1998 JAGUAR X308 Drive shaft
[x] Cancel search: Drive shaftPage 1027 of 2490
Ignition coil
failure(s)
HT sho
rt to ground (tracking)
check rubber boots for cracks/damage
Spark plug
failure/fouled/incorrect
gap
Cy
linder compression low
F
uel delivery pressure (low/high)
F
uel injectors restricted/leaking
Fuel contamination
P
AS pulley bolts loose (see Service
Action S462)
W
orn camshaft/broken valve
springs
P
inpoint Test
A.
.
Check fuel
pressure,
REFER to Section 310
-00
Fuel
Sy
stem
- General
Information
.
Chec
k fuel injectors,
REFER to Fuel Injectors
- in t
his
section.
Check service actions.
P0301Misfire
detected, Cyl 1
R
EFER to possible sources for P0300
R
EFER to actions for P0300.
P0302Misfire
detected, Cyl 3
P0303Misfire
detected, Cyl 5
P0304Misfire
detected, Cyl 7
P0305Misfire
detected, Cyl 2
P0306Misfire
detected, Cyl 4
P0307Misfire
detected, Cyl 6
P0308Misfire
detected, Cyl 8
P0460F
uel level sense signal performance
Fue
l level sensor
to instrument
cluster circuits in termittent short
or open circuit
F
uel level sensor failure
Instrument cluster
faul
t (incorrect
fuel level data)
F
or fuel level sensor tests,GO to
Pinpoint Test B.
.
P1224Throttl
e control position error
Thro
ttle adaptations not performed
after battery disconnect
TP se
nsor disconnected
TP se
nsor to ECM sense circuits;
open circuit, hi gh resistance
Throttl
e motor relay failure
Th
rottle motor relay to ECM circuit
fault
Throttl
e motor relay power supply
open circuit
ECM ground circuit faul
t (relay coil
drive)
Throttl
e motor to ECM drive
circuits; open circuit, short circuit, high resistance
Throttl
e motor failure
Throttl
e body failure
Carry
out the throttle adaptation
procedure,
REFER to Section 303
-14
Electronic
Engine
Controls
.
ECM adaptations. For
throttle motor
relay tests, throttle position sensor tests, ECM ground tests,
REFER to Section 303
-14
Electronic
Engine
Controls
.
P1229Throttl
e motor control circuit
malfunction
Throttl
e motor disconnected
Throttl
e motor to ECM drive
circuits; short circuit or open circuit
Throttl
e motor failure
Fo
r throttle moto
r relay tests,
REFER to Section 303
-14
Electronic
Engine
Controls
.
P1250Engine
load malfunction
Air
intake leak
Engine
breather leak
TP se
nsor circuit fault (DTC P0121)
Throttl
e valve spring failure
F
or air intake system,
REFER to Section 303
-12
Intake Air
Distribu
tion and Filtering
.
Chec
k engine breather system for
leaks. For TP sensor tests,
REFER to Section 303
-14
Electronic
Engine
Controls
.
P1313Right-hand cylinders misfire rate
cat
alyst damage (this DTC will flag
only when accompanied by an
individual cylinder misfire DTC: P0300-P0308)
R
efer to possible causes for P0300-P0308
R
efer to actions for P0300-P0308.
P1314L
eft-hand cylinders misfire rate
catalyst damage (this DTC will flag only when accompanied by an
individual cylinder misfire DTC: P0300-P0308)
R
efer to possible causes for P0300-P0308
R
efer to actions for P0300-P0308.
Page 1040 of 2490
Fuel Char
ging and Controls - Fu
el Injectors4.0L SC V8 - AJ26
Remo
val and Installation
Remov
a
l
Installation
1. Disc onne
ct battery ground cable (IMPORTANT, see SRO
86.15.19 for further information).
2. WARNING: BEFORE PROCEEDING, IT IS ESSENTIAL THAT
THE WARNING NOTES GIVEN IN SECTION 100-00 (UNDER THE
HEADING 'SAFETY PRECAUTIONS') ARE READ AND
UNDERSTOOD.
Depressurize fuel syst em; refer to 19.50.02.
3. Drain radiator coolant; refer to 2
6.10.01.
4. Remove air cleaner cover / inta ke assembly; refer 19.10.30.
5. Remove throttle body; refer to 19.70.04.
6. Remove throttle induction elbo w; refer to (SC) 19.70.28.
7. Remove exhaust gas re-circulation valve (EGR) if fitted; refer
to 17.45.01.
8. Remove supercharger outlet duct and gasket; refer to
18.50.16.
9. Remove coolant outlet pipe; refer to (SC) 26.31.08 .
10. Remove supercharger drive belt; refer to 18.50.08.
11. Remove supercharger assembly; refer to 18.50.15.
12. Remove bank 1 or 2 charge air cooler as required; refer to
18.50.18 and / or 18.50.19.
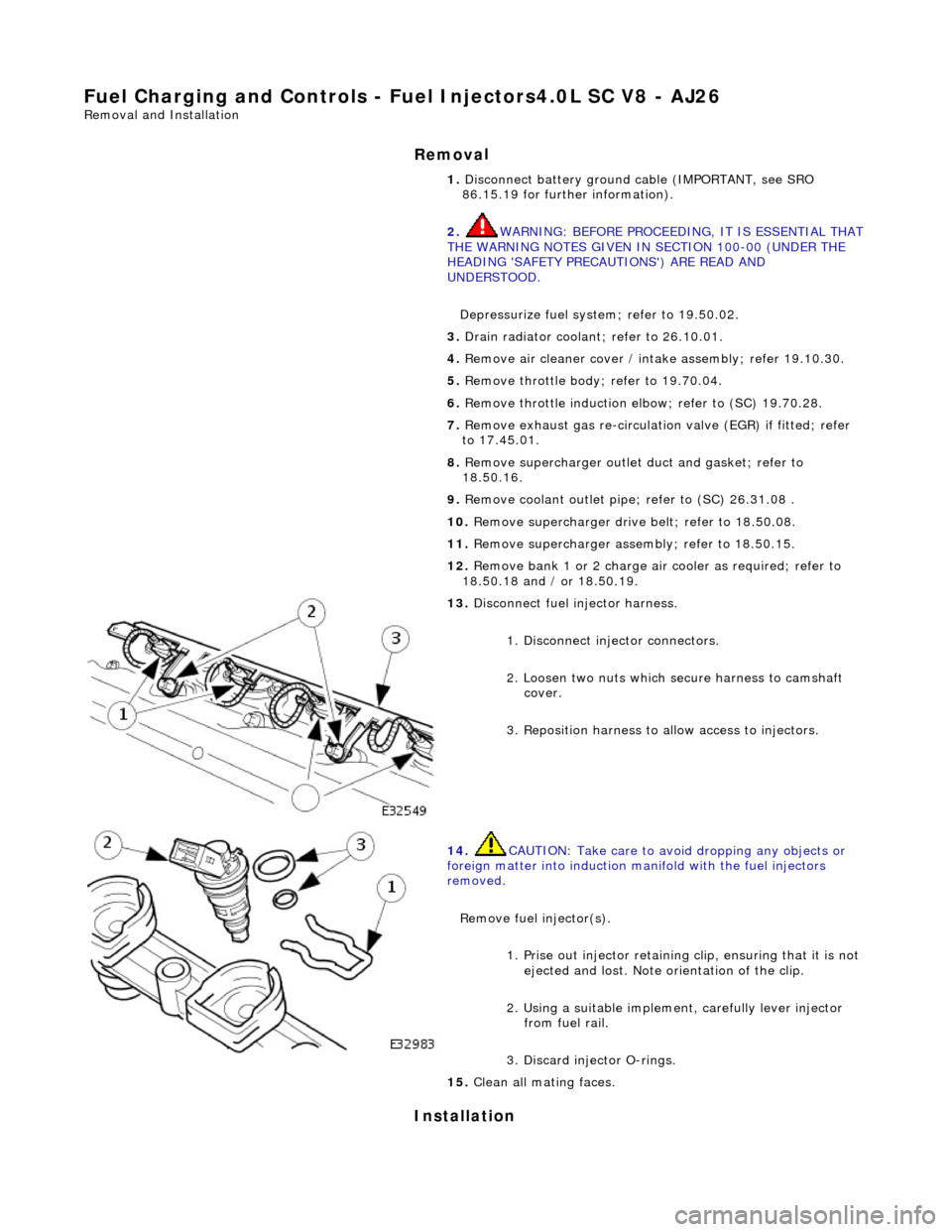
13 . Di
sconnect fuel injector harness.
1. Disconnect injector connectors.
2. Loosen two nuts which se cure harness to camshaft
cover.
3. Reposition harness to al low access to injectors.
14. CAUTI
ON: Take care to avoi
d dropping any objects or
foreign matter into induction ma nifold with the fuel injectors
removed.
Remove fuel injector(s). 1. Prise out injector retaining clip, ensuring that it is not
ejected and lost. Note orientation of the clip.
2. Using a suitable implemen t, carefully lever injector
from fuel rail.
3. Discard injector O-rings.
15 . Cle
an all mating faces.
Page 1049 of 2490
Accessory Drive - Accessory Drive
Description an
d Operation
Parts List
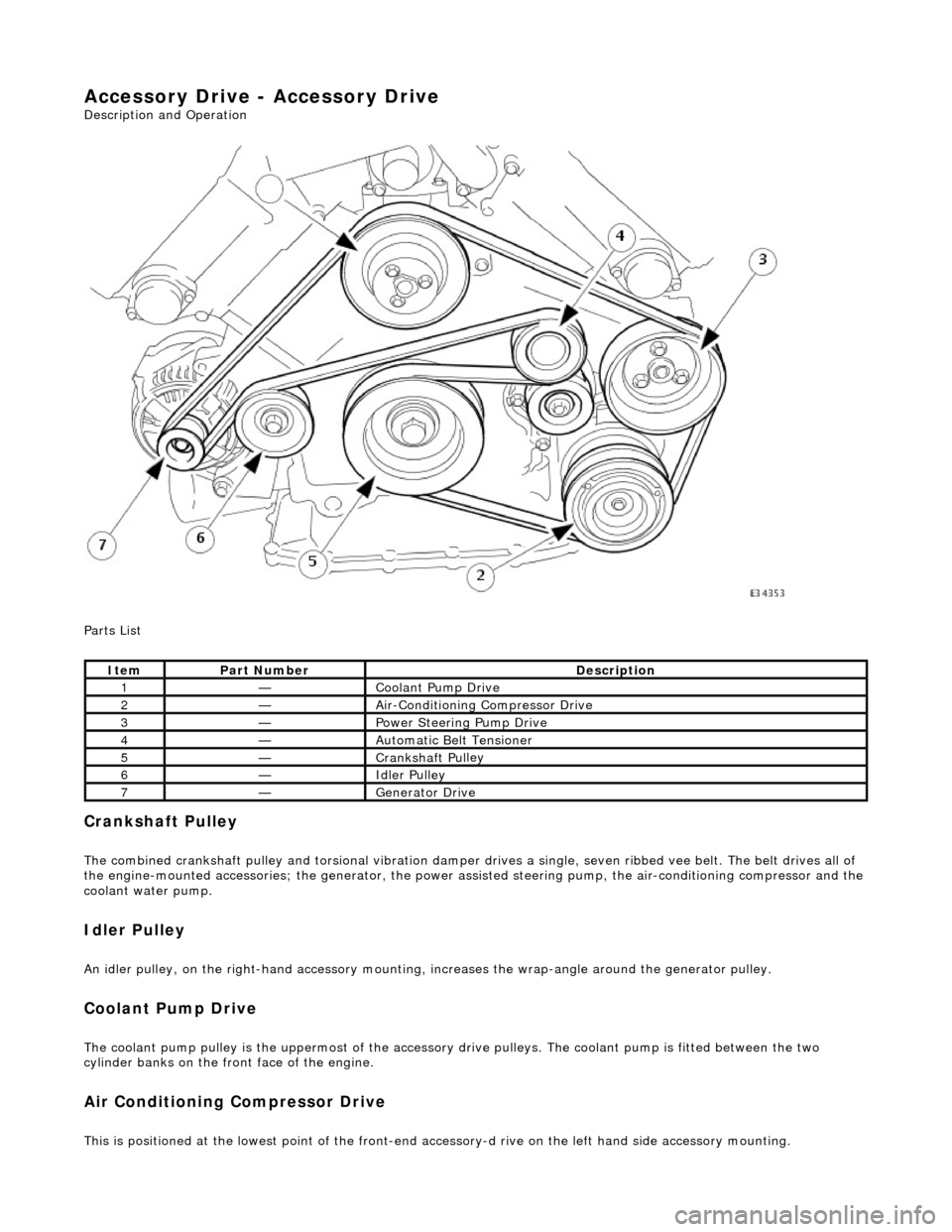
Cran
kshaft Pulley
The combined crankshaft
pulley and torsio
nal vibration damper drives a single, seve n ribbed vee belt. The belt drives all of
the engine-mounted accessories; the generator, the power assi sted steering pump, the air-conditioning compressor and the
coolant water pump.
I
dler Pulley
An i
dler pulley, on the right-hand
accessory mounting, increases the wrap-angle around the generator pulley.
Coolant Pump Drive
The coolan
t pump pulley is the
uppermost of the accessory drive pulleys. Th e coolant pump is fitted between the two
cylinder banks on the front face of the engine.
Air Conditioning Compressor Drive
Thi
s is positioned at the lowest poin
t of the front-end accessory-d rive on the left hand side accessory mounting.
It
em
Par
t Number
De
scription
1—Coo
lant Pump Drive
2—Ai
r-Conditioning Compressor Drive
3—Power Steer
ing Pump Drive
4—Au
tomatic Belt Tensioner
5—Crankshaft Pul
ley
6—Idle
r Pulley
7—Generator Dri
ve
Page 1063 of 2490

Th
e starter drive plate is attached to the rear of the crankshaft by eight bolts.
Timing Disc
A timing disc, for the engine speed sensor, is spot-w elded to the front face of the starter drive plate.
Starter Drive Plate
Page 1109 of 2490
P
arts List
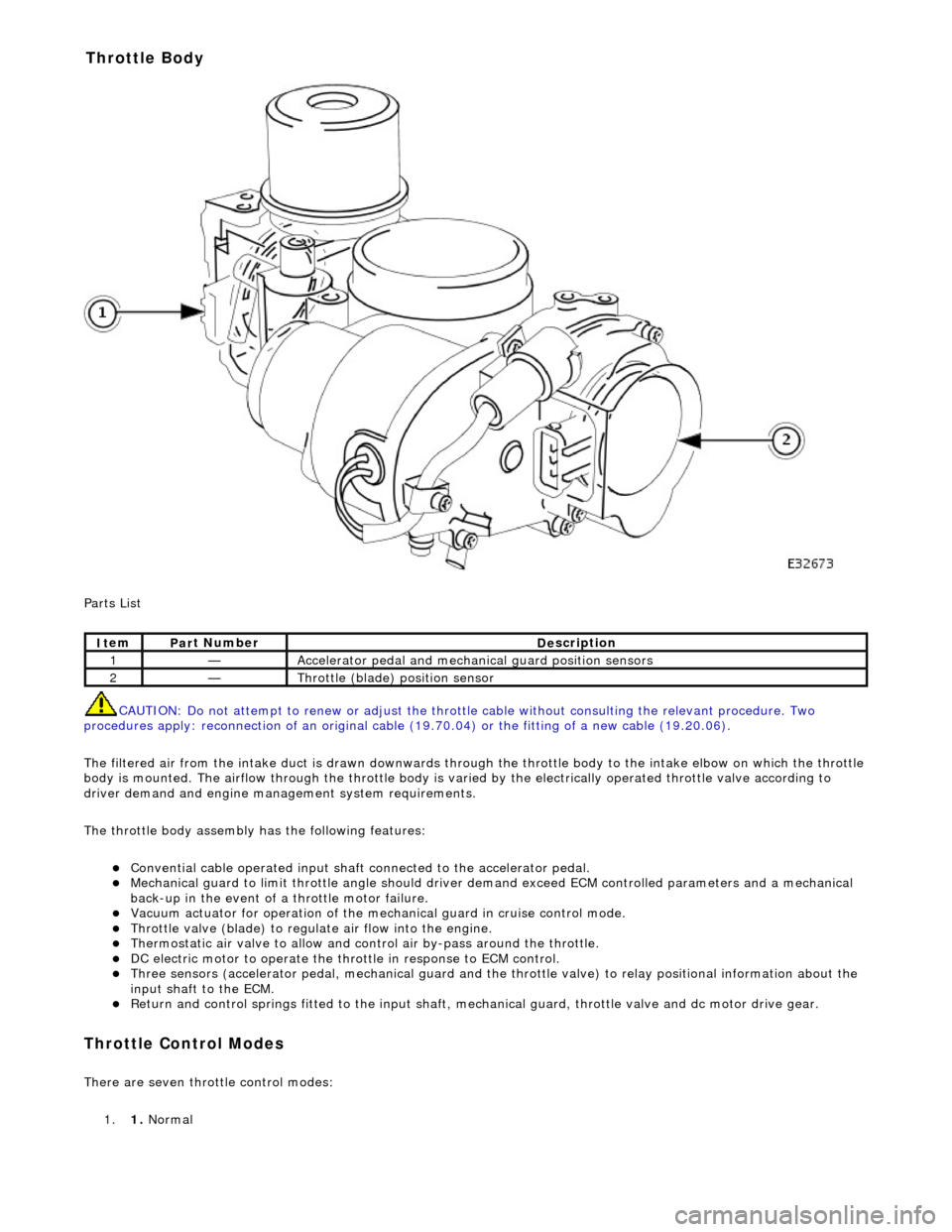
CAUTION: Do not attempt to renew or adjust the throttle cable without consulting the relevant procedure. Two
procedures apply: reconnection of an original cable (19.70.04) or the fitting of a new cable (19.20.06).
The filtered air from the intake duct is drawn downwards through the throttle body to the intake elbow on which the throttle
body is mounted. The airflow through the throttle body is vari ed by the electrically operated throttle valve according to
driver demand and engine mana gement system requirements.
The throttle body assembly has the following features:
Con
vential cable operated input shaft connected to the accelerator pedal.
M
echanical guard to limit throttle angl
e should driver demand exceed ECM co ntrolled parameters and a mechanical
back-up in the event of a throttle motor failure.
Vacuum actuator for operation of the mech anical guard in cru
ise control mode.
Thr
ottle valve (blade) to regula
te air flow into the engine.
Thermostatic air valve to allow and con
t
rol air by-pass around the throttle.
D
C electric motor to operate the thro
ttle in response to ECM control.
Three
sensors (accelerator pedal, mechan
ical guard and the throttle valve) to relay positional information about the
input shaft to the ECM.
R
eturn and control springs fitted to th
e input shaft, mechanical guard, thro ttle valve and dc motor drive gear.
Throttle Cont
rol Modes
There are seven throttle control
modes:
1. 1. Normal
It
em
Par
t Number
De
scription
1—Acce
lerator pedal and mechanic
al guard position sensors
2—Throttl
e (blade)
position sensor
Throttle Body
Page 1110 of 2490

2.2. Cruise
3. 3. Mechanica l
guard
4. 4. Fixed idle
5. 5. Redundancy
6. 6. Full authority
7. 7. Engine shut-down
Normal mode occurs when the EC M uses the mechanical and monitoring arrangem ent of the throttle valve to control throttle
opening. The ECM does not permit driver demand to be exceeded but it can be restricted to allow for such features as
stability / traction control, or engine power limitation.
The ECM determines engine idle speed by controlling the throttle valve motor to vary the blade angle between the non-
adjustable preset limits of the mechanic al guard and the throttle valve motor.
Cruise mode is engaged as a result of the ECM calculating and controlling the required throttle valve opening via the
vacuum system. When the driver releases the throttle pedal, the input shaft disengages from the mechanical guard or the
vacuum actuator pulls the guard away from th e throttle valve. The throttle pedal will feel light should it be pushed again to
accelerate (pressing the pedal further will re-engage the input shaft with the mechanical guard and restore normal feel).
The ECM utilizes sensors to monitor the relative positions of the mechanical guard and throttle valve and adjusts them to
maintain the set cruise speed.
Mechanical guard mode permits full mechanical operation of the throttle if the ECM detects that a problem has been
encountered with the throttle valve position sensor, dc motor, associated harnesses / connecto rs or the ECM.
Fixed idle mode occurs when any two of the three sensors (two input shaft sensors and the mechanical guard sensor) fail.
The ECM will assume values which represent a blade angl e of approximately 2,5° and 1200 rpm (unloaded) maximum
engine speed.
Redundancy mode occurs when any one of the three sensors (two input shaft sensors and the mechanical guard sensor)
fails. The operational pair will be deemed to be safe to co ntinue without intervention, but cruise will be inhibited.
Full authority mode is invoked when a mech anical guard failure occurs which indicates that the guard is stuck fully open.
The red warning lamp will be lit and road speed will be li mited to 120 kph.
Engine shut-down mode will occur followin g multiple failures, such as mechanical guard mode following full authority mode
(or vice versa) or the throttle blade sticks.
Intake Elbow
The intake elbow directs the metered airflow from the electronic throttle to the intake manifold. Stub pipes on both sides of
Page 1178 of 2490
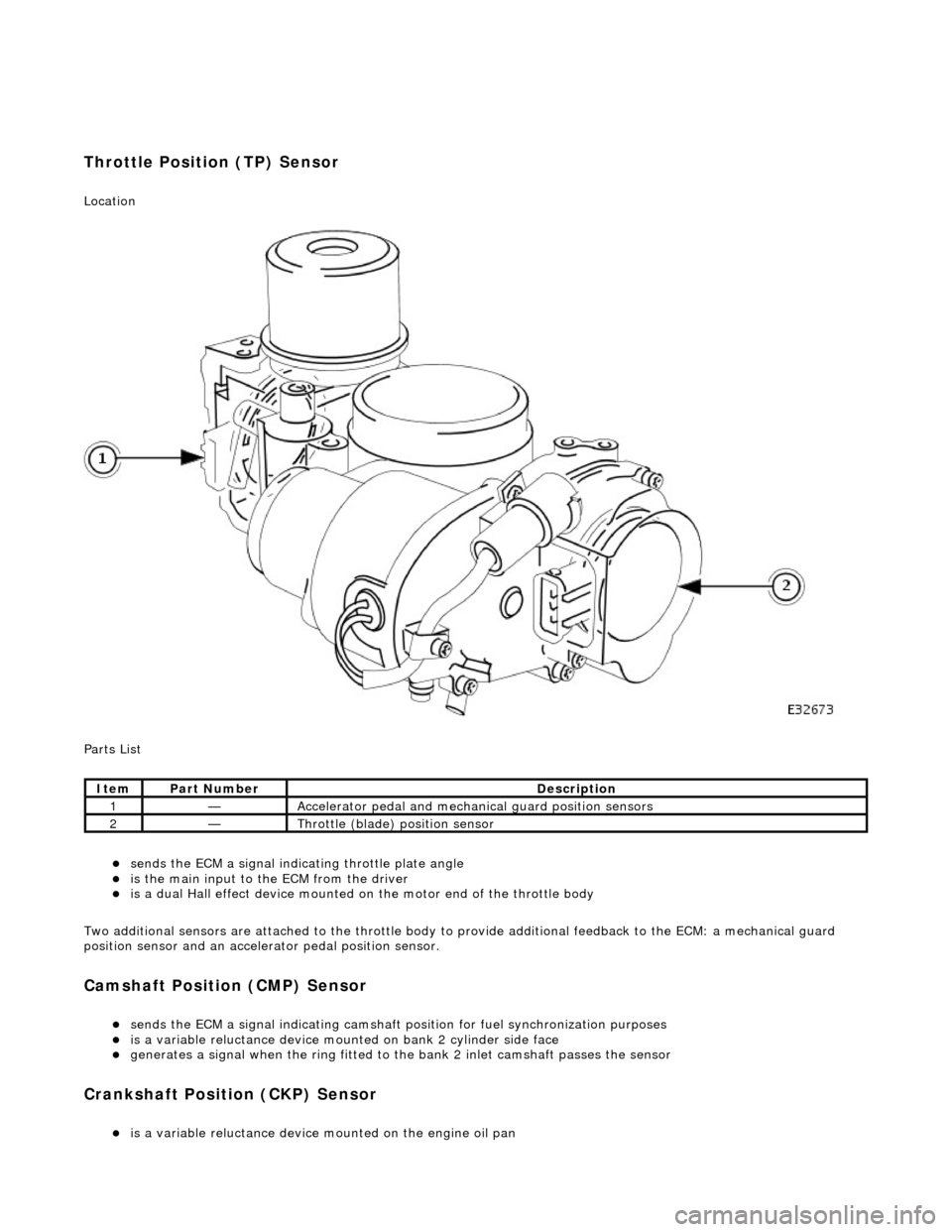
Throttle Position (TP) Sensor
Location
P
arts List
sen
d
s the ECM a signal indica
ting throttle plate angle
is
the main input to the ECM from the driver
i
s
a dual Hall effect devi
ce mounted on the motor en d of the throttle body
Two additional sensors are attached to the throttle body to provide additional feedback to the ECM: a mechanical guard
position sensor and an accelerator pedal position sensor.
Cam s
haft Position (CMP) Sensor
sen
d
s the ECM a signal indicating camshaft po
sition for fuel synchronization purposes
is
a variable reluctance device mounted on bank 2 cylinder side face
generates a signal when the ri
ng
fitted to the bank 2 inlet
camshaft passes the sensor
Cranksha
ft Position (CKP) Sensor
i
s
a variable reluctance device
mounted on the engine oil pan
Ite
m
Par
t
Number
De
scr
iption
1—Acce
le
rator pedal and mechanic
al guard position sensors
2—Throttle
(blade)
position sensor
Page 1200 of 2490
KS fail
ure
P0335Cranksh
a
ft positi
on (CKP) sensor
circuit malfunction
CK P
sensor disconnected
CKP sensor air gap
i
n
correct/foreign matter on face
CKP sensor sen
s
ing circuit open
circuit, short circuit to ground,
short circuit to high voltage
CKP s e
nsor failure
F
or CKP sensor circ ui
t tests,GO to
Pinpoint Test N.
.
P0340Camshaft position
(CMP) sensor
circuit malfunction
CM P
sensor disconnected
CMP sensor air gap
i
n
correct/foreign matter on face
CMP sensor sen
s
ing circuit open
circuit, short circuit to ground,
short circuit to high voltage
CMP s e
nsor failure
F
or CMP sensor circ ui
t tests,GO to
Pinpoint Test O.
.
P0351Igniti
on coil primary/secondary
circuit malfunction, cyl 1
ECM to ignit
ion module primary
circuit open circuit, short circuit to
ground, high resistance
Igniti
on module to ignition coil
primary circuit open circuit, short
circuit to ground, high resistance
Ignition modu le
ground circuit
open circuit, hi gh resistance
Ignition coil fail
ure
Ignition modul
e
failure
F
o
r ignition circuit tests,
REFER to Section 303
-07 En
gine
Ignition. P0352Ignit
i
on coil primary/secondary
circuit malfunction, cyl 3
P0353Ignit i
on coil primary/secondary
circuit malfunction, cyl 5
P0354Ignit i
on coil primary/secondary
circuit malfunction, cyl 7
P0355Ignit i
on coil primary/secondary
circuit malfunction, cyl 2
P0356Ignit i
on coil primary/secondary
circuit malfunction, cyl 4
P0357Ignit i
on coil primary/secondary
circuit malfunction, cyl 6
P0358Ignit i
on coil primary/secondary
circuit malfunction, cyl 8
P0400Exhaus t gas
recirculation (EGR)
flow malfunction
EGR valve c
onnector pins high
resistance
EGR pipe/exhaust manifol
d leak
EGR pipe blocke
d
EGR valve st
uck open/closed,
blocked
EGR valve fai
lure
For EGR
pinpoint t
ests,
REFER to Section 303
-08 En
gine
Emission Control.
P0405Exhaus
t gas
recirculation (EGR)
drive circuits open circuit
EGR valve power supply circuit
o p
en circuit
EGR valve t
o
ECM drive circuit pair
- EGR pins 1/3, 4/6 open circuit,
high resistance
EGR val v
e failure (stepper motor
open circuit)
For EGR pinpoint t
ests,
REFER to Section 303
-08 En
gine
Emissi
on Control.
P0406Exhaus t gas
recirculation (EGR)
drive circuits short circuit
EGR valve t o
ECM drive circuit pair
- EGR pins 1/3, 4/6 short circuit to
ground or high voltage
EGR val v
e failure (stepper motor
short circuit)
For EGR pinpoint t
ests,
REFER to Section 303
-08 En
gine
Emissi
on Control.
P0420Right-
hand catalytic converter
efficiency below threshold
HO2S di
sconnected.
HO2
S
to ECM wiring fault.
HO2
S
heater to ECM wiring fault.
HO2
S
heater failure.
HO2
S
failure.
Cat
a
lyst monitor sensor failure.
Catal
y
tic converter failure.
R
e
fer to pinpoint tests for components
listed. Visually inspect catalytic
converters.
P0442Evaporati v
e emissions system
(EVAP) leak detected
Fue l
filler cap missing
Fu
el filler cap seal faulty
EVAP system
leak (can
ister
damage, pipework damage)
EVAP v a
lve to ECM drive circuit
open circuit, short circuit, high
resistance
EVAP valve to engine pu rge pipe
damaged/blocked/leaking
EVAP ope r
ating vacuum hose
F
or evaporati
ve emissions pinpoint
tests,
REFER to Section 303
-1 3
Evaporative
Emissi
ons
.