1998 JAGUAR X308 Fuel tank
[x] Cancel search: Fuel tankPage 1083 of 2490
Diagnostic Trouble Code (D
TC) index
D
iagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index
DT
C
De
scription
Possib
le Source
Acti
on
P0300Ran
dom misfire detected
ECM t
o ignition coil primary circuit
faults (cylinder misfire detected
DTCs also logged)
Ignition coil
ground circuit; open
circuit, high resistance
F
uel injector circuit fault(s)
(injector DTCs also logged)
Ignition coil
failure(s)
Check f
or water ingress into spark
plug wells
HT sho
rt to ground (tracking)
check rubber boots for
cracks/damage
Spark plug
failure/fouled/incorrect
gap
Cy
linder compression low
F
uel delivery pressure (low/high)
F
uel injectors restricted/leaking
Fuel contamination
P
AS pulley bolts loose (see Service
Actions)
W
orn camshaft/broken valve
springs
For ign
ition system tests,GO
to Pinpoint Test A.
. For
inje
ctor circuit tests,
REFER to: Fuel Charging and
Controls (30
3-04 Fuel
Charging and Controls,
Description and Operation).
Check compressions. For
spark plug tests,GO to
Pinpoint Test B.
.
Check fuel
pressure,
REFER to: Fuel System
Pressure Check (31
0-00 Fuel
System - General
Information, General
Procedures).
For fuel injectors,
REFER to: Fuel Charging and
Controls (30
3-04 Fuel
Charging and Controls,
Diagnosis and Testing).
For fuel tank and lines
information,
REFER to: Fuel Tank and
Lin
es
(310-01 Fuel Tank and
Lines, Description and
Operation).
Check PAS pulley bolt torque
(REFER to technical service
bulletins). For engine
information,
REFER to: Specifications
(3
03-01 Engine,
Specifications).
P0301Misfire
detected, Cyl 1
R
EFER to possible sources for P0300
R
EFER to actions for P0300.
P0302Misfire
detected, Cyl 3
P0303Misfire
detected, Cyl 5
P0304Misfire
detected, Cyl 7
P0305Misfire
detected, Cyl 2
P0306Misfire
detected, Cyl 4
P0307Misfire
detected, Cyl 6
P0308Misfire
detected, Cyl 8
P0351Igni
tion coil primary/secondary circuit
malfunction, cyl 1
ECM to
ignition module primary
circuit open circuit, short circuit to
ground, high resistance
Igni
tion module to ignition coil
primary circuit open circuit, short
circuit to ground, high resistance
Ignition modu
le ground circuit
open circuit, hi gh resistance
Ignition coil
failure
Ignition modul
e failure
F
or ignition circuit tests,GO to
Pinpoint Test A.
.
P0352Igni
tion coil primary/secondary circuit
malfunction, cyl 3
P0353Igni
tion coil primary/secondary circuit
malfunction, cyl 5
P0354Igni
tion coil primary/secondary circuit
malfunction, cyl 7
P0355Igni
tion coil primary/secondary circuit
malfunction, cyl 2
P0356Igni
tion coil primary/secondary circuit
malfunction, cyl 4
P0357Igni
tion coil primary/secondary circuit
malfunction, cyl 6
P0358Igni
tion coil primary/secondary circuit
malfunction, cyl 8
P1313Misfire rate
catalyst damage, Right-hand
cylinders. NOTE. This DTC will flag only
when accompanied by a random or
individual cylinder misfire DTC; P0300,
R
efer to possible causes for P0300-P0308
R
efer to actions for P0300-
P0308.
Page 1095 of 2490
Diagnostic Trouble Code (D
TC) Index
Pinpoint Tests
Fue
l lines
Harness damage
Throttl
e sensors
Throttl
e motor
Spark plugs
fouled
Ignition coil
failure(s)
HT sho
rt to ground (tracking) check
rubber boots for cracks/damage
Exhaus
t gas recirculation (EGR)
F
or air intake syst
em information,
REFER to Section 303
-12
Intake Air
Distribu
tion and Filtering
.
F
or fuel pressure
regulator tests,
REF
ER to Section 303
-04
Fuel
Charging and Con
trols
.
F
or fuel line information,
REFER to Section 310
-01
Fuel Tank
and Lines.
F
or throttle sensor
circuit tests,
REFER to Section 303
-14
Electronic
Engine
Controls
.
Fo
r throttle motor
circuit tests,
REFER to Section 303
-04
Fuel
Charging and Con
trols
.
For ign
ition system tests,
REFER to Section 303
-07
Engine
Ignition.
Inspe
ct EGR components, for circuit
tests, GO to Pinpoint Test A.
.
DT
C
De
scription
Possib
le Source
Acti
on
P0400Exhaus
t gas
recirculation (EGR) flow malfunction
EGR
valve connector pins high
resistance
EGR pipe/exhaust manifold leak EGR pipe block
ed
EGR val
ve stuck open/closed,
blocked
EGR
valve failure
Check the EGR pi
pe, valve and manifold for
leaks/blockages. Check the EGR valve function.
For EGR valve circuit tests,GO to Pinpoint Test A.
.
P0405Exhaus
t gas
recirculation (EGR) drive
circuits open circuit
EGR valve power supply circuit o
pen circuit
EGR valve t
o ECM drive circuit
pair - EGR pins 1/3, 4/6 open circuit, high resistance
EGR val
ve failure (stepper motor
open circuit)
F
or EGR valve circuit tests,GO to Pinpoint Test
A.
.
P0406Exhaus
t gas
recirculation (EGR) drive
circuits short circuit
EGR valve t
o ECM drive circuit
pair - EGR pins 1/3, 4/6 short
circuit to ground or high voltage
EGR val
ve failure (stepper motor
short circuit)
F
or EGR valve circuit tests,GO to Pinpoint Test
A.
.
P
INPOINT TEST A : DTC P0400, P0405; EGR VALV
E FLOW MALFUNCTION/DRIVE CIRCUITS OPEN
CIRCUIT
TE
ST
CONDITIONS
D
ETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS
A1: CHECK
THE EMS POWER SU
PPLIES TO THE EGR VALVE
D
isconnect the EGR valve electrical connector, PI34.
1
Turn the ignition swi
tch to the ON
position.
2
Make sure the EMS re lay i
s energized.
Vehicles with AJ26 engine:
Me
asure the voltage between PI34, pins 02 and 05 (WP) and GROUND
Vehicles with AJ27 engine:
Me
asure the voltage between PI34, pins 02 and 05 (WU) and GROUND
3
Is th
e voltage at either pin less than 10 volts?
Yes
Page 1148 of 2490
Evaporative E
missions - Evaporative Emissions
Description an
d Operation
To reduce the emission of fuel vapour, th e fuel tank is vented to atmosphere through activated charcoal adsorption canister
(s) which collects the fuel droplets. The ch arcoal is periodically purged of fuel when the EVAP Canister Purge Valve opens
the vapour line between the canister(s) and the air intake induct ion elbow. This action allows manifold depression to draw
air through the canister atmospheric vent, taking up the deposited fuel from the charcoal adsorber and burning the resulting
fuel vapour in the engine.
The EVAP Canister Purge Valve is controlled by the engine management system ECM. Purging is carried out in accordance
with the engine management fu eling strategy (see below).
The fuel tank vapour outlet is via a removeable flange assemb ly on the top surface of the tank. The vapour storage canister
or canisters are fitted on the underside of the vehicle below the rear seats.
There are three variants of the evaporativ e system. All systems use the charcoal adsorber storage canisters and purge valve
and operate as described above. The specific features of each system are described below. The evaporative systems are
designated as :
sin g
le canister system
ru
nn
ing loss system
ru
nn
ing loss with On-board Re-fueling Vapour Recovery (ORVR) system
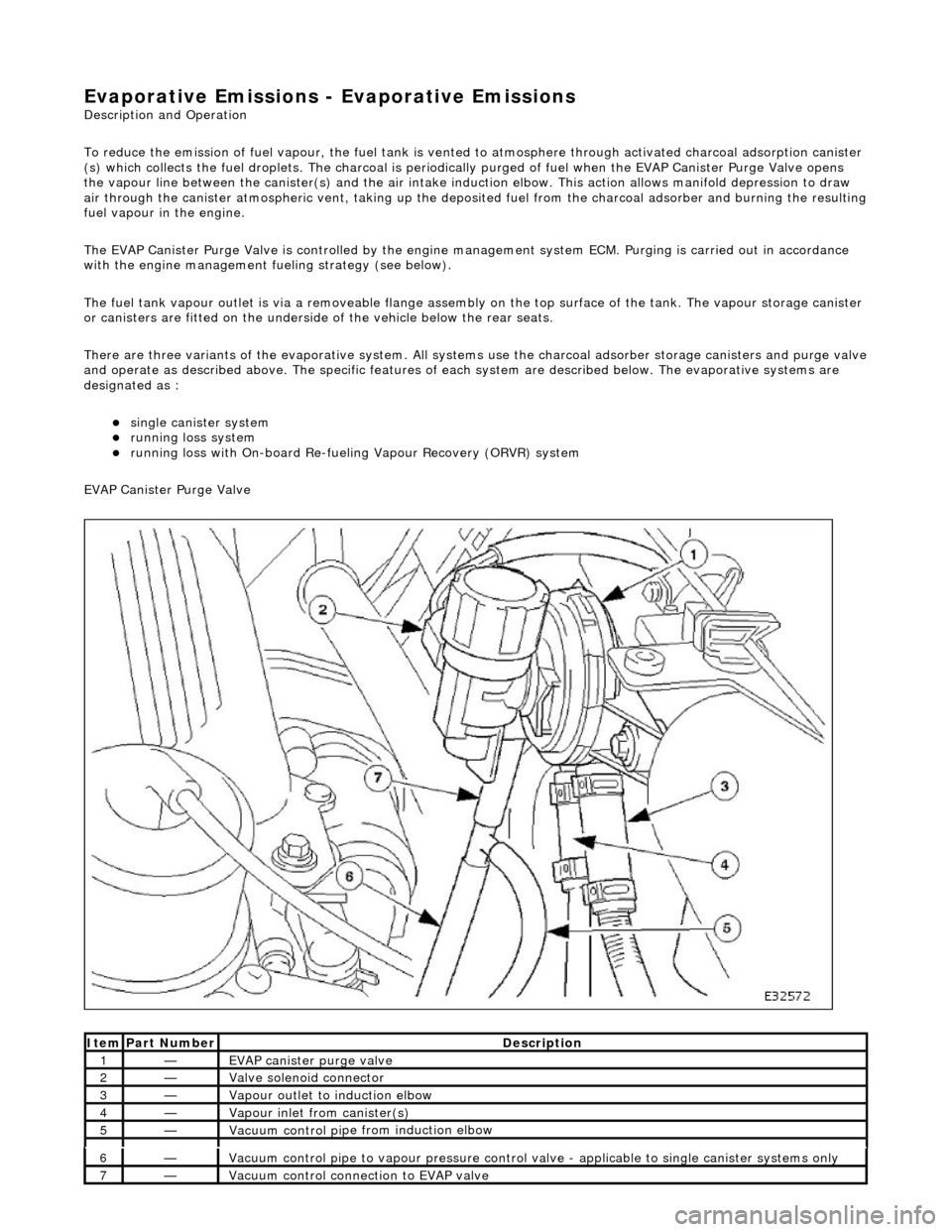
EVAP Canister Purge Valve
Ite
m
Par
t
Number
De
scr
iption
1—EVAP canister purge v
alve
2—Valve s
olenoid connector
3—Vapour outlet to indu
ction elbow
4—Vapour
inlet from canister(s)
5—Vacuum contro
l pi
pe from induction elbow
6—Vacuum contro
l pi
pe to vapour pressure control va
lve - applicable to single canister systems only
7—Vacuum
control connection to EVAP valve
Page 1150 of 2490
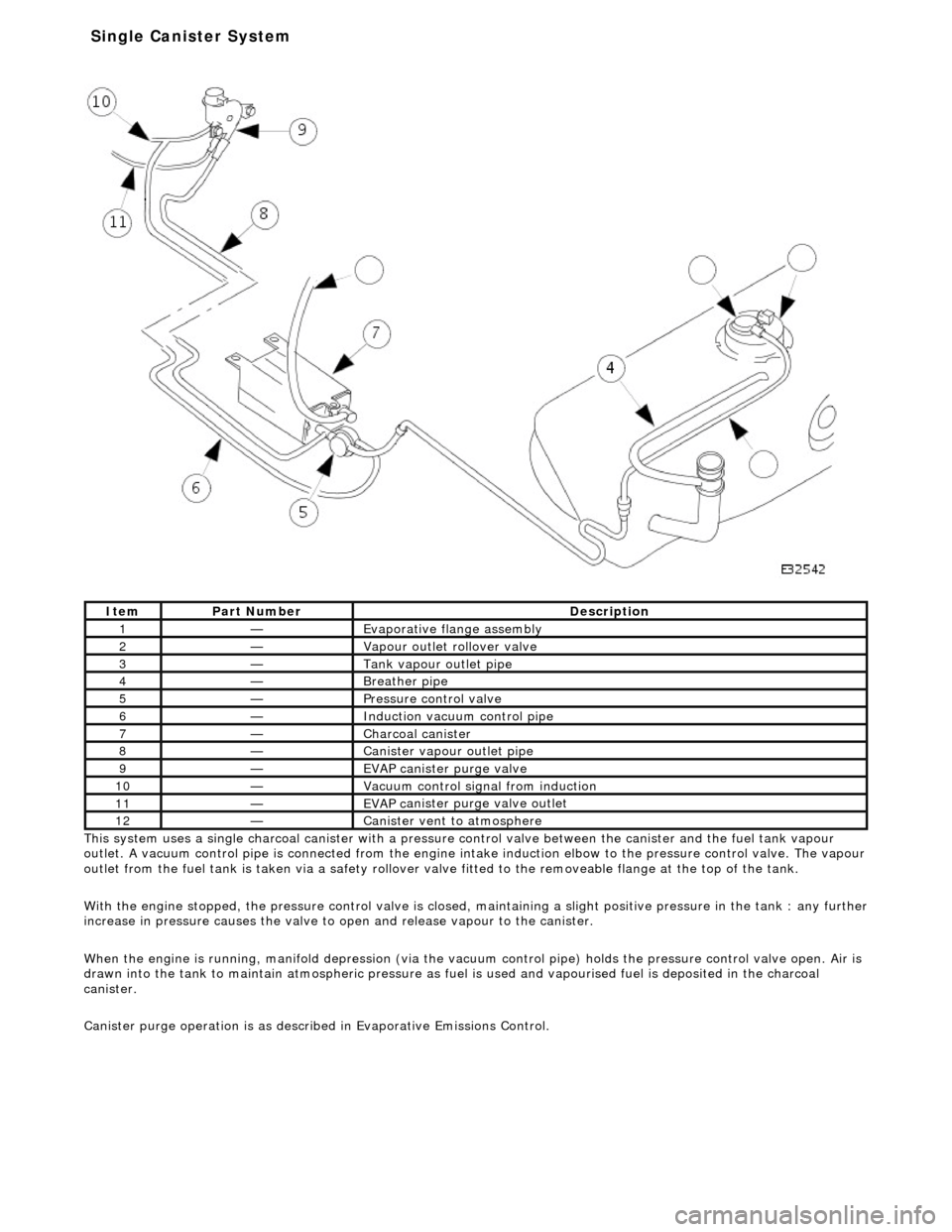
Thi s
system uses a single charcoal canister with a pressure
control valve between the canister and the fuel tank vapour
outlet. A vacuum control pipe is connecte d from the engine intake induction elbow to the pressure control valve. The vapour
outlet from the fuel tank is taken via a safety rollover valve fitted to the re moveable flange at the top of the tank.
With the engine stopped, the pressure control valve is closed, maintaining a slight positive pre ssure in the tank : any further
increase in pressure causes the valve to open and release vapour to the canister.
When the engine is running, manifold depr ession (via the vacuum control pipe) holds the pressure control valve open. Air is
drawn into the tank to maintain atmospheric pressure as fuel is used and vapourised fuel is deposited in the charcoal
canister.
Canister purge operation is as described in Evaporative Emissions Control.
It e
m
Par
t
Number
De
scr
iption
1—Evaporative flan
ge assembly
2—Vapour outlet rol
lover valve
3—Tank vapour outlet pipe
4—Breather
pipe
5—Pressure control valve
6—Induct
ion vacuum control pipe
7—Charcoal can
i
ster
8—Canister vapour outlet pipe
9—EVAP canister purge v
a
lve
10—Vacuu
m
control sign
al from induction
11—EVAP ca
nister purge valve outlet
12—Canist
er vent
to atmosphere
Single Ca
nister System
Page 1151 of 2490
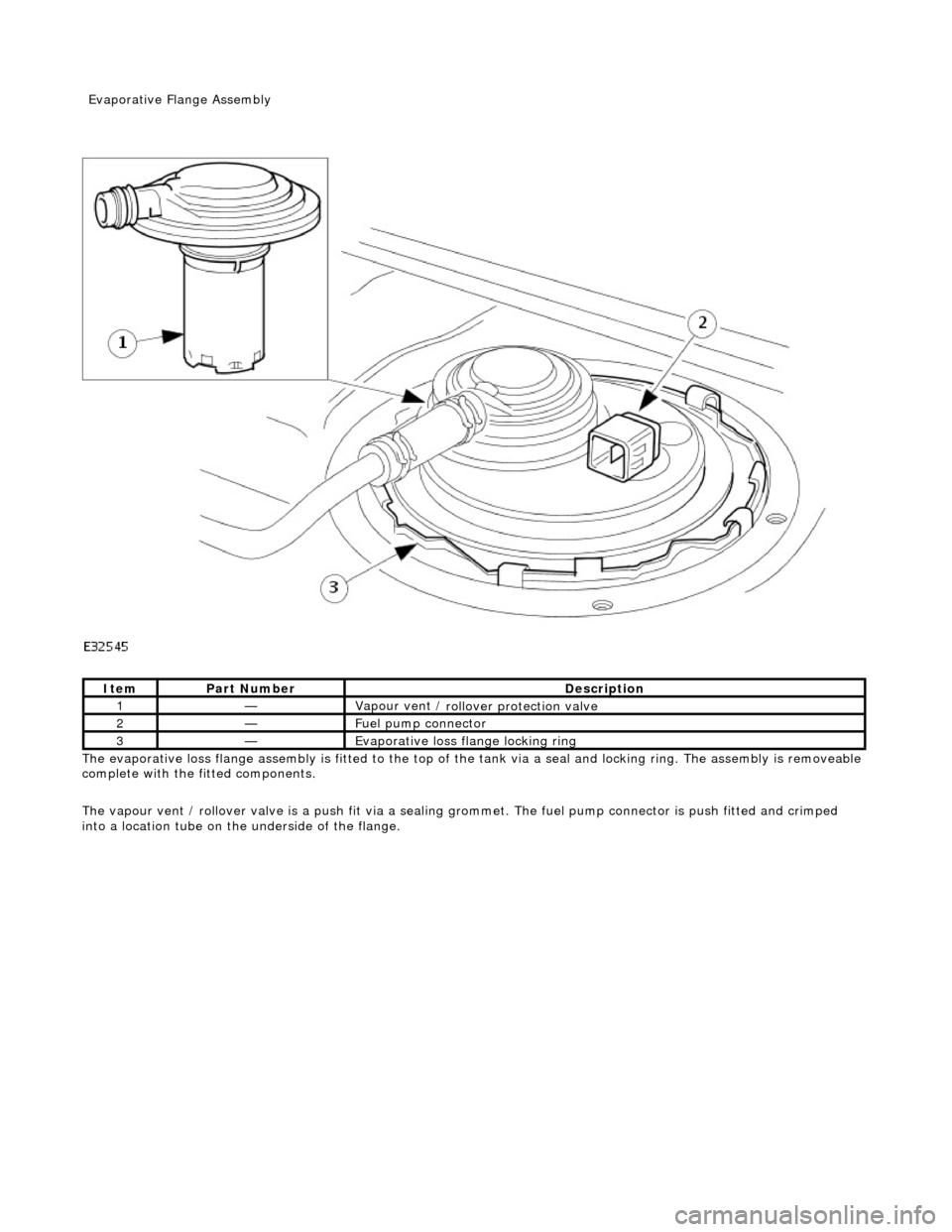
The evaporative l
oss flange assembly is fitted to the top of the tank via a seal and locking ring. The assembly is removeable
complete with the fitted components.
The vapour vent / rollover valve is a push fit via a sealing grommet. The fuel pump connector is push fitted and crimped
into a location tube on the underside of the flange.
It
em
Par
t Number
De
scription
1—Vapour vent /
rollover protection valve
2—Fue
l pump connector
3—Evaporative loss flange locking rin
g
Evaporative Flang
e Assembly
Page 1152 of 2490
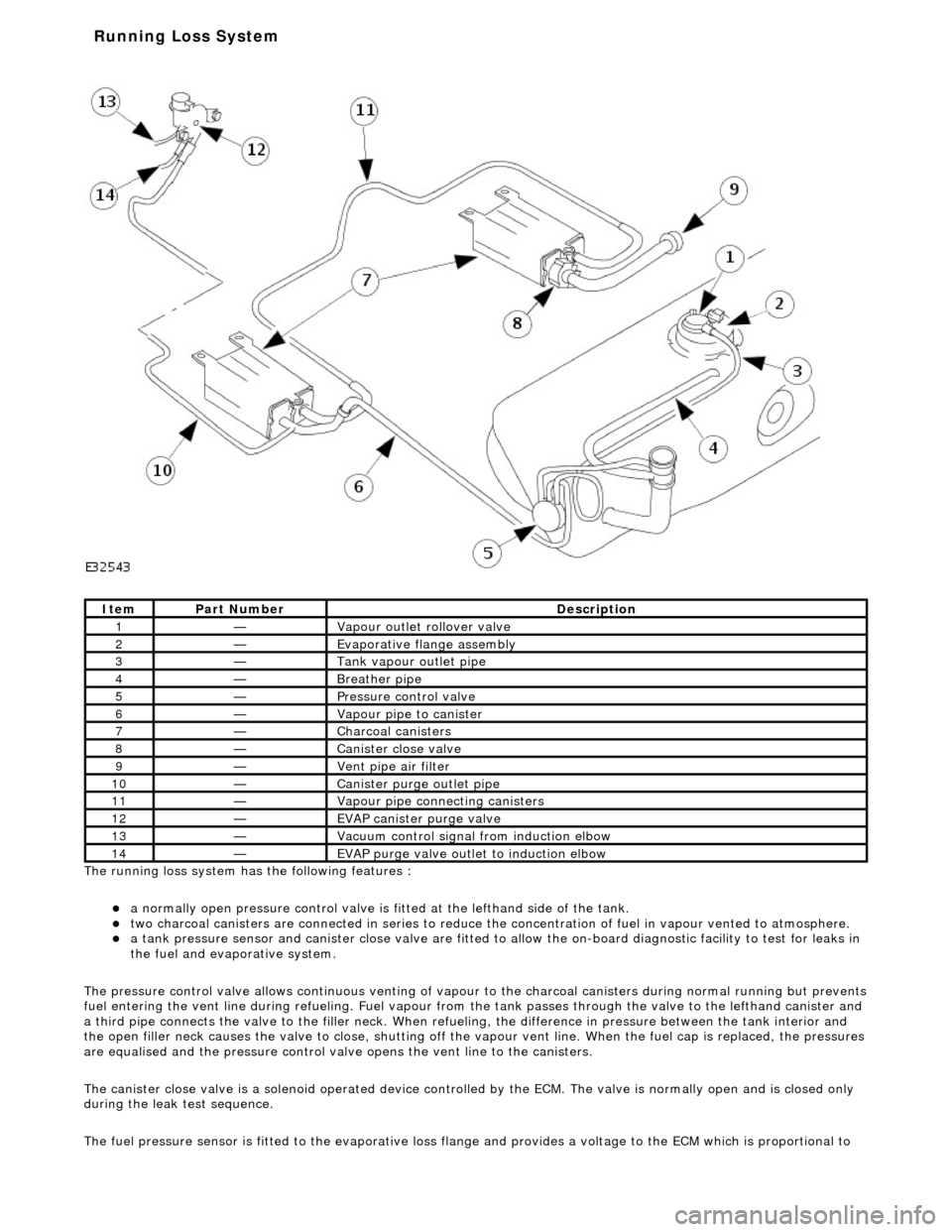
The ru nning loss
system has the following features :
a
normall
y open pressure control valve is fi
tted at the lefthand side of the tank.
two charcoal
canisters are connected in series to reduce th
e concentration of fuel in vapour vented to atmosphere.
a t
ank pressure sensor and canister close
valve are fitted to allow the on-board di agnostic facility to test for leaks in
the fuel and evaporative system.
The pressure control valve allows continuo us venting of vapour to the charcoal canisters during normal running but prevents
fuel entering the vent line duri ng refueling. Fuel vapour from the tank passes through the valve to the lefthand canister and
a third pipe connects the valve to the fill er neck. When refueling, the difference in pressure betw een the tank interior and
the open filler neck causes the valve to cl ose, shutting off the vapour vent line. Wh en the fuel cap is replaced, the pressures
are equalised and the pressure control valve opens the vent line to the canisters.
The canister close valve is a solenoid operated device controlled by the ECM. The valve is normally open and is closed only
during the leak test sequence.
The fuel pressure sensor is fitted to th e evaporative loss flange and provides a volt age to the ECM which is proportional to
Ite
m
Par
t
Number
De
scr
iption
1—Vapour outl
et rol
lover valve
2—Evaporative flan
ge assembly
3—Tank vapour outlet pipe
4—Breather pipe
5—Pressure control
valve
6—Vapour pipe to canister
7—Charcoal cani
sters
8—Cani
st
er close valve
9—Vent pi
pe ai
r filter
10—Canister purge ou
tlet pipe
11—Vapour pipe conn
ecting canisters
12—EVAP canister purge v
a
lve
13—Vacuu
m
control signal from induction elbow
14—EVAP pu
rge valve outlet to induction elbow
Running Loss Sys
tem
Page 1153 of 2490
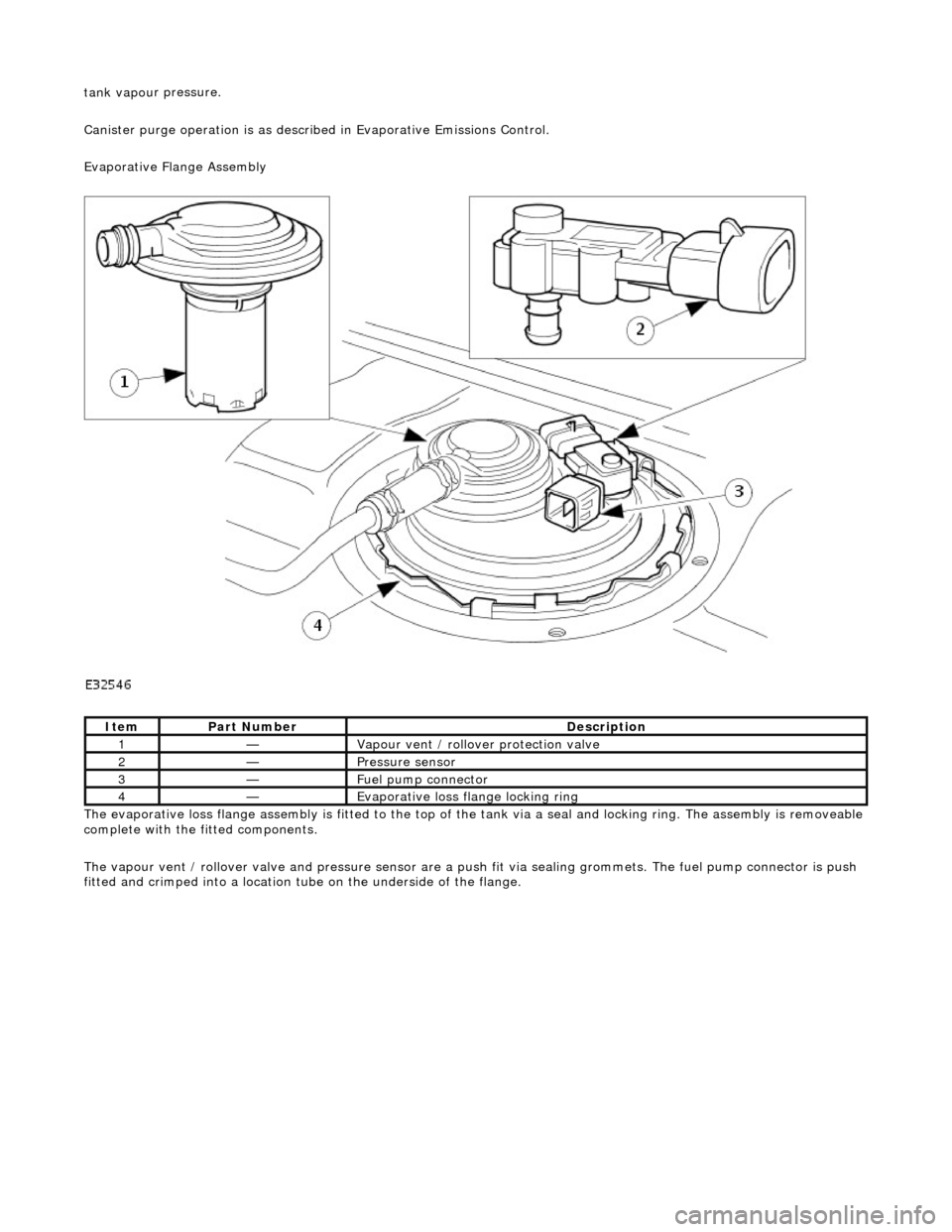
tank vapou
r pressure.
Canister purge operation is as described in Evaporative Emissions Control.
Evaporative Flange Assembly
The evaporative loss flange assembly is fitted to the top of the tank via a seal and locking ring. The assembly is removeable
complete with the fitted components.
The vapour vent / rollover valve and pressure sensor are a pu sh fit via sealing grommets. The fuel pump connector is push
fitted and crimped into a location tu be on the underside of the flange.
It
em
Par
t Number
De
scription
1—Vapour vent /
rollover protection valve
2—Pres
sure sensor
3—Fue
l pump connector
4—Evaporative loss flange locking rin
g
Page 1156 of 2490
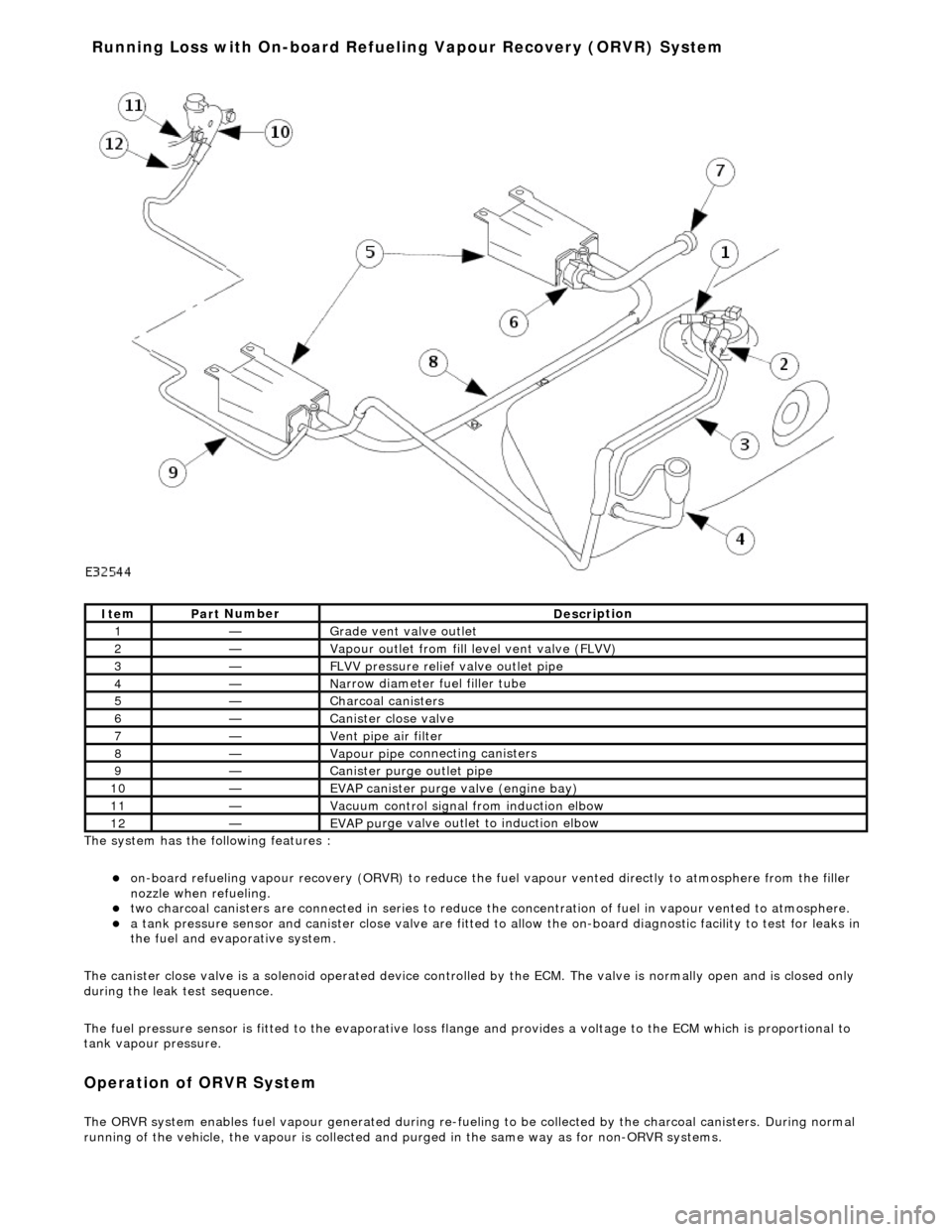
The system has the
following features :
o
n
-board refueling vapour recovery (ORVR) to reduce the fu
el vapour vented directly to atmosphere from the filler
nozzle when refueling.
two ch arcoal
canisters are connected in series to reduce th
e concentration of fuel in vapour vented to atmosphere.
a t
ank pressure sensor and canister close
valve are fitted to allow the on-board di agnostic facility to test for leaks in
the fuel and evaporative system.
The canister close valve is a solenoid operated device controlled by the ECM. The valve is normally open and is closed only
during the leak test sequence.
The fuel pressure sensor is fitted to th e evaporative loss flange and provides a volt age to the ECM which is proportional to
tank vapour pressure.
Op era
tion of ORVR System
The ORVR system enabl
e
s fuel vapour generated during re-fueling to be collected by
the charcoal canisters. During normal
running of the vehicle, the vapour is collected and purged in the same way as for non-ORVR systems.
Ite
m
Par
t
Number
De
scr
iption
1—Grade vent
valve outl
et
2—Vapour outl
et from fil
l level vent valve (FLVV)
3—F
L
VV pressure relief valve outlet pipe
4—N
a
rrow diameter fuel filler tube
5—Charcoal can
i
sters
6—Cani
st
er close valve
7—Vent pi
pe ai
r filter
8—Vapour pipe
conn
ecting canisters
9—Canister purge ou
tlet pipe
10—EVAP canister purge v a
lve (engine bay)
11—Vacuu
m
control signal from induction elbow
12—EVAP pu
rge valve outlet to induction elbow
Running Loss with On-board R
efuelin
g Vapour Recovery (ORVR) System