1998 OPEL FRONTERA transmission
[x] Cancel search: transmissionPage 2068 of 6000
6E–175 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
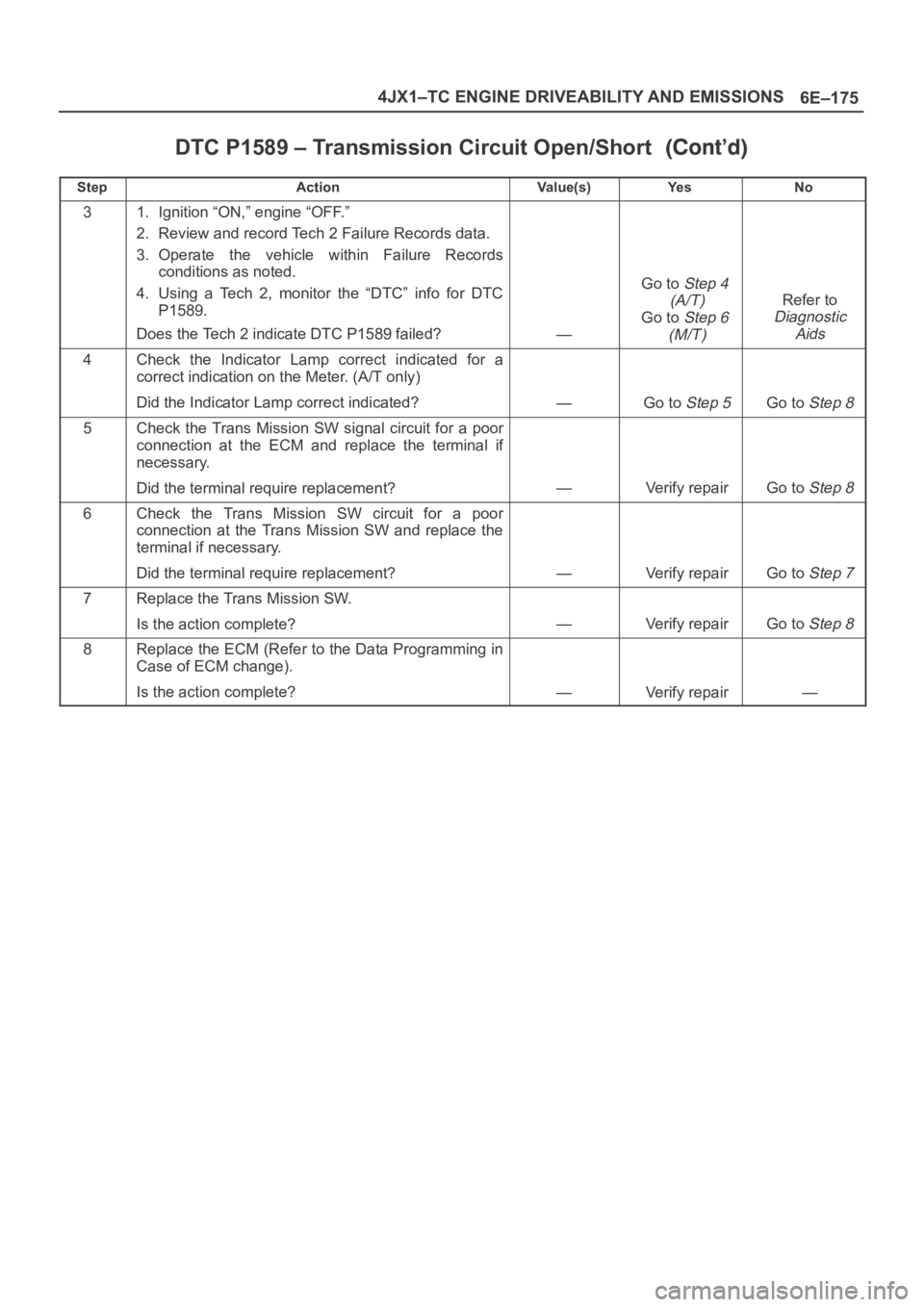
DTC P1589 – Transmission Circuit Open/Short
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
31. Ignition “ON,” engine “OFF.”
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data.
3. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor the “DTC” info for DTC
P1589.
Does the Tech 2 indicate DTC P1589 failed?
—
Go toStep 4
(A/T)
Go toStep 6
(M/T)
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
4Check the Indicator Lamp correct indicated for a
correct indication on the Meter. (A/T only)
Did the Indicator Lamp correct indicated?
—Go to Step 5Go to Step 8
5Check the Trans Mission SW signal circuit for a poor
connection at the ECM and replace the terminal if
necessary.
Did the terminal require replacement?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
6Check the Trans Mission SW circuit for a poor
connection at the Trans Mission SW and replace the
terminal if necessary.
Did the terminal require replacement?
—Verify repairGo to Step 7
7Replace the Trans Mission SW.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
8Replace the ECM (Refer to the Data Programming in
Case of ECM change).
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
Page 2072 of 6000
6E–179 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
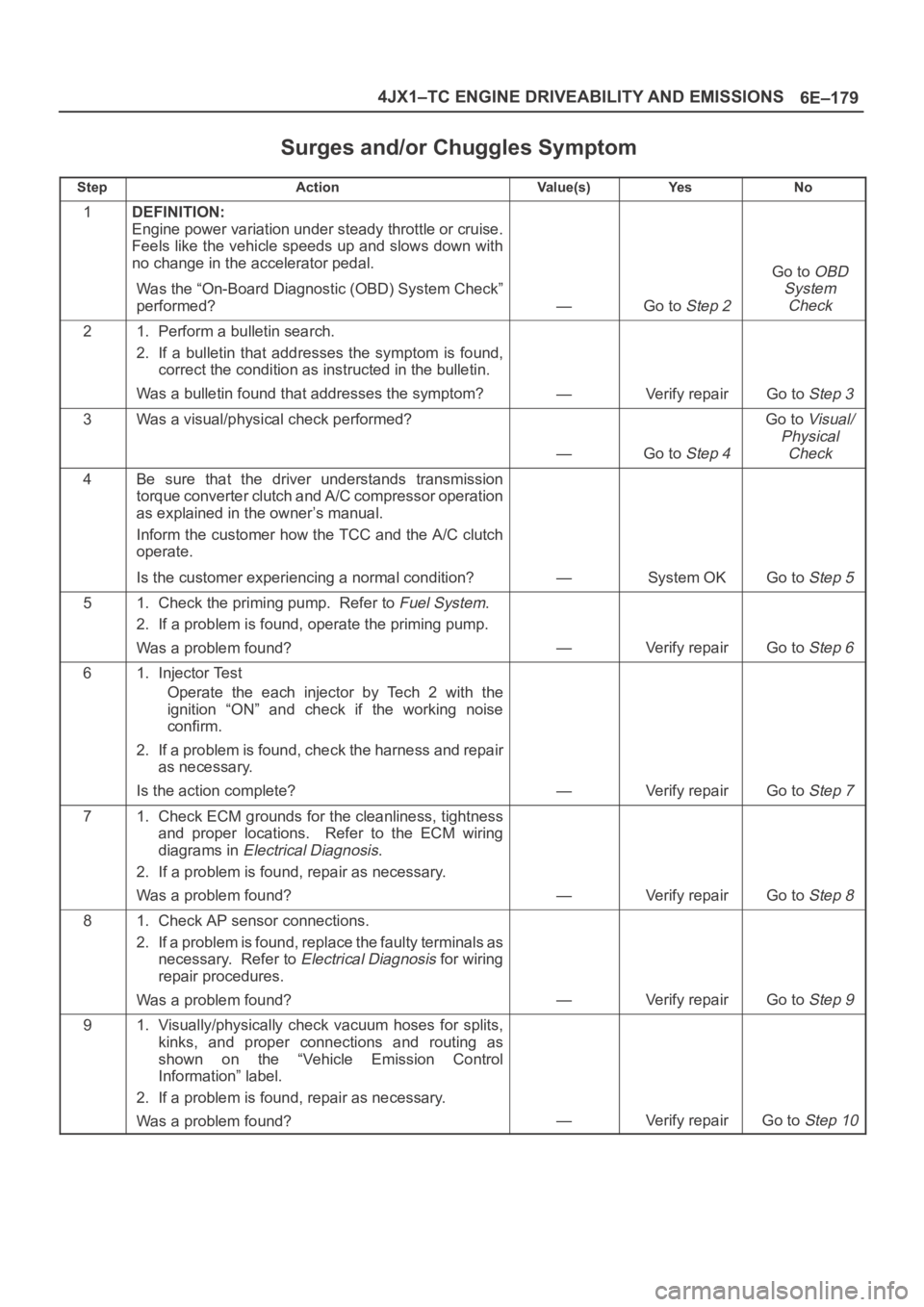
Surges and/or Chuggles Symptom
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1DEFINITION:
Engine power variation under steady throttle or cruise.
Feels like the vehicle speeds up and slows down with
no change in the accelerator pedal.
Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom?
—Verify repairGo to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to Visual/
Physical
Check
4Be sure that the driver understands transmission
torque converter clutch and A/C compressor operation
as explained in the owner’s manual.
Inform the customer how the TCC and the A/C clutch
operate.
Is the customer experiencing a normal condition?
—System OKGo to Step 5
51. Check the priming pump. Refer to Fuel System.
2. If a problem is found, operate the priming pump.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 6
61. Injector Test
Operate the each injector by Tech 2 with the
ignition “ON” and check if the working noise
confirm.
2. If a problem is found, check the harness and repair
as necessary.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repairGo to Step 7
71. Check ECM grounds for the cleanliness, tightness
and proper locations. Refer to the ECM wiring
diagrams in
Electrical Diagnosis.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
81. Check AP sensor connections.
2. If a problem is found, replace the faulty terminals as
necessary. Refer to
Electrical Diagnosis for wiring
repair procedures.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 9
91. Visually/physically check vacuum hoses for splits,
kinks, and proper connections and routing as
shown on the “Vehicle Emission Control
Information” label.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 10
Page 2074 of 6000
6E–181 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
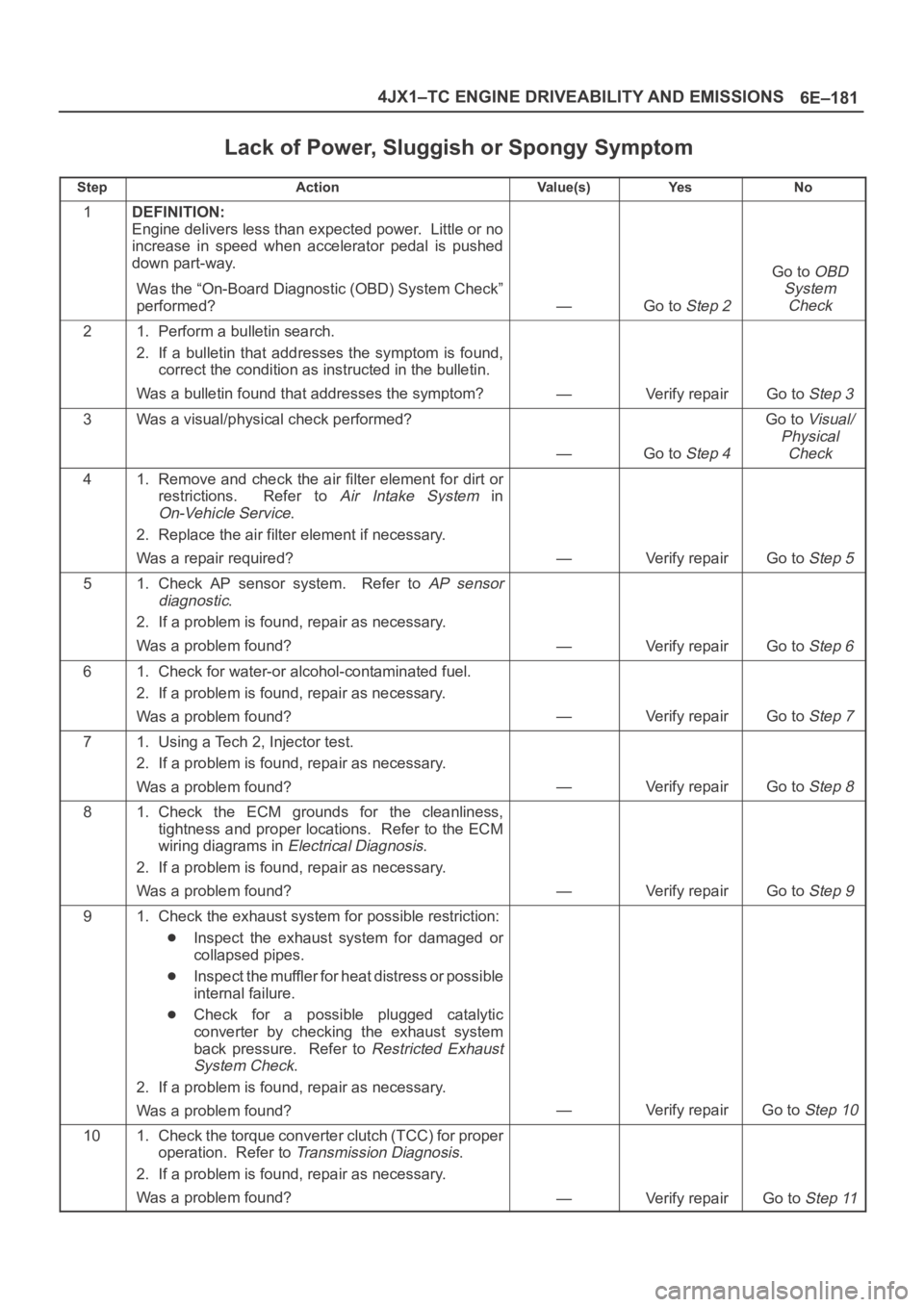
Lack of Power, Sluggish or Spongy Symptom
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1DEFINITION:
Engine delivers less than expected power. Little or no
increase in speed when accelerator pedal is pushed
down part-way.
Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom?
—Verify repairGo to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to Visual/
Physical
Check
41. Remove and check the air filter element for dirt or
restrictions. Refer to
Air Intake System in
On-Vehicle Service.
2. Replace the air filter element if necessary.
Was a repair required?
—Verify repairGo to Step 5
51. Check AP sensor system. Refer to AP sensor
diagnostic
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 6
61. Check for water-or alcohol-contaminated fuel.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 7
71. Using a Tech 2, Injector test.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
81. Check the ECM grounds for the cleanliness,
tightness and proper locations. Refer to the ECM
wiring diagrams in
Electrical Diagnosis.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 9
91. Check the exhaust system for possible restriction:
Inspect the exhaust system for damaged or
collapsed pipes.
Inspect the muffler for heat distress or possible
internal failure.
Check for a possible plugged catalytic
converter by checking the exhaust system
back pressure. Refer to
Restricted Exhaust
System Check
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 10
101. Check the torque converter clutch (TCC) for proper
operation. Refer to
Transmission Diagnosis.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 11
Page 2076 of 6000

6E–183 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle, Stalling Symptom
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1DEFINITION:
Engine runs unevenly at idle. If severe, the engine or
vehicle may shake. Engine idle speed may vary in
RPM. Either condition may be severe enough to stall
the engine.
Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom?
—Go to Step 6Go to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to Visual/
Physical
Check
41. Check the ECM grounds for cleanliness, tightness
and proper routing. Refer to the ECM wiring
diagrams in
Electrical Diagnosis.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 5
51. Check for incorrect idle speed. Ensure that the
following conditions are present:
The engine is fully warm.
The accessories are “OFF.”
2. Using a Tech 2, monitor the AP position.
Is the AP position within the specified values?
0%Go to Step 10Go to Step 9
61. Visually/physically inspect for the following
conditions:
Restricted air intake system. Check for a
possible collapsed air intake duct, restricted
air filter element, or foreign objects blocking
the air intake system.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 7
71. Injector Test
Operate the each injector by Tech 2 with the
ignition “ON” and check if the working noise
confirm.
2. If a problem is found, check the harness or replace
the injector.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
81. Check the transmission range switch circuit. Use a
Tech 2 and be sure the Tech 2 indicates that the
vehicle is in drive with the gear selector in drive or
overdrive.
2. If a problem is found, diagnose and repair the
transmission range switch as necessary (Refer to
Automatic Transmission Diagnosis).
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 9
Page 2079 of 6000
6E–186
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
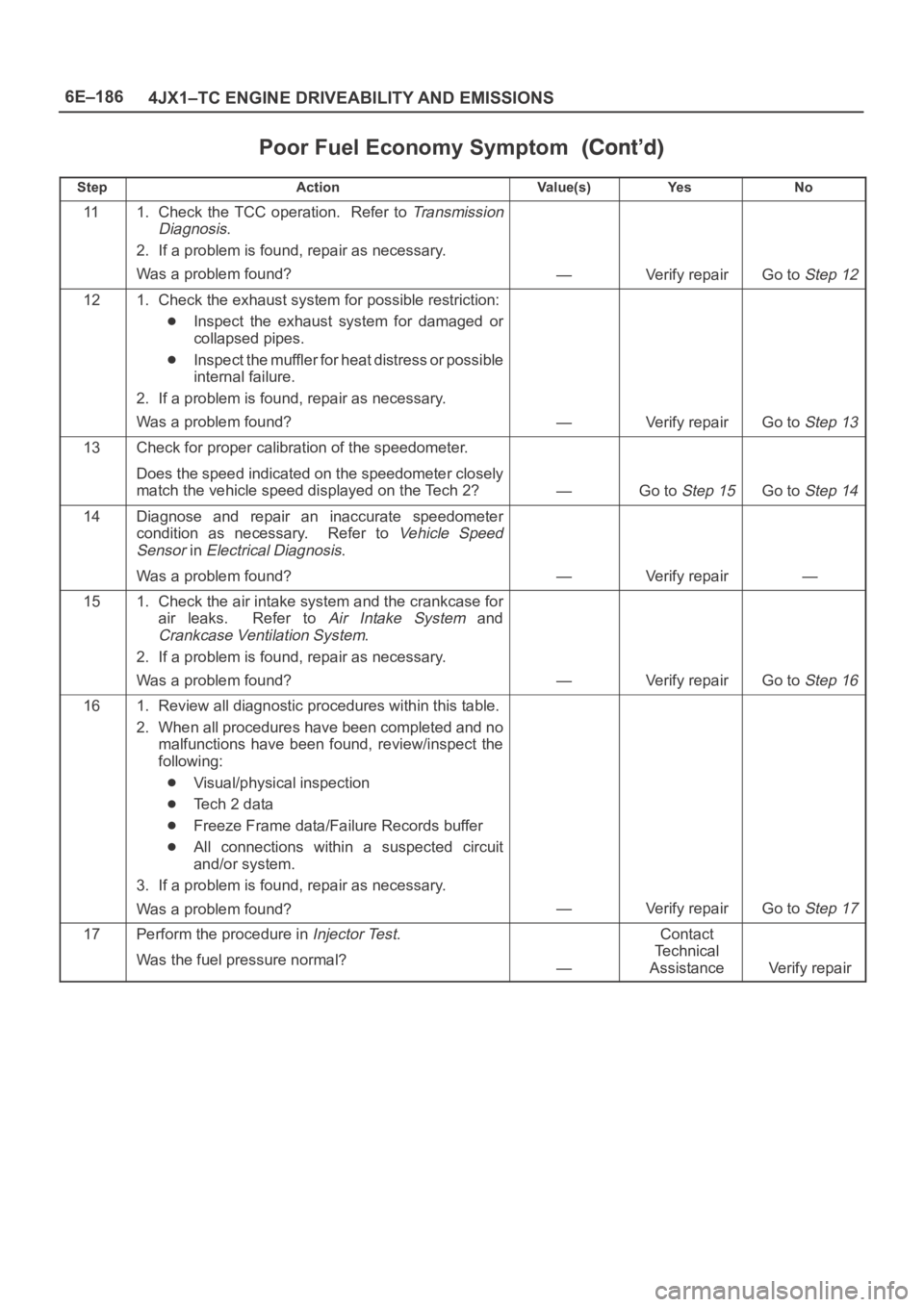
Poor Fuel Economy Symptom
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
111. Check the TCC operation. Refer to Transmission
Diagnosis
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 12
121. Check the exhaust system for possible restriction:
Inspect the exhaust system for damaged or
collapsed pipes.
Inspect the muffler for heat distress or possible
internal failure.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 13
13Check for proper calibration of the speedometer.
Does the speed indicated on the speedometer closely
match the vehicle speed displayed on the Tech 2?
—Go to Step 15Go to Step 14
14Diagnose and repair an inaccurate speedometer
condition as necessary. Refer to
Vehicle Speed
Sensor
in Electrical Diagnosis.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repair—
151. Check the air intake system and the crankcase for
air leaks. Refer to
Air Intake System and
Crankcase Ventilation System.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 16
161. Review all diagnostic procedures within this table.
2. When all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
Visual/physical inspection
Te c h 2 d a t a
Freeze Frame data/Failure Records buffer
All connections within a suspected circuit
and/or system.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 17
17Perform the procedure in Injector Test.
Was the fuel pressure normal?
—
Contact
Te c h n i c a l
Assistance
Verify repair
Page 2082 of 6000
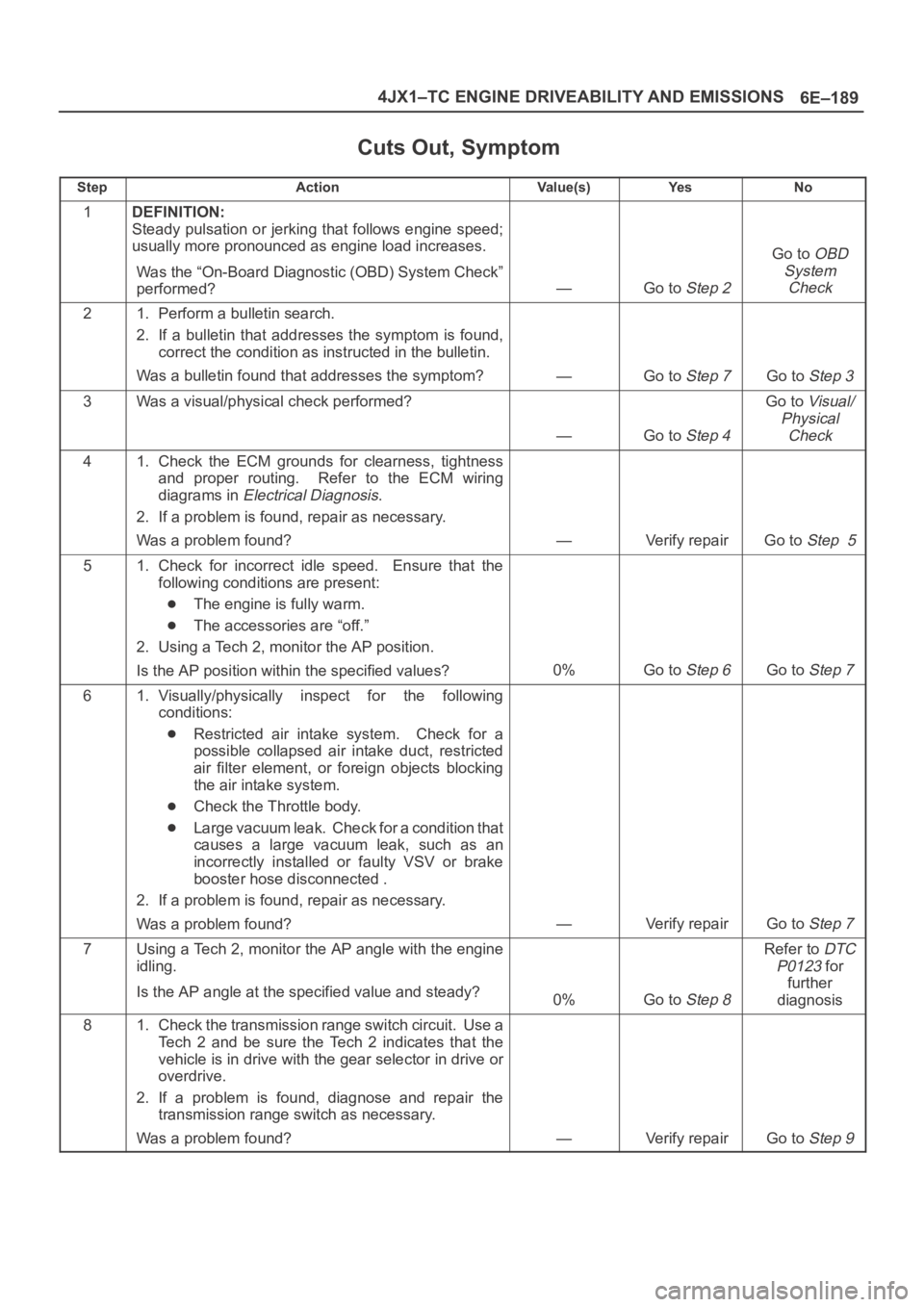
6E–189 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Cuts Out, Symptom
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1DEFINITION:
Steady pulsation or jerking that follows engine speed;
usually more pronounced as engine load increases.
Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom?
—Go to Step 7Go to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to Visual/
Physical
Check
41. Check the ECM grounds for clearness, tightness
and proper routing. Refer to the ECM wiring
diagrams in
Electrical Diagnosis.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 5
51. Check for incorrect idle speed. Ensure that the
following conditions are present:
The engine is fully warm.
The accessories are “off.”
2. Using a Tech 2, monitor the AP position.
Is the AP position within the specified values?
0%Go to Step 6Go to Step 7
61. Visually/physically inspect for the following
conditions:
Restricted air intake system. Check for a
possible collapsed air intake duct, restricted
air filter element, or foreign objects blocking
the air intake system.
Check the Throttle body.
Large vacuum leak. Check for a condition that
causes a large vacuum leak, such as an
incorrectly installed or faulty VSV or brake
booster hose disconnected .
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 7
7Using a Tech 2, monitor the AP angle with the engine
idling.
Is the AP angle at the specified value and steady?
0%Go to Step 8
Refer to DTC
P0123
for
further
diagnosis
81. Check the transmission range switch circuit. Use a
Tech 2 and be sure the Tech 2 indicates that the
vehicle is in drive with the gear selector in drive or
overdrive.
2. If a problem is found, diagnose and repair the
transmission range switch as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 9
Page 2092 of 6000
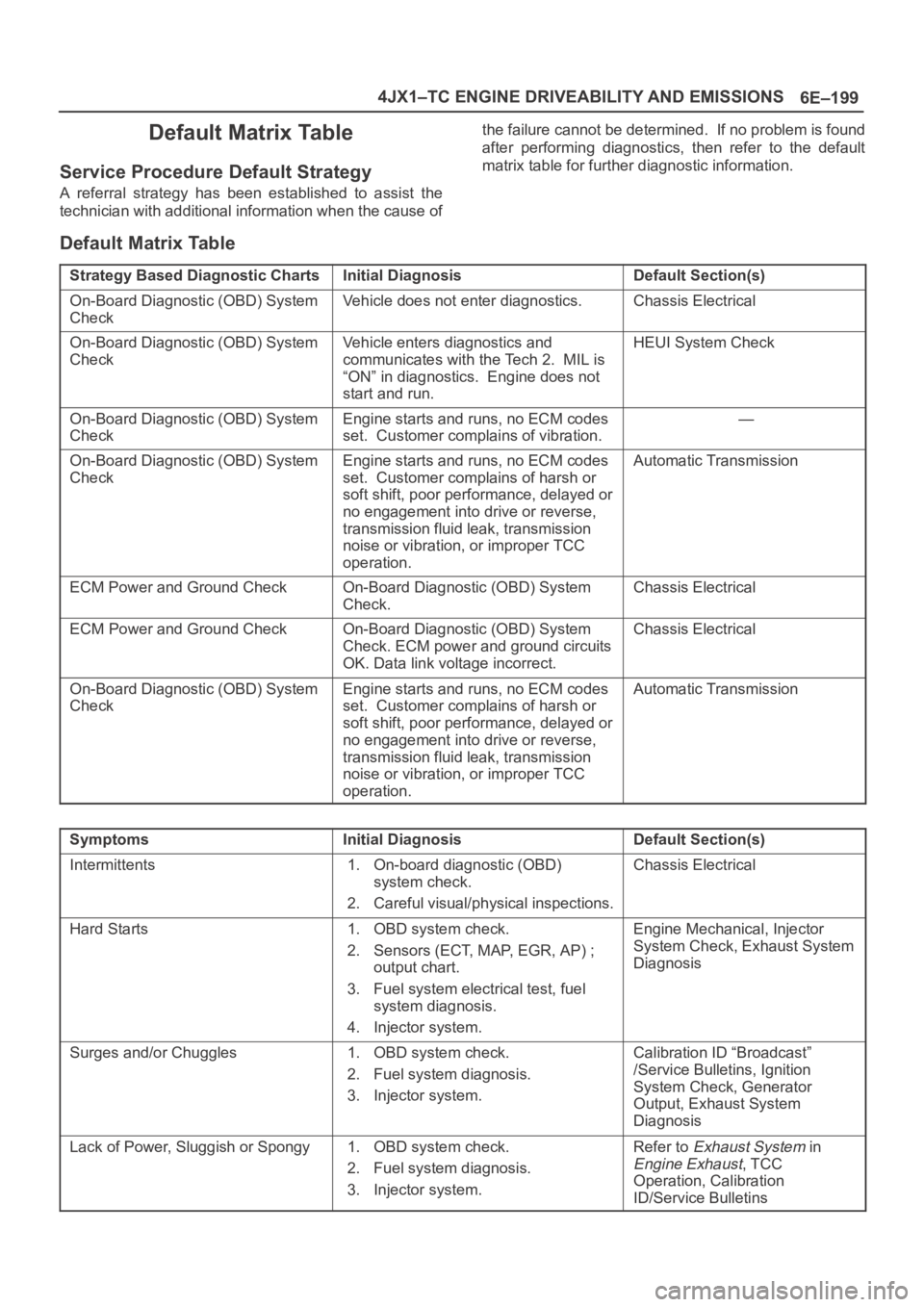
6E–199 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Default Matrix Table
Service Procedure Default Strategy
A referral strategy has been established to assist the
technician with additional information when the cause ofthe failure cannot be determined. If no problem is found
after performing diagnostics, then refer to the default
matrix table for further diagnostic information.
Default Matrix Table
Strategy Based Diagnostic ChartsInitial DiagnosisDefault Section(s)
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
CheckVehicle does not enter diagnostics.Chassis Electrical
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
CheckVehicle enters diagnostics and
communicates with the Tech 2. MIL is
“ON” in diagnostics. Engine does not
start and run.HEUI System Check
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
CheckEngine starts and runs, no ECM codes
set. Customer complains of vibration.—
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
CheckEngine starts and runs, no ECM codes
set. Customer complains of harsh or
soft shift, poor performance, delayed or
no engagement into drive or reverse,
transmission fluid leak, transmission
noise or vibration, or improper TCC
operation.Automatic Transmission
ECM Power and Ground CheckOn-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check.Chassis Electrical
ECM Power and Ground CheckOn-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check. ECM power and ground circuits
OK. Data link voltage incorrect.Chassis Electrical
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
CheckEngine starts and runs, no ECM codes
set. Customer complains of harsh or
soft shift, poor performance, delayed or
no engagement into drive or reverse,
transmission fluid leak, transmission
noise or vibration, or improper TCC
operation.Automatic Transmission
SymptomsInitial DiagnosisDefault Section(s)
Intermittents1. On-board diagnostic (OBD)
system check.
2. Careful visual/physical inspections.Chassis Electrical
Hard Starts1. OBD system check.
2. Sensors (ECT, MAP, EGR, AP) ;
output chart.
3. Fuel system electrical test, fuel
system diagnosis.
4. Injector system.Engine Mechanical, Injector
System Check, Exhaust System
Diagnosis
Surges and/or Chuggles1. OBD system check.
2. Fuel system diagnosis.
3. Injector system.Calibration ID “Broadcast”
/Service Bulletins, Ignition
System Check, Generator
Output, Exhaust System
Diagnosis
Lack of Power, Sluggish or Spongy1. OBD system check.
2. Fuel system diagnosis.
3. Injector system.Refer to Exhaust System in
Engine Exhaust, TCC
Operation, Calibration
ID/Service Bulletins
Page 2120 of 6000

6E–227 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
QOS
Diagnostics
– Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Service Engine
Soon lamp)
– Data Link Connector (DLC)
– Data Output
ECM Service Precautions
The ECM is designed to withstand normal current draws
associated with vehicle operation. Avoid overloading any
circuit. When testing for opens and shorts, do not ground
or apply voltage to any of the ECM’s circuits unless
instructed to do so. These circuits should only be tested
using digital voltmeter. The ECM should remain
connected to the ECM or to a recommended breakout
box.
Intake Throttle Position (ITP) Sensor
ITP sensor is a potentiometer type and installed to the
intake throttle valve body. A voltage of 5V is applied
constantly from ECM to ITP sensor thereby to determine
by change in voltage the opening of the intake throttle
valve during warming up.
Transmission Range Switch
IMPORTANT:The vehicle should not be driven with the
transmission range switch disconnected; idle quality will
be affected.
The four inputs from the transmission range switch
indicate to the ECM which position is selected by the
transmission selector lever.
For more information on the transmission on the
transmission range switch, refer to
Automatic
Tr a n s m i s s i o n
.
Accelerator Position Sensor (AP)
AP sensor is a potentiometer type and installed to
accelerator pedal bracket. A voltage of 5V constantly
applied from ECM to the sensor thereby to determine the
accelerator pedaling angle by change in voltage. Further,
this sensor is provided with an accelerator switch, which
is set off only when the accelerator pedal is stepped on.
Aftermarket Electrical and Vacuum
Equipment
Aftermarket (add-on) electrical and vacuum equipment is
defined as any equipment which connects to the vehicle’s
electrical or vacuum systems that is installed on a vehicle
after it leaves the factory. No allowances have been
made in the vehicle design for this type of equipment.
NOTE: No add-on vacuum equipment should be added
to this vehicle.
NOTE: Add-on electrical equipment must only be
connected to the vehicle’s electrical system at the battery
(power and ground).
Add-on electrical equipment, even when installed to
these guidelines, may still cause the powertrain system to
malfunction. This may also include equipment not
connected to the vehicle electrical system such asportable telephones and radios. Therefore, the first step
in diagnosing any powertrain problem is to eliminate all
aftermarket electrical equipment from the vehicle. After
this is done, if the problem still exists, it may be diagnosed
in the normal manner.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electronic components used in the ECM are often
designed to carry very low voltage. Electronic
components are susceptible to damage caused by
electrostatic discharge. Less than 100 volts of static
electricity can cause damage to some electronic
components. By comparison, it takes as much as 4000
volts for a person to feel even the zap of a static
discharge.
TS23793
There are several ways for a person to become statically
charged. The most common methods of charging are by
friction and induction.
An example of charging by friction is a person sliding
across a vehicle seat.
Charge by induction occurs when a person with well
insulated shoes stands near a highly charged object
and momentary touches ground. Charges of the
same polarity are drained off leaving the person
highly charged with the opposite polarity. Static
charges can cause damage, therefore it is important
to use care when handling and testing electronic
components.
NOTE: To prevent possible electrostatic discharge
damage, follow these guidelines:
Do not touch the ECM connector pins or soldered
components on the ECM circuit board.
Do not open the replacement part package until the
part is ready to be installed.
Before removing the part from the package, ground
the package to a known good ground on the vehicle.
If the part has been handled while sliding across the
seat, while sitting down from a standing position, or
while walking a distance, touch a known good ground
before installing the part.