1998 DODGE RAM 1500 differential
[x] Cancel search: differentialPage 297 of 2627

REMOVAL
(1) Remove the front rotor (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/ROTORS -
REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the wheel speed sensor mounting bolt
from the hub. (Fig. 3)
(3) Remove the wheel speed sensor from the hub.
(4) Remove the wiring from the clips and discon-
nect the electrical connector.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the wiring to the clips and Reconnect
the electrical connector.
(2) Install the wheel speed sensor to the hub.
(3) Install the wheel speed sensor mounting bolt to
the hub. Tighten the bolt to 21 N´m (190 in. lbs.).
(4) Install the front rotor and brake caliper assem-
bly (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANI-
CAL/ROTORS - INSTALLATION).
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR WHEEL
ANTILOCK
Diagnosis of base brake conditions which are
mechanical in nature should be performed first. This
includes brake noise, lack of power assist, parking
brake, or vehicle vibration during normal braking.
The RWAL brake system performs several self-
tests every time the ignition switch is turned on and
the vehicle is driven. The CAB monitors the system
inputs and outputs circuits to verify the system is
operating properly. If the CAB senses a malfunction
in the system it will set a DTC into memory and trig-
ger the warning lamp.NOTE: The MDS or DRB III scan tool is used to
diagnose the RWAL system. For test procedures
refer to the Chassis Diagnostic Manual.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
(2) Remove the brake line mounting nut and
remove the brake line from the sensor stud.
(3) Remove the mounting stud from the sensor and
shield (Fig. 4).
(4) Remove the sensor and shield from the differ-
ential housing.
(5) Disconnect the sensor wire harness and remove
the sensor.
INSTALLATION
(1) Connect the harness to the sensor.Be sure
the seal is securely in place between the sensor
and the wiring connector.
(2) Install the O-ring on the sensor (if removed).
(3) Insert the sensor in the differential housing.
(4) Install the sensor shield.
(5) Install the sensor mounting stud and tighten to
24 N´m (200 in. lbs.).
(6) Install the brake line on the sensor stud and
install the nut.
(7) Lower the vehicle.
Fig. 3 WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
1 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR MOUNTING BOLT
2 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
3 - HUB/BEARINGFig. 4 REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
1 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
2 - MOUNTING BOLT
3 - AXLE HOUSING
5 - 48 BRAKES - ABSDR
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1234 of 2627

(12) Disconnect heater hoses from heater core and
remove hose assembly.
(13) Disconnect throttle and speed control cables.
(14) Remove upper radiator hose from engine.
(15) Remove lower radiator hose from engine.
(16) Remove radiator/cooling module assembly.
(17) Disconnect the engine to body ground straps
at the left side of cowl.
(18) Disconnect the engine wiring harness at the
following points:
²Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor
²Fuel Injectors
²Throttle Position (TPS) Switch
²Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor
²Engine Oil Pressure Switch
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
²Manifold Absolute Pressure MAP) Sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
²Coil Over Plugs
²Crankshaft Position Sensor
(19) Remove coil over plugs.
(20) Release fuel rail pressure.
(21) Remove fuel rail and secure away from
engine.
NOTE: It is not necessary to release the quick con-
nect fitting from the fuel supply line for engine
removal.
(22) Remove the PCV hose.
(23) Remove the breather hoses.
(24) Remove the vacuum hose for the power brake
booster.
(25) Disconnect knock sensors.
(26) Remove engine oil dipstick tube.
(27) Remove intake manifold.
(28) Install engine lifting fixture,special tool#8247,
using original fasteners from the removed intake
manifold, and fuel rail. Torque to factory specifica-
tions.
NOTE: Recheck bolt torque for engine lift plate
before removing engine.
(29) Secure the left and right engine wiring har-
nesses away from engine.
(30) Raise vehicle.
(31) Disconnect oxygen sensor wiring.
(32) Disconnect crankshaft postion sensor.
(33) Disconnect the engine block heater power
cable, if equipped.
(34) Disconnect the front propshaft at the front
differential and secure out of way.
NOTE: It is necessary to disconnect the front prop-
shaft for access to the starter and left side exhaust
flange.(35) Remove the starter.
(36) Remove the ground straps from the left and
right side of the block.
(37) Disconnect the right and left exhaust pipes at
the manifolds and from the crossover, and remove
from the vehicle.
NOTE: The exhaust clamps at the manifolds cannot
be reused. New clamps must be used or leaks may
occur.
(38) Remove the structural cover.
(39) Remove torque convertor bolts, and mark
location for reassembly.
(40) Remove transmission bellhousing to engine
bolts.
(41) Remove left and right engine mount thru
bolts.
(42) Lower the vehicle.
(43) Support the transmission with a suitable jack.
(44) Connect a suitable engine hoist to the engine
lift plate.
(45) Remove engine from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the engine in the vehicle.
(2) Install both left and right side engine mounts
onto engine.
(3) Raise the vehicle.
(4) Install the transmission bellhousing to engine
mounting bolts. Tighten the bolts to 41 N´m (30ft.
lbs.).
(5) Tighten the engine mount thru bolts.
(6) Install the torque convertor bolts.
(7) Connect the ground straps on the left and right
side of the engine.
(8) Install the starter.
(9) Connect the crankshaft position sensor.
(10) Install the engine block heater power cable, if
equipped.
CAUTION: The structural cover requires a specific
torque sequence. Failure to follow this sequence
may cause severe damage to the cover.
(11) Install the structural cover.
NOTE: New clamps must be used on exhaust man-
ifold flanges. Failure to use new clamps may result
in exhaust leaks.
(12) Install the left and right exhaust pipes.
(13) Connect the left and right oxygen sensors.
(14) Lower vehicle.
(15) Remove the engine lift plate.
(16) Connect the knock sensors.
DRENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 11
ENGINE - 3.7L (Continued)
Page 1843 of 2627

valve moves the overdrive piston into contact with
the overdrive clutch. The direct clutch is disengaged
before the overdrive clutch is engaged. The boost
valve provides increased fluid apply pressure to the
overdrive clutch during 3-4 upshifts, and when accel-
erating in fourth gear. The 3-4 accumulator cushions
overdrive clutch engagement to smooth 3-4 upshifts.
The accumulator is charged at the same time as
apply pressure acts against the overdrive piston.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
Automatic transmission problems can be a result of
poor engine performance, incorrect fluid level, incor-
rect linkage or cable adjustment, band or hydraulic
control pressure adjustments, hydraulic system mal-
functions or electrical/mechanical component mal-
functions. Begin diagnosis by checking the easily
accessible items such as: fluid level and condition,
linkage adjustments and electrical connections. A
road test will determine if further diagnosis is neces-
sary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY
Two basic procedures are required. One procedure
for vehicles that are drivable and an alternate proce-
dure for disabled vehicles (will not back up or move
forward).
VEHICLE IS DRIVEABLE
(1) Check for transmission fault codes using DRBt
scan tool.
(2) Check fluid level and condition.
(3) Adjust throttle and gearshift linkage if com-
plaint was based on delayed, erratic, or harsh shifts.
(4) Road test and note how transmission upshifts,
downshifts, and engages.
(5) Perform hydraulic pressure test if shift prob-
lems were noted during road test.
(6) Perform air-pressure test to check clutch-band
operation.
VEHICLE IS DISABLED
(1) Check fluid level and condition.
(2) Check for broken or disconnected gearshift or
throttle linkage.
(3) Check for cracked, leaking cooler lines, or loose
or missing pressure-port plugs.
(4) Raise and support vehicle on safety stands,
start engine, shift transmission into gear, and note
following:
(a) If propeller shaft turns but wheels do not,
problem is with differential or axle shafts.
(b) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is noisy, stop engine. Remove oil pan, and
check for debris. If pan is clear, remove transmis-
sion and check for damaged drive plate, converter,
oil pump, or input shaft.
(c) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is not noisy, perform hydraulic-pressure test to
determine if problem is hydraulic or mechanical.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TESTING
Before road testing, be sure the fluid level and con-
trol cable adjustments have been checked and
adjusted if necessary. Verify that diagnostic trouble
codes have been resolved.
Observe engine performance during the road test.
A poorly tuned engine will not allow accurate analy-
sis of transmission operation.
Operate the transmission in all gear ranges. Check
for shift variations and engine flare which indicates
slippage. Note if shifts are harsh, spongy, delayed,
early, or if part throttle downshifts are sensitive.
Slippage indicated by engine flare, usually means
clutch, band or overrunning clutch problems. If the
condition is advanced, an overhaul will be necessary
to restore normal operation.
A slipping clutch or band can often be determined
by comparing which internal units are applied in the
various gear ranges. The Clutch and Band Applica-
tion chart provides a basis for analyzing road test
results.
21 - 140 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1861 of 2627

STANDARD PROCEDURE - ALUMINUM
THREAD REPAIR
Damaged or worn threads in the aluminum trans-
mission case and valve body can be repaired by the
use of Heli-CoilsŸ, or equivalent. This repair con-
sists of drilling out the worn-out damaged threads.
Then tap the hole with a special Heli-CoilŸ tap, or
equivalent, and installing a Heli-CoilŸ insert, or
equivalent, into the hole. This brings the hole back to
its original thread size.
Heli-CoilŸ, or equivalent, tools and inserts are
readily available from most automotive parts suppli-
ers.
REMOVAL
NOTE: The overdrive unit can be removed and ser-
viced separately. It is not necessary to remove the
entire transmission assembly to perform overdrive
unit repairs.
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Remove the transfer case skid plate (Fig. 12), if
equipped.(4) Disconnect and lower or remove necessary
exhaust components.
(5) Remove engine-to-transmission struts.
(6) Remove starter motor. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/STARTING/STARTER MOTOR - REMOVAL)
(7) Disconnect and remove the crankshaft position
sensor. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJEC-
TION/CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
REMOVAL) Retain the sensor attaching bolts.
(8) If transmission is being removed for overhaul,
remove transmission oil pan, drain fluid and reinstall
pan.
(9) Remove torque converter access cover.
(10) Rotate crankshaft in clockwise direction until
converter bolts are accessible. Then remove bolts one
at a time. Rotate crankshaft with socket wrench on
dampener bolt.
(11) Mark propeller shaft and axle yokes for
assembly alignment. Then disconnect and remove
propeller shaft. On4x4models, remove both propel-
ler shafts. (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIV-
ELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT -
REMOVAL)
(12) Disconnect wires from the transmission range
sensor and transmission solenoid connector.
(13) Disconnect gearshift cable (Fig. 13) from the
transmission.
Fig. 12 Transfer Case Skid Plate
1 - FRAME RAIL
2 - SKID PLATE
3 - BOLTS (6)
Fig. 13 Gearshift Cable At Transmission
1 - GEARSHIFT CABLE
2 - TRANSMISSION MANUAL LEVER
3 - CABLE SUPPORT BRACKET
21 - 158 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1878 of 2627

(13) Install bolts attaching converter housing to
engine.
(14) Install rear support.
(15) Install the rear transmission crossmember.
(16) Lower transmission onto crossmember and
install bolts attaching transmission mount to cross-
member.
(17) Remove engine support fixture.
(18) Install the transfer case, if equipped.
(19) Install crankshaft position sensor. (Refer to 14
- FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/CRANKSHAFT
POSITION SENSOR - INSTALLATION)
(20) Connect gearshift cable (Fig. 64) and throttle
cable to transmission.
(21) Connect wires to the transmission range sen-
sor and transmission solenoid connector. Be sure the
transmission harnesses are properly routed.
CAUTION: It is essential that correct length bolts be
used to attach the converter to the driveplate. Bolts
that are too long will damage the clutch surface
inside the converter.(22) Install torque converter-to-driveplate bolts.
(23) Install converter housing access cover.
(24) Install starter motor and cooler line bracket.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/STARTING/STARTER
MOTOR - INSTALLATION)
(25) Connect cooler lines (Fig. 65) to transmission.
(26) Install transmission fill tube. Install new seal
on tube before installation.
(27) Install any exhaust components previously
removed.
(28) Align and connect propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 -
DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER
SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT - INSTALLATION)
(29) Adjust gearshift cable and throttle valve
cable, if necessary.
(30) Install the transfer case skid plate, if
equipped.
(31) Lower vehicle.
(32) Fill transmission with MopartATF +4, Auto-
matic Transmission fluid.
Fig. 64 Gearshift Cable At Transmission
1 - GEARSHIFT CABLE
2 - TRANSMISSION MANUAL LEVER
3 - CABLE SUPPORT BRACKET
Fig. 65 Transmission Cooler Lines
1 - TRANSMISSION
2 - RADIATOR
3 - COOLER LINES
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 175
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1921 of 2627
OVERDRIVE UNIT
REMOVAL
(1) Shift transmission into PARK.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Remove transfer case, if equipped.
(4) Mark propeller shaft universal joint(s) and axle
pinion yoke, or the companion flange and flange
yoke, for alignment reference at installation, if neces-
sary.
(5) Disconnect and remove the rear propeller shaft,
if necessary. (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIV-
ELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT -
REMOVAL)
(6) Remove transmission oil pan, remove gasket,
drain oil and reinstall pan.
(7) If overdrive unit had malfunctioned, or if fluid
is contaminated, remove entire transmission. If diag-
nosis indicated overdrive problems only, remove just
the overdrive unit.
(8) Support transmission with transmission jack.
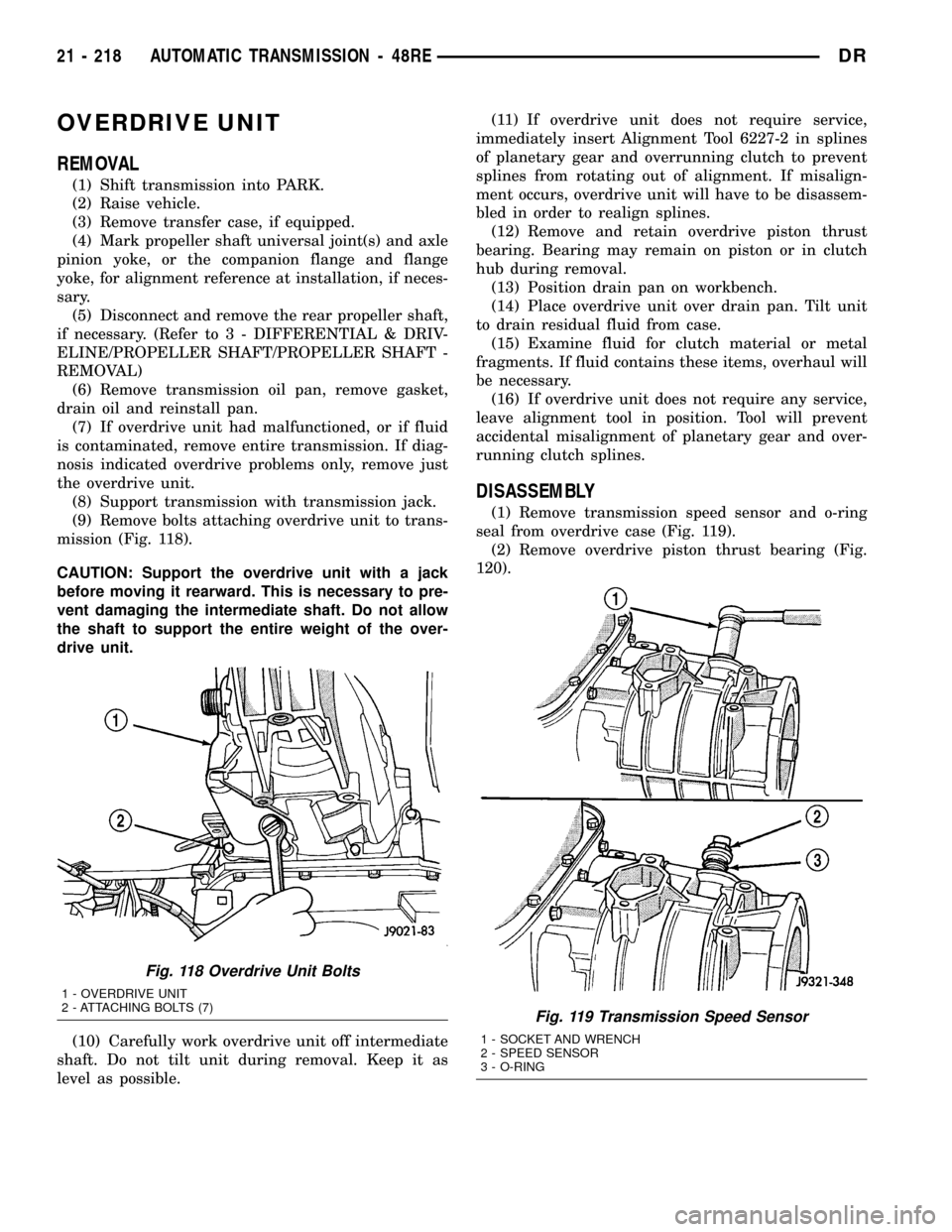
(9) Remove bolts attaching overdrive unit to trans-
mission (Fig. 118).
CAUTION: Support the overdrive unit with a jack
before moving it rearward. This is necessary to pre-
vent damaging the intermediate shaft. Do not allow
the shaft to support the entire weight of the over-
drive unit.
(10) Carefully work overdrive unit off intermediate
shaft. Do not tilt unit during removal. Keep it as
level as possible.(11) If overdrive unit does not require service,
immediately insert Alignment Tool 6227-2 in splines
of planetary gear and overrunning clutch to prevent
splines from rotating out of alignment. If misalign-
ment occurs, overdrive unit will have to be disassem-
bled in order to realign splines.
(12) Remove and retain overdrive piston thrust
bearing. Bearing may remain on piston or in clutch
hub during removal.
(13) Position drain pan on workbench.
(14) Place overdrive unit over drain pan. Tilt unit
to drain residual fluid from case.
(15) Examine fluid for clutch material or metal
fragments. If fluid contains these items, overhaul will
be necessary.
(16) If overdrive unit does not require any service,
leave alignment tool in position. Tool will prevent
accidental misalignment of planetary gear and over-
running clutch splines.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove transmission speed sensor and o-ring
seal from overdrive case (Fig. 119).
(2) Remove overdrive piston thrust bearing (Fig.
120).
Fig. 118 Overdrive Unit Bolts
1 - OVERDRIVE UNIT
2 - ATTACHING BOLTS (7)
Fig. 119 Transmission Speed Sensor
1 - SOCKET AND WRENCH
2 - SPEED SENSOR
3 - O-RING
21 - 218 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
Page 1938 of 2627

INSTALLATION
(1) Be sure overdrive unit Alignment Tool 6227-2
is fully seated before moving unit. If tool is not
seated and gear splines rotate out of alignment, over-
drive unit will have to be disassembled in order to
realign splines.
(2) If overdrive piston retainer was not removed
during service and original case gasket is no longer
reusable, prepare new gasket by trimming it.
(3) Cut out old case gasket around piston retainer
with razor knife (Fig. 176).
(4) Use old gasket as template and trim new gas-
ket to fit.
(5) Position new gasket over piston retainer and
on transmission case. Use petroleum jelly to hold
gasket in place if necessary. Do not use any type of
sealer to secure gasket. Use petroleum jelly only.
(6) Install selective spacer on intermediate shaft, if
removed. Spacer goes in groove just rearward of
shaft rear splines (Fig. 177).
(7) Install thrust bearing in overdrive unit sliding
hub. Use petroleum jelly to hold bearing in position.
CAUTION: Be sure the shoulder on the inside diam-
eter of the bearing is facing forward.(8) Verify that splines in overdrive planetary gear
and overrunning clutch hub are aligned with Align-
ment Tool 6227-2. Overdrive unit cannot be installed
if splines are not aligned. If splines have rotated out
of alignment, unit will have to be disassembled to
realign splines.
(9) Carefully slide Alignment Tool 6227-2 out of
overdrive planetary gear and overrunning clutch
splines.
(10) Raise overdrive unit and carefully slide it
straight onto intermediate shaft. Insert park rod into
park lock reaction plug at same time. Avoid tilting
overdrive during installation as this could cause
planetary gear and overrunning clutch splines to
rotate out of alignment. If this occurs, it will be nec-
essary to remove and disassemble overdrive unit to
realign splines.
(11) Work overdrive unit forward on intermediate
shaft until seated against transmission case.
(12) Install bolts attaching overdrive unit to trans-
mission unit. Tighten bolts in diagonal pattern to 34
N´m (25 ft-lbs).
(13) Connect the transmission speed sensor and
overdrive wiring connectors.
(14) Install the transfer case, if equipped.
(15) Align and install rear propeller shaft, if nec-
essary. (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/
PROPELLER SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT -
INSTALLATION)
Fig. 176 Trimming Overdrive Case Gasket
1 - GASKET
2 - SHARP KNIFE
Fig. 177 Intermediate Shaft Selective Spacer
Location
1 - SELECTIVE SPACER
2 - SPACER GROOVE
3 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 235
OVERDRIVE UNIT (Continued)
Page 1987 of 2627
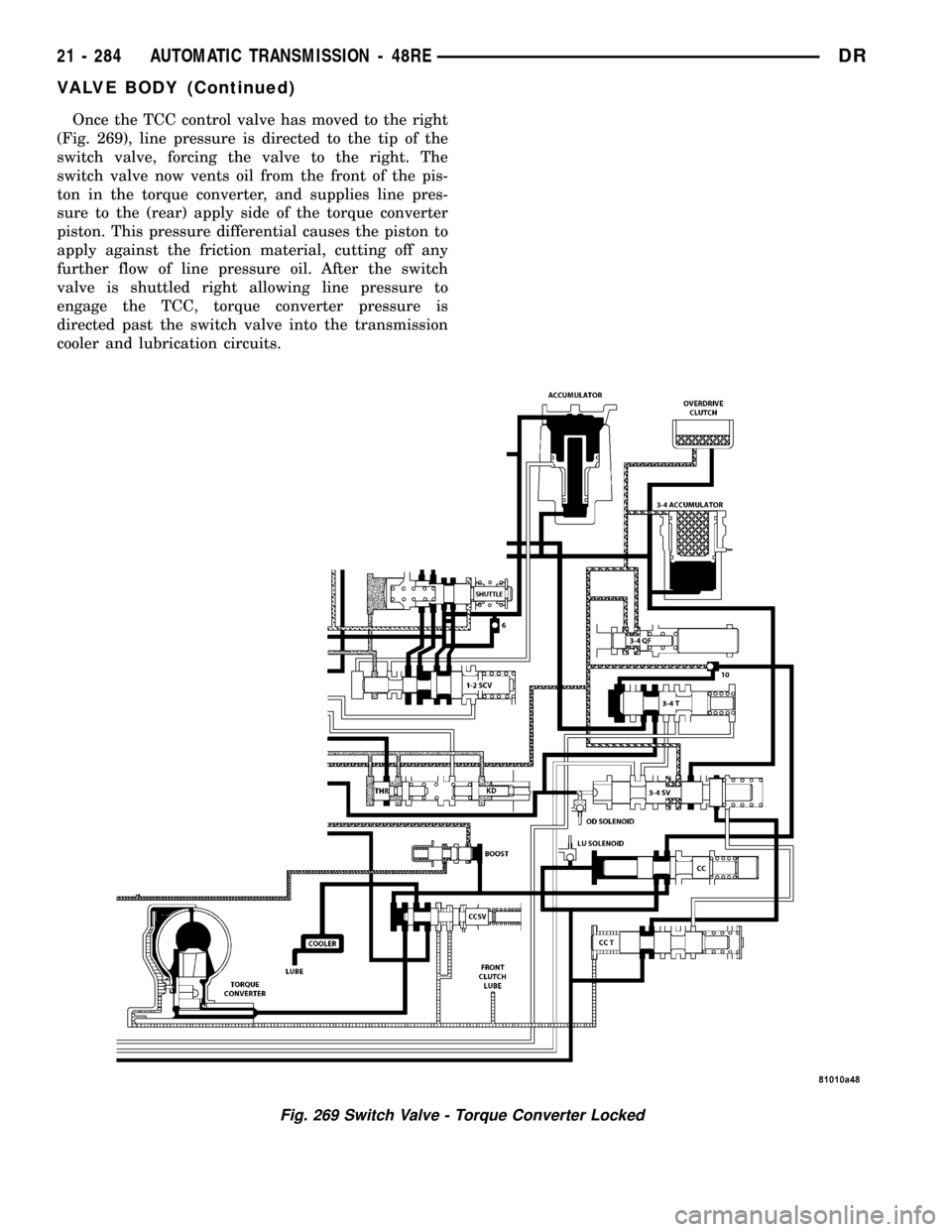
Once the TCC control valve has moved to the right
(Fig. 269), line pressure is directed to the tip of the
switch valve, forcing the valve to the right. The
switch valve now vents oil from the front of the pis-
ton in the torque converter, and supplies line pres-
sure to the (rear) apply side of the torque converter
piston. This pressure differential causes the piston to
apply against the friction material, cutting off any
further flow of line pressure oil. After the switch
valve is shuttled right allowing line pressure to
engage the TCC, torque converter pressure is
directed past the switch valve into the transmission
cooler and lubrication circuits.
Fig. 269 Switch Valve - Torque Converter Locked
21 - 284 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)