1998 DODGE RAM 1500 checking oil
[x] Cancel search: checking oilPage 1905 of 2627

(2) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repair
The use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The torque converter should also be replaced when-
ever a failure generates sludge and debris. This is
necessary because normal converter flushing proce-
dures will not remove all contaminants.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, thegeartrain churns up foam and cause the same condi-
tions which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transmission vent where it may be mis-
taken for a leak.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
The transmission has a dipstick to check oil level.
It is located on the right side of the engine. Be sure
to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle before removing.
Fluid level is checked with the engine running at
curb idle speed, the transmission in NEUTRAL and
the transmission fluid at normal operating tempera-
ture.The engine should be running at idle
speed for at least one minute, with the vehicle
on level ground.
The transmission fluid level can be checked two
ways.
PROCEDURE ONE
(1) Transmission fluid must be at normal operat-
ing temperature for accurate fluid level check. Drive
vehicle if necessary to bring fluid temperature up to
normal hot operating temperature of 82ÉC (180ÉF).
(2) Position vehicle on level surface.
(3) Start and run engine at curb idle speed.
(4) Apply parking brakes.
(5) Shift transmission momentarily into all gear
ranges. Then shift transmission back to NEUTRAL.
(6) Clean top of filler tube and dipstick to keep
dirt from entering tube.
(7) Remove dipstick (Fig. 87) and check fluid level
as follows:
(a) Correct acceptable level is in crosshatch area.
(b) Correct maximum level is to MAX arrow
mark.
(c) Incorrect level is at or below MIN line.
(d) If fluid is low, add only enough MopartAT F
+4 to restore correct level. Do not overfill.
Fig. 87 Dipstick Fluid Level Marks - Typical
1 - DIPSTICK
2 - MAXIMUM CORRECT FLUID LEVEL
3 - ACCEPTABLE FLUID LEVEL
21 - 202 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 1906 of 2627

PROCEDURE TWO
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2) Shift the transmission into DRIVE for approxi-
mately 2 seconds.
(3) Shift the transmission into REVERSE for
approximately 2 seconds.
(4) Shift the transmission into PARK.
(5) Hook up DRBtscan tool and select engine.
(6) Select sensors.
(7) Read the transmission temperature value.
(8) Compare the fluid temperature value with the
chart.
(9) Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the
dipstick according to the chart (Fig. 88).
NOTE: After adding any fluid to the transmission,
wait a minimum of 2 minutes for the oil to fully
drain from the fill tube into the transmission before
rechecking the fluid level.
(10) Check transmission for leaks.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
REPLACEMENT
For proper service intervals (Refer to LUBRICA-
TION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTENANCE SCHED-
ULES - DESCRIPTION). The service fluid fill after a
filter change is approximately 3.8 liters (4.0 quarts).
REMOVAL
(1) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(2) Place a large diameter shallow drain pan
beneath the transmission pan.
(3) Remove bolts holding front and sides of pan to
transmission (Fig. 89).
(4) Loosen bolts holding rear of pan to transmis-
sion.
Fig. 88 48RE Fluid Fill Graph
Fig. 89 Transmission Pan
1 - TRANSMISSION
2 - REUSABLE GASKET
3-PAN
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 203
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 1918 of 2627

CAUTION: The reaction shaft support seal rings will
break if overspread, or twisted. If new rings are
being installed, spread them only enough for instal-
lation. Also be very sure the ring ends are securely
hooked together after installation. Otherwise, the
rings will either prevent pump installation, or break
during installation.
Fig. 112 Oil Pump Assembly
1 - OIL SEAL 7 - BOLTS (6)
2 - VENT BAFFLE 8 - #1 THRUST WASHER (SELECTIVE)
3 - OIL PUMP BODY 9 - INNER GEAR
4 - GASKET 10 - OUTER GEAR
5 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT 11 - ªOº RING
6 - SEAL RINGS 12 - TORQUE CONVERTER SEAL RING
Fig. 113 Checking Pump Gear Tip Clearance
1 - FEELER GAUGE
2 - INNER GEAR
3 - OUTER GEAR
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 215
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 2014 of 2627

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE
DESCRIPTION........................312
OPERATION..........................313
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION.....................314
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING -
PRELIMINARY.......................314
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD
TESTING...........................314
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TEST....................316
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIR CHECKING
TRANSMISSION CLUTCH OPERATION....317
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CONVERTER
HOUSING FLUID LEAK................318
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ALUMINUM
THREAD REPAIR.....................318
REMOVAL............................318
DISASSEMBLY........................320
CLEANING...........................326
INSPECTION.........................326
ASSEMBLY...........................326
INSTALLATION........................333
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS
HYDRAULIC SCHEMATICS.............337
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSMISSION.....................358
SPECIAL TOOLS
RFE TRANSMISSION.................359
4C RETAINER/BULKHEAD
DISASSEMBLY........................362
ASSEMBLY...........................363
ADAPTER HOUSING SEAL
REMOVAL............................364
INSTALLATION........................364
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION........................364
OPERATION..........................364
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK......364
ADJUSTMENTS - BRAKE TRANSMISSION
SHIFT INTERLOCK...................365
FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL.............366
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID.......................366DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION....................366
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK............................366
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND
FILTER REPLACEMENT...............367
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TRANSMISSION
FILL...............................368
GEARSHIFT CABLE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - GEARSHIFT
CABLE.............................368
REMOVAL............................369
INSTALLATION........................370
ADJUSTMENTS
GEARSHIFT CABLE..................370
HOLDING CLUTCHES
DESCRIPTION........................371
OPERATION..........................372
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION........................373
OPERATION..........................373
DISASSEMBLY........................374
ASSEMBLY...........................378
INPUT SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................382
OPERATION..........................382
REMOVAL............................382
INSTALLATION........................382
LINE PRESSURE (LP) SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................382
OPERATION..........................383
REMOVAL............................383
INSTALLATION........................383
LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH
DISASSEMBLY........................384
CLEANING...........................385
INSPECTION.........................385
ASSEMBLY...........................385
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION........................386
OPERATION..........................386
STANDARD PROCEDURE - OIL PUMP
VOLUME CHECK.....................387
DISASSEMBLY........................388
CLEANING...........................390
INSPECTION.........................390
ASSEMBLY...........................390
OIL PUMP FRONT SEAL
REMOVAL............................391
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 311
Page 2017 of 2627

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
CAUTION: Before attempting any repair on a RFE
automatic transmission, check for Diagnostic Trou-
ble Codes with the DRBTscan tool.
Transmission malfunctions may be caused by these
general conditions:
²Poor engine performance
²Improper adjustments
²Hydraulic malfunctions
²Mechanical malfunctions
²Electronic malfunctions
Diagnosis of these problems should always begin
by checking the easily accessible variables: fluid level
and condition, gearshift cable adjustment. Then per-
form a road test to determine if the problem has been
corrected or if more diagnosis is necessary. If the
problem persists after the preliminary tests and cor-
rections are completed, hydraulic pressure checks
should be performed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY
Two basic procedures are required. One procedure
for vehicles that are drivable and an alternate proce-
dure for disabled vehicles (will not back up or move
forward).
VEHICLE IS DRIVABLE
(1) Check for transmission fault codes using DRBt
scan tool.
(2) Check fluid level and condition.
(3) Adjust gearshift cable if complaint was based
on delayed, erratic, or harsh shifts.
(4) Road test and note how transmission upshifts,
downshifts, and engages.
(5) Perform hydraulic pressure test if shift prob-
lems were noted during road test.(6) Perform air-pressure test to check clutch oper-
ation.
VEHICLE IS DISABLED
(1) Check fluid level and condition.
(2) Check for broken or disconnected gearshift
cable.
(3) Check for cracked, leaking cooler lines, or loose
or missing pressure-port plugs.
(4) Raise and support vehicle on safety stands,
start engine, shift transmission into gear, and note
following:
(a) If propeller shaft turns but wheels do not,
problem is with differential or axle shafts.
(b) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is noisy, stop engine. Remove oil pan, and
check for debris. If pan is clear, remove transmis-
sion and check for damaged driveplate, converter,
oil pump, or input shaft.
(c) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is not noisy, perform hydraulic-pressure test to
determine if problem is hydraulic or mechanical.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TESTING
Before road testing, be sure the fluid level and con-
trol cable adjustments have been checked and
adjusted if necessary. Verify that all diagnostic trou-
ble codes have been resolved.
Observe engine performance during the road test.
A poorly tuned engine will not allow accurate analy-
sis of transmission operation.
Operate the transmission in all gear ranges. Check
for shift variations and engine flare which indicates
slippage. Note if shifts are harsh, spongy, delayed,
early, or if part throttle downshifts are sensitive.
Slippage indicated by engine flare, usually means
clutch, overrunning clutch, or line pressure problems.
A slipping clutch can often be determined by com-
paring which internal units are applied in the vari-
ous gear ranges. The Clutch Application charts
provide a basis for analyzing road test results.
21 - 314 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE (Continued)
Page 2020 of 2627
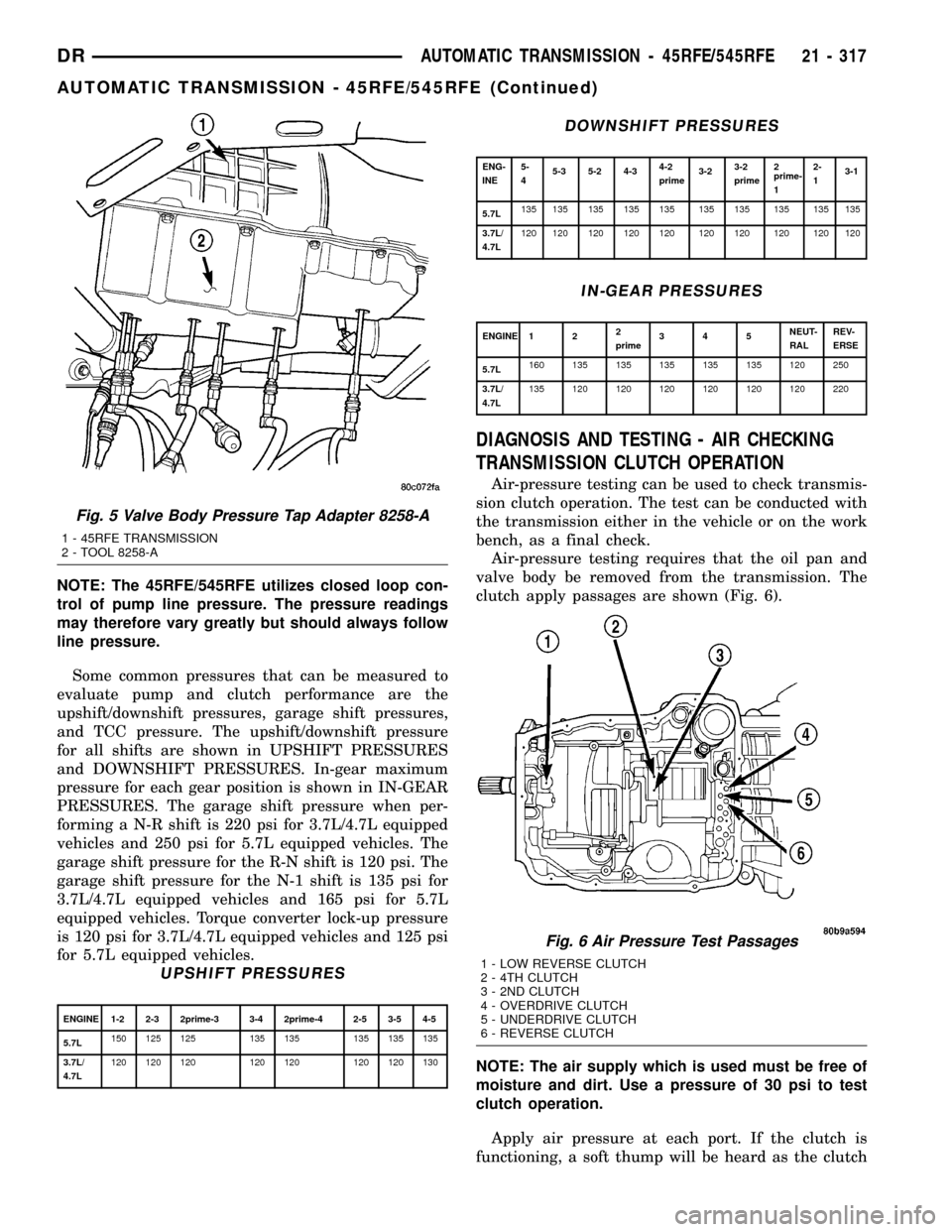
NOTE: The 45RFE/545RFE utilizes closed loop con-
trol of pump line pressure. The pressure readings
may therefore vary greatly but should always follow
line pressure.
Some common pressures that can be measured to
evaluate pump and clutch performance are the
upshift/downshift pressures, garage shift pressures,
and TCC pressure. The upshift/downshift pressure
for all shifts are shown in UPSHIFT PRESSURES
and DOWNSHIFT PRESSURES. In-gear maximum
pressure for each gear position is shown in IN-GEAR
PRESSURES. The garage shift pressure when per-
forming a N-R shift is 220 psi for 3.7L/4.7L equipped
vehicles and 250 psi for 5.7L equipped vehicles. The
garage shift pressure for the R-N shift is 120 psi. The
garage shift pressure for the N-1 shift is 135 psi for
3.7L/4.7L equipped vehicles and 165 psi for 5.7L
equipped vehicles. Torque converter lock-up pressure
is 120 psi for 3.7L/4.7L equipped vehicles and 125 psi
for 5.7L equipped vehicles.
UPSHIFT PRESSURES
ENGINE 1-2 2-3 2prime-3 3-4 2prime-4 2-5 3-5 4-5
5.7L150 125 125 135 135 135 135 135
3.7L/
4.7L120 120 120 120 120 120 120 130
DOWNSHIFT PRESSURES
ENG-
INE5-
45-3 5-2 4-34-2
prime3-23-2
prime2
prime-
12-
13-1
5.7L135 135 135 135 135 135 135 135 135 135
3.7L/
4.7L120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120
IN-GEAR PRESSURES
ENGINE 1 22
prime345NEUT-
RALREV-
ERSE
5.7L160 135 135 135 135 135 120 250
3.7L/
4.7L135 120 120 120 120 120 120 220
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIR CHECKING
TRANSMISSION CLUTCH OPERATION
Air-pressure testing can be used to check transmis-
sion clutch operation. The test can be conducted with
the transmission either in the vehicle or on the work
bench, as a final check.
Air-pressure testing requires that the oil pan and
valve body be removed from the transmission. The
clutch apply passages are shown (Fig. 6).
NOTE: The air supply which is used must be free of
moisture and dirt. Use a pressure of 30 psi to test
clutch operation.
Apply air pressure at each port. If the clutch is
functioning, a soft thump will be heard as the clutch
Fig. 5 Valve Body Pressure Tap Adapter 8258-A
1 - 45RFE TRANSMISSION
2 - TOOL 8258-A
Fig. 6 Air Pressure Test Passages
1 - LOW REVERSE CLUTCH
2 - 4TH CLUTCH
3 - 2ND CLUTCH
4 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
5 - UNDERDRIVE CLUTCH
6 - REVERSE CLUTCH
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 317
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE (Continued)
Page 2037 of 2627

o-ring is properly installed and is free of any debris.
The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging pump
seal at installation.
(2) If a replacement transmission is being
installed, transfer any components necessary, such as
the manual shift lever and shift cable bracket, from
the original transmission onto the replacement trans-
mission.
(3) Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission
fluid.
(4) Align converter and oil pump.(5) Carefully insert converter in oil pump. Then
rotate converter back and forth until fully seated in
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with steel scale and
straightedge (Fig. 53). Surface of converter lugs
should be at least 13mm (1/2 in.) to rear of straight-
edge when converter is fully seated.
(7) Temporarily secure converter with C-clamp.
(8) Position transmission on jack and secure it
with chains.
(9) Check condition of converter driveplate.
Replace the plate if cracked, distorted or damaged.
Also be sure transmission dowel pins are seated
in engine block and protrude far enough to
hold transmission in alignment.
(10) Apply a light coating of MopartHigh Temp
Grease to the torque converter hub pocket in the rear
pocket of the engine's crankshaft.
(11) Raise transmission (Fig. 54) and align the
torque converter with the drive plate and transmis-
sion converter housing with the engine block.
(12) Move transmission forward. Then raise, lower
or tilt transmission to align the converter housing
with engine block dowels.
(13) Carefully work transmission forward and over
engine block dowels until converter hub is seated in
crankshaft. Verify that no wires, or the transmission
vent hose, have become trapped between the engine
block and the transmission.
(14) Install two bolts to attach the transmission to
the engine.
(15) Install remaining torque converter housing to
engine bolts. Tighten to 68 N´m (50 ft.lbs.).
Fig. 51 Install Primary Oil and Cooler Filters
1 - PRIMARY OIL FILTER
2 - COOLER RETURN FILTER
3 - COOLER RETURN FILTER BYPASS VALVE
4 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 52 Install Input, Output, and Line Pressure
Sensors
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 53 Checking Torque Converter Seating - Typical
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
21 - 334 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE (Continued)
Page 2069 of 2627

FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve and clutch operation. Foaming also causes fluid
expansion which can result in fluid overflow from the
transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can eas-
ily be mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has three primary causes.
(1) Internal clutch slippage, usually caused by low
line pressure, inadequate clutch apply pressure, or
clutch seal failure.
(2) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.
(3) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repairThe use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The torque converter should also be replaced when-
ever a failure generates sludge and debris. This is
necessary because normal converter flushing proce-
dures will not remove all contaminants.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, the
geartrain churns up foam and cause the same condi-
tions which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transmission vent where it may be mis-
taken for a leak.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
The transmission has a dipstick to check oil level.
It is located on the right side of the engine. Be sure
to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle before removing.
The torque converter fills in both the P (PARK)
and N (NEUTRAL) positions. Place the selector lever
in P (PARK) to be sure that the fluid level check is
accurate.The engine should be running at idle
speed for at least one minute, with the vehicle
on level ground.At normal operating temperature
(approximately 82 C. or 180 F.), the fluid level is cor-
rect if it is in the HOT region (cross-hatched area) on
the oil level indicator. The fluid level will be approx-
21 - 366 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR