Page 469 of 2490

Buzz (E
lectrical)
A
different steering buzz can be caused by
pulse width modulated (PWM) electric actuators used in variable assist steering
systems. This buzz is felt by turning the ignition key to run without starting the engine and holding onto the steering wheel.
In extreme cases, the buzz can be felt with the engine running also.
Column/Steering Wheel
Shake
Column shake is a low f
requenc
y vertical vibration excited by primary engine vibrations.
Nibble (Shimm
y)
Steeri
ng nibble is a rotary oscillation or
vibration of the steering wheel, which can be excited at a specific vehicle speed.
Nibble is driven by wheel and tire imbalance exciting a suspensi on recession mode, which then translates into steering gear
travel and finally steering wheel nibble.
Shudder (Judd
er)
Shudder i
s a low frequency oscillation of th
e entire steering system (tire, wheels, st eering gear and linkage, etc.) when the
vehicle is steered during static-park or at low sp eeds. Shudder is very dependent on road surface.
Torque Ri
pple
Torque rippl
e is a concern with Electric Power Steering (EPS) sy
stems. Torque ripple is most evident at static-park steering
the wheel very slowly from lock to lock. Torque ripple is primarily caused by motor commutation.
Torque/Veloc
ity Variation
(Phasing/Effort Cycling)
Steeri
ng wheel torque variation oc
curring twice in one revolution is normally as a result of problems with the lower steering
column (intermediate shaft), but foul cond itions generally result in either constant stiffnes s or single point stiffness.
Depending upon the orientation of the joints, the steering can fe el asymmetric (torque falling off in one direction and rising
in the other) or else it can simply have pronounced peaks and troughs as the steering moves from lock to lock.
Wheel Fight
(Kick Back)
W
heel fight is excess feedback of sudden road forces through th
e steering system and back to the driver. It is evaluated at
all vehicle speeds over cobblestones, rough roads, and potholes . The tires, wheels, and suspension generate forces into the
steering systems. Steering friction, hydraulic damping, hydr aulic compliance, mechanical compliance, steering ratio, and
assist gain all affect how much is transmitted to the driver.
Stee
ring Linkage
CAUTI
ON: Steering gear boots must be
handled carefully to avoid damage. Use new clamps when installing steering
gear boots.
Inspect the boots for cuts, deterioration, tw isting or distortion. Check the steering gear boots to make sure they are tight.
Install new boots or clamps as necessary.
• NOTE: The following steps must be carried out with assistance.
1. 1. With the wheels in the straight ahead po sition, gently turn the steering wheel to the left and the right to check for
free play.
2. 2. Free play should be between 0 and 6 mm (0 and 0.24 in) at the steering wheel rim. If the free play exceeds this
limit, either the ball joints are worn, the lower steering column joints are worn or the backlash of the steering gear
is excessive.
Page 508 of 2490
The te
lescopic slider provides driver crash
protection by retracting automatically in the event of an accident; it is clamped in
position to a preset torque.
The motorized upper steering column has the following serviceable parts:
Igniti
on switch assembly.
Igni
ti
on key interlock solenoid.
Ti
lt
motor assembly.
Reach motor assembly.
Manu al Upper Column Assembly
Ite
m
Par
t
Number
De
scr
iption
1-L
o
wer mounting bracket
2-Crash tube
3-Harnes
s c
onnector bracket
4-Tilt motor
5-Reach m
otor
6-Upper
moun
ting bracket
7-Ignition switc
h
(hidden)
8-Igni
ti
on key interlock solenoid
9-S
t
eering wheel mounting shaft
It
e
m
Par
t
Number
De
scr
iption
1-Upper
cowl
2-Lower cowl
3-Colu
mn tilt adjustment lever
4-Col
u
mn reach adjustment lever
5-Di
mm
er switch
Motorized Upper Co
lumn Components
Page 509 of 2490

Is adjustable for both til
t and reach.
Has ca
ble operated reach adjustment, using a rack an
d wedge, with approximately 16 latched positions.
Has si
x latched tilt positions steppe
d at approximately 3° intervals.
Has an u
nlatched top tilt position, allowing the column to be
pulled down to engage the first detent without using the
tilt lever.
Has an instrument li
ghti
ng dimmer switch installed on the left-hand side of the lower cowl.
Manual Upper Column Components
The telescopic slider provides driver crash protection by retracting automatically in the event of an accident; it is clamped in
position to a preset torque.
The manual upper steering column has the following serviceable parts:
Igni
tion switch assembly.
Igni
tion key interlock solenoid.
Bowden
cable and lever assembly.
It
em
Par
t Number
De
scription
1-L
ower mounting bracket
2-Crash tube
3-Harnes
s connector bracket
4-Upper
mounting bracket
5-Ignition switc
h (hidden)
6-Igni
tion key interlock solenoid
7-S
teering wheel mounting shaft
The manu
al upper
steering column:
Page 515 of 2490
Steering Column Switches - Steering Column Switches
Description an
d Operation
Ig
nition Switch
The k
ey-operated ignition switch is located on the right-hand side of the steering colu
mn and has four positions.
Position 'O'
OFF. The only position in which the key can be inserted or re moved. With the key removed, the steering lock engages. The
key can only be removed when the tran smission is in the Park position.
Position 'I'
AUXILIARY. Certain circuits , i.e. radio and windows, can be operat ed without switching on the ignition.
Position 'II'
Page 516 of 2490

IGNITION.
All circuits, except the star
ter motor, are activated. The key rema ins in this position when driving.
Position 'III'
START. The starter operates for as long as the key is held in this position, ag ainst spring pressure. If the engine fails to
start, the key must be returned to position 'I' befo re another start is attempted.
Lighting Switch
The li
ghting switch is on the left-h
and side of the steering column and controls the following functions.
Direction Indicators
The direction in
dicators:
Operate
when the ignition switch is in position II.
Are operat
ed by movi
ng the switch stalk up or down until it latches in position, to in
dicate a right or left turn
respectively.
Can be o p
erated while the switch stalk is held against
spring pressure before reaching the latch position.
Cancel
automatically upon completion of a turn, the
column switch returning to the center position.
An audible ticking and a flashing green warning lamp on the in strument cluster indicate that the direction indicators are
Ite
m
De
scr
iption
1D
i
rection indicator LH or RH position
2All lamps OFF
3Side
lamps ON
4Headlamps ON
5Headlamps AUT O
(where fitted)
6He
adlam
p main beam position
7Mai
n
beam flash position
8M
e
ssage center function button
Page 928 of 2490
combin
ed with the outlet duct and consequently, there is no separate housin
g assembly fitted above the water pump, as used
on the normally aspirated engine. The illustration shows the outlet duct viewed from the engine.
Thermostat Housing
The plastic housing for the thermostat is fitted between th e two cylinder banks immediately above the coolant pump.
Controlling the coolant flow through the radiator, the thermostat starts to open at 80 ° to 84 °C and is fully open at 96 °C.
A duct in the cylinder block connects the thermostat housing outlet to the coolant pump inlet. The joint between the
thermostat housing and the cylinder block is via an in-groove seal.
An air bleed outlet vents an y air in the system into the expansion reservoir, durin
g normal operation. A removable cap (usin g
a hex key) allows air to vent from the system when filling from empty.
On supercharged engines, the thermostat housin g is combined with the coolant outlet duct.
Radiator
Page 1062 of 2490
Starting System - Starting System
Description and Operation
Manufacturer - NipponDenso
Type - RA1.4.
Weight - 3.75 kg (8.27 lb)
Output - 1.4 kW
Rated Time - 30 seconds
Rotation - Clockwise, viewed from pinion end
The starter is of the pre-engaged type; loca ted at the rear left-side of the engine.
When the starter is operated from the key-switch, the engagement lever moves the pinion into mesh with the engine ring
gear teeth, the electrical contacts within the solenoid complete the high power circuit and the starter motor operates to turn
the engine.
Starter Relay
The starter motor control relay is, relay nu mber 5, located inside the engine compartment enclosure (left side of vehicle
RHD and right side of vehicle on LHD).
Page 1064 of 2490
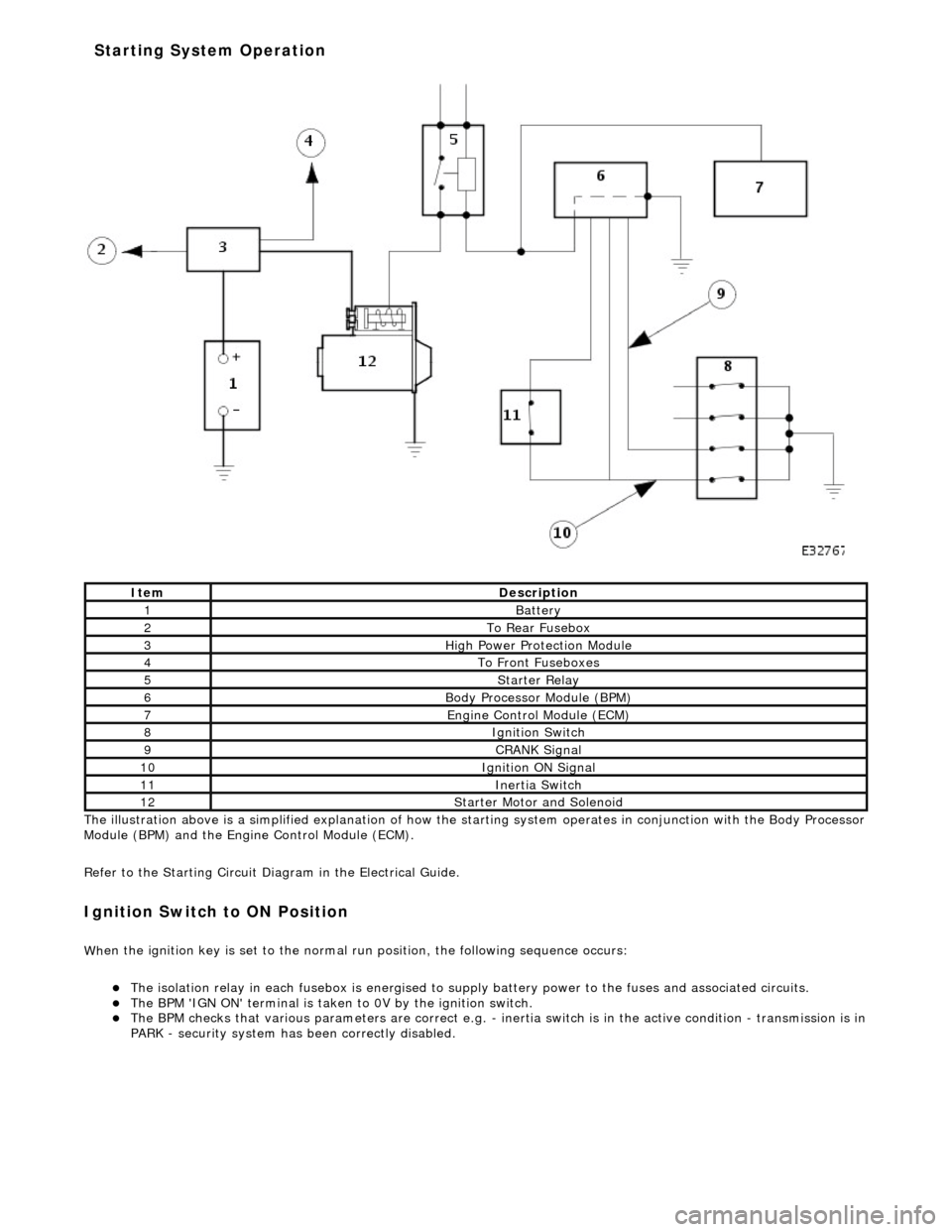
The il
lustration above is a simplified expl
anation of how the starting system operates in conjunction with the Body Processor
Module (BPM) and the Engine Control Module (ECM).
Refer to the Starting Circuit Diagram in the Electrical Guide.
I g
nition Switch to ON Position
W
h
en the ignition key is set to the normal run position, the following sequence occurs:
The
is
olation relay in each fusebox is
energised to supply battery power to the fuses and associated circuits.
The BPM 'IGN
ON' terminal
is taken to 0V by the ignition switch.
The BPM
checks that various parameters are correct e.g. -
inertia switch is in the active condition - transmission is in
PARK - security system has been correctly disabled.
It e
m
De
scr
iption
1Batt
ery
2To Re ar
Fusebox
3Hi
gh Power Pr
otection Module
4To Front
Fu
seboxes
5Starter Re
lay
6Body Processor M
odule (BPM)
7Engine
C
ontrol Module (ECM)
8Ignition Switch
9CRANK Signal
10Ignition ON Signal
11Inertia Switch
12St
arte
r Motor and Solenoid
Starting System Operation