1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Ball bearings
[x] Cancel search: Ball bearingsPage 37 of 2627

OPERATION
²CASTERis the forward or rearward tilt of the
steering knuckle from vertical. Tilting the top of the
knuckle forward provides less positive caster. Tilting
the top of the knuckle rearward provides more posi-
tive caster. Positive caster promotes directional sta-
bility. This angle enables the front wheels to return
to a straight ahead position after turns (Fig. 1)
²CAMBERis the inward or outward tilt of the
wheel relative to the center of the vehicle. Tilting the
top of the wheel inward provides negative camber.
Tilting the top of the wheel outward provides positive
camber. Incorrect camber will cause wear on the
inside or outside edge of the tire (Fig. 1)
²TOEis the difference between the leading inside
edges and trailing inside edges of the front tires.
Wheel toe position out of specification cause's unsta-
ble steering, uneven tire wear and steering wheel off-
center. The wheel toe position is thefinalfront
wheel alignment adjustment (Fig. 1)
²THRUST ANGLEis the angle of the rear axle
relative to the centerline of the vehicle. Incorrect
thrust angle can cause off-center steering and exces-sive tire wear. This angle is not adjustable, damaged
component(s) must be replaced to correct the thrust
angle (Fig. 1)
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRE-ALIGNMENT
INSPECTION
Before starting wheel alignment, the following
inspection and necessary corrections must be com-
pleted. Refer to Suspension and Steering System
Diagnosis Chart below for additional information.
(1) Inspect tires for size, air pressure and tread
wear.
(2) Inspect front wheel bearings for wear.
(3) Inspect front wheels for excessive radial or lat-
eral runout and balance.
(4) Inspect ball studs, linkage pivot points and
steering gear for looseness, roughness or binding.
(5) Inspect suspension components for wear and
noise.
(6) On 4x4 vehicles check suspension height (LD
only).
(7) Road test the vehicle.
SUSPENSION AND STEERING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
FRONT END NOISE 1. Loose or worn wheel bearing. 1. Replace wheel bearing.
2. Loose or worn steering or
suspension components.2. Tighten or replace components as
necessary.
3. Loose or worn steering or
suspension components.3. Tighten or replace components as
necessary.
EXCESSIVE PLAY IN
STEERING1. Loose or worn wheel bearing. 1. Replace wheel bearing.
2. Loose or worn steering or
suspension components.2. Tighten or replace components as
necessary.
3. Loose or worn steering gear. 3. Replace steering gear.
FRONT WHEELS SHIMMY 1. Loose or worn wheel bearing. 1. Replace wheel bearing.
2. Loose or worn steering or
suspension components.2. Tighten or replace components as
necessary.
3. Tires worn or out of balance. 3. Replace or balance tires.
4. Alignment. 4. Align vehicle to specifications.
VEHICLE INSTABILITY 1. Loose or worn wheel bearing. 1. Replace wheel bearing.
2. Loose or worn steering or
suspension components.2. Tighten or replace components as
necessary.
3. Tire pressure. 3. Adjust tire pressure.
4. Alignment. 4. Align vehicle to specifications.
2 - 2 WHEEL ALIGNMENTDR
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 44 of 2627

FRONT - INDEPENDENT
FRONT SUSPENSION
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
The front suspension is designed to allow each
wheel to adapt to different road surfaces indepen-
dently. The wheels are mounted to hub/bearings
units bolted to the steering knuckle. The double-row
hub bearings are sealed and lubricated for life. The
steering knuckles turn (pivot) on ball joints.
The front suspension is comprised of (Fig. 1) (Fig.
2):
²Shock absorbers
²Torsion bar - 4X4 (LD only)
²Coil Spring - 4X2
²Control arms
²Steering knuckles
²Stabilizer bar
²Stabilizer link
²Tie Rod Ends
²Hub/Bearing
²Rack & Pinion
²Ball Joints
NOTE: Components attached with a nut must be
torqued to specification.
NOTE: Suspension components with rubber/ure-
thane bushings should be tightened with the vehi-
cle at normal ride height. It is important to have the
springs supporting the weight of the vehicle when
the fasteners are torqued. If springs are not at their
normal ride position, vehicle ride comfort could be
affected and premature bushing wear may occur.
Fig. 1 FRONT SUSPENSION - 4X2
1 - STABILIZER BAR
2 - UPPER CONTROL ARM
3 - STEERING KNUCKLE
4 - ROTOR
5 - CALIPER ADAPTER
6 - OUTER TIE ROD END
7 - STABILIZER LINK
8 - LOWER CONTROL ARM
9 - RACK & PINION
10 - COIL SPRING
11 - SHOCK ABSORBER
DRFRONT - INDEPENDENT FRONT SUSPENSION 2 - 9
Page 1496 of 2627

If the crankshaft is within limits, replace the bear-
ing. If the crankshaft is out of limits, grind the
crankshaft to the next smaller size and use oversize
rod bearings.
CRANKSHAFT AND GEAR
DESCRIPTION
The crankshaft (Fig. 64) is a forged steel, integrally
balanced unit. It is supported by seven main bear-
ings, with position number six designated as the
thrust journal. The crankshaft is held in place by
main caps and 12 mm capscrews. The crankshaft
also has internal cross drillings to supply the con-
necting rods with engine oil.
REMOVAL - GEAR
(1) Remove the gear housing cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/GEAR HOUSING COVER
- REMOVAL)
(2) Split the gear and remove it from the crank-
shaft.
INSTALLATION - GEAR
(1) Remove all burrs and make sure the gear sur-
face on the end of the crankshaft is smooth.
(2) If removed, install a new alignment pin. Drive
the pin in using a ball- peen hammer, leaving it pro-truding 1.0 mm (0.039 inch) to 1.5 mm (0.059 inch)
above the crankshaft (Fig. 65).
WARNING: WEAR PROTECTIVE GLOVES TO PRE-
VENT INJURY.
CAUTION: DO NOT heat the gear longer than 45
minutes.
(3) Heat the crankshaft gear for 45 minutes at a
temperature of 149ÉC (300ÉF).Do not use torch,
gear failure will occur.
(4) Apply a thin coat of lubricant to the nose of the
crankshaft.
(5) Position the gear with the timing mark out and
install it on the crankshaft using the alignment pin.
Make sure the gear contacts the shoulder.
Fig. 63 Connecting Rod Journal Diameter Limits
CONNECTING ROD JOURNAL DIAMETER
LIMITS CHART
DESCRIPTION MEASUREMENT
CRANKSHAFT ROD JOURNAL
DIAMETERMin. 68.96 mm (2.715 in.)
Max. 69.01 mm (2.717 in.)
BEARING CLEARANCE Min. 0.04 mm (.002 in.)
Max. 0.12 mm (0.005 in.)
Fig. 64 Crankshaft
Fig. 65 Installing Alignment Pin
1 - ALIGNMENT PIN
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 273
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 1658 of 2627
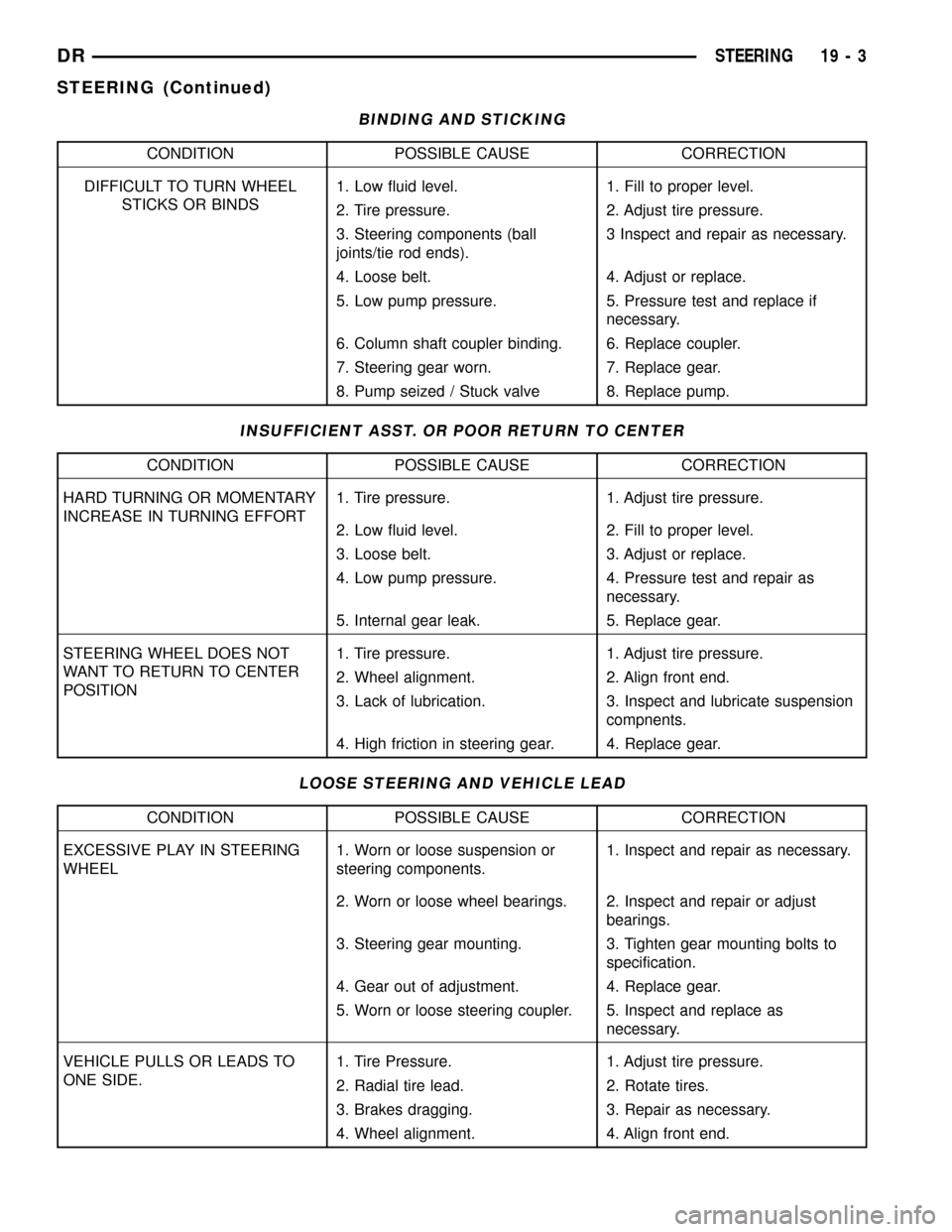
BINDING AND STICKING
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
DIFFICULT TO TURN WHEEL
STICKS OR BINDS1. Low fluid level. 1. Fill to proper level.
2. Tire pressure. 2. Adjust tire pressure.
3. Steering components (ball
joints/tie rod ends).3 Inspect and repair as necessary.
4. Loose belt. 4. Adjust or replace.
5. Low pump pressure. 5. Pressure test and replace if
necessary.
6. Column shaft coupler binding. 6. Replace coupler.
7. Steering gear worn. 7. Replace gear.
8. Pump seized / Stuck valve 8. Replace pump.
INSUFFICIENT ASST. OR POOR RETURN TO CENTER
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
HARD TURNING OR MOMENTARY
INCREASE IN TURNING EFFORT1. Tire pressure. 1. Adjust tire pressure.
2. Low fluid level. 2. Fill to proper level.
3. Loose belt. 3. Adjust or replace.
4. Low pump pressure. 4. Pressure test and repair as
necessary.
5. Internal gear leak. 5. Replace gear.
STEERING WHEEL DOES NOT
WANT TO RETURN TO CENTER
POSITION1. Tire pressure. 1. Adjust tire pressure.
2. Wheel alignment. 2. Align front end.
3. Lack of lubrication. 3. Inspect and lubricate suspension
compnents.
4. High friction in steering gear. 4. Replace gear.
LOOSE STEERING AND VEHICLE LEAD
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
EXCESSIVE PLAY IN STEERING
WHEEL1. Worn or loose suspension or
steering components.1. Inspect and repair as necessary.
2. Worn or loose wheel bearings. 2. Inspect and repair or adjust
bearings.
3. Steering gear mounting. 3. Tighten gear mounting bolts to
specification.
4. Gear out of adjustment. 4. Replace gear.
5. Worn or loose steering coupler. 5. Inspect and replace as
necessary.
VEHICLE PULLS OR LEADS TO
ONE SIDE.1. Tire Pressure. 1. Adjust tire pressure.
2. Radial tire lead. 2. Rotate tires.
3. Brakes dragging. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Wheel alignment. 4. Align front end.
DRSTEERING 19 - 3
STEERING (Continued)
Page 1704 of 2627

TRANSMISSION AND TRANSFER CASE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500..........1
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500..........43
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600..........88
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE........130
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE.311
TRANSFER CASE - NV241 GENII...........415TRANSFER CASE - NV271................447
TRANSFER CASE - NV243................482
TRANSFER CASE - NV244 GENII...........512
TRANSFER CASE - NV273................542
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................3
REMOVAL.............................3
DISASSEMBLY..........................4CLEANING............................15
INSPECTION..........................16
ASSEMBLY............................17
INSTALLATION.........................39
SPECIFICATIONS.......................40
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................40
MANUAL TRANSMISSION -
NV3500
DESCRIPTION
The transmission is a medium-duty 5-speed, con-
stant mesh fully synchronized manual transmission
with fifth gear overdrive range. The transmission is
available in two and four-wheel drive configurations.
The transmission gear case consists of two aluminum
housings (Fig. 1). The clutch housing is an integral
part of the transmission front housing.
A combination of roller and ball bearings are used
to support the transmission shafts in the two hous-
ings. The transmission gears all rotate on caged type
needle bearings. A roller bearing is used between the
input and output shaft.
The transmission has a single shaft shift mecha-
nism with three shift forks all mounted on the shaft.
The shaft is supported in the front and rear housings
by bushings and one linear ball bearing. Internal
shift components consist of the forks, shaft, shift
lever socket and detent components
OPERATION
The manual transmission receives power through the
clutch assembly from the engine. The clutch disc issplined to the transmission input shaft and is turned at
engine speed at all times that the clutch is engaged.
The input shaft is connected to the transmission coun-
tershaft through the mesh of fourth speed gear on the
input shaft and the fourth countershaft gear. At this
point, all the transmission gears are spinning.
The driver selects a particular gear by moving the
shift lever to the desired gear position. This movement
moves the internal transmission shift components to
begin the shift sequence. As the shift lever moves the
selected shift rail, the shift fork attached to that rail
begins to move. The fork is positioned in a groove in the
outer circumference of the synchronizer sleeve. As the
shift fork moves the synchronizer sleeve, the synchro-
nizer begins to speed-up or slow down the selected gear
(depending on whether we are up-shifting or down-shift-
ing). The synchronizer does this by having the synchro-
nizer hub splined to the mainshaft and moving the
blocker ring into contact with the gear's friction cone. As
the blocker ring and friction cone come together, the
gear speed is brought up or down to the speed of the
synchronizer. As the two speeds match, the splines on
the inside of the synchronizer sleeve become aligned
with the teeth on the blocker ring and the friction cone
and eventually will slide over the teeth, locking the gear
to the mainshaft, or countershaft, through the synchro-
nizer.
DRTRANSMISSION AND TRANSFER CASE 21 - 1
Page 1718 of 2627

(16) Remove fifth-reverse synchro hub and sleeve
with shop press (Fig. 45).
(17) Remove reverse gear and needle bearing (Fig.
46).
REVERSE IDLER
(1) Remove idler gear snap rings (Fig. 47).
(2) Remove thrust washer, wave washer, thrust
plate and idler gear from shaft.
(3) Remove idler gear needle bearing from shaft.
CLEANING
Clean the gears, shafts, shift components and
transmission housings with a standard parts clean-
ing solvent. Do not use acid or corrosive base sol-
vents. Dry all parts except bearings with compressed
air.
Clean the shaft bearings with a mild solvent such
as Mopar degreasing solvent, Gunk or similar sol-
vents. Do not dry the bearings with compressed air.
Allow the bearings to either air dry or wipe them dry
with clean shop towels.
Fig. 45 FIFTH-REVERSE SYNCHRO
1 - PRESS
2 - FIFTH-REVERSE SYNCHRO HUB AND SLEEVE
3 - REVERSE GEAR
4 - OUTPUT SHAFT
Fig. 46 REVERSE GEAR & NEEDLE BEARING
1 - REVERSE GEAR AND NEEDLE BEARING
Fig. 47 Reverse Idler Components
1 - SNAP RING
2 - FLAT WASHER
3 - WAVE WASHER
4 - THRUST WASHER
5 - REVERSE IDLER GEAR6 - IDLER GEAR BEARING
7 - IDLER SHAFT
8 - THRUST WASHER
9 - SNAP RING
10 - THRUST WASHER LOCKBALLS
DRMANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 21 - 15
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 (Continued)
Page 1720 of 2627

Inspect output shaft bearing retainer, the
U-shaped retainer must be flat and free of distortion.
Replace the retainer if the threads are damaged or if
the retainer is bent or cracked.
COUNTERSHAFT BEARINGS AND RACES
The countershaft bearings and races are machine
lapped during manufacture to form matched sets.
The bearings and races should not be interchanged.
NOTE: The bearing races are a permanent press fit
in the housings and are NOT serviceable. If a bear-
ing race becomes damaged, the front or rear hous-
ing must be replaced. A new countershaft bearing
will be supplied with each new housing for service
use.
REVERSE IDLER COMPONENTS
Inspect the idler gear, bearing, shaft, thrust
washer, wave washer and thrust plate. Replace the
bearing if any of the needle bearing rollers are worn,
chipped, cracked, flat-spotted or brinnelled. Also
replace the bearing if the plastic bearing cage is
damaged or distorted.
Replace thrust washer, wave washer or thrust
plate if cracked, chipped or worn. Replace idler gear
if the teeth are chipped, cracked or worn thin.
Replace shaft if worn, scored or the bolt threads are
damaged beyond repair. Replace support segment if
cracked or chipped and replace the idler attaching
bolts if the threads are damaged.
Shift Socket
Inspect the shift socket for wear or damage.
Replace the socket if the roll pin or shift shaft bores
are damaged. Minor nicks in the shift lever ball seat
in the socket can be smoothed down with 400 grit
emery or wet/dry paper. Replace the socket if the ball
seat is worn or cracked. Do not reuse the original
shift socket roll pin. Install anewpin during assem-
bly. The socket roll pin is approximately 33 mm
(1-1/4 in.) long.
Output Shaft And Geartrain
Inspect all gears for worn, cracked, chipped or bro-
ken teeth. Also check condition of the bearing bore in
each gear. The bores should be smooth and free of
surface damage. Discoloration of the gear bores is a
normal occurrence and is not a reason for replace-
ment. Replace gears only when tooth damage has
occurred or if the bores are brinnelled or severely
scored.
Inspect the shaft splines and bearings surfaces.
Minor nicks on the bearing surfaces can be smoothed
with 320/420 grit emery and final polished with cro-
cus cloth. Replace the shaft if the splines are dam-aged or bearing surfaces are deeply scored, worn or
brinnelled.
ASSEMBLY
NOTE: Sealers are used at all case joints. Use
Mopar Gasket Maker or equivalent for all case joints
and Mopar silicone sealer or equivalent for the
input shaft bearing retainer.
SYNCHRONIZER
(1) Slide sleeve onto the hub, leaving enough room
to install the spring in the hub and strut in the hub
groove.
(2) Install first spring in the hub, then install a
strut over the spring. Verify spring is seated in the
spring bore in the strut.
(3) Slide sleeve onto the hub far enough to hold
the first strut and spring in place.
(4) Place detent ball in the top of the strut, then
press the ball into place with a small screwdriver.
Work the sleeve over the ball to hold it in place.
(5) Repeat procedure for the remaining springs,
struts and balls. Use tape or rubber bands to tempo-
rarily secure each strut and ball as they are
installed.
(6) Verify the synchro three springs, struts and
detent balls are all in place (Fig. 49).
Fig. 49 SYNCHRONIZER COMPONENTS
1 - SLEEVE
2 - HUB SHOULDER
3 - SPRING (3)
4 - STRUT (3)
5 - DETENT BALL (3)
6 - HUB
DRMANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 21 - 17
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 (Continued)
Page 1729 of 2627

(8) Install front thrust washer on shaft and slide
washer up against gear and over lock ball (Fig. 80).
(9) Install wave washer, flat washer and remain-
ing snap ring on idler shaft (Fig. 80). Verify snap
ring is seated.
SHIFT SHAFT AND DETENT PLUNGER BUSHINGS/
BEARINGS
(1) Inspect shift shaft bushing and bearing for
damage.
(2) If necessary, the shift shaft bushing can be
replaced as follows:
(a) Locate a bolt that will thread into the bush-
ing without great effort.
(b) Thread the bolt into the bushing, allowing
the bolt to make its own threads in the bushing.
(c) Attach a slide hammer or suitable puller to
the bolt and remove bushing.(d) Use the short end of Installer 8119 to install
the new bushing.
(e) Bushing is correctly installed if flush with
the transmission case.
(3) If necessary, the shift shaft bearing can be
replaced as follows:
(a) Locate a bolt that will thread into the bear-
ing without great effort.
(b) Thread the bolt into the bearing as much as
possible.
(c) Attach a slide hammer or suitable puller to
the bolt and remove the bearing.
(d) Use the short end of Installer 8119 to install
the new bearing.
(e) Bearing is correctly installed if flush with the
transmission case.
(4) Inspect detent plunger bushings for damage.
NOTE: The detent plunger bushings are installed to
a specific depth. The space between the two bush-
ings when correctly installed contain an oil feed
hole. Do not attempt to install the bushings with
anything other than the specified tool or this oil
hole may become restricted.
(5) If necessary, the detent plunger bushings can
be replaced as follows:
(a) Using the long end of Installer 8119, drive
the detent bushings through the outer case and
into the shift shaft bore.
(b) Remove the bushings from the shift shaft
bore.
(c) Install a new detent plunger bushing on the
long end of Installer 8118.
(d) Start bushing in the detent plunger bore in
the case.
(e) Drive bushing into the bore until the tool
contacts the transmission case.
(f) Install a new detent plunger bushing on the
short end of Installer 8118.
(g) Start the bushing in the detent plunger bore
in the case.
(h) Drive bushing into the bore until the tool
contacts the transmission case.
Fig. 80 IDLER GEAR & SHAFT ASSEMBLY
1 - REAR OF SHAFT
2 - GEAR
3 - THRUST WASHER AND BALL
4 - WAVE WASHER
5 - FLAT WASHER
6 - FRONT OF SHAFT
7 - SNAP RING
8 - SNAP RING
21 - 26 MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500DR
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 (Continued)