1998 DODGE RAM 1500 lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 2244 of 2627

SHIFT MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The shift motor (Fig. 85) consists of a permanent
magnet D.C. motor with gear reduction to convert a
high speed-low torque device into a low speed-high
torque device. The output of the device is coupled to
a shaft which internally moves the mode and range
forks that change the transfer case operating ranges.
The motor is rated at 25 amps maximum at 72É F
with 10 volts at the motor leads.
OPERATION
The transfer case shift motor responds to the
Transfer Case Control Module (TCCM) commands to
move the transfer case shift sector bi-directionally, as
required, to obtain the transfer case operating mode
indicated by the instrument panel mounted selector
switch.
REMOVAL
NOTE: New shift motor assemblies are shipped in
the 2WD/AWD position. If a new shift motor assem-
bly will be installed, it will be necessary to shift the
transfer case to the 2WD/AWD position prior to
motor removal.
(1) Raise the vehicle on a suitable hoist.
(2) Disengage the wiring connectors from the shift
motor and mode sensor.
(3) Remove the bolts holding the shift motor and
mode sensor assembly onto the transfer case.
(4) Separate the shift motor and mode sensor
assembly from the transfer case.
INSTALLATION
(1) Verify that the shift sector o-ring is clean and
properly positioned over the shift sector and against
the transfer case.
NOTE: Verify that the shift motor position and sec-
tor shaft orientation are aligned. It may be neces-
sary to manually shift the transfer case if the shift
motor and sector shaft are not aligned.
(2) Position the shift motor and mode sensor
assembly onto the transfer case.
(3) Install the bolts to hold the assembly onto the
transfer case. Tighten the bolts to 16-24 N´m (12-18
ft.lbs.).
CAUTION: If the original shift motor and mode sen-
sor assembly bolts are reused, be sure to use
MoparTLock & Seal or LoctiteŸ 242 to replenish
the lock patch material originally found on the bolts
(4) Engage the wiring connectors to the shift motor
and mode sensor.
(5) Refill the transfer case as necessary.
(6) Lower vehicle and verify transfer case opera-
tion.
Fig. 85 Shift Motor - Shown Inverted - Typical
1 - SHIFT MOTOR
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV244 GENII 21 - 541
Page 2257 of 2627

(8) Remove bottom tabbed thrust washer from low
range planetary (Fig. 38).
CLEANING
Clean the transfer case parts with a standard
parts cleaning solvent. Remove all traces of sealer
from the cases and retainers with a scraper and
3MŸ all purpose cleaner. Use compressed air to
remove solvent residue from oil feed passages in the
case halves, retainers, gears, and shafts.
INSPECTION
MAINSHAFT/SPROCKET/HUB INSPECTION
Inspect the splines on the hub and shaft and the
teeth on the sprocket. Minor nicks and scratches can
be smoothed with an oilstone. However, replace any
part that is damaged.
Check the contact surfaces in the sprocket bore
and on the mainshaft. Minor nicks and scratches can
be smoothed with 320-400 grit emery cloth but do not
try to salvage the shaft if nicks or wear is severe.
INPUT GEAR AND PLANETARY CARRIER
Check the teeth on the gear (Fig. 39). Minor nicks
can be dressed off with an oilstone but replace the
gear if any teeth are broken, cracked, or chipped. The
bearing surface on the gear can be smoothed with
300-400 grit emery cloth if necessary.
Examine the carrier body and pinion gears for
wear or damage. Check the pinion gear thrust wash-
ers on the pinon pins for damage. The carrier will
have to be replaced as an assembly if the body, pin-
ion pins, or pinion gears are damaged.
Check the lock ring and both thrust washers for
wear or cracks. Replace them if necessary. Also
replace the lock retaining ring if bent, distorted, or
broken.
Fig. 39 Input Gear And Carrier Components
1 - PLANETARY CARRIER 4 - CARRIER LOCK RING
2 - REAR THRUST WASHER 5 - CARRIER LOCK RETAINING RING
3 - FRONT THRUST WASHER 6 - INPUT GEAR
Fig. 38 Remove Bottom Input Gear Thrust Plate
1 - PLANETARY
2 - THRUST PLATE
21 - 554 TRANSFER CASE - NV273DR
TRANSFER CASE - NV273 (Continued)
Page 2278 of 2627

have not been met. This is in an attempt to notify
the driver that the transmission needs to be put into
NEUTRAL, the vehicle speed is too great, or some
other condition outlined (other than a diagnostic fail-
ure that would prevent this shift) elsewhere (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/TRANSFER CASE CONTROL MODULE -
OPERATION) is not met. Note that this flashing will
continue indefinitely until the conditions are eventu-
ally met, or the selector switch position is changed,
or if diagnostic routines no longer allow the
requested shift.
²
If the driver attempts to make a shift into transfer
case NEUTRAL, and any of the driver controllable con-
ditions are not met, the request will be ignored until all
of the conditions are met or until the NEUTRAL select
button is released. Additionally the neutral lamp will
flash, or begin to flash while the button is depressed
and operator controllable conditions are not being met.
All of the LED's except the Neutral will flash if any of
the operator controllable conditions for shifting are not
met while the Neutral button is depressed. This9toggle9
type of feature is necessary because the TCCM would
interpret another request immediately after the shift
into transfer case NEUTRAL has completed.
²No LED's illuminated indicate a fault in the
transfer case control system.
SHIFT MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The shift motor (Fig. 96) consists of a permanent
magnet D.C. motor with gear reduction to convert a
high speed-low torque device into a low speed-high
torque device. The output of the device is coupled to
a shaft which internally moves the mode and range
forks that change the transfer case operating ranges.
The motor is rated at 25 amps maximum at 72É F
with 10 volts at the motor leads.
OPERATION
The transfer case shift motor responds to the
Transfer Case Control Module (TCCM) commands to
move the transfer case shift sector bi-directionally, as
required, to obtain the transfer case operating mode
indicated by the instrument panel mounted selector
switch.
REMOVAL
NOTE: New shift motor assemblies are shipped in
the 2WD/AWD position. If a new shift motor assem-
bly will be installed, it will be necessary to shift the
transfer case to the 2WD/AWD position prior to
motor removal.(1) Raise the vehicle on a suitable hoist.
(2) Disengage the wiring connectors from the shift
motor and mode sensor.
(3) Remove the bolts holding the shift motor and
mode sensor assembly onto the transfer case.
(4) Separate the shift motor and mode sensor
assembly from the transfer case.
INSTALLATION
(1) Verify that the shift sector o-ring is clean and
properly positioned over the shift sector and against
the transfer case.
NOTE: Verify that the shift motor position and sec-
tor shaft orientation are aligned. It may be neces-
sary to manually shift the transfer case if the shift
motor and sector shaft are not aligned.
(2) Position the shift motor and mode sensor
assembly onto the transfer case.
(3) Install the bolts to hold the assembly onto the
transfer case. Tighten the bolts to 16-24 N´m (12-18
ft.lbs.).
CAUTION: If the original shift motor and mode sen-
sor assembly bolts are reused, be sure to use
MoparTLock & Seal or LoctiteŸ 242 to replenish
the lock patch material originally found on the bolts
(4) Engage the wiring connectors to the shift motor
and mode sensor.
(5) Refill the transfer case as necessary.
(6) Lower vehicle and verify transfer case
operation.
Fig. 96 Shift Motor - Shown Inverted - Typical
1 - SHIFT MOTOR
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV273 21 - 575
SELECTOR SWITCH (Continued)
Page 2285 of 2627
TIRES
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - SPARE TIRE / TEMPORARY
The temporary spare tire is designed for emer-
gency use only. The original tire should be repaired
or replaced at the first opportunity, then reinstalled.
Do not exceed speeds of 50 M.P.H. when using the
temporary spare tire. Refer to Owner's Manual for
complete details.
DESCRIPTION - TIRES
Tires are designed and engineered for each specific
vehicle. They provide the best overall performance
for normal operation. The ride and handling charac-
teristics match the vehicle's requirements. With
proper care they will give excellent reliability, trac-
tion, skid resistance, and tread life.
Driving habits have more effect on tire life than
any other factor. Careful drivers will obtain in most
cases, much greater mileage than severe use or care-
less drivers. A few of the driving habits which will
shorten the life of any tire are:
²Rapid acceleration
²Severe brake applications
²High speed driving
²Excessive speeds on turns
²Striking curbs and other obstacles
Radial-ply tires are more prone to irregular tread
wear. It is important to follow the tire rotation inter-
val shown in the section on Tire Rotation, (Refer to
22 - TIRES/WHEELS - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
This will help to achieve a greater tread life.
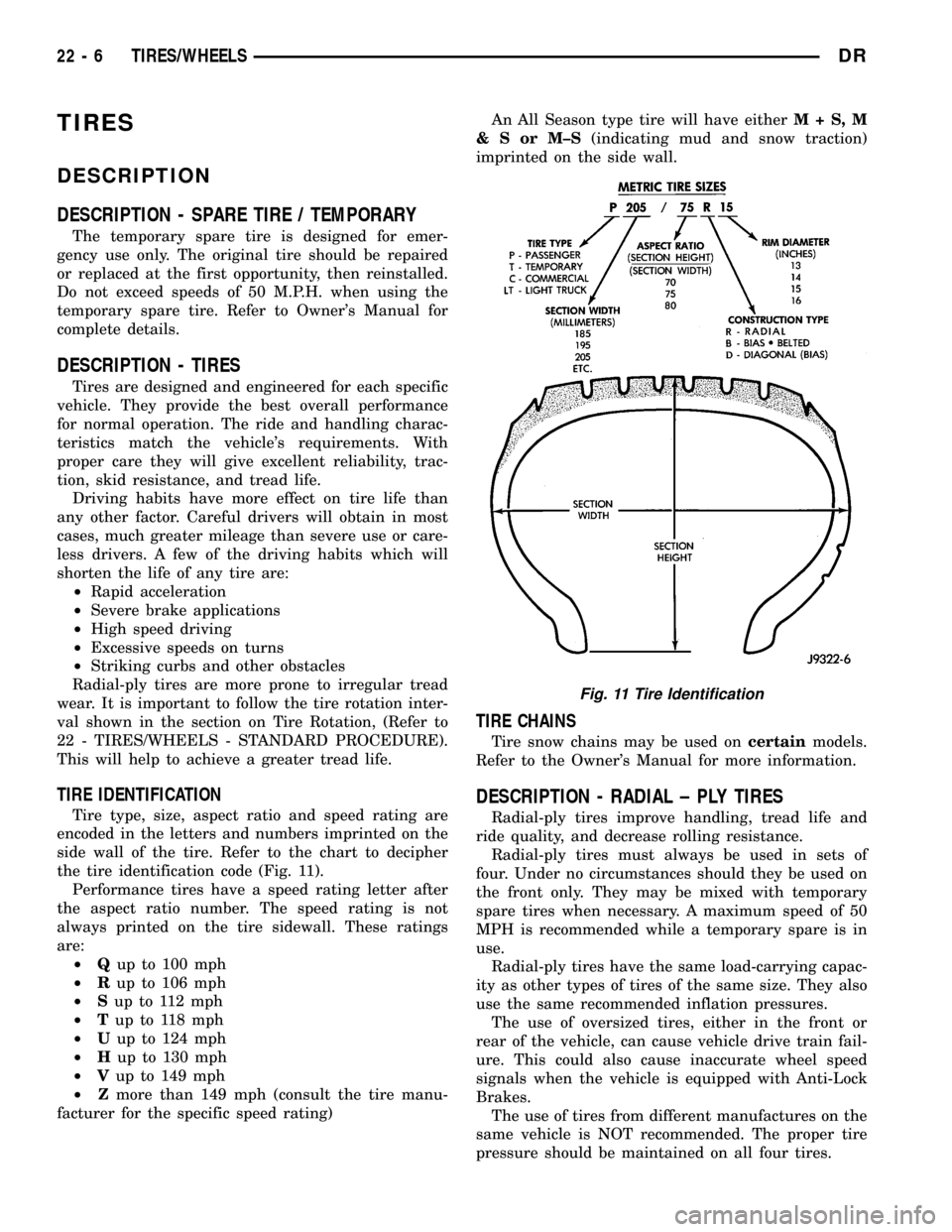
TIRE IDENTIFICATION
Tire type, size, aspect ratio and speed rating are
encoded in the letters and numbers imprinted on the
side wall of the tire. Refer to the chart to decipher
the tire identification code (Fig. 11).
Performance tires have a speed rating letter after
the aspect ratio number. The speed rating is not
always printed on the tire sidewall. These ratings
are:
²Qup to 100 mph
²Rup to 106 mph
²Sup to 112 mph
²Tup to 118 mph
²Uup to 124 mph
²Hup to 130 mph
²Vup to 149 mph
²Zmore than 149 mph (consult the tire manu-
facturer for the specific speed rating)An All Season type tire will have eitherM+S,M
&SorM±S(indicating mud and snow traction)
imprinted on the side wall.
TIRE CHAINS
Tire snow chains may be used oncertainmodels.
Refer to the Owner's Manual for more information.
DESCRIPTION - RADIAL ± PLY TIRES
Radial-ply tires improve handling, tread life and
ride quality, and decrease rolling resistance.
Radial-ply tires must always be used in sets of
four. Under no circumstances should they be used on
the front only. They may be mixed with temporary
spare tires when necessary. A maximum speed of 50
MPH is recommended while a temporary spare is in
use.
Radial-ply tires have the same load-carrying capac-
ity as other types of tires of the same size. They also
use the same recommended inflation pressures.
The use of oversized tires, either in the front or
rear of the vehicle, can cause vehicle drive train fail-
ure. This could also cause inaccurate wheel speed
signals when the vehicle is equipped with Anti-Lock
Brakes.
The use of tires from different manufactures on the
same vehicle is NOT recommended. The proper tire
pressure should be maintained on all four tires.
Fig. 11 Tire Identification
22 - 6 TIRES/WHEELSDR
Page 2296 of 2627

BODY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BODY
WARNING
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS . . . 1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WATER LEAKS . 1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WIND NOISE . . . 2
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BODY
LUBRICATION.........................3
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HEAT STAKING . . 3
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PLASTIC BODY
PANEL REPAIR........................3
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BUZZ, SQUEAK
& RATTLE...........................11
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE..............12SPECIAL TOOLS
BODY..............................14
TAILGATE..............................15
DOOR - FRONT.........................18
DOORS - REAR.........................28
EXTERIOR.............................36
HOOD.................................46
INSTRUMENT PANEL.....................49
INTERIOR..............................62
PAINT.................................73
SEATS................................75
STATIONARY GLASS.....................86
WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS...................91
BODY STRUCTURE......................95
BODY
WARNING
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS
WARNING: USE AN OSHA APPROVED BREATHING
FILTER WHEN SPRAYING PAINT OR SOLVENTS IN
A CONFINED AREA. PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
²AVOID PROLONGED SKIN CONTACT WITH
PETROLEUM OR ALCOHOL ± BASED CLEANING
SOLVENTS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
²DO NOT STAND UNDER A HOISTED VEHICLE
THAT IS NOT PROPERLY SUPPORTED ON SAFETY
STANDS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
CAUTION: When holes must be drilled or punched
in an inner body panel, verify depth of space to the
outer body panel, electrical wiring, or other compo-
nents. Damage to vehicle can result.
²Do not weld exterior panels unless combustible
material on the interior of vehicle is removed from
the repair area. Fire or hazardous conditions, can
result.
²Always have a fire extinguisher ready for use
when welding.
²Disconnect the negative (-) cable clamp from
the battery when servicing electrical components
that are live when the ignition is OFF. Damage to
electrical system can result.²Do not use abrasive chemicals or compounds
on painted surfaces. Damage to finish can result.
²Do not use harsh alkaline based cleaning sol-
vents on painted or upholstered surfaces. Damage
to finish or color can result.
²Do not hammer or pound on plastic trim panel
when servicing interior trim. Plastic panels can
break.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WATER LEAKS
Water leaks can be caused by poor sealing,
improper body component alignment, body seam
porosity, missing plugs, or blocked drain holes. Cen-
trifugal and gravitational force can cause water to
drip from a location away from the actual leak point,
making leak detection difficult. All body sealing
points should be water tight in normal wet-driving
conditions. Water flowing downward from the front of
the vehicle should not enter the passenger or luggage
compartment. Moving sealing surfaces will not
always seal water tight under all conditions. At
times, side glass or door seals will allow water to
enter the passenger compartment during high pres-
sure washing or hard driving rain (severe) condi-
tions. Overcompensating on door or glass
adjustments to stop a water leak that occurs under
severe conditions can cause premature seal wear and
excessive closing or latching effort. After completing
a repair, water test vehicle to verify leak has stopped
before returning vehicle to use.
DRBODY 23 - 1
Page 2298 of 2627

ROAD TESTING WIND NOISE
(1) Drive the vehicle to verify the general location
of the wind noise.
(2) Apply 50 mm (2 in.) masking tape in 150 mm
(6 in.) lengths along weatherstrips, weld seams or
moldings. After each length is applied, drive the vehi-
cle. If noise goes away after a piece of tape is applied,
remove tape, locate, and repair defect.
POSSIBLE CAUSE OF WIND NOISE
²Moldings standing away from body surface can
catch wind and whistle.
²Gaps in sealed areas behind overhanging body
flanges can cause wind-rushing sounds.
²Misaligned movable components.
²Missing or improperly installed plugs in pillars.
²Weld burn through holes.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BODY LUBRICATION
All mechanisms and linkages should be lubricated
when necessary. This will maintain ease of operation
and provide protection against rust and excessive
wear. The weatherstrip seals should be lubricated to
prolong their life as well as to improve door sealing.
All applicable exterior and interior vehicle operat-
ing mechanisms should be inspected and cleaned.
Pivot/sliding contact areas on the mechanisms should
then be lubricated.
(1) When necessary, lubricate the operating mech-
anisms with the specified lubricants.
(2) Apply silicone lubricant to a cloth and wipe it
on door seals to avoid over-spray that can soil pas-
senger's clothing.
(3) Before applying lubricant, the component
should be wiped clean. After lubrication, any excess
lubricant should be removed.
(4) The hood latch, latch release mechanism, latch
striker, and safety latch should be lubricated period-
ically.
(5) The door lock cylinders should be lubricated
twice each year (preferably autumn and spring).
²Spray a small amount of lock cylinder lubricant
directly into the lock cylinder.
²Apply a small amount to the key and insert it
into the lock cylinder.
²Rotate it to the locked position and then back to
the unlocked position several times.
²Remove the key. Wipe the lubricant from it with
a clean cloth to avoid soiling of clothing.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HEAT STAKING
(1) Remove trim panel.(2) Bend or move the trim panel components at
the heat staked joints. Observe the heat staked loca-
tions and/or component seams for looseness.
(3) Heat stake the components.
(a) If the heat staked or component seam loca-
tion is loose, hold the two components tightly
together and using a soldering gun with a flat tip,
melt the material securing the components
together. Do not over heat the affected area, dam-
age to the exterior of the trim panel may occur.
(b) If the heat staked material is broken or miss-
ing, use a hot glue gun to apply new material to
the area to be repaired. The panels that are being
heat staked must be held together while the apply-
ing the glue. Once the new material is in place, it
may be necessary to use a soldering gun to melt
the newly applied material. Do not over heat the
affected area, damage to the exterior of the trim
panel may occur.
(4) Allow the repaired area to cool and verify the
repair.
(5) Install trim panel.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PLASTIC BODY
PANEL REPAIR
There are many different types of plastics used in
today's automotive environment. We group plastics in
three different categories: Rigid, Semi-Rigid, and
Flexible. Any of these plastics may require the use of
an adhesion promoter for repair. These types of plas-
tic are used extensively on DaimlerChrysler Motors
vehicles. Always follow repair material manufactur-
er's plastic identification and repair procedures.
Rigid Plastics:
Examples of rigid plastic use: Fascias, Hoods,
Doors, and other Body Panels, which include SMC,
ABS, and Polycarbonates.
Semi-Rigid Plastics:
Examples of semi-rigid plastic use: Interior Panels,
Under Hood Panels, and other Body Trim Panels.
Flexible Plastics:
Examples of flexible plastic use: Fascias, Body
Moldings, and upper and lower Fascia Covers.
Repair Procedure:
The repair procedure for all three categories of
plastics is basically the same. The one difference is
the material used for the repair. The materials must
be specific for each substrate, rigid repair material
for rigid plastic repair, semi-rigid repair material for
semi-rigid plastic repair and flexible repair material
for flexible plastic repair.
DRBODY 23 - 3
BODY (Continued)
Page 2300 of 2627
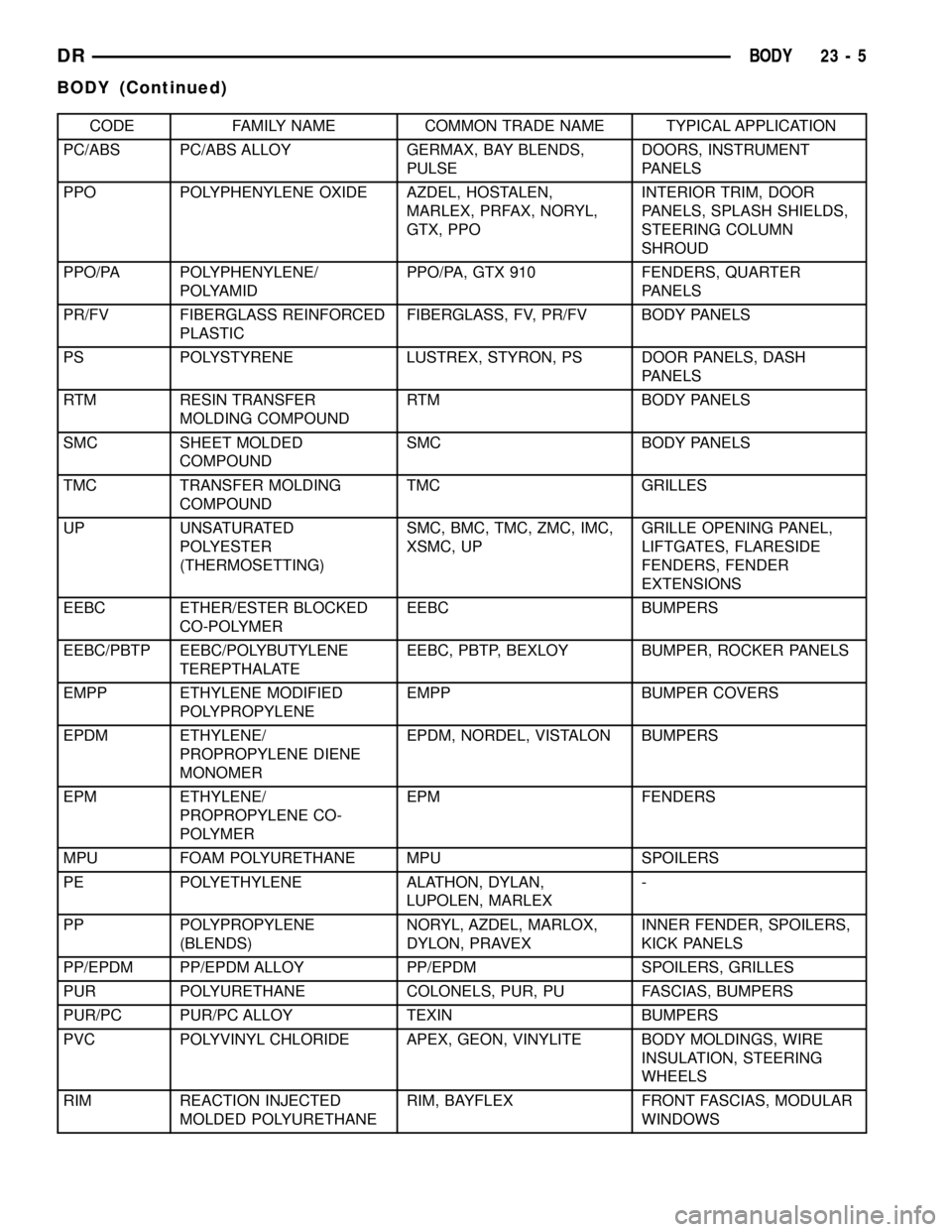
CODE FAMILY NAME COMMON TRADE NAME TYPICAL APPLICATION
PC/ABS PC/ABS ALLOY GERMAX, BAY BLENDS,
PULSEDOORS, INSTRUMENT
PANELS
PPO POLYPHENYLENE OXIDE AZDEL, HOSTALEN,
MARLEX, PRFAX, NORYL,
GTX, PPOINTERIOR TRIM, DOOR
PANELS, SPLASH SHIELDS,
STEERING COLUMN
SHROUD
PPO/PA POLYPHENYLENE/
POLYAMIDPPO/PA, GTX 910 FENDERS, QUARTER
PANELS
PR/FV FIBERGLASS REINFORCED
PLASTICFIBERGLASS, FV, PR/FV BODY PANELS
PS POLYSTYRENE LUSTREX, STYRON, PS DOOR PANELS, DASH
PANELS
RTM RESIN TRANSFER
MOLDING COMPOUNDRTM BODY PANELS
SMC SHEET MOLDED
COMPOUNDSMC BODY PANELS
TMC TRANSFER MOLDING
COMPOUNDTMC GRILLES
UP UNSATURATED
POLYESTER
(THERMOSETTING)SMC, BMC, TMC, ZMC, IMC,
XSMC, UPGRILLE OPENING PANEL,
LIFTGATES, FLARESIDE
FENDERS, FENDER
EXTENSIONS
EEBC ETHER/ESTER BLOCKED
CO-POLYMEREEBC BUMPERS
EEBC/PBTP EEBC/POLYBUTYLENE
TEREPTHALATEEEBC, PBTP, BEXLOY BUMPER, ROCKER PANELS
EMPP ETHYLENE MODIFIED
POLYPROPYLENEEMPP BUMPER COVERS
EPDM ETHYLENE/
PROPROPYLENE DIENE
MONOMEREPDM, NORDEL, VISTALON BUMPERS
EPM ETHYLENE/
PROPROPYLENE CO-
POLYMEREPM FENDERS
MPU FOAM POLYURETHANE MPU SPOILERS
PE POLYETHYLENE ALATHON, DYLAN,
LUPOLEN, MARLEX-
PP POLYPROPYLENE
(BLENDS)NORYL, AZDEL, MARLOX,
DYLON, PRAVEXINNER FENDER, SPOILERS,
KICK PANELS
PP/EPDM PP/EPDM ALLOY PP/EPDM SPOILERS, GRILLES
PUR POLYURETHANE COLONELS, PUR, PU FASCIAS, BUMPERS
PUR/PC PUR/PC ALLOY TEXIN BUMPERS
PVC POLYVINYL CHLORIDE APEX, GEON, VINYLITE BODY MOLDINGS, WIRE
INSULATION, STEERING
WHEELS
RIM REACTION INJECTED
MOLDED POLYURETHANERIM, BAYFLEX FRONT FASCIAS, MODULAR
WINDOWS
DRBODY 23 - 5
BODY (Continued)
Page 2305 of 2627

PATCHED PANEL SURFACING
After patch panel is installed, the patch area can
be finished using the same methods as finishing
other types of body panels. If mesh material is
exposed in the patched area, grind surface down, and
apply a coat of high quality rigid plastic body filler.
Prime, block sand, and paint as required.
Fig. 12 INSTALL SCREWS
1 - PATCH
2 - GAP
Fig. 13 GRIND SURFACE
1 - PATCH
2 - GAP
3 - DISC GRINDER
Fig. 14 COVER GAPS WITH MESH
1 - GROUND DOWN AREA
2 - PATCH
3 - MESH
Fig. 15 COVER MESH WITH ADHESIVE
1 - ADHESIVE
2 - MESH
3 - PATCH
4 - SPREADER
23 - 10 BODYDR
BODY (Continued)