1998 OPEL FRONTERA check oil
[x] Cancel search: check oilPage 2159 of 6000

7A–5 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Normal Operation Of 1998 4L30–E
Tr a n s m i s s i o n
Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
Application Conditions:
The TCC is normally applied in 2nd, 3rd and 4th gears
only when all of the following conditions exist:
— The engine coolant temperature is above 70
C
(158
F).
— The brake pedal is released.
— The shift pattern requests TCC apply.
Moreover, TCC is always applied in 2nd, 3rd and 4th
gears when the transmission oil temperature is above
135
C (275F).
This mode should be canceled at 125
C (257F).
ATF Warning Lamp
The ATF warning lamp will be constantly on (not flashing)
if the transmission oil temperature is above 140
C
(284
F).
The ATF warning lamp goes off again when the
transmission oil temperature is below 130
C (266F).
Special Shift Pattern When The Engine Is
Cold:
A special shift pattern is activated when the engine
coolant temperature is below 70
C (158F). (3–4 shifts,
for example, are delayed for small throttle openings and
will occur a few MPH higher.)
Diagnosis
Introduction
The systematic troubleshooting information covered by
this Section offers a practical and systematic approach to
diagnosing 4L30–E transmission, using information that
can be obtained from road tests, electrical diagnosis, oil
pressure checks or noise evaluation.
The key to correcting a complaint is to make use of all of
the available symptoms and logically letting them direct
you to the cause.
When dealing with automatic transmission complaints, it
is best to gather as many symptoms as possible before
making the decision to remove the transmission from the
vehicle.
Frequently, the correction of the complaint does not
require removal of the transmission from the vehicle.
Driver Information
To analyze the problem fill out a complete description of
the owner’s complaint.
Please draw a circle around the right information and
complete the following form. (The next page is an
example of a completed form). You can draw a circle
around many numbers if you are not sure.
Page 2164 of 6000

7A–10
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Checking Transmission Fluid Level
and Condition
Checking fluid level and condition (color and odor) at
regular intervals will provide early diagnosis information
about the transmission. This information may be used to
correct a condition that, if not detected early, could result
in major transmission repairs.
IMPORTANT:When new, automatic transmission fluid
is red in color. As the vehicle is driven, the transmission
fluid will begin to look darker in color. The color may
eventually appear light brown.
A dark brown color with burnt odor may indicate
excessive fluid deterioration and signal a need for fluid
change.
Fluid Level
When adding or changing fluid, use only DEXRON –III.
Refer to Maintenance and Lubrication in General
Information section for maintenance information and
servicing interval.
CAUTION: DO NOT OVERFILL.
Overfilling will cause foaming, loss of fluid, abnor-
mal shifting and possible damage to the transmis-
sion.
1. Park the vehicle on level ground and apply the parking
brake firmly.
2. Check fluid level with engine running at idle.
NOTE: Be sure that transmission fluid temperature is
below 30
C (86F).
3. Move the selector lever through all gear ranges.
4. Move the selector lever to “Park”.
5. Let engine idle for 3 minutes and open the overfill
screw (1).
6. Add released transmission fluid until it flows out over
the overfill screw opening.
7. Let engine idle until a fluid temperature between 32
C
(90
F) and 57C (135F) is reached, then close the
overfill screw (1).
Torque: 38 N
m (3.9 kgꞏm/28 lb ft)
NOTE: To prevent fluid leaks, the overfill screw and oil
drain screws gasket must be replaced each time these
screws are removed.NOTE: Check transmission fluid temperature with scan
tool.
Minimum fluid level
57C (135F)
Maximum fluid level
32C (90F)
242RW003
CAUTION: Do not open overfill screw with engine
stopped.
CAUTION: DO NOT CHECK FLUID LEVEL UNDER
THESE CONDITIONS:
Immediately after driving at sustained highway
speeds.
In heavy city traffic during hot weather.
If vehicle is towing a trailer.
If the vehicle has been operated under these conditions,
shut the engine off and allow the vehicle to “cool” for thirty
(30) minutes. After the cool down period, restart the
vehicle and continue from step 2 above.
Page 2172 of 6000

7A–18
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Chart 9c: Coastdown Harsh Shift Or Clunk At 3–2 Downshift
StepActionYe sNo
1Check line pressure. Refer to Line Pressure Test in this section.
Was line pressure normal?
Go to Step 2
Use Chart 15b:
Possible Causes
of High Line
Pressure in this
section
2Does DTC P1850 set?
Diagnose P1850
first
Replace band
apply solenoid
(PWM) (323)
Chart 10: Intermittent 4TH TO 2ND Gear Downshift At Steady Speed
StepActionYe sNo
1Check for consistent speed sensor reading with scan tool.
Was the reading correct?Replace mode
switch for
intermittent
contact.
Go to Step 2
21. Check for wiring harness damage or short to ground. If OK, go
to (2).
2. Check transmission speed sensor connections. If OK, go to
(3).
3. Replace transmission speed sensor.
Was the replacement complete?
—
Replace speed
sensor.
Chart 11: Engine Flare At Shifting During Turning Only (Usually With Warm Engine)
StepActionYe sNo
1Check for oil leaks at transmission.
Was the problem found?Replace
transmission oil
filter and gasket
—
Chart 12: Engine Flare During 1–2 Or 2–3 Shift
StepActionYe sNo
1Check line pressure. Refer to Line Pressure Test in this section.
Was line pressure normal?
Go to Step 2
Use Chart 15a:
Possible Causes
of Low Line
Pressure in this
section
21. Check for a stuck 1–2 accumulator valve (320).
2. Check for servo piston (106) leaks.
3. Check for a stuck band apply solenoid (323).
Was line pressure normal?
Repair or replace—
Page 2173 of 6000

7A–19 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Chart 13: Shudder Only During Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Applying
StepActionYe sNo
11. TCC shudder is one of the most commonly misdiagnosed
conditions in an automatic transmission. The key to
diagnosing TCC shudder is to note when it happens and under
what conditions. Once the TCC has been fully applied, it is
nearly impossible to make it shudder. TCC shudder (short
burst of noise normally less than 1 second) will only occur
during clutch applying. It is not a steady state condition.
2. Drive until whole drivetrain is at normal operating temperature.
– On 4WD vehicles, the test must be performed with transfer
case selector lever in “2H” position.
– Shudder is a short burst of noise normally less than 1 second
in duration, and can be induced by the following maneuver:
3. From coast condition at 50 mph in “D” range (Normal mode),
depress the throttle to 1/4-1/3 throttle. If present, shudder will
occur within 5 seconds together with TCC application.(The
scan tool may be used to determine the exact time of TCC
applying)
Was the problem found?
Replace
transmission fluid
and filter (remove
both pans) and
flush cooler lines.
Replace
converter
assembly and
O-ring on turbine
shaft
Perform
mechanical
inspection of
other drivetrain
components.
Chart 14: Possible Causes Of Transmission Noise
CAUTION: Before checking transmission for what
is believed to be transmission noise, ensure
presence and positioning of insulating plugs, pads
etc. Also make sure that noise does not come from
other drivetrain components.
Condition
Possible causeCorrection
Whine or BuzzOil level lowFill with ATF, check for external
leaks.
Plugged or restricted oil filterInspect oil filter.
Replace oil filter or ATF as necessary.
Damaged oil filter gasketReplace oil filter gasket.
Knocking noise from front of
transmission
Loose bolts (Converter to flex plate)Tighten to specifications.
transmission.Cracked or broken flex plateReplace flex plate.
Converter damagedReplace converter.
Knocking noise while driving, mostly
on acceleration.Transmission mount loose or brokenTighten mount bolts or replace
transmission mount.
Cooler line mounts loose or brokenTighten or replace cooler line
mounts.
Cooler lines touching body or frameRepair or replace as necessary.
Knocking noise when vehicle is
stationary
Loose flex plate mounting boltsTighten to specifications.
stationary.Cracked or broken flex plateReplace flex plate.
Damaged converterReplace converter.
Page 2174 of 6000

7A–20
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Chart 15a: Possible Causes of Low Line Pressure
StepActionYe sNo
1Check oil level.
Was the problem found?
Fill with ATFGo to Step 2
2Check for defective throttle position sensor.
Was the problem found?Replace throttle
position sensor
Go to Step 3
3Check for plugged, loose, or damaged oil filter (79).
Was the problem found?Inspect oil filter,
tighten bolts or
replace oil filter
(79)
Go to Step 4
4Check for a stuck force motor plunger (404). (Adapter case valve
body)
Was the problem found?Replace force
motor plunger
(404)
Go to Step 5
5Check for a stuck feed limit valve (412). (Adapter case valve body)
Was the problem found?Replace feed limit
valve (412)
Go to Step 6
6Check for loose converter bolts (4 & 5).
Was the problem found?Tighten converter
bolts (4 & 5)
Go to Step 7
7Check for a stuck pressure regulator valve (208). (Oil pump)
Was the problem found?Replace pressure
regulator valve
(208)
Go to Step 8
8Check for a stuck boost valve (205).(Oil pump)
Was the problem found?Replace boost
valve (205)
Go to Step 9
9Check for blocked intermediate oil passages to pressure
regulator valve. (Oil pump)
Was the problem found?
Replace oil pumpGo to Step 10
10Check for defective oil pump (9, 201, 202 & 209).
Was the problem found?
Replace oil pumpGo to Step 11
11Check for internal leaks.
– Check balls missing or out of location in valve bodies
– Seals cut or damaged
– Gaskets defective, etc.
Was the problem found?Install balls, or
correct ball
location
Replace seals
Replace gaskets
—
Page 2175 of 6000
7A–21 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
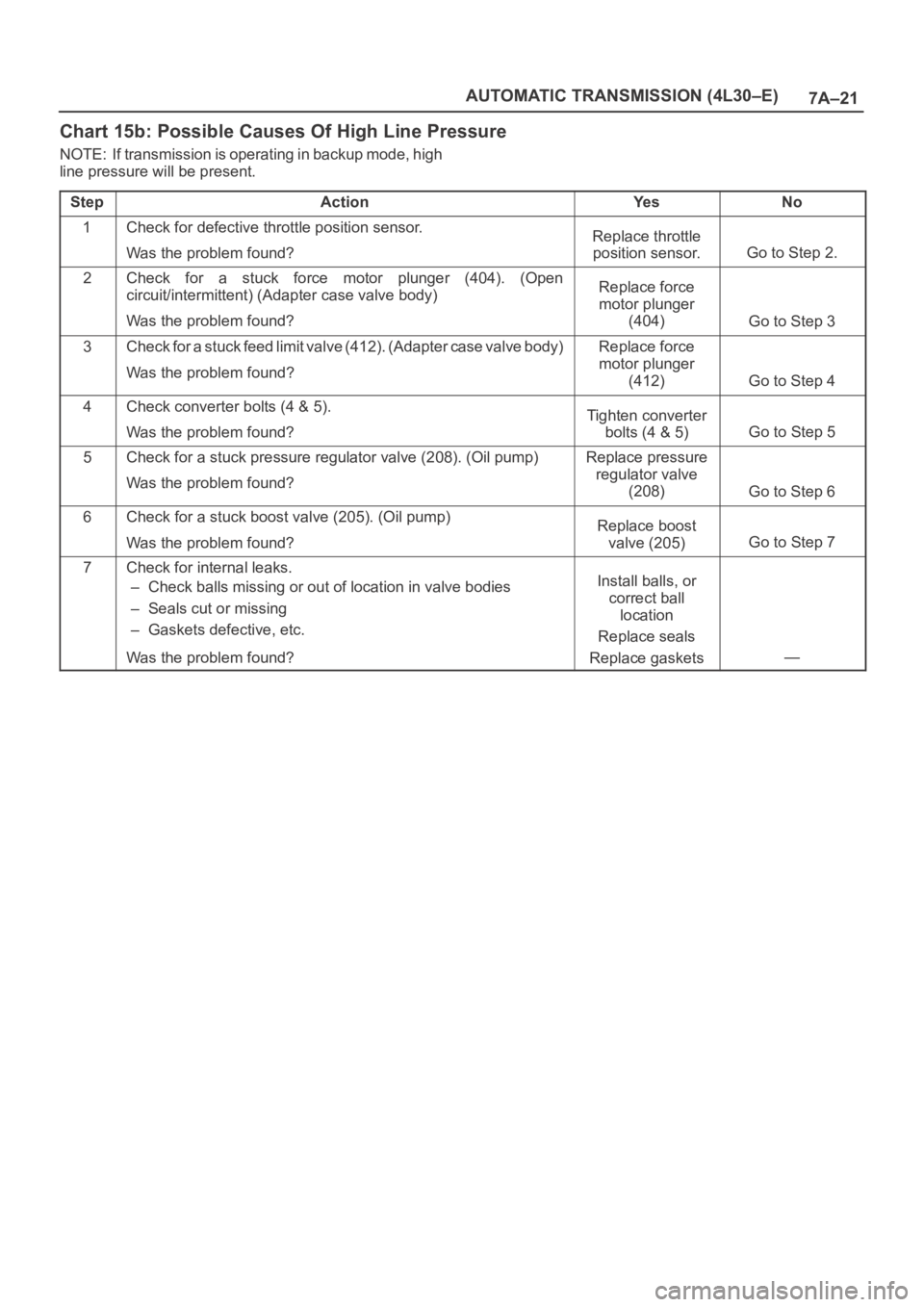
Chart 15b: Possible Causes Of High Line Pressure
NOTE: If transmission is operating in backup mode, high
line pressure will be present.
Step
ActionYe sNo
1Check for defective throttle position sensor.
Was the problem found?Replace throttle
position sensor.
Go to Step 2.
2Check for a stuck force motor plunger (404). (Open
circuit/intermittent) (Adapter case valve body)
Was the problem found?Replace force
motor plunger
(404)
Go to Step 3
3Check for a stuck feed limit valve (412). (Adapter case valve body)
Was the problem found?Replace force
motor plunger
(412)
Go to Step 4
4Check converter bolts (4 & 5).
Was the problem found?Tighten converter
bolts (4 & 5)
Go to Step 5
5Check for a stuck pressure regulator valve (208). (Oil pump)
Was the problem found?Replace pressure
regulator valve
(208)
Go to Step 6
6Check for a stuck boost valve (205). (Oil pump)
Was the problem found?Replace boost
valve (205)
Go to Step 7
7Check for internal leaks.
– Check balls missing or out of location in valve bodies
– Seals cut or missing
– Gaskets defective, etc.
Was the problem found?Install balls, or
correct ball
location
Replace seals
Replace gaskets
—
Page 2176 of 6000
7A–22
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Chart 16: Possible Causes Of
Transmission Fluid Leaks
Before attempting to correct an oil leak, the actual source
of the leak must be determined. In many cases, the
source of the leak may be difficult to determine due to
“wind flow” around the engine and transmission.
The suspected area should be wiped clean before in-
specting for the source of the leak.Oil leaks around the engine and transmission are gener-
ally carried toward the rear of the vehicle by the air
stream. In determining the source of an leak, the following
two checks should be made:
1. With the engine running, check for external line
pressure leaks.
2. With the engine off, check for oil leaks due to the
raised oil level caused by drainback of converter oil
into the transmission.
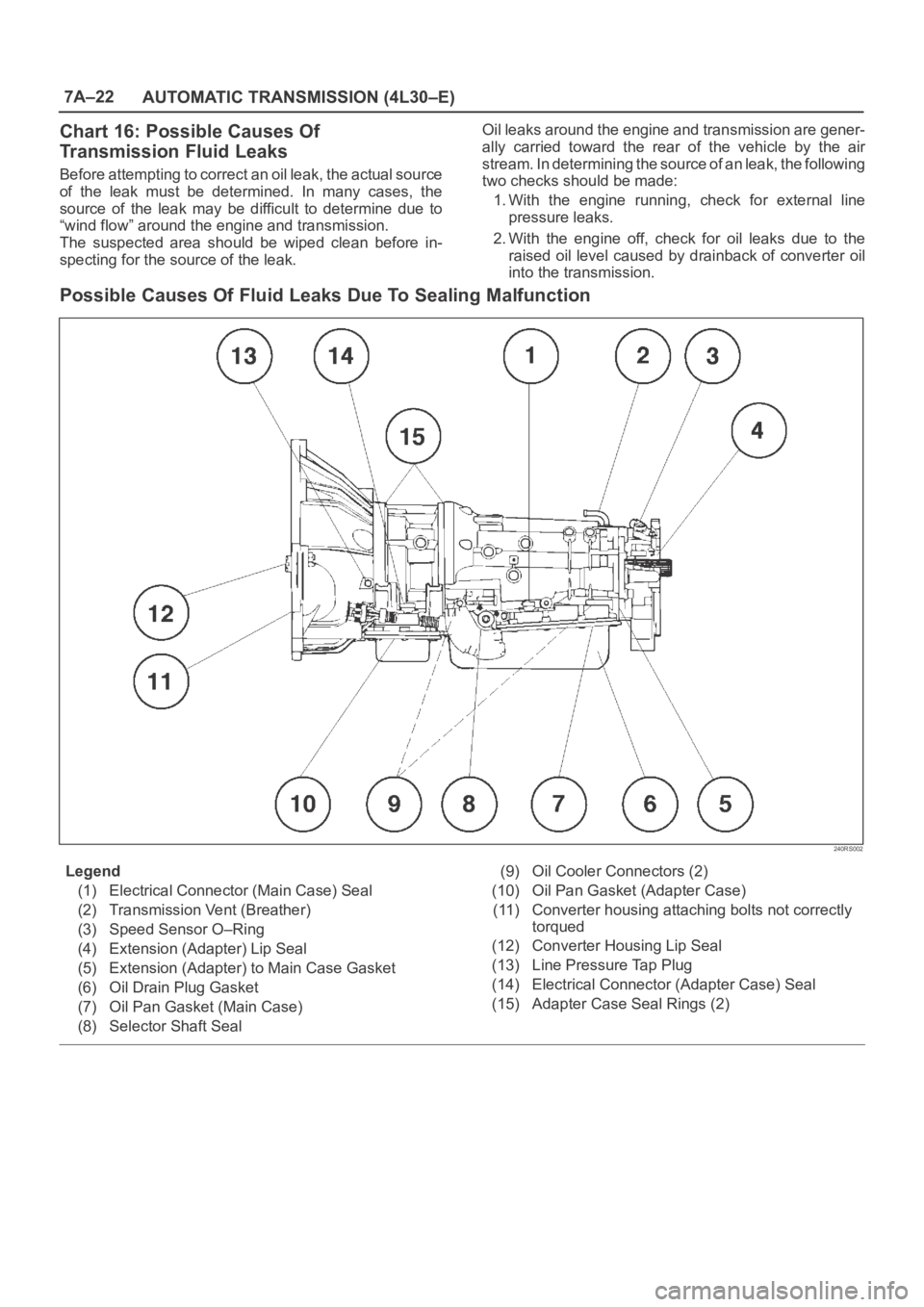
Possible Causes Of Fluid Leaks Due To Sealing Malfunction
240RS002
Legend
(1) Electrical Connector (Main Case) Seal
(2) Transmission Vent (Breather)
(3) Speed Sensor O–Ring
(4) Extension (Adapter) Lip Seal
(5) Extension (Adapter) to Main Case Gasket
(6) Oil Drain Plug Gasket
(7) Oil Pan Gasket (Main Case)
(8) Selector Shaft Seal(9) Oil Cooler Connectors (2)
(10) Oil Pan Gasket (Adapter Case)
(11) Converter housing attaching bolts not correctly
torqued
(12) Converter Housing Lip Seal
(13) Line Pressure Tap Plug
(14) Electrical Connector (Adapter Case) Seal
(15) Adapter Case Seal Rings (2)
Page 2177 of 6000

7A–23 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Stall Test
The stall test allows you to check the transmission for
internal abrasion and the one way clutch for slippage.
Torque converter performance can also be evaluated.
The stall test results together with the road test results will
identify transmission components requiring servicing or
adjustment.
Stall Test Procedure:
1. Check the level of the engine coolant, the engine oil,
and the automatic transmission fluid. Replenish if
necessary.
2. Block the wheels and set the parking brake.
3. Connect a tachometer to the engine.
4. Start the engine and allow it to idle until the engine
coolant temperature reaches 70 – 80
C (158 –
176
F).
5. Hold the brake pedal down as far as it will go.
6. Place the selector in the “D” range.
7. Gradually push the accelerator pedal to the floor.
The throttle valve will be fully open.
Note the engine speed at which the tachometer
needle stabilizes.
Stall Speed : 2,100
150 rpm
NOTE: Do not continuously run this test longer than 5
seconds.
8. Release the accelerator pedal.
9. Place the selector in the “N” range.
10. Run the engine at 1,200 rpm for one minute.
This will cool the transmission fluid.
11. Repeat Steps 7 – 10 for the “3”, “2”, “L” and “R”
ranges.
Line Pressure Test
The line pressure test checks oil pump and control valve
pressure regulator valve function. It will also detect oil
leakage.
Line Pressure Test Procedure:
1. Check the level of the engine coolant, the engine oil,
and the automatic transmission fluid.
Replenish if required.
2. Block the wheels and set the parking brake.
3. Remove the pressure detection plug at the left side of
the transmission case.
Set 5–8840–0004–0 pressure gauge and adapter to
the pressure detection plug hole.
241RS001
4. Start the engine and allow it to idle until the engine
coolant temperature reaches 70 – 80
C (158 –
176
F).
5. Hold the brake pedal down as far as it will go.
6. Place the selector in the “D” range.
7. Note the pressure gauge reading with the engine
idling.
8. Gradually push the accelerator pedal to the floor. The
throttle valve will be fully open.
Note the pressure gauge reading with the accelerator
pedal fully depressed.
NOTE: Do not continuously run this test longer than 5
seconds.
9. Release the accelerator pedal.
10. Place the selector in the “N” range.
11. Run the engine at 1,200 rpm for one minute.
This will cool the transmission fluid.
12. Repeat Steps 7 – 11 for the “3”, “2”, “L”, and “R”
ranges.
13. Install a pressure detection plug to the transmission
case, applying recommended thread locking agent
(LOCTITE 242) or its equivalent to thread of plug.
Make sure that thread is cleaned before applying
locking agents.
14. Tighten the pressure detection plug to the specified
torque.
Torque:9–14Nꞏm(0.9–1.4kgꞏm/7–10lbft)