1998 DODGE RAM 1500 change time
[x] Cancel search: change timePage 1436 of 2627

INSPECTION
Check the connecting rod journal for excessive
wear, taper and scoring (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/EN-
GINE BLOCK/CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Check the connecting rod for signs of twist or bend-
ing.
Check the piston for taper and elliptical shape
before it is fitted into the cylinder bore (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON & CONNECT-
ING ROD - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Check the piston for scoring, or scraping marks in
the piston skirts. Check the ring lands for cracks
and/or deterioration.
INSTALLATION
(1) Before installing piston and connecting rod
assemblies into the bore, install the piston rings(Re-
fer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON RINGS
- STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Immerse the piston head and rings in clean
engine oil. Position a ring compressor over the piston
and rings. Tighten ring compressor.Ensure posi-
tion of rings do not change during this opera-
tion.
(3) Position bearing onto connecting rod. Lubricate
bearing surface with clean engine oil.
(4) Install Special Tool 8507 Connecting Rod
Guides into connecting rod bolt threads.
(5) The pistons are marked on the piston pin bore
surface with an raised ªFº or arrow on top of piston
indicating installation position. This mark must be
pointing toward the front of engine on both cylinder
banks.
(6) Wipe cylinder bore clean and lubricate with
engine oil.
(7) Rotate crankshaft until connecting rod journal
is on the center of cylinder bore. Insert rod and pis-
ton into cylinder bore and carefully position connect-
ing rod guides over crankshaft journal.
(8) Tap piston down in cylinder bore using a ham-
mer handle. While at the same time, guide connect-
ing rod into position on rod journal.
CAUTION: Connecting Rod Bolts are Torque to
Yield Bolts and Must Not Be Reused. Always
replace the Rod Bolts whenever they are loosened
or removed.
(9) Lubricate rod bolts and bearing surfaces with
engine oil. Install connecting rod cap and bearing.
Tighten bolts to 21 N´m (15 ft. lbs.) plus a 90É turn.
(10) Install the following components:
²Cylinder head(s). (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLIN-
DER HEAD - INSTALLATION).²Cylinder head covers (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) -
INSTALLATION).
²Install the intake manifold.
²Oil pan and gasket/windage tray. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLA-
TION).
(11) Fill crankcase with proper engine oil to cor-
rect level.
(12) Connect negative cable to battery.
PISTON RINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON RING
FITTING
Before reinstalling used rings or installing new
rings, the ring clearances must be checked.
(1) Wipe the cylinder bore clean.
(2) Insert the ring in the cylinder bore.
NOTE: The ring gap measurement must be made
with the ring positioned at least 12mm (0.50 inch.)
from bottom of cylinder bore.
(3) Using a piston, to ensure that the ring is
squared in the cylinder bore, slide the ring downward
into the cylinder.
(4) Using a feeler gauge check the ring end gap
(Fig. 13). Replace any rings not within specification.
PISTON RING SIDE CLEARANCE
NOTE: Make sure the piston ring grooves are clean
and free of nicks and burrs.
Fig. 13 Ring
1 - FEELER GAUGE
DRENGINE - 5.7L 9 - 213
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1446 of 2627

minutes before checking oil level. Checking engine oil
level on a cold engine is not accurate.
To ensure proper lubrication of an engine, the
engine oil must be maintained at an acceptable level.
The acceptable levels are indicated between the ADD
and SAFE marks on the engine oil dipstick.
(1) Position vehicle on level surface.
(2) With engine OFF, allow approximately five
minutes for oil to settle to bottom of crankcase,
remove engine oil dipstick.
(3) Wipe dipstick clean.
(4) Install dipstick and verify it is seated in the
tube.
(5) Remove dipstick, with handle held above the
tip, take oil level reading.
(6) Add oil only if level is below the ADD mark on
dipstick.
ENGINE OIL CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in Maintenance Schedules(Refer to LUBRI-
CATION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTENANCE
SCHEDULES - DESCRIPTION).
Run engine until achieving normal operating tem-
perature.
(1) Position the vehicle on a level surface and turn
engine off.
(2) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(3) Remove oil fill cap.
(4) Place a suitable drain pan under crankcase
drain.
(5) Remove drain plug from crankcase and allow
oil to drain into pan. Inspect drain plug threads for
stretching or other damage. Replace drain plug if
damaged.
(6) Install drain plug in crankcase. Torque to 34
N´m ( 25 ft. lbs.).
(7) Lower vehicle and fill crankcase with specified
type and amount of engine oil described in this sec-
tion.
(8) Install oil fill cap.
(9) Start engine and inspect for leaks.
(10) Stop engine and inspect oil level.
USED ENGINE OIL DISPOSAL
Care should be exercised when disposing used
engine oil after it has been drained from a vehicle
engine. Refer to the WARNING at beginning of this
section.
OIL FILTER
REMOVAL
All engines are equipped with a high quality full-
flow, disposable type oil filter. DaimlerChrysler Cor-
poration recommends a Mopartor equivalent oil
filter be used.
(1) Position a drain pan under the oil filter.
(2) Using a suitable oil filter wrench loosen filter.
(3) Rotate the oil filter counterclockwise to remove
it from the cylinder block oil filter boss.
(4) When filter separates from cylinder block oil
filter boss, tip gasket end upward to minimize oil
spill. Remove filter from vehicle.
NOTE: Make sure filter gasket was removed with fil-
ter.
(5) With a wiping cloth, clean the gasket sealing
surface of oil and grime.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lightly lubricate oil filter gasket with engine
oil.
(2) Thread filter onto adapter nipple. When gasket
makes contact with sealing surface, (Fig. 29) hand
tighten filter one half turn, or 180É,do not over
tighten.
(3) Add oil, verify crankcase oil level and start
engine. Inspect for oil leaks.
Fig. 29 Oil Filter Sealing Surface - Typical
1 - SEALING SURFACE
2 - RUBBER GASKET
3 - OIL FILTER
DRENGINE - 5.7L 9 - 223
OIL (Continued)
Page 1459 of 2627
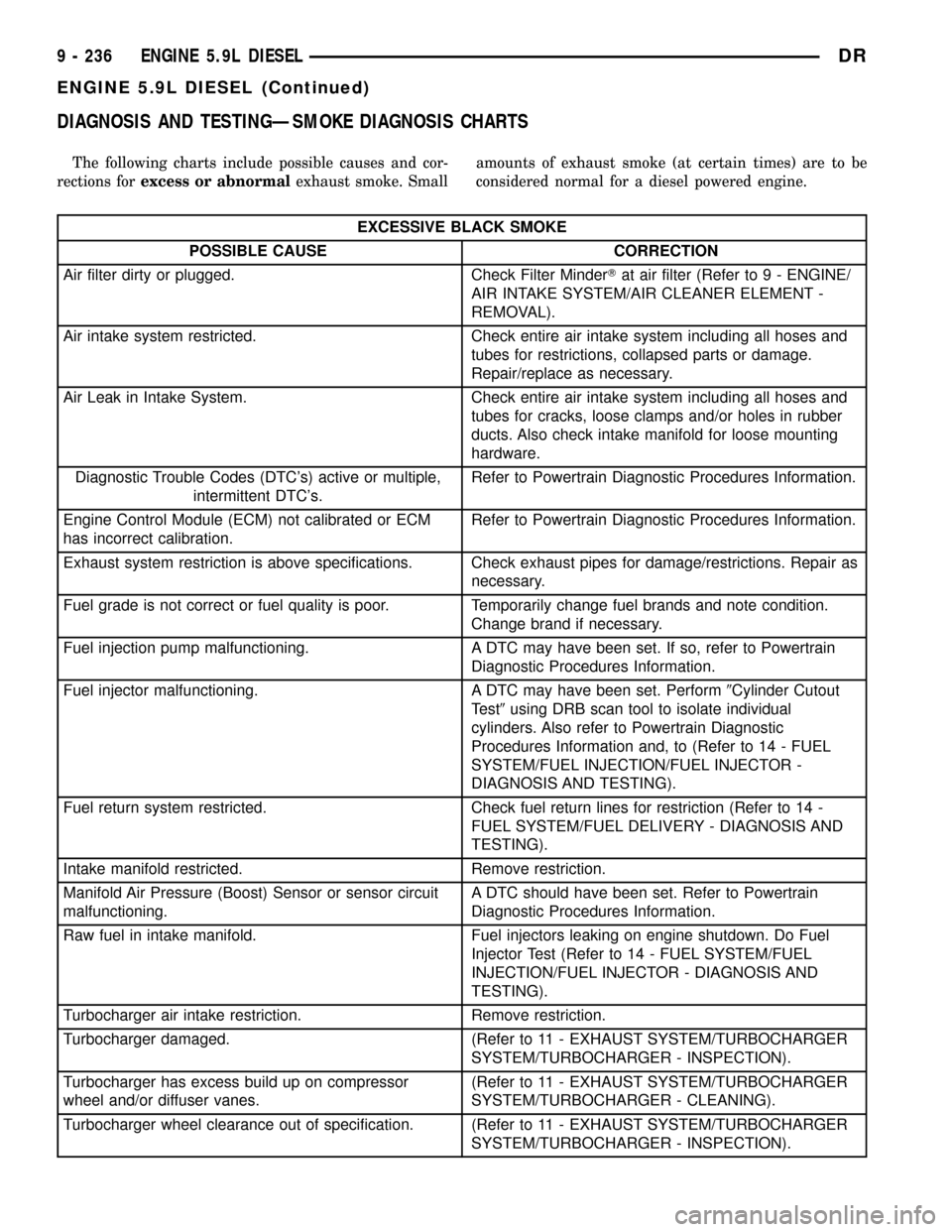
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐSMOKE DIAGNOSIS CHARTS
The following charts include possible causes and cor-
rections forexcess or abnormalexhaust smoke. Smallamounts of exhaust smoke (at certain times) are to be
considered normal for a diesel powered engine.
EXCESSIVE BLACK SMOKE
POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Air filter dirty or plugged. Check Filter MinderTat air filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
AIR INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER ELEMENT -
REMOVAL).
Air intake system restricted. Check entire air intake system including all hoses and
tubes for restrictions, collapsed parts or damage.
Repair/replace as necessary.
Air Leak in Intake System. Check entire air intake system including all hoses and
tubes for cracks, loose clamps and/or holes in rubber
ducts. Also check intake manifold for loose mounting
hardware.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) active or multiple,
intermittent DTC's.Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Engine Control Module (ECM) not calibrated or ECM
has incorrect calibration.Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Exhaust system restriction is above specifications. Check exhaust pipes for damage/restrictions. Repair as
necessary.
Fuel grade is not correct or fuel quality is poor. Temporarily change fuel brands and note condition.
Change brand if necessary.
Fuel injection pump malfunctioning. A DTC may have been set. If so, refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Fuel injector malfunctioning. A DTC may have been set. Perform9Cylinder Cutout
Test9using DRB scan tool to isolate individual
cylinders. Also refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information and, to (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Fuel return system restricted. Check fuel return lines for restriction (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Intake manifold restricted. Remove restriction.
Manifold Air Pressure (Boost) Sensor or sensor circuit
malfunctioning.A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Raw fuel in intake manifold. Fuel injectors leaking on engine shutdown. Do Fuel
Injector Test (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Turbocharger air intake restriction. Remove restriction.
Turbocharger damaged. (Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER - INSPECTION).
Turbocharger has excess build up on compressor
wheel and/or diffuser vanes.(Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER - CLEANING).
Turbocharger wheel clearance out of specification. (Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER - INSPECTION).
9 - 236 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1466 of 2627

(8) Replace injector o-ring and sealing washer on
injectors #5 and #6. Install injectors and torque using
the following steps:
²Step 1ÐInstall injector hold-down capscrews
and torque to 5 N´m (44 in. lbs.) torque.
²Step 2ÐLoosen injector hold-down capscrews.
²Step 3ÐInstall HPC connector tube and nut.
Torque nut to 15 N´m (11 ft. lbs.) torque.
²Step 4ÐTorque injector hold-down capscrews to
10 N´m (89 in. lbs.) torque.
²Step 5ÐTorque HPC connector tube nut to 50
N´m (37 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install #5 and #6 high pressure fuel lines. Fol-
low correct torque sequence per section 14. Torque
fuel line fittings to 30 N-m (22 ft-lb). Torque brace
capscrew to 24 N-m (18 ft-lb).
(10) Install rear engine lift bracket. Torque to 77
N-m (57 ft-lb).
(11) Install push tubes, rocker arms, and pedestals
for cylinders #4, #5, and #6. Torque the mounting
bolts to 36 N-m (27 ft-lbs).
(12) Reset valve lash on cylinders #4, #5, and #6.
Torque adjusting nuts to 24 N-m (18 ft-lbs).
(13) Install cylinder head cover. Torque to 24 N-m
(18 ft-lbs).(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD -
INSTALLATION).
(14) Connect breather tube and lube oil drain tube
to breather housing cover. Install breather housing.
Torque capscrews to 24 N-m (18 ft-lbs)
(15) Connect fuel supply and return hoses.
(16) Connect ECM ground to hydroform screw.
Connect ECM power connector.
(17) Install the APPS cable(s) to the APPS. Install
the throttle linkage cover.
(18) Install the power steering pump.
(19) Install the damper and speed indicator ring.
Torque to 40 N-m (30 ft-lb) plus 60 degrees.
(20) Connect the engine block heater connection.
(21) Connect the A/C compressor and pressure sen-
sor connectors
(22) Install the charge air cooler and a/c condenser
(if equipped). Install and tighten the charge air
cooler mounting bolts to 2 N-m (17 in-lbs).
(23) Connect the charge air cooler piping. Torque
all clamps to 8 N-m (72 in-lbs).
(24) Connect the a/c refrigerant lines to the a/c
condenser (if equipped).
(25) Install the radiator upper support panel.
(26) Install radiator.
(27) Connect the transmission quick-connect oil
cooler lines.(28) Raise vehicle.
(29) Connect a/c compressor suction/discharge hose
(if equipped).
(30) Install the radiator lower hose and clamps.
(31) Install the battery negative cables to the
engine block on the driver and passenger side.
(32) Install the transmission adapter with a new
camshaft rectangular ring seal. Torque to 77 N-m (57
ft-lb).
(33) Install the flywheel/flexplate. Torque to 137
N-m (101 ft-lb).
(34) Install the starter motor. Torque to 43 N-m
(32 ft-lb). (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/STARTING/
STARTER MOTOR - INSTALLATION).
(35) Connect engine to vehicle harness connectors.
(36) Install transmission and transfer case (if
equipped).
(37) Connect the exhaust pipe to the turbocharger
elbow.
(38) Connect the transmission auxiliary oil cooler
lines (if equipped).
(39) Lower the vehicle.
(40) Connect the heater core supply and return
hoses.
(41) Install the cooling fan and upper fan shroud
at the same time. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
RADIATOR FAN - INSTALLATION).
(42) Install the coolant recovery bottle.
(43) Install the windshield washer bottle.
(44) Install the upper radiator hose and clamps.
(45) Raise vehicle.
(46) Connect electronically controlled fan drive
wire harness. Install lower radiator fan shroud.
(47) Change oil filter and install new engine oil.
(48) Fill the cooling system with coolant. (Refer to
7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(49) Connect grid heater harness at grid heater
relays.
(50) Connect electrical connections to rear of alter-
nator.
(51) Start the engine and inspect for engine oil,
coolant, and fuel leaks.
INSTALLATIONÐCRANKCASE BREATHER
(1) Install a new o-ring onto the breather element.
(2) Lubricate o-ring and install into cylinder head
cover. Torque capscrews to 10 N´m (89 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect breather tube and lube oil drain tube.
(4) Install breather cover (Fig. 4). Torque to 24
N´m (18 ft. lbs.)
(5) Install oil fill cap.
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 243
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1512 of 2627

LUBRICATION
DESCRIPTION
NOTE: Refer to (Fig. 105) and (Fig. 106) for circuit
illustrations.
A gear driven gerotor type oil pump is mounted
behind the front gear cover in the lower right portion
on the engine.
OPERATION
A gerotor style oil pump draws oil from the crank-
case through the suction tube and delivers it through
the block where it enters the oil cooler cover and
pressure regulator valve. When oil pressure exceeds
517 kPa (75 PSI), the valve opens exposing the dump
port, which routes excess oil back to the oil pump.
At the same time, oil is directed to a cast in pas-
sage in the oil cooler cover, leading to the oil cooler
element. As the oil travels through the element
plates, it is cooled by engine coolant traveling past
the outside of the plates. It is then routed to the oil
filter head and through a full flow oil filter. If a
plugged filter is encountered, the filter by-pass valve
opens, allowing unfiltered oil to lubricate the engine.
This condition can be avoided by frequent oil and fil-
ter changes, per the maintenance schedules found in
the owners manual. The by-pass valve is calibrated
to open when it sees a pressure drop of more than
345 kPa (50 psi) across the oil filter.
The oil filter head then divides the oil between the
engine and the turbocharger. The turbocharger
receives filtered, cooled and pressurized oil through a
supply line from the filter head. The oil lubricates
the turbocharger and returns to the pan by way of a
drain tube connecting the bottom of the turbocharger
to a pressed in tube in the cylinder block.
Oil is then carried across the block to an angle
drilling which intersects the main oil rifle. The main
oil rifle runs the length of the block and delivers oil
to the crankshaft main journals and valve train. Oil
travels to the crankshaft through a series of transfer
drillings (one for each main bearing) and lubricates a
groove in the main bearing upper shell. From there
another drilling feeds the camshaft main journals.The saddle jet piston cooling nozzles are also sup-
plied by the main bearing upper shell. J-jet piston
cooling nozzles are supplied by a separate oil rifle.
Plugs are used in place of saddle jets when J-jets are
used. J-jet hole locations are plugged when saddle jet
cooling nozzles are used. Crankshaft internal cross-
drillings supply oil to the connecting rod journals.
Another series of transfer drillings intersecting the
main oil rifle supply the valve train components. Oil
travels up the drilling, through a hole in the head
gasket, and through a drilling in the cylinder head
(one per cylinder), where it enters the rocker arm
pedestal and is divided between the intake and
exhaust rocker arm. Oil travels up and around the
rocker arm mounting bolt, and lubricates the rocker
shaft by cross drillings that intersect the mounting
bolt hole. Grooves at both ends of the rocker shaft
supply oil through the rocker arm where the oil trav-
els to the push rod and socket balls (Fig. 105) and
(Fig. 106).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE OIL
PRESSURE
(1) Remove the 1/8 npt plug from the top of the oil
filter housing.
(2) Install Oil Pressure Line and Gauge Tool
C-3292 with a suitable adapter.
(3) Start engine and warm to operating tempera-
ture.
(4) Record engine oil pressure and compare with
engine oil pressure chart.
CAUTION: If engine oil pressure is zero at idle, DO
NOT RUN THE ENGINE.
Engine Oil Pressure (MIN)
At Idle 68.9 kPa (10 psi)
At 2500 rpm 206.9 kPa (30 psi)
If minimum engine oil pressure is below these
ranges, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
(5) Remove oil pressure gauge and install the 1/8
npt plug.
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 289
Page 1597 of 2627

REMOVAL
The fuel pump relay is located in the Power Distri-
bution Center (PDC) (Fig. 13). Refer to label on PDC
cover for relay location.
(1) Remove PDC cover.
(2) Remove relay from PDC.
(3) Check condition of relay terminals and PDC
connector terminals for damage or corrosion. Repair
if necessary before installing relay.
(4) Check for pin height (pin height should be the
same for all terminals within the PDC connector).
Repair if necessary before installing relay.
INSTALLATION
The fuel pump relay is located in the Power Distri-
bution Center (PDC). Refer to label on PDC cover for
relay location.
(1) Install relay to PDC.
(2) Install cover to PDC.
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
A separate IAC motor is not used with the 5.7L V-8
engine.
The IAC stepper motor is mounted to the throttle
body, and regulates the amount of air bypassing the
control of the throttle plate. As engine loads and
ambient temperatures change, engine rpm changes.
A pintle on the IAC stepper motor protrudes into apassage in the throttle body, controlling air flow
through the passage. The IAC is controlled by the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) to maintain the
target engine idle speed.
OPERATION
A separate IAC motor is not used with the 5.7L V-8
engine.
At idle, engine speed can be increased by retract-
ing the IAC motor pintle and allowing more air to
pass through the port, or it can be decreased by
restricting the passage with the pintle and diminish-
ing the amount of air bypassing the throttle plate.
The IAC is called a stepper motor because it is
moved (rotated) in steps, or increments. Opening the
IAC opens an air passage around the throttle blade
which increases RPM.
The PCM uses the IAC motor to control idle speed
(along with timing) and to reach a desired MAP dur-
ing decel (keep engine from stalling).
The IAC motor has 4 wires with 4 circuits. Two of
the wires are for 12 volts and ground to supply elec-
trical current to the motor windings to operate the
stepper motor in one direction. The other 2 wires are
also for 12 volts and ground to supply electrical cur-
rent to operate the stepper motor in the opposite
direction.
To make the IAC go in the opposite direction, the
PCM just reverses polarity on both windings. If only
1 wire is open, the IAC can only be moved 1 step
(increment) in either direction. To keep the IAC
motor in position when no movement is needed, the
PCM will energize both windings at the same time.
This locks the IAC motor in place.
In the IAC motor system, the PCM will count
every step that the motor is moved. This allows the
PCM to determine the motor pintle position. If the
memory is cleared, the PCM no longer knows the
position of the pintle. So at the first key ON, the
PCM drives the IAC motor closed, regardless of
where it was before. This zeros the counter. From
this point the PCM will back out the IAC motor and
keep track of its position again.
When engine rpm is above idle speed, the IAC is
used for the following:
²Off-idle dashpot (throttle blade will close quickly
but idle speed will not stop quickly)
²Deceleration air flow control
²A/C compressor load control (also opens the pas-
sage slightly before the compressor is engaged so
that the engine rpm does not dip down when the
compressor engages)
²Power steering load control
The PCM can control polarity of the circuit to con-
trol direction of the stepper motor.
Fig. 13 PDC LOCATION
1 - BATTERY
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE (IPM)
14 - 28 FUEL INJECTION - GASDR
FUEL PUMP RELAY (Continued)
Page 1598 of 2627

IAC Stepper Motor Program:The PCM is also
equipped with a memory program that records the
number of steps the IAC stepper motor most recently
advanced to during a certain set of parameters. For
example: The PCM was attempting to maintain a
1000 rpm target during a cold start-up cycle. The last
recorded number of steps for that may have been
125. That value would be recorded in the memory
cell so that the next time the PCM recognizes the
identical conditions, the PCM recalls that 125 steps
were required to maintain the target. This program
allows for greater customer satisfaction due to
greater control of engine idle.
Another function of the memory program, which
occurs when the power steering switch (if equipped),
or the A/C request circuit, requires that the IAC step-
per motor control engine rpm, is the recording of the
last targeted steps into the memory cell. The PCM
can anticipate A/C compressor loads. This is accom-
plished by delaying compressor operation for approx-
imately 0.5 seconds until the PCM moves the IAC
stepper motor to the recorded steps that were loaded
into the memory cell. Using this program helps elim-
inate idle-quality changes as loads change. Finally,
the PCM incorporates a9No-Load9engine speed lim-
iter of approximately 1800 - 2000 rpm, when it rec-
ognizes that the TPS is indicating an idle signal and
IAC motor cannot maintain engine idle.
A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani-
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate.Never attempt to adjust the engine idle
speed using this screw.All idle speed functions are
controlled by the IAC motor through the PCM.
REMOVAL
3.7L V-6
The Idle Air Control (IAC) motor is located on the
side of the throttle body (Fig. 14).
(1) Remove air resonator box at throttle body.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from IAC motor.
(3) Remove two mounting bolts (screws).
(4) Remove IAC motor from throttle body.
4.7L V-8
The Idle Air Control (IAC) motor is located on the
side of the throttle body (Fig. 15).
(1) Remove air resonator box at throttle body.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from IAC motor.
(3) Remove two mounting bolts (screws).
(4) Remove IAC motor from throttle body.
5.7L V-8
The IAC motor is not serviceable on the 5.7L V-8
engine.
INSTALLATION
3.7L V-6
The Idle Air Control (IAC) motor is located on the
side of the throttle body (Fig. 14).
(1) Install IAC motor to throttle body.
(2) Install and tighten two mounting bolts (screws)
to 7 N´m (60 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install electrical connector.
(4) Install air resonator to throttle body.
4.7L V-8
The Idle Air Control (IAC) motor is located on the
side of the throttle body (Fig. 15).
(1) Install IAC motor to throttle body.
(2) Install and tighten two mounting bolts (screws)
to 7 N´m (60 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install electrical connector.
(4) Install air resonator to throttle body.
5.7L V-8
The IAC motor is not serviceable on the 5.7L V-8
engine.
Fig. 14 IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR - 3.7L V-6
1 - THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS)
2 - MOUNTING SCREWS
3 - IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR (IAC)
4 - MOUNTING SCREWS
DRFUEL INJECTION - GAS 14 - 29
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR (Continued)
Page 1601 of 2627

(3) Position sensor into intake manifold and rotate
clockwise until past release tab.
(4) Install electrical connector.
5.7L V-8
The intake manifold air temperature (IAT) sensor
is installed into the front of the intake manifold air
box plenum (Fig. 19).
(1) Check condition of sensor o-ring.
(2) Clean sensor mounting hole in intake manifold.
(3) Position sensor into intake manifold and rotate
clockwise until past release tab.
(4) Install electrical connector.
MAP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
3.7L V-6
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor is
mounted into the front of the intake manifold with 2
screws.
4.7L V-8
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor is
mounted into the front of the intake manifold with 2
screws.
5.7L V-8
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor is
mounted to the front of the intake manifold air ple-
num box.
OPERATION
The MAP sensor is used as an input to the Power-
train Control Module (PCM). It contains a silicon
based sensing unit to provide data on the manifold
vacuum that draws the air/fuel mixture into the com-
bustion chamber. The PCM requires this information
to determine injector pulse width and spark advance.
When manifold absolute pressure (MAP) equals
Barometric pressure, the pulse width will be at max-
imum.
A 5 volt reference is supplied from the PCM and
returns a voltage signal to the PCM that reflects
manifold pressure. The zero pressure reading is 0.5V
and full scale is 4.5V. For a pressure swing of 0±15
psi, the voltage changes 4.0V. To operate the sensor,
it is supplied a regulated 4.8 to 5.1 volts. Ground is
provided through the low-noise, sensor return circuit
at the PCM.
The MAP sensor input is the number one contrib-
utor to fuel injector pulse width. The most important
function of the MAP sensor is to determine baromet-
ric pressure. The PCM needs to know if the vehicle is
at sea level or at a higher altitude, because the air
density changes with altitude. It will also help to cor-
rect for varying barometric pressure. Barometric
pressure and altitude have a direct inverse correla-
tion; as altitude goes up, barometric goes down. At
key-on, the PCM powers up and looks at MAP volt-
age, and based upon the voltage it sees, it knows the
current barometric pressure (relative to altitude).
Once the engine starts, the PCM looks at the voltage
again, continuously every 12 milliseconds, and com-
pares the current voltage to what it was at key-on.
The difference between current voltage and what it
was at key-on, is manifold vacuum.
During key-on (engine not running) the sensor
reads (updates) barometric pressure. A normal range
can be obtained by monitoring a known good sensor.
As the altitude increases, the air becomes thinner
(less oxygen). If a vehicle is started and driven to a
very different altitude than where it was at key-on,
the barometric pressure needs to be updated. Any
time the PCM sees Wide Open Throttle (WOT), based
upon Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) angle and RPM,
it will update barometric pressure in the MAP mem-
ory cell. With periodic updates, the PCM can make
its calculations more effectively.
The PCM uses the MAP sensor input to aid in cal-
culating the following:
²Manifold pressure
²Barometric pressure
Fig. 20 5.7L IAT SENSOR R/I
1 - FRONT OF INTAKE MANIFOLD PLENUM
2 - IAT SENSOR
3 - RELEASE TAB
14 - 32 FUEL INJECTION - GASDR
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR (Continued)