1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Starter solenoid location
[x] Cancel search: Starter solenoid locationPage 446 of 2627

Large eyelet type terminals are crimped onto the
opposite end of the battery cable wire and then sol-
der-dipped. The battery positive cable wires have a
red insulating jacket to provide visual identification
and feature a larger female battery terminal clamp
to allow connection to the larger battery positive ter-
minal post. The battery negative cable wires have a
black insulating jacket and a smaller female battery
terminal clamp.
OPERATION
The battery cables connect the battery terminal
posts to the vehicle electrical system. These cables
also provide a return path for electrical current gen-
erated by the charging system for restoring the volt-
age potential of the battery. The female battery
terminal clamps on the ends of the battery cable
wires provide a strong and reliable connection of the
battery cable to the battery terminal posts. The ter-
minal pinch bolts allow the female terminal clamps
to be tightened around the male terminal posts on
the top of the battery. The eyelet terminals secured
to the ends of the battery cable wires opposite the
female battery terminal clamps provide secure and
reliable connection of the battery to the vehicle elec-
trical system.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY CABLES
A voltage drop test will determine if there is exces-
sive resistance in the battery cable terminal connec-
tions or the battery cables. If excessive resistance is
found in the battery cable connections, the connec-
tion point should be disassembled, cleaned of all cor-
rosion or foreign material, then reassembled.
Following reassembly, check the voltage drop for the
battery cable connection and the battery cable again
to confirm repair.
When performing the voltage drop test, it is impor-
tant to remember that the voltage drop is giving an
indication of the resistance between the two points at
which the voltmeter probes are attached.EXAM-
PLE:When testing the resistance of the battery pos-
itive cable, touch the voltmeter leads to the battery
positive cable terminal clamp and to the battery pos-
itive cable eyelet terminal at the starter solenoid
B(+) terminal stud. If you probe the battery positive
terminal post and the battery positive cable eyelet
terminal at the starter solenoid B(+) terminal stud,
you are reading the combined voltage drop in the
battery positive cable terminal clamp-to-terminal
post connection and the battery positive cable.
VOLTAGE DROP TEST
WARNING: MODELS EQUIPPED WITH A DIESEL
ENGINE HAVE AN AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN (ASD)RELAY LOCATED IN THE POWER DISTRIBUTION
CENTER (PDC). REMOVAL OF THE ASD RELAY
MAY NOT PREVENT THE DIESEL ENGINE FROM
STARTING. BE CERTAIN TO DISCONNECT THE
FUEL SHUTDOWN SOLENOID WIRE HARNESS
CONNECTOR TO PREVENT THE ENGINE FROM
STARTING. FAILURE TO DO SO MAY RESULT IN
PERSONAL INJURY.
The following operation will require a voltmeter
accurate to 1/10 (0.10) volt. Before performing this
test, be certain that the following procedures are
accomplished:
²The battery is fully-charged and tested (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
²Fully engage the parking brake.
²If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic
transmission, place the gearshift selector lever in the
Park position. If the vehicle is equipped with a man-
ual transmission, place the gearshift selector lever in
the Neutral position and block the clutch pedal in the
fully depressed position.
²Verify that all lamps and accessories are turned
off.
²To prevent a gasoline engine from starting,
remove the Automatic ShutDown (ASD) relay. The
ASD relay is located in the Integrated Power Module
(IPM), in the engine compartment. See the fuse and
relay layout label on the underside of the IPM cover
for ASD relay identification and location.
(1) Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to
the battery negative terminal post. Connect the neg-
ative lead of the voltmeter to the battery negative
cable terminal clamp (Fig. 11). Rotate and hold the
ignition switch in the Start position. Observe the
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct the poor con-
nection between the battery negative cable terminal
clamp and the battery negative terminal post.
NOTE: If the vehicle is equipped with two 12v bat-
teries, step #1 must be performed twice, once for
each battery.
(2) Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to
the battery positive terminal post. Connect the nega-
tive lead of the voltmeter to the battery positive cable
terminal clamp (Fig. 12). Rotate and hold the ignition
switch in the Start position. Observe the voltmeter. If
voltage is detected, correct the poor connection
between the battery positive cable terminal clamp
and the battery positive terminal post.
NOTE: If the vehicle is equipped with two 12v bat-
teries, step #2 must be performed twice, once for
each battery.
DRBATTERY SYSTEM 8F - 15
BATTERY CABLES (Continued)
Page 460 of 2627

TESTING
COLD CRANKING TEST
For complete starter wiring circuit diagrams, refer
to 8, Wiring Diagrams. The battery must be fully-
charged and load-tested before proceeding. Refer to
Batteryin 8, Battery.
(1) Connect volt-ampere tester to battery terminals
(Fig. 1). See instructions provided by manufacturer of
volt-ampere tester being used.Note: Certain diesel
equipped models use dual batteries. If equipped
with dual battery system, tester should be con-
nected to battery on left side of vehicle only.
Also, tester current reading must be taken from
positive battery cable lead that connects to
starter motor.
(2) Fully engage parking brake.
(3) If equipped with manual transmission, place
gearshift selector lever in Neutral position and block
clutch pedal in fully depressed position. If equipped
with automatic transmission, place gearshift selector
lever in Park position.
(4) Verify that all lamps and accessories are
turned off.
(5) To prevent a gasoline engine from starting,
remove Automatic ShutDown (ASD) relay. To prevent
a diesel engine from starting, remove Fuel Pump
Relay. These relays are located in Power Distribution
Center (PDC). Refer to label on PDC cover for relay
location.
WARNING: IF EQUIPPED WITH DIESEL ENGINE,
ATTEMPT TO START ENGINE A FEW TIMES
BEFORE PROCEEDING WITH FOLLOWING STEP.(6) Rotate and hold ignition switch in Start posi-
tion. Note cranking voltage and current (amperage)
draw readings shown on volt-ampere tester.
(a) If voltage reads below 9.6 volts, refer to
Starter Motorin Diagnosis and Testing. If starter
motor is OK, refer toEngine Diagnosisin 9,
Engine for further testing of engine. If starter
motor is not OK, replace faulty starter motor.
(b) If voltage reads above 9.6 volts and current
(amperage) draw reads below specifications, refer
toFeed Circuit Testin this section.
(c) If voltage reads 12.5 volts or greater and
starter motor does not turn, refer toControl Cir-
cuit Testingin this section.
(d) If voltage reads 12.5 volts or greater and
starter motor turns very slowly, refer toFeed Cir-
cuit Testin this section.
NOTE: A cold engine will increase starter current
(amperage) draw reading, and reduce battery volt-
age reading.
FEED CIRCUIT TEST
The starter feed circuit test (voltage drop method)
will determine if there is excessive resistance in
high-amperage feed circuit. For complete starter wir-
ing circuit diagrams, refer 8, Wiring Diagrams.
When performing these tests, it is important to
remember that voltage drop is giving an indication of
resistance between two points at which voltmeter
probes are attached.
Example:When testing resistance of positive bat-
tery cable, touch voltmeter leads to positive battery
cable clamp and cable connector at starter solenoid.
If you probe positive battery terminal post and cable
connector at starter solenoid, you are reading com-
bined voltage drop in positive battery cable clamp-to-
terminal post connection and positive battery cable.
The following operation will require a voltmeter
accurate to 1/10 (0.10) volt. Before performing tests,
be certain that following procedures are accom-
plished:
²Battery is fully-charged and load-tested. Refer to
Batteryin 8, Battery.
²Fully engage parking brake.
²If equipped with manual transmission, place
gearshift selector lever in Neutral position and block
clutch pedal in fully depressed position. If equipped
with automatic transmission, place gearshift selector
lever in Park position.
²Verify that all lamps and accessories are turned
off.
Fig. 1 VOLTS-AMPS TESTER CONNECTIONS -
TYPICAL
1 - POSITIVE CLAMP
2 - NEGATIVE CLAMP
3 - INDUCTION AMMETER CLAMP
DRSTARTING 8F - 29
STARTING (Continued)
Page 461 of 2627

²To prevent a gasoline engine from starting,
remove Automatic ShutDown (ASD) relay. To prevent
a diesel engine from starting, remove Fuel Pump
Relay. These relays are located in Power Distribution
Center (PDC). Refer to label on PDC cover for relay
location.
(1) Connect positive lead of voltmeter to negative
battery cable terminal post. Connect negative lead of
voltmeter to negative battery cable clamp (Fig. 2).
Rotate and hold ignition switch in Start position.
Observe voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct poor
contact between cable clamp and terminal post.
Note: Certain diesel equipped models use dual
batteries. If equipped with dual battery system,
procedure must be performed twice, once for
each battery.
(2) Connect positive lead of voltmeter to positive
battery terminal post. Connect negative lead of volt-
meter to battery positive cable clamp (Fig. 3). Rotate
and hold ignition switch in Start position. Observe
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct poor contact
between cable clamp and terminal post.Note: Cer-
tain diesel equipped models use dual batteries.
If equipped with dual battery system, this pro-
cedure must be performed twice, once for each
battery.
(3) Connect voltmeter to measure between battery
positive terminal post and starter solenoid battery
terminal stud (Fig. 4). Rotate and hold ignition
switch in Start position. Observe voltmeter. If read-
ing is above 0.2 volt, clean and tighten battery cable
connection at solenoid. Repeat test. If reading is still
above 0.2 volt, replace faulty positive battery cable.
Note: Certain diesel equipped models use dual
batteries. If equipped with dual battery system,
this procedure must be performed on driver
side battery only.(4) Connect voltmeter to measure between nega-
tive battery terminal post and a good clean ground
on engine block (Fig. 5). Rotate and hold ignition
switch in Start position. Observe voltmeter. If read-
ing is above 0.2 volt, clean and tighten negative bat-
tery cable attachment on engine block. Repeat test. If
reading is still above 0.2 volt, replace faulty negative
battery cable.Note: Certain diesel equipped mod-
els use dual batteries. If equipped with dual
battery system, this procedure must be per-
formed twice, once for each battery.
Fig. 2 TEST BATTERY NEGATIVE CONNECTION
RESISTANCE - TYPICAL
1 - VOLTMETER
2 - BATTERY
Fig. 3 TEST BATTERY POSITIVE CONNECTION
RESISTANCE - TYPICAL
1 - VOLTMETER
2 - BATTERY
Fig. 4 TEST BATTERY POSITIVE CABLE
RESISTANCE - TYPICAL
1 - BATTERY
2 - VOLTMETER
3 - STARTER MOTOR
8F - 30 STARTINGDR
STARTING (Continued)
Page 466 of 2627

5.7L
(1) Connect solenoid wire to starter motor (snaps
on).
(2) Position battery cable to solenoid stud. Install
and tighten battery cable eyelet nut. Refer to Torque
Specifications. Do not allow starter motor to hang
from wire harness.
(3) Position starter motor to engine.
(4) If equipped with automatic transmission, slide
cooler tube bracket into position.
(5) Install and tighten both mounting bolts. Refer
to Torque Specifications.
(6) Lower vehicle.
(7) Connect negative battery cable.
5.9L Diesel
(1)If Equipped:Position and hold aluminum
spacer to rear of starter while positioning starter to
engine.
(2) Connect solenoid wire to starter motor. Tighten
nut.
(3) Position battery cable to starter stud. Install
and tighten battery cable nut. Refer to Torque Spec-
ifications. Do not allow starter motor to hang from
wire harness.
(4) Position starter motor to transmission.
(5) If equipped with automatic transmission, slide
cooler tube bracket into position.
(6) Install and tighten 3 starter mounting bolts.
Refer to Torque Specifications.
(7) Lower vehicle.
(8) Connect both negative battery cables to both
batteries.
STARTER MOTOR RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The starter relay is an electromechanical device
that switches battery current to the pull-in coil of the
starter solenoid when ignition switch is turned to
Start position. The starter relay is located in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC) in the engine com-
partment. See PDC cover for relay identification and
location.
The starter relay is a International Standards
Organization (ISO) relay. Relays conforming to ISO
specifications have common physical dimensions, cur-
rent capacities, terminal patterns, and terminal func-
tions.
The starter relay cannot be repaired or adjusted. If
faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
Fig. 12 STARTER R/I - 5.9L DIESEL
1 - MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
2 - STARTER MOTOR
3 - SPACER (CERTAIN TRANSMISSIONS)
Fig. 13 STARTER ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS -
5.9L DIESEL
1 - STARTER MOTOR
2 - BATTERY CABLE NUT
3 - SOLENOID NUT
4 - HARNESS ASSEMBLY
DRSTARTING 8F - 35
STARTER MOTOR (Continued)
Page 467 of 2627

OPERATION
The ISO relay consists of an electromagnetic coil, a
resistor or diode, and three (two fixed and one mov-
able) electrical contacts. The movable (common feed)
relay contact is held against one of the fixed contacts
(normally closed) by spring pressure. When electro-
magnetic coil is energized, it draws the movable con-
tact away from normally closed fixed contact, and
holds it against the other (normally open) fixed con-
tact.
When electromagnetic coil is de-energized, spring
pressure returns movable contact to normally closed
position. The resistor or diode is connected in parallel
with electromagnetic coil within relay, and helps to
dissipate voltage spikes produced when coil is de-en-
ergized.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTER RELAY
The starter relay (Fig. 14) is located in Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC). Refer to PDC cover for relay
identification and location. For complete starter relay
wiring circuit diagrams, refer to 8, Wiring Diagrams.
(1) Remove starter relay from PDC.
(2) A relay in de-energized position should have
continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and no
continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go to
Step 3. If not OK, replace faulty relay.
(3) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 75 5 ohms. If OK, go to Step
4. If not OK, replace faulty relay.
(4) Connect 12V battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, perform Relay Circuit Test that fol-
lows. If not OK, replace faulty relay.
RELAY CIRCUIT TEST
(1) The relay common feed terminal cavity (30) is
connected to battery voltage and should be hot at all
times. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair open cir-
cuit to fuse in PDC as required.
(2) The relay normally closed terminal (87A) is
connected to terminal 30 in the de-energized position,
but is not used for this application. Go to Step 3.
(3) The relay normally open terminal (87) is con-
nected to common feed terminal (30) in the energized
position. This terminal supplies battery voltage to
starter solenoid field coils. There should be continu-
ity between cavity for relay terminal 87 and starter
solenoid terminal at all times. If OK, go to Step 4. If
not OK, repair open circuit to starter solenoid as
required.(4) The coil battery terminal (86) is connected to
electromagnet in relay. It is energized when ignition
switch is held in Start position. On vehicles with
manual transmission, clutch pedal must be fully
depressed for this test. Check for battery voltage at
cavity for relay terminal 86 with ignition switch in
Start position, and no voltage when ignition switch is
released to On position. If OK, go to Step 5. If not
OK with automatic transmission, check for open or
short circuit to ignition switch and repair, if required.
If circuit to ignition switch is OK, refer toIgnition
Switch and Key Lock Cylinder. If not OK with a
manual transmission, check circuit between relay
and clutch pedal position switch for open or a short.
If circuit is OK, refer toClutch Pedal Position
Switchin 6 , Clutch.
(5) The coil ground terminal (85) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. On vehicles with
manual transmission, it is grounded at all times. On
vehicles with automatic transmission, it is grounded
through park/neutral position switch only when gear-
shift selector lever is in Park or Neutral positions.
Check for continuity to ground at cavity for relay ter-
minal 85. If not OK with manual transmission,
repair circuit to ground as required. If not OK with
automatic transmission, check for pen or short circuit
to park/neutral position switch and repair, if
required. If circuit to park/neutral position switch is
OK, refer toPark/Neutral Position Switchin 21,
Transmission.
Fig. 14 TYPE 1 RELAY
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
8F - 36 STARTINGDR
STARTER MOTOR RELAY (Continued)
Page 1161 of 2627
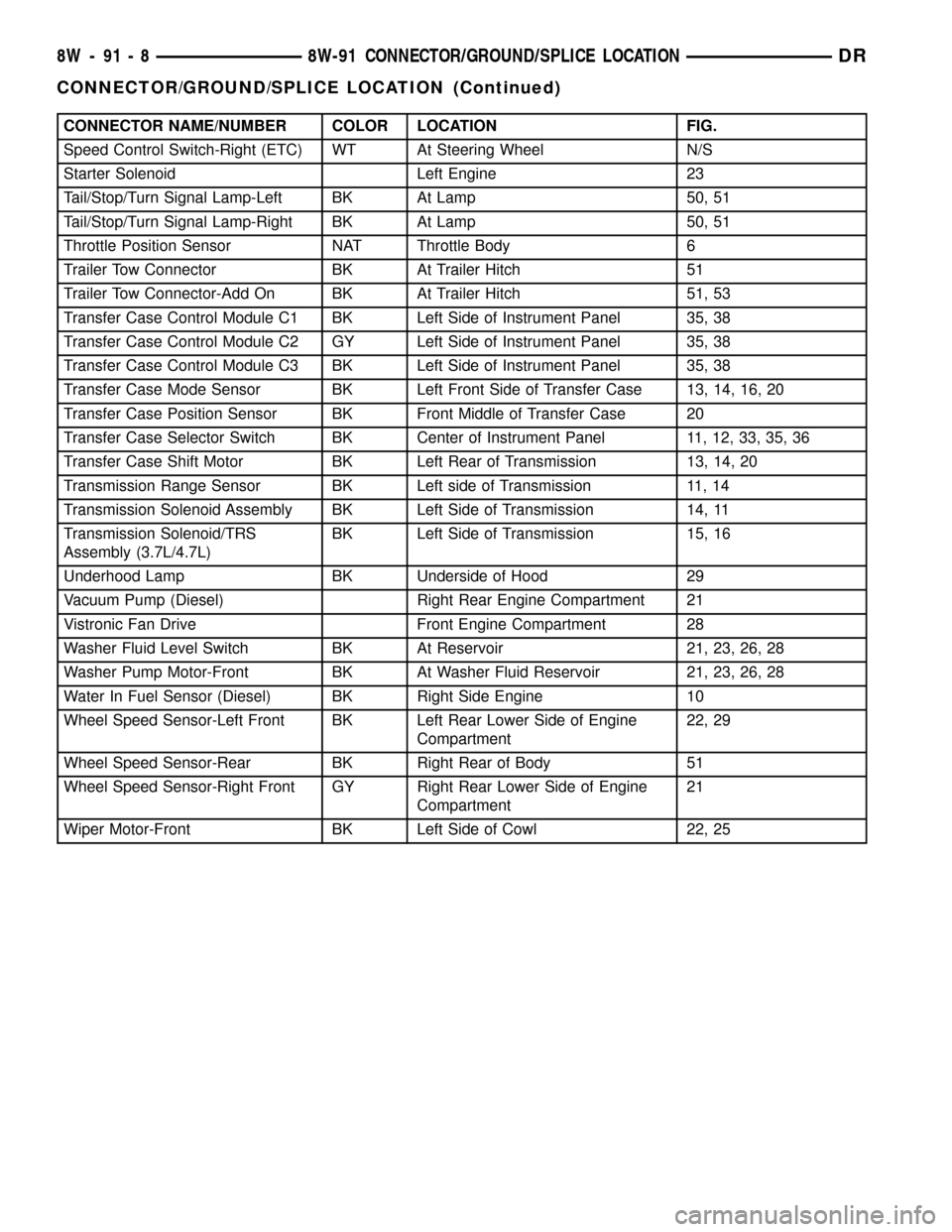
CONNECTOR NAME/NUMBER COLOR LOCATION FIG.
Speed Control Switch-Right (ETC) WT At Steering Wheel N/S
Starter Solenoid Left Engine 23
Tail/Stop/Turn Signal Lamp-Left BK At Lamp 50, 51
Tail/Stop/Turn Signal Lamp-Right BK At Lamp 50, 51
Throttle Position Sensor NAT Throttle Body 6
Trailer Tow Connector BK At Trailer Hitch 51
Trailer Tow Connector-Add On BK At Trailer Hitch 51, 53
Transfer Case Control Module C1 BK Left Side of Instrument Panel 35, 38
Transfer Case Control Module C2 GY Left Side of Instrument Panel 35, 38
Transfer Case Control Module C3 BK Left Side of Instrument Panel 35, 38
Transfer Case Mode Sensor BK Left Front Side of Transfer Case 13, 14, 16, 20
Transfer Case Position Sensor BK Front Middle of Transfer Case 20
Transfer Case Selector Switch BK Center of Instrument Panel 11, 12, 33, 35, 36
Transfer Case Shift Motor BK Left Rear of Transmission 13, 14, 20
Transmission Range Sensor BK Left side of Transmission 11, 14
Transmission Solenoid Assembly BK Left Side of Transmission 14, 11
Transmission Solenoid/TRS
Assembly (3.7L/4.7L)BK Left Side of Transmission 15, 16
Underhood Lamp BK Underside of Hood 29
Vacuum Pump (Diesel) Right Rear Engine Compartment 21
Vistronic Fan Drive Front Engine Compartment 28
Washer Fluid Level Switch BK At Reservoir 21, 23, 26, 28
Washer Pump Motor-Front BK At Washer Fluid Reservoir 21, 23, 26, 28
Water In Fuel Sensor (Diesel) BK Right Side Engine 10
Wheel Speed Sensor-Left Front BK Left Rear Lower Side of Engine
Compartment22, 29
Wheel Speed Sensor-Rear BK Right Rear of Body 51
Wheel Speed Sensor-Right Front GY Right Rear Lower Side of Engine
Compartment21
Wiper Motor-Front BK Left Side of Cowl 22, 25
8W - 91 - 8 8W-91 CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATIONDR
CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATION (Continued)
Page 2618 of 2627

SOLENOID - DESCRIPTION, EVAP/PURGE . 25-12
SOLENOID - INSTALLATION, EVAP/
PURGE.............................25-12
SOLENOID - OPERATION..............21-252
SOLENOID - OPERATION, EVAP/PURGE . . . 25-12
SOLENOID - REMOVAL, EVAP/PURGE.....25-12
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE -
DESCRIPTION......................21-398
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE - OPERATION . 21-398
SOLENOIDS - DESCRIPTION...........21-398
SOLENOIDS - OPERATION.............21-399
SOLENOID/TRS ASSEMBLY -
DESCRIPTION, TRANSMISSION........21-406
SOLENOID/TRS ASSEMBLY -
INSTALLATION, TRANSMISSION........21-408
SOLENOID/TRS ASSEMBLY -
OPERATION, TRANSMISSION..........21-406
SOLENOID/TRS ASSEMBLY - REMOVAL,
TRANSMISSION.....................21-407
SOLID LIFTERS/TAPPETS - CLEANING....9-279
SOLID LIFTERS/TAPPETS - INSPECTION . . 9-279
SOLID LIFTERS/TAPPETS -
INSTALLATION.......................9-280
SOLID LIFTERS/TAPPETS - REMOVAL....9-279
SPARE / TEMPORARY TIRE -
DESCRIPTION.......................22-15
SPARE TIRE / TEMPORARY -
DESCRIPTION........................22-6
SPARE WHEEL WITH MATCHING TIRE -
DESCRIPTION, FULL SIZE..............22-15
SPARK PLUG - DESCRIPTION...........8I-17
SPARK PLUG - REMOVAL..............8I-19
SPARK PLUG CABLE - DESCRIPTION.....8I-21
SPARK PLUG CABLE - INSTALLATION.....8I-22
SPARK PLUG CABLE - OPERATION.......8I-21
SPARK PLUG CABLE - REMOVAL........8I-22
SPARK PLUG CABLE RESISTANCE,
SPECIFICATIONS......................8I-4
SPARK PLUG CONDITIONS - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING........................8I-17
SPARK PLUGS, SPECIFICATIONS..........8I-4
SPEAKER - DESCRIPTION..............8A-13
SPEAKER - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING....8A-13
SPEAKER - INSTALLATION.............8A-15
SPEAKER - OPERATION...............8A-13
SPEAKER - REMOVAL.................8A-14
SPECIFICATIONS......................7-20
SPEED CONTROL - DESCRIPTION........8P-1
SPEED CONTROL - OPERATION..........8P-2
SPEED CONTROL - TORQUE.............8P-3
SPEED SENSOR - DESCRIPTION........21-253
SPEED SENSOR - DESCRIPTION, FRONT
WHEEL.............................5-47
SPEED SENSOR - DESCRIPTION, INPUT . 21-382
SPEED SENSOR - DESCRIPTION,
OUTPUT...........................21-391
SPEED SENSOR - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, REAR WHEEL................5-49
SPEED SENSOR - INSTALLATION, FRONT
WHEEL.............................5-48
SPEED SENSOR - INSTALLATION, INPUT . 21-382
SPEED SENSOR - INSTALLATION,
OUTPUT...........................21-392
SPEED SENSOR - INSTALLATION, REAR
WHEEL.............................5-48
SPEED SENSOR - OPERATION.........21-253
SPEED SENSOR - OPERATION, FRONT
WHEEL.............................5-47
SPEED SENSOR - OPERATION, INPUT . . . 21-382
SPEED SENSOR - OPERATION, OUTPUT . . 21-391
SPEED SENSOR - REMOVAL, FRONT
WHEEL.............................5-48
SPEED SENSOR - REMOVAL, INPUT.....21-382
SPEED SENSOR - REMOVAL, OUTPUT . . . 21-391
SPEED SENSOR - REMOVAL, REAR
WHEEL.............................5-48
SPEEDOMETER - DESCRIPTION.........8J-37
SPEEDOMETER - OPERATION...........8J-37
SPEEDS - DESCRIPTION, TIRE
PRESSURE FOR HIGH
..................22-7
SPLASH SHIELD - INSTALLATION,
FRONT WHEELHOUSE
.................23-41
SPLASH SHIELD - INSTALLATION, REAR
WHEELHOUSE
.......................23-41
SPLASH SHIELD - REMOVAL, FRONT
WHEELHOUSE
.......................23-41
SPLASH SHIELD - REMOVAL, REAR
WHEELHOUSE
.......................23-41SPLICE INFORMATION - DESCRIPTION,
CONNECTOR, GROUND..............8W-01-7
SPLICING - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
WIRE...........................8W-01-15
SPRING - DESCRIPTION................2-44
SPRING - INSTALLATION.......2-23,2-39,2-44
SPRING - OPERATION..................2-44
SPRING - REMOVAL...........2-22,2-39,2-44
SPRING AND SHOCK - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING............................2-41
SPRING BUMPERS (3500) -
INSTALLATION, AUXILIARY..............2-43
SPRING BUMPERS (3500) - REMOVAL,
AUXILIARY..........................2-43
SPRING TIP INSERTS - INSTALLATION....2-45
SPRING TIP INSERTS - REMOVAL........2-44
SPRINGS - DESCRIPTION, VALVE . . . 9-126,9-32,
9-38
SPRINGS - INSTALLATION, VALVE . . 9-127,9-204,
9-32,9-38
SPRINGS - REMOVAL, VALVE . 9-126,9-204,9-32,
9-38
SPRINGS - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
VALVES, GUIDES.....................9-256
SPRINGS AND SEALS - REMOVAL,
VALVE .............................9-260
SPROCKETS - INSPECTION, TIMING
BELT/CHAIN.....................9-174,9-84
SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION, TIMING
BELT/CHAIN.....................9-176,9-85
SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION,
TIMING/CHAIN........................9-228
SPROCKETS - REMOVAL, TIMING
BELT/CHAIN.....................9-172,9-83
SPROCKETS - REMOVAL, TIMING/CHAIN . . 9-228
SQUEAK & RATTLE - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, BUZZ...................23-11
STABILIZER BAR - DESCRIPTION.........2-24
STABILIZER BAR - INSTALLATION....2-25,2-40
STABILIZER BAR - OPERATION...........2-25
STABILIZER BAR - REMOVAL........2-25,2-39
STAKING - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
HEAT ...............................23-3
STANDARD CAB - INSTALLATION . . 8O-35,8O-61
STANDARD CAB - REMOVAL......8O-32,8O-59
STARTER MOTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING...........................8F-32
STARTER MOTOR - INSTALLATION.......8F-34
STARTER MOTOR - REMOVAL..........8F-33
STARTER MOTOR RELAY - DESCRIPTION . 8F-35
STARTER MOTOR RELAY -
INSTALLATION.......................8F-37
STARTER MOTOR RELAY - OPERATION . . . 8F-36
STARTER MOTOR RELAY - REMOVAL.....8F-37
STARTER RELAY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING...........................8F-36
STARTING - DESCRIPTION.............8F-26
STARTING - OPERATION...............8F-26
STARTING - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
JUMP...............................0-19
STARTING SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING...........................8F-27
STARTING SYSTEM - SPECIFICATIONS,
TORQUE............................8F-32
STARTING SYSTEM, SPECIFICATIONS
.....8F-31
STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE -
DESCRIPTION
........................25-1
STEERING - DESCRIPTION
..............19-1
STEERING - OPERATION
................19-1
STEERING COLUMN - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING
............................19-7
STEERING COLUMN OPENING COVER -
INSTALLATION
.......................23-60
STEERING COLUMN OPENING COVER -
REMOVAL
..........................23-60
STEERING COLUMN OPENING SUPPORT
BRACKET - INSTALLATION
.............23-60
STEERING COLUMN OPENING SUPPORT
BRACKET - REMOVAL
.................23-60
STEERING COUPLING - INSTALLATION,
UPPER
.............................19-13
STEERING COUPLING - REMOVAL,
UPPER
.............................19-13
STEERING FLOW AND PRESSURE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, POWER
.......19-4
STEERING FLUID - DESCRIPTION,
POWER
..............................0-3STEERING FLUID LEVEL CHECKING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE, POWER.......19-43
STEERING GEAR INPUT SHAFT SEAL -
INSTALLATION.......................19-29
STEERING GEAR INPUT SHAFT SEAL -
REMOVAL..........................19-27
STEERING GEAR, SPECIAL TOOLS -
POWER............................19-23
STEERING GEAR, SPECIFICATIONS -
POWER............................19-22
STEERING LINKAGE, SPECIAL TOOLS....19-35
STEERING PRESSURE SWITCH -
DESCRIPTION, POWER................19-46
STEERING PRESSURE SWITCH -
OPERATION, POWER..................19-46
STEERING PUMP - INITIAL OPERATION -
STANDARD PROCEDURE, POWER.......19-40
STEERING, SPECIAL TOOLS.............19-5
STEERING SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, POWER.....................19-2
STEERING SYSTEM - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, FLUSHING POWER........19-40
STEERING WHEEL - INSTALLATION......19-15
STEERING WHEEL - REMOVAL..........19-15
STEM SEALS - DESCRIPTION, VALVE....9-127,
9-203
STOP LAMP - INSTALLATION, CENTER
HIGH MOUNTED.....................8L-11
STOP LAMP - REMOVAL, CENTER HIGH
MOUNTED..........................8L-11
STOP LAMP UNIT - INSTALLATION,
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED..............8L-11
STOP LAMP UNIT - REMOVAL, CENTER
HIGH MOUNTED.....................8L-11
STORAGE BIN - INSTALLATION..........23-61
STORAGE BIN - INSTALLATION, UNDER
SEAT ..............................23-80
STORAGE BIN - REMOVAL.............23-61
STORAGE BIN - REMOVAL, UNDER SEAT . . 23-80
STORAGE BIN COVERING -
INSTALLATION, UNDER SEAT...........23-80
STORAGE BIN COVERING - REMOVAL,
UNDER SEAT........................23-80
STORAGE BIN LATCH - INSTALLATION,
UNDER SEAT........................23-80
STORAGE BIN LATCH - REMOVAL,
UNDER SEAT........................23-80
STORAGE BIN LID - INSTALLATION,
UNDER SEAT........................23-80
STORAGE BIN LID - REMOVAL, UNDER
SEAT ..............................23-80
STRAP - DESCRIPTION, RADIO NOISE
SUPPRESSION GROUND................8A-9
STRAP - INSTALLATION, RADIO NOISE
SUPPRESSION GROUND...............8A-10
STRAP - OPERATION, RADIO NOISE
SUPPRESSION GROUND................8A-9
STRAP - REMOVAL, RADIO NOISE
SUPPRESSION GROUND................8A-9
STRIKER - INSTALLATION, LATCH . . 23-17,23-23,
23-33
STRIKER - REMOVAL, LATCH . 23-16,23-23,23-33
STRIKER / SECONDARY CATCH -
INSTALLATION, LATCH................23-48
STRIKER / SECONDARY CATCH -
REMOVAL, LATCH....................23-47
STRUCTURAL ADHESIVE LOCATIONS -
SPECIFICATIONS....................23-112
STRUCTURAL COVER - DESCRIPTION....9-145,
9-216,9-57
STRUCTURAL COVER - INSTALLATION . . . 9-145,
9-216,9-57
STRUCTURAL COVER - OPERATION.....9-145,
9-216,9-57
STRUCTURAL COVER - REMOVAL . . 9-145,9-216,
9-57
STUDS - INSTALLATION...............22-14
STUDS - REMOVAL...................22-14
SUCTION LINE - DESCRIPTION..........24-70
SUN VISOR - INSTALLATION...........23-70
SUN VISOR - REMOVAL
...............23-70
SUN VISOR SUPPORT - INSTALLATION
. . . 23-71
SUN VISOR SUPPORT - REMOVAL
.......23-70
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
DEPLOYMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, SERVICE AFTER A
.........8O-7
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
..............8O-6
DRINDEX 31
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page