ground
the package to a known good ground on the vehicle.
If the part has been handled while sliding across the
seat, or while sitting down from a standing position, or
while walking a distance, touch a known good ground
before installing the part.
NOTE: To prevent internal PCM damage, the ignition
must be in the “OFF” position in order to disconnect or
reconnect power to the PCM (for example: battery cable,
PCM pigtail, PCM fuse, jumper cables, etc.).
IMPORTANT:When replacing the production PCM
with a service PCM, it is important to transfer the
broadcast code and production PCM number to the
service PCM label. This will allow positive identification of
PCM parts throughout the service life of the vehicle. Do
not record this information on the metal PCM cover.
IMPORTANT:The ignition should always be in the
“OFF” position in order to install or remove the PCM
connectors.
Service of the PCM should normally consist of either re-
placement of the PCM or EEPROM programming. If the
diagnostic procedures call for the PCM to be replaced,
the PCM should be checked first to ensure it is the correct
part. If it is, remove the faulty PCM and install the new
service PCM.
The service PCM EEPROM will not be programmed.
DTC P0601 indicates the check sum error.
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Block the wheels.
3. Remove the front console assembly.
1. Remove the four screws.
TS23755
2. Remove the transfer shift lever knob by
unscrewing the knob.
3. Move the transmission gear selector out of the
park position.
4. Lift up sharply on the back edge of the assembly.
5. Disconnect the seat heater switch connectors (if
equipped).
6. Disconnect the POWER and WINTER switch
connectors.
7. Lift out the front console assembly.
TS23756
Page 4976 of 6000
6E–319 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
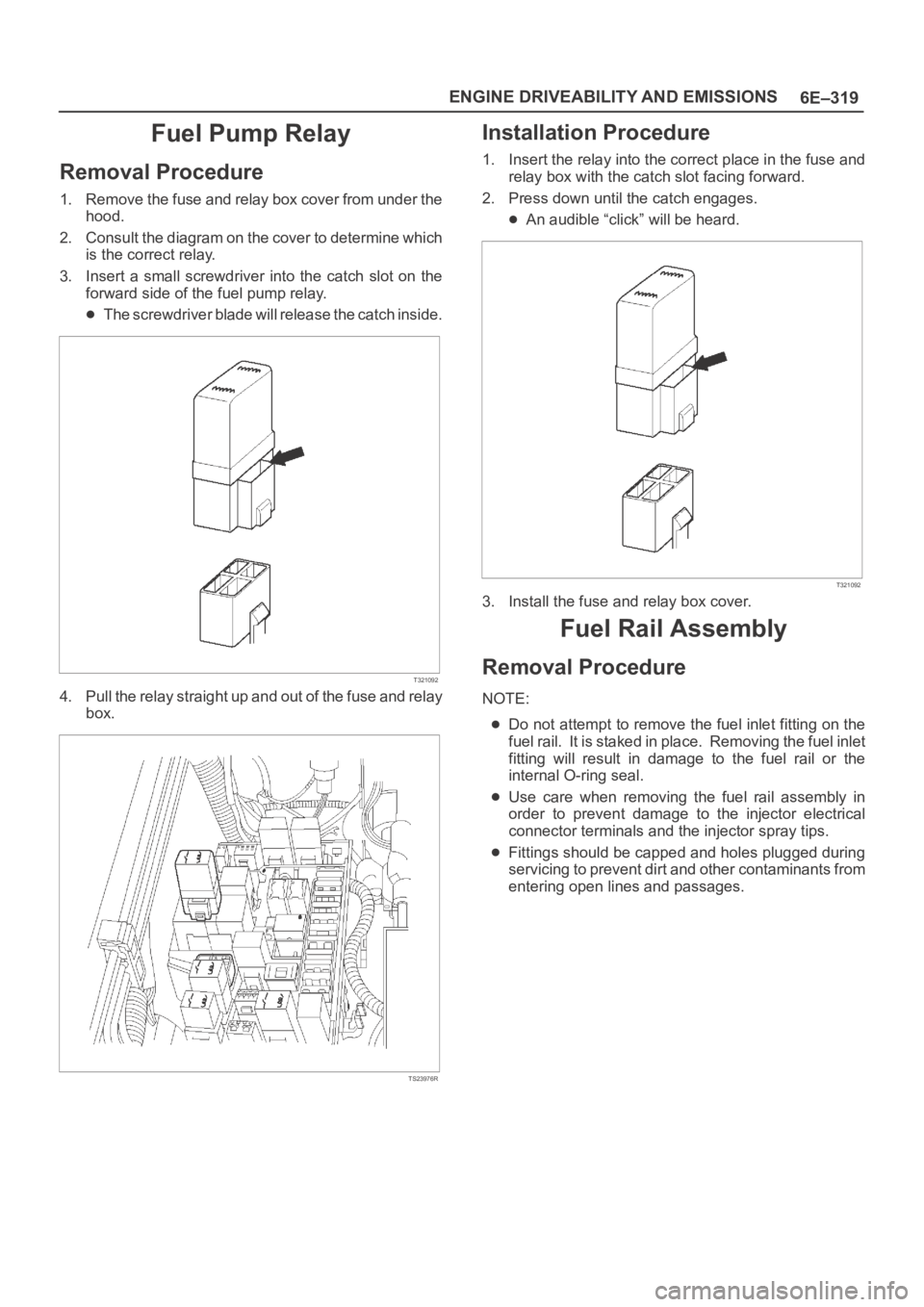
Fuel Pump Relay
Removal Procedure
1. Remove the fuse and relay box cover from under the
hood.
2. Consult the diagram on the cover to determine which
is the correct relay.
3. Insert a small screwdriver into the catch slot on the
forward side of the fuel pump relay.
The screwdriver blade will release the catch inside.
T321092
4. Pull the relay straight up and out of the fuse and relay
box.
TS23976R
Installation Procedure
1. Insert the relay into the correct place in the fuse and
relay box with the catch slot facing forward.
2. Press down until the catch engages.
An audible “click” will be heard.
T321092
3. Install the fuse and relay box cover.
Fuel Rail Assembly
Removal Procedure
NOTE:
Do not attempt to remove the fuel inlet fitting on the
fuel rail. It is staked in place. Removing the fuel inlet
fitting will result in damage to the fuel rail or the
internal O-ring seal.
Use care when removing the fuel rail assembly in
order to prevent damage to the injector electrical
connector terminals and the injector spray tips.
Fittings should be capped and holes plugged during
servicing to prevent dirt and other contaminants from
entering open lines and passages.
Page 4980 of 6000

6E–323 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
11. Connect the fuel filler fuse at the tank.
12. Connect the air breather hose at the tank.
TS23796
13. Fill the fuel tank with fuel.
14. Tighten the fuel filler cap.
15. Connect the negative battery cable.
Throttle Body (TB)
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Drain the cooling system. Refer to
Cooling System.
3. Remove the accelerator cable assembly. Refer to
Accelerator Cable in Engine Speed Control System..
4. Disconnect the electrical connectors:
Throttle position (TP) sensor.
Idle air control (IAC) solenoid.
Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor. Refer to
Intake Air Temperature Sensor.
035RW023
5. Disconnect the vacuum hose below the air horn.
6. Remove the intake air duct clamp.
7. Disconnect the intake air duct.
8. Disconnect the coolant lines from the throttle body.
9. Remove the bolts from the common chamber.
10. Remove the throttle body from the common chamber.
11. Remove the gasket from the upper intake manifold.
035RW024
12. Remove the IAC. Refer to Idle Air Control (IAC)
Solenoid
.
13. Remove the TP sensor. Refer to
Throttle Position
(TP) Sensor
.
Inspection Procedure
NOTE: Do not use solvent of any type when you clean the
gasket surfaces on the intake manifold and the throttle
body assembly. The gasket surfaces and the throttle
body assembly may be damaged as a result.
If the throttle body gasket needs to be replaced,
remove any gasket material that may be stuck to the
mating surfaces of the manifold.
Do not leave any scratches in the aluminum casting.
Installation Procedure
1. Install the TP sensor. Refer to Throttle Position (TP)
Sensor
.
2. Install the IAC. Refer to
Idle Air Control (IAC)
Solenoid
.
3. Install the gasket on the common chamber.
4. Install the throttle body on the common chamber.
Page 4982 of 6000

6E–325 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Spark Plug Gap Check
Check the gap of all spark plugs before installation.
Use a round wire feeler gauge to ensure an accurate
check.
Plugs installed with the wrong gap can cause poor
engine performance and excessive emissions.
Installation Procedure
NOTE: The plug must thread smoothly into the cylinder
head and be fully seated. Use a thread chaser if
necessary to clean the threads in the cylinder head.
Cross-threading or failure to fully seat the spark plug can
cause plug overheating, exhaust blow-by gas, or thread
damage. Do not overtighten the spark plugs. Over
tightening can cause aluminum threads to strip.
1. Install the spark plug in the engine. Use the
appropriate spark plug socket.
Tighten
Tighten the spark plug to 18 Nꞏm (13 lb ft.).
2. Install the ignition coil and spark plug boot over the
spark plug.
014RW108
3. Secure the ignition coil to the rocker cover with two
screws.
014RW091
4. Connect the electrical connector at the ignition coil.
5. Connect the negative battery cable.
Catalytic Converter
Removal and Installation Procedure
Refer to Engine Exhaust in Engine.
Air Conditioning Relay
Removal Procedure
1. Remove the fuse and relay box cover from under the
hood.
2. Consult the diagram on the cover to determine which
is the correct relay.
3. Insert a small screwdriver into the catch slot on the
forward side of the fuel pump relay.
The screwdriver blade will release the catch inside.
T321092
Page 4983 of 6000
6E–326
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
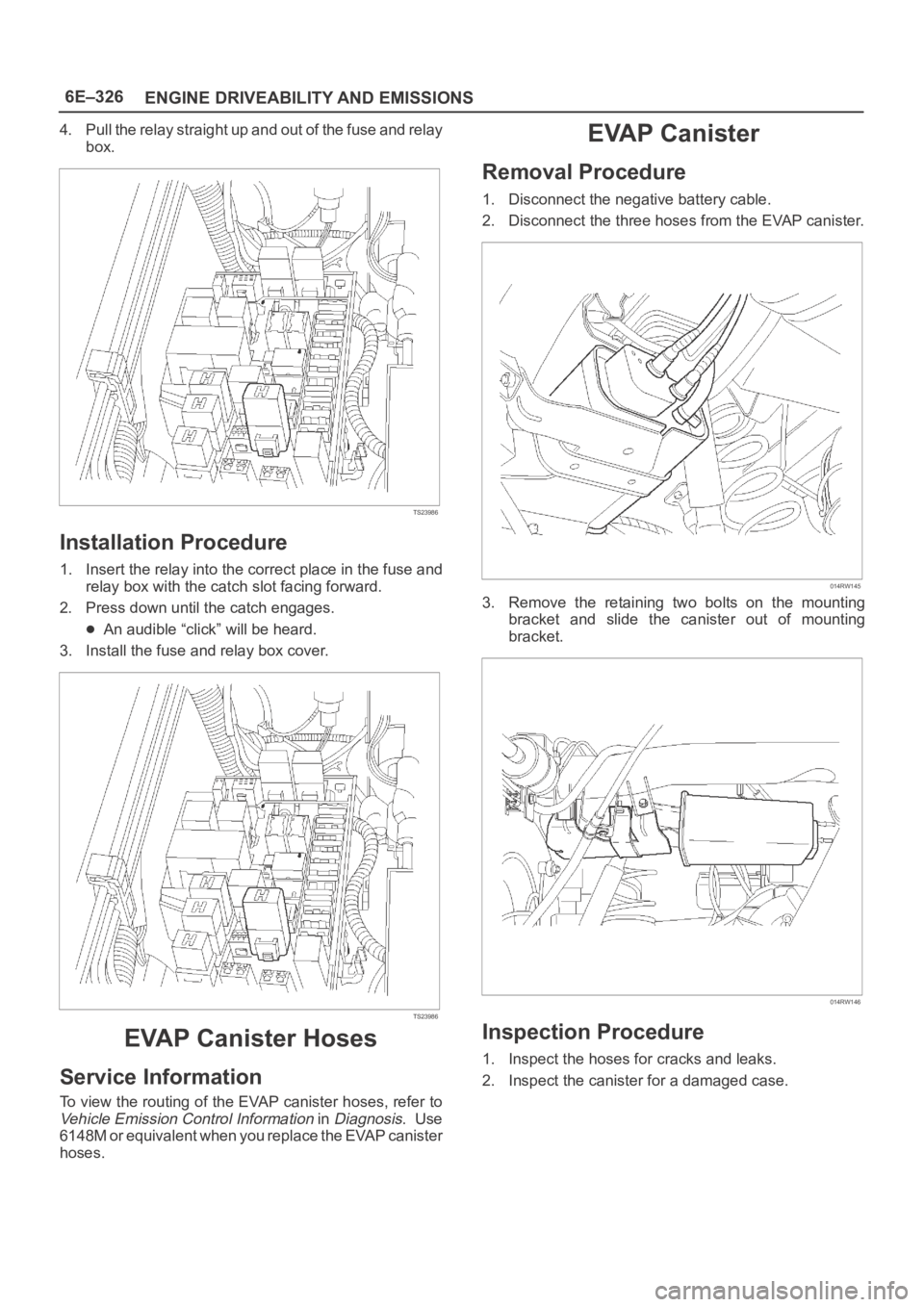
4. Pull the relay straight up and out of the fuse and relay
box.
TS23986
Installation Procedure
1. Insert the relay into the correct place in the fuse and
relay box with the catch slot facing forward.
2. Press down until the catch engages.
An audible “click” will be heard.
3. Install the fuse and relay box cover.
TS23986
EVAP Canister Hoses
Service Information
To view the routing of the EVAP canister hoses, refer to
Vehicle Emission Control Information in Diagnosis. Use
6148M or equivalent when you replace the EVAP canister
hoses.
EVAP Canister
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the three hoses from the EVAP canister.
014RW145
3. Remove the retaining two bolts on the mounting
bracket and slide the canister out of mounting
bracket.
014RW146
Inspection Procedure
1. Inspect the hoses for cracks and leaks.
2. Inspect the canister for a damaged case.
Page 4987 of 6000

6E–330
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Wiring and Connectors
Wiring Harness Service
The control module harness electrically connects the
control module to the various solenoids, switches and
sensors in the vehicle engine compartment and
passenger compartment.
Replace wire harnesses with the proper part number
replacement.
Because of the low amperage and voltage levels utilized
in powertrain control systems, it is essential that all wiring
in environmentally exposed areas be repaired with crimp
and seal splice sleeves.
The following wire harness repair information is intended
as a general guideline only. Refer to
Chassis Electrical f o r
all wire harness repair procedures.
Connectors and Terminals
Use care when probing a connector and when replacing
terminals. It is possible to short between opposite
terminals. Damage to components could result. Always
use jumper wires between connectors for circuit
checking. NEVER probe through Weather-Pack seals.
Use an appropriate connector test adapter kit which
contains an assortment of flexible connectors used to
probe terminals during diagnosis. Use an appropriate
fuse remover and test tool for removing a fuse and to
adapt the fuse holder to a meter for diagnosis.
Open circuits are often difficult to locate by sight because
oxidation or terminal misalignment are hidden by the
connectors. Merely wiggling a connector on a sensor, or
in the wiring harness, may temporarily correct the open
circuit. Intermittent problems may also be caused by
oxidized or loose connections.
Be certain of the type of connector/terminal before
making any connector or terminal repair. Weather-Pack
and Com-Pack III terminals look similar, but are serviced
differently.
PCM Connectors and Terminals
Removal Procedure
1. Remove the connector terminal retainer.
2. Push the wire connected to the affected terminal
through the connector face so that the terminal is
exposed.
3. Service the terminal as necessary.
Installation Procedure
1. Bend the tab on the connector to allow the terminal to
be pulled into position within the connector.
2. Pull carefully on the wire to install the connector
terminal retainer.
Wire Harness Repair: Twisted
Shielded Cable
Removal Procedure
1. Remove the outer jacket.
2. Unwrap the aluminum/mylar tape. Do not remove the
mylar.
047
3. Untwist the conductors.
4. Strip the insulation as necessary.
048
Page 5002 of 6000

6E–345 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
0014
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor provides a signal
used by the powertrain control module (PCM) to calculate
the ignition sequence. The sensor initiates the 58X
reference pulses which the PCM uses to calculate RPM
and crankshaft position. Refer to
Electronic Ignition
System
for additional information.
Electronic Ignition
The electronic ignition system controls fuel combustion
by providing a spark to ignite the compressed air/fuel
mixture at the correct time. To provide optimum engine
performance, fuel economy, and control of exhaust
emissions, the PCM controls the spark advance of the
ignition system. Electronic ignition has the following
advantages over a mechanical distributor system:
No moving parts.
Less maintenance.
Remote mounting capability.
No mechanical load on the engine.
More coil cooldown time between firing events.
Elimination of mechanical timing adjustments.
Increased available ignition coil saturation time.
0013
Ignition Coils
A separate coil-at-plug module is located at each spark
plug. The coil-at-plug module is attached to the engine
with two screws. It is installed directly to the spark plug by
an electrical contact inside a rubber boot. A three-way
connector provides 12-volt primary supply from the
15-amp ignition fuse, a ground-switching trigger line from
the PCM, and a ground.
0001
Ignition Control
The ignition control (IC) spark timing is the PCM’s method
of controlling the spark advance and the ignition dwell.
The IC spark advance and the ignition dwell are
calculated by the PCM using the following inputs:
Engine speed.
Page 5007 of 6000

6E–350
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
to the intake manifold through an orifice with a PCM
controlled pintle. During operation, the PCM controls
pintle position by monitoring the pintle position feedback
signal. The feedback signal can be monitored with Tech 2
as “Actual EGR Pos.” “Actual EGR Pos.” should always
be near the commanded EGR position (”Desired EGR
Pos.”). If a problem with the EGR system will not allow the
PCM to control the pintle position properly, DTC P1406
will set. The PCM also tests for EGR flow. If incorrect flow
is detected, DTC P0401 will set. If DTCs P0401 and/or
P1406 are set, refer to the DTC charts.
The linear EGR valve is usually activated under the
following conditions:
Warm engine operation.
Above-idle speed.
Too much EGR flow at idle, cruise or cold operation may
cause any of the following conditions to occur:
Engine stalls after a cold start.
Engine stalls at idle after deceleration.
Vehicle surges during cruise.
Rough idle.
Too little or no EGR flow may allow combustion
temperatures to get too high. This could cause:
Spark knock (detonation).
Engine overheating.
Emission test failure.
DTC P0401 (EGR flow test).
Poor fuel economy.
0017
EGR Pintle Position Sensor
The PCM monitors the EGR valve pintle position input to
endure that the valve responds properly to commands
from the PCM and to detect a fault if the pintle position
sensor and control circuits are open or shorted. If the
PCM detects a pintle position signal voltage outside the
normal range of the pintle position sensor, or a signal
voltage that is not within a tolerance considered
acceptable for proper EGR system operation, the PCM
will set DTC P1406.
General Description (Positive
Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) System)
Crankcase Ventilation System Purpose
The crankcase ventilation system is use to consume
crankcase vapors in the combustion process instead of
venting them to the atmosphere. Fresh air from the
throttle body is supplied to the crankcase and mixed with
blow-by gases. This mixture is then passed through the
positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) valve into the
common chamber.
Crankcase Ventilation System Operation
The primary control is through the positive crankcase
v e n t i l a t i o n ( P C V ) v a l v e . T h e PCV valve meters the flow at
a rate that depends on the intake vacuum. The PCV valve
restricts the flow when the inlet vacuum is highest. In
addition, the PCV valve can seal the common chamber
off in case of sudden high pressure in the crankcase.
028RV002
While the engine is running, exhaust fuses and small
amounts of the fuel/air mixture escape past the piston