1998 DODGE RAM 1500 tow
[x] Cancel search: towPage 1217 of 2627

SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS
CIGAR LIGHTER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION
On models equipped a cigar lighter outlet is
installed to the left of the center stack area in the
lower instrument panel. The cigar lighter outlet is
secured by a snap fit within the bezel.
The cigar lighter outlet, plastic cap and the knob
and heating element unit are available for service
replacement. These components cannot be repaired
and, if faulty or damaged, they must be replaced.
OPERATION
The cigar lighter consists of two major components:
a knob and heating element unit, and the cigar
lighter base or outlet shell. The receptacle shell is
connected to ground, and an insulated contact in the
bottom of the shell is connected to battery current.
The cigar lighter receives battery voltage from a fuse
in the junction block when the ignition switch is in
the Accessory or Run positions.
The cigar lighter knob and heating element are
encased within a spring-loaded housing, which also
features a sliding protective heat shield. When the
knob and heating element are inserted in the outlet
shell, the heating element resistor coil is grounded
through its housing to the outlet shell. If the cigar
lighter knob is pushed inward, the heat shield slides
up toward the knob exposing the heating element,
and the heating element extends from the housing
toward the insulated contact in the bottom of the
outlet shell.
Two small spring-clip retainers are located on
either side of the insulated contact inside the bottom
of the outlet shell. These clips engage and hold the
heating element against the insulated contact longenough for the resistor coil to heat up. When the
heating element is engaged with the contact, battery
current can flow through the resistor coil to ground,
causing the resistor coil to heat.
When the resistor coil becomes sufficiently heated,
excess heat radiates from the heating element caus-
ing the spring-clips to expand. Once the spring-clips
expand far enough to release the heating element,
the spring-loaded housing forces the knob and heat-
ing element to pop back outward to their relaxed
position. When the cigar lighter knob and element
are pulled out of the outlet shell, the protective heat
shield slides downward on the housing so that the
heating element is recessed and shielded around its
circumference for safety.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CIGAR LIGHTER
OUTLET
For complete circuit diagrams, refer toWiring
Diagrams.
(1) Check the fused B(+) fuse in the integrated
power module. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair
the shorted circuit or component as required and
replace the faulty fuse.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the Run position.
Check for battery voltage at the fused B(+) fuse in
the integrated power module. If OK, go to Step 3. If
not OK, repair the open or short as required.
(3) Remove the cigar lighter knob and element
from the cigar lighter outlet shell. Check for continu-
ity between the inside circumference of the cigar
lighter outlet shell and a good ground. there should
be continuity. If OK, go to Step 4. If not OK, go to
Step 5.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the Run position.
Check for battery voltage at the insulated contact
located at the back of the cigar lighter outlet shell. If
OK, replace the faulty cigar lighter knob and ele-
ment. If not OK, go to Step 5.
(5) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
Disconnect and isolate the battery negative cable.
Check for continuity between the ground circuit cav-
ity of the cigar lighter wire harness connector and a
good ground. There should be continuity. If OK, go to
Step 6. If not OK, repair the open ground circuit to
ground as required.
(6) Connect the battery negative cable. Turn the
ignition switch to the Accessory or Run positions.
Check for battery voltage at the fused B(+) circuit
cavity of the cigar lighter wire harness connector. If
OK, replace the faulty cigar lighter outlet. If not OK,
repair the open fused B(+) circuit to the integrated
power module fuse as required.Terminal Pick Kit 6680
8W - 97 - 2 8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTIONDR
POWER DISTRIBUTION (Continued)
Page 1222 of 2627

becomes transparent and the fuse that has been
assigned the IOD designation becomes only another
Fused B(+) circuit fuse.
The IOD fuse can be used by the vehicle owner as
a convenient means of reducing battery depletion
when a vehicle is to be stored for periods not to
exceed about thirty days. However, it must be
remembered that disconnecting the IOD fuse will not
eliminate IOD, but only reduce this normal condition.
If a vehicle will be stored for more than about thirty
days, the battery negative cable should be discon-
nected to eliminate normal IOD; and, the battery
should be tested and recharged at regular intervals
during the vehicle storage period to prevent the bat-
tery from becoming discharged or damaged.
REMOVAL
The Ignition-Off Draw (IOD) fuse is disconnected
from Integrated Power Module fuse cavity # 51 when
the vehicle is shipped from the assembly plant.
Dealer personnel must reconnect the IOD fuse when
the vehicle is being prepared for delivery in order to
restore full electrical system operation.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
(2) Remove the Integrated Power Module cover.
(3) Grasp the outer tabs of the IOD fuse holder
unit in fuse cavity # 51 between the thumb and fore-
finger and pull the unit firmly upward.
(4) Install the Integrated Power Module cover.
INSTALLATION
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
(2) Remove the Integrated Power Module cover.
(3) To install the IOD fuse, use a thumb to press
the IOD fuse holder unit in fuse cavity # 51 firmly
into the Integrated Power Module.
(4) Install the Integrated Power Module cover.
POWER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION
Two power outlets are utilized on this model. One
in the instrument panel center lower bezel and the
other in the center console. The power outlet bases
are secured by a snap fit within the instrument
panel or trim panel. A plastic protective cap snaps
into the power outlet base when the power outlet is
not being used, and hangs from the power outlet base
mount by an integral bail strap while the power out-
let is in use.The power outlet receptacle unit and the accessory
power outlet protective cap are available for service.
The power outlet receptacle cannot be repaired and,
if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The power outlet base or receptacle shell is con-
nected to ground, and an insulated contact in the
bottom of the shell is connected to battery current.
The power outlet receives battery voltage from a fuse
in the integrated power module at all times.
While the power outlet is very similar to a cigar
lighter base unit, it does not include the two small
spring-clip retainers inside the bottom of the recepta-
cle shell that are used to secure the cigar lighter
heating element to the insulated contact.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER OUTLET
For complete circuit diagrams, refer toWiring
Diagrams.
(1) Check the fused B(+) fuse in the integrated
power module. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair
the shorted circuit or component as required and
replace the faulty fuse.
(2) Check for battery voltage at the fused B(+) fuse
in the integrated power module. If OK, go to Step 3.
If not OK, repair the open fused B(+) circuit to the
battery as required.
(3) Remove the plastic protective cap from the
power outlet receptacle. Check for continuity between
the inside circumference of the power outlet recepta-
cle and a good ground. There should be continuity. If
OK, go to Step 4. If not OK, go to Step 5.
(4) Check for battery voltage at the insulated con-
tact located at the back of the power outlet recepta-
cle. If not OK, go to Step 5.
(5) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Remove the power outlet receptacle from the
instrument panel. Disconnect the wire harness con-
nector from the power outlet receptacle. Check for
continuity between the ground circuit cavity of the
power outlet wire harness connector and a good
ground. There should be continuity. If OK, go to Step
6. If not OK, repair the open ground circuit to ground
as required.
(6) Connect the battery negative cable. Check for
battery voltage at the fused B(+) circuit cavity of the
power outlet wire harness connector. If OK, replace
the faulty power outlet receptacle. If not OK, repair
the open fused B(+) circuit to the integrated power
module fuse as required.
DR8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION 8W - 97 - 7
IOD FUSE (Continued)
Page 1233 of 2627

of oil and coolant. Can be used on threaded and
machined parts under all temperatures. This mate-
rial is used on engines with multi-layer steel (MLS)
cylinder head gaskets. This material also will pre-
vent corrosion. MopartGasket Sealant is available in
a 13 oz. aerosol can or 4oz./16 oz. can w/applicator.
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKET AND SEALER
APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care but it's easier than using precut gas-
kets.
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 in.) diameter or less of sealant
to one gasket surface. Be certain the material sur-
rounds each mounting hole. Excess material can eas-
ily be wiped off. Components should be torqued in
place within 15 minutes. The use of a locating dowel
is recommended during assembly to prevent smear-
ing material off the location.
MopartEngine RTV GEN II or ATF RTV gasket
material should be applied in a continuous bead
approximately 3 mm (0.120 in.) in diameter. All
mounting holes must be circled. For corner sealing, a
3.17 or 6.35 mm (1/8 or 1/4 in.) drop is placed in the
center of the gasket contact area. Uncured sealant
may be removed with a shop towel. Components
should be torqued in place while the sealant is still
wet to the touch (within 10 minutes). The usage of a
locating dowel is recommended during assembly to
prevent smearing material off the location.
MopartGasket Sealant in an aerosol can should be
applied using a thin, even coat sprayed completely
over both surfaces to be joined, and both sides of a
gasket. Then proceed with assembly. Material in a
can w/applicator can be brushed on evenly over the
sealing surfaces. Material in an aerosol can should be
used on engines with multi-layer steel gaskets.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE GASKET
SURFACE PREPARATION
To ensure engine gasket sealing, proper surface
preparation must be performed, especially with the
use of aluminum engine components and multi-layer
steel cylinder head gaskets.
Neveruse the following to clean gasket surfaces:
²Metal scraper
²Abrasive pad or paper to clean cylinder block
and head
²High speed power tool with an abrasive pad or a
wire brush (Fig. 2)
NOTE: Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) head gaskets require
a scratch free sealing surface.
Only use the following for cleaning gasket surfaces:²Solvent or a commercially available gasket
remover
²Plastic or wood scraper (Fig. 2)
²Drill motor with 3M RolocŸ Bristle Disc (white
or yellow) (Fig. 2)
CAUTION: Excessive pressure or high RPM (beyond
the recommended speed), can damage the sealing
surfaces. The mild (white, 120 grit) bristle disc is
recommended. If necessary, the medium (yellow, 80
grit) bristle disc may be used on cast iron surfaces
with care.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Remove hood. Mark hood hinge location for
reinstallation.
(3) Remove air cleaner assembly.
(4) Remove radiator core support bracket.
(5) Remove fan shroud with viscous fan assembly.
(6) Remove drive belt.
(7) Remove A/C compressor and secure away from
engine.
(8) Remove generator and secure away from
engine.
NOTE: Do NOT remove the phenolic pulley from the
P/S pump. It is not required for P/S pump removal.
(9) Remove power steering pump with lines
attached and secure away from engine.
(10) Drain cooling system.
(11) Disconnect the heater hoses from the engine.
Fig. 2 Proper Tool Usage For Surface Preparation
1 - ABRASIVE PAD
2 - 3M ROLOCŸ BRISTLE DISC
3 - PLASTIC/WOOD SCRAPER
9 - 10 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
ENGINE - 3.7L (Continued)
Page 1250 of 2627
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate camshaft journals with clean engine
oil.
NOTE: Position the left side camshaft so that the
camshaft sprocket dowel is near the 1 o'clock posi-
tion, This will place the camshaft at the neutral
position easing the installation of the camshaft
bearing caps.
(2) Position the camshaft into the cylinder head.
(3) Install the camshaft bearing caps, hand tighten
the retaining bolts.
NOTE: Caps should be installed so that the
stamped numbers on the caps are in numerical
order, ( 1 thru 4 ) from the front to the rear of the
engine. All caps should be installed so that the
stamped arrows on the caps point toward the front
of the engine.
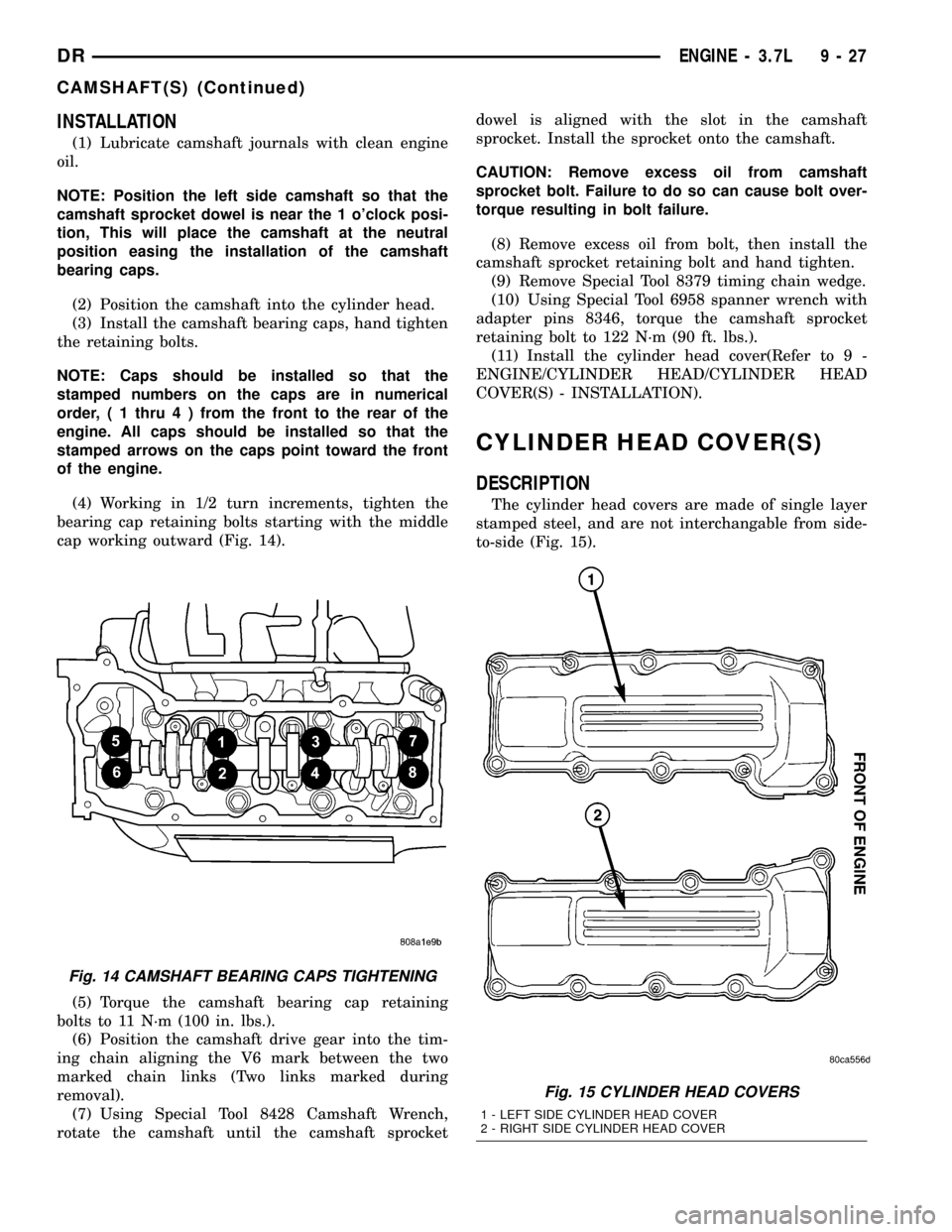
(4) Working in 1/2 turn increments, tighten the
bearing cap retaining bolts starting with the middle
cap working outward (Fig. 14).
(5) Torque the camshaft bearing cap retaining
bolts to 11 N´m (100 in. lbs.).
(6) Position the camshaft drive gear into the tim-
ing chain aligning the V6 mark between the two
marked chain links (Two links marked during
removal).
(7) Using Special Tool 8428 Camshaft Wrench,
rotate the camshaft until the camshaft sprocketdowel is aligned with the slot in the camshaft
sprocket. Install the sprocket onto the camshaft.
CAUTION: Remove excess oil from camshaft
sprocket bolt. Failure to do so can cause bolt over-
torque resulting in bolt failure.
(8) Remove excess oil from bolt, then install the
camshaft sprocket retaining bolt and hand tighten.
(9) Remove Special Tool 8379 timing chain wedge.
(10) Using Special Tool 6958 spanner wrench with
adapter pins 8346, torque the camshaft sprocket
retaining bolt to 122 N´m (90 ft. lbs.).
(11) Install the cylinder head cover(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S)
DESCRIPTION
The cylinder head covers are made of single layer
stamped steel, and are not interchangable from side-
to-side (Fig. 15).
Fig. 14 CAMSHAFT BEARING CAPS TIGHTENING
Fig. 15 CYLINDER HEAD COVERS
1 - LEFT SIDE CYLINDER HEAD COVER
2 - RIGHT SIDE CYLINDER HEAD COVER
DRENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 27
CAMSHAFT(S) (Continued)
Page 1259 of 2627
(5) Position Special Tool 8379 timing chain wedge
between the timing chain strands. Tap the tool to
securely wedge the timing chain against the ten-
sioner arm and guide.
(6) Remove the camshaft position sensor.
(7) Hold the camshaft with Special Tool 8428 Cam-
shaft Wrench, while removing the camshaft sprocket
bolt and sprocket.
(8) Starting at the outside working inward, loosen
the camshaft bearing cap retaining bolts 1/2 turn at
a time. Repeat until all load is off the bearing caps.
CAUTION: DO NOT STAMP OR STRIKE THE CAM-
SHAFT BEARING CAPS. SEVERE DAMAGE WILL
OCCUR TO THE BEARING CAPS.
NOTE: When the camshaft is removed the rocker
arms may slide downward, mark the rocker arms
before removing camshaft.
(9) Remove the camshaft bearing caps and the
camshaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate camshaft journals with clean engine
oil.
NOTE: Position the right side camshaft so that the
camshaft sprocket dowel is near the 10 o'clock
position, This will place the camshaft at the neutral
position easing the installation of the camshaft
bearing caps.
(2) Position the camshaft into the cylinder head.
(3) Install the camshaft bearing caps, hand tighten
the retaining bolts.
NOTE: Caps should be installed so that the
stamped numbers on the caps are in numerical
order, ( 1 thru 4 ) from the front to the rear of the
engine. All caps should be installed so that the
stamped arrows on the caps point toward the front
of the engine.
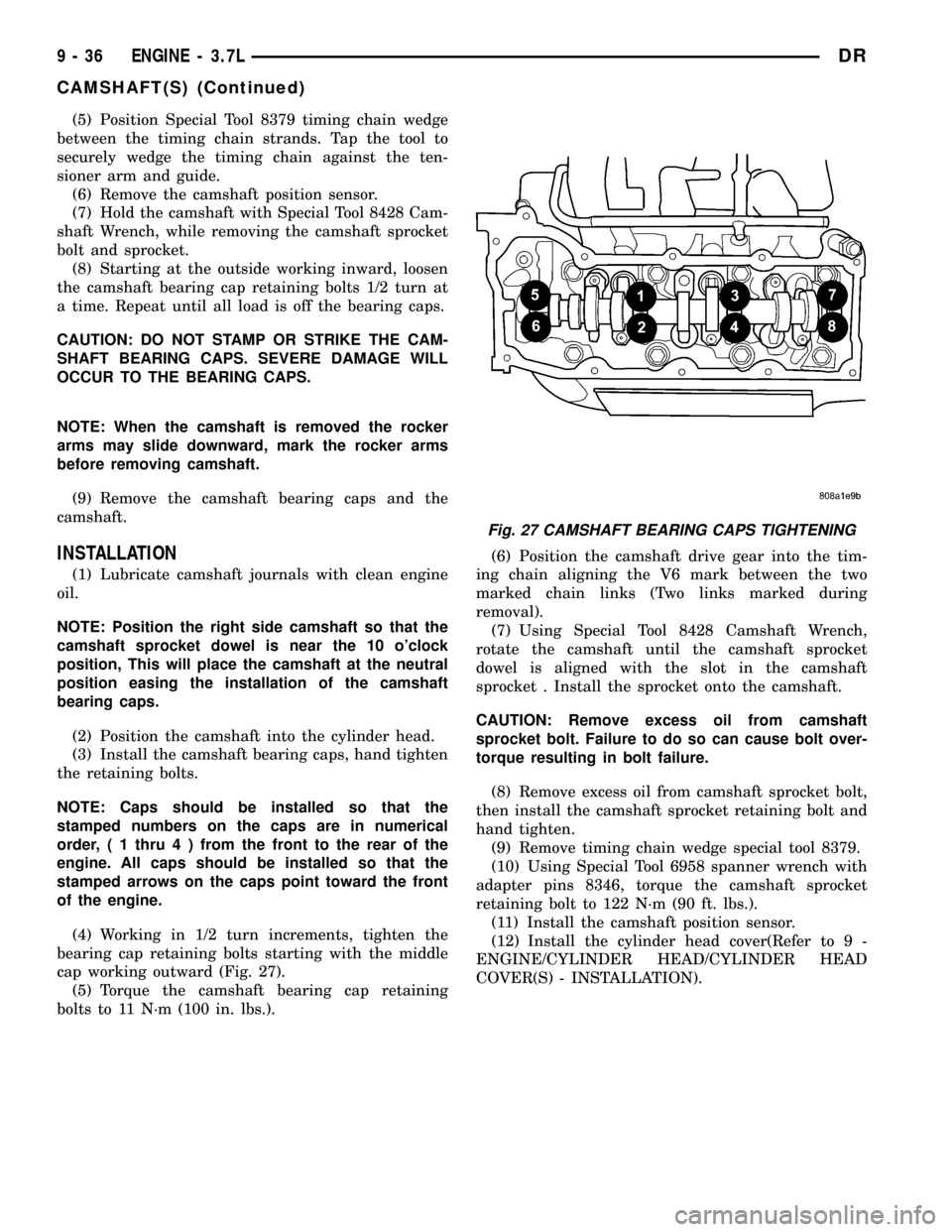
(4) Working in 1/2 turn increments, tighten the
bearing cap retaining bolts starting with the middle
cap working outward (Fig. 27).
(5) Torque the camshaft bearing cap retaining
bolts to 11 N´m (100 in. lbs.).(6) Position the camshaft drive gear into the tim-
ing chain aligning the V6 mark between the two
marked chain links (Two links marked during
removal).
(7) Using Special Tool 8428 Camshaft Wrench,
rotate the camshaft until the camshaft sprocket
dowel is aligned with the slot in the camshaft
sprocket . Install the sprocket onto the camshaft.
CAUTION: Remove excess oil from camshaft
sprocket bolt. Failure to do so can cause bolt over-
torque resulting in bolt failure.
(8) Remove excess oil from camshaft sprocket bolt,
then install the camshaft sprocket retaining bolt and
hand tighten.
(9) Remove timing chain wedge special tool 8379.
(10) Using Special Tool 6958 spanner wrench with
adapter pins 8346, torque the camshaft sprocket
retaining bolt to 122 N´m (90 ft. lbs.).
(11) Install the camshaft position sensor.
(12) Install the cylinder head cover(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
Fig. 27 CAMSHAFT BEARING CAPS TIGHTENING
9 - 36 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
CAMSHAFT(S) (Continued)
Page 1261 of 2627

VALVE GUIDE SEALS
DESCRIPTION
The valve guide seals are made of rubber and
incorporate an integral steel valve spring seat. The
integral garter spring maintains consistent lubrica-
tion control to the valve stems.
VALVE SPRINGS
DESCRIPTION
The valve springs are made from high strength
chrome silicon steel. There are different springs for
intake and exhaust applications. The exhaust spring
has an external damper. The valve spring seat is
integral with the valve stem seal, which is a positive
type seal to control lubrication.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cylinder head cover(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) Using Special Tool 8516 Valve Spring Compres-
sor, remove the rocker arms and the hydraulic lash
adjusters.
(3) Remove the spark plug for the cylinder the
valve spring and seal are to be removed from.
(4) Apply shop air to the cylinder to hold the
valves in place when the spring is removed.
NOTE: All six valve springs and seals are removed
in the same manner; this procedure only covers
one valve seal and valve spring.
(5) Using Special Tool 8387 Valve Spring Compres-
sor, compress the valve spring.
NOTE: It may be necessary to tap the top of the
valve spring to loosen the spring retainers locks
enough to be removed.
(6) Remove the two spring retainer lock halves.
NOTE: the valve spring is under tension use care
when releasing the valve spring compressor.
(7) Remove the valve spring compressor.
NOTE: The valve springs are NOT common between
intake and exhaust.
(8) Remove the spring retainer, and the spring.
(9) Remove the valve stem seal.
NOTE: The valve stem seals are common between
intake and exhaust.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: All six valve springs and seals are removed
in the same manner; this procedure only covers
one valve seal and valve spring.
(1) Apply shop air to the cylinder to hold the
valves in place while the spring is installed.
NOTE: The valve stem seals are common between
intake and exhaust.
(2) Install the valve stem seal.
NOTE: The valve springs are NOT common between
intake and exhaust.
(3) Install the spring retainer, and the spring.
(4) Using Special Tool 8387 Valve Spring Compres-
sor, compress the valve spring.
(5) Install the two spring retainer lock halves.
NOTE: the valve spring is under tension use care
when releasing the valve spring compressor.
(6) Remove the valve spring compressor.
(7) Disconnect the shop air to the cylinder.
(8) Install the spark plug for the cylinder the valve
spring and seal was installed on.
(9) Using Special Tool 8516 Valve Spring Compres-
sor, install the rocker arms and the hydraulic lash
adjusters.
(10) Install the cylinder head cover(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
ENGINE BLOCK
DESCRIPTION
The cylinder block is made of cast iron. The block
is a closed deck design with the left bank forward. To
provide high rigidity and improved NVH an
enhanced compacted graphite bedplate is bolted to
the block. The block design allows coolant flow
between the cylinders bores, and an internal coolant
bypass to a single poppet inlet thermostat is included
in the cast aluminum front cover.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER BORE
HONING
Before honing, stuff plenty of clean shop towels
under the bores and over the crankshaft to keep
abrasive materials from entering the crankshaft
area.
(1) Used carefully, the Cylinder Bore Sizing Hone
C-823, equipped with 220 grit stones, is the best tool
9 - 38 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
Page 1273 of 2627
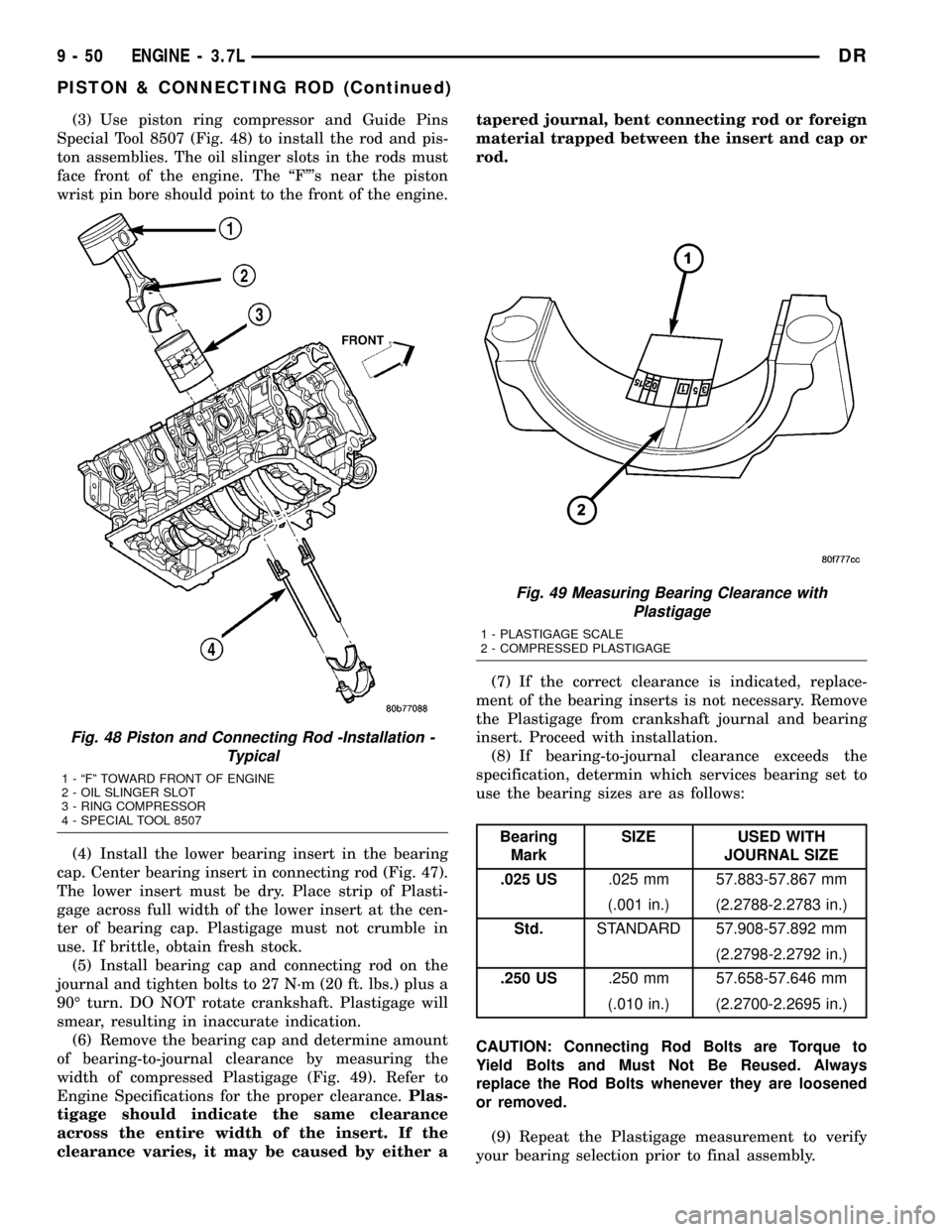
(3) Use piston ring compressor and Guide Pins
Special Tool 8507 (Fig. 48) to install the rod and pis-
ton assemblies. The oil slinger slots in the rods must
face front of the engine. The ªFº's near the piston
wrist pin bore should point to the front of the engine.
(4) Install the lower bearing insert in the bearing
cap. Center bearing insert in connecting rod (Fig. 47).
The lower insert must be dry. Place strip of Plasti-
gage across full width of the lower insert at the cen-
ter of bearing cap. Plastigage must not crumble in
use. If brittle, obtain fresh stock.
(5) Install bearing cap and connecting rod on the
journal and tighten bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) plus a
90É turn. DO NOT rotate crankshaft. Plastigage will
smear, resulting in inaccurate indication.
(6) Remove the bearing cap and determine amount
of bearing-to-journal clearance by measuring the
width of compressed Plastigage (Fig. 49). Refer to
Engine Specifications for the proper clearance.Plas-
tigage should indicate the same clearance
across the entire width of the insert. If the
clearance varies, it may be caused by either atapered journal, bent connecting rod or foreign
material trapped between the insert and cap or
rod.
(7) If the correct clearance is indicated, replace-
ment of the bearing inserts is not necessary. Remove
the Plastigage from crankshaft journal and bearing
insert. Proceed with installation.
(8) If bearing-to-journal clearance exceeds the
specification, determin which services bearing set to
use the bearing sizes are as follows:
Bearing
MarkSIZE USED WITH
JOURNAL SIZE
.025 US.025 mm 57.883-57.867 mm
(.001 in.) (2.2788-2.2783 in.)
Std.STANDARD 57.908-57.892 mm
(2.2798-2.2792 in.)
.250 US.250 mm 57.658-57.646 mm
(.010 in.) (2.2700-2.2695 in.)
CAUTION: Connecting Rod Bolts are Torque to
Yield Bolts and Must Not Be Reused. Always
replace the Rod Bolts whenever they are loosened
or removed.
(9) Repeat the Plastigage measurement to verify
your bearing selection prior to final assembly.
Fig. 48 Piston and Connecting Rod -Installation -
Typical
1 - ªFº TOWARD FRONT OF ENGINE
2 - OIL SLINGER SLOT
3 - RING COMPRESSOR
4 - SPECIAL TOOL 8507
Fig. 49 Measuring Bearing Clearance with
Plastigage
1 - PLASTIGAGE SCALE
2 - COMPRESSED PLASTIGAGE
9 - 50 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1275 of 2627

²Timing chain cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S)
- REMOVAL).
²Cylinder head(s) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLIN-
DER HEAD - REMOVAL) and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(3) If necessary, remove top ridge of cylinder bores
with a reliable ridge reamer before removing pistons
from cylinder block.Be sure to keep tops of pis-
tons covered during this operation.Pistons and
connecting rods must be removed from top of cylinder
block. When removing piston and connecting rod
assemblies from the engine, rotate crankshaft so the
each connecting rod is centered in cylinder bore.
CAUTION: DO NOT use a number stamp or a punch
to mark connecting rods or caps, as damage to
connecting rods could occur
NOTE: Connecting rods and bearing caps are not
interchangeable and should be marked before
removing to ensure correct reassembly.
(4) Mark connecting rod and bearing cap positions
using a permanent ink marker or scribe tool.
CAUTION: Care must be taken not to damage the
fractured rod and cap joint face surfaces, as engine
damage may occur.
(5) Remove connecting rod cap. Install Special Tool
8507 Connecting Rod Guides into the connecting rod
being removed. Remove piston from cylinder bore.
Repeat this procedure for each piston being removed.
CAUTION: Care must be taken not to nick crank-
shaft journals, as engine damage may occur
(6) Immediately after piston and connecting rod
removal, install bearing cap on the mating connect-
ing rod to prevent damage to the fractured cap and
rod surfaces.
CLEANING
CAUTION: DO NOT use a wire wheel or other abra-
sive cleaning devise to clean the pistons or con-
necting rods. The pistons have a Moly coating, this
coating must not be damaged.
(1) Using a suitable cleaning solvent clean the pis-
tons in warm water and towel dry.
(2) Use a wood or plastic scraper to clean the ring
land grooves.
CAUTION: DO NOT remove the piston pin from the
piston and connecting rod assembly.
INSPECTION
Check the connecting rod journal for excessive
wear, taper and scoring (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/EN-
GINE BLOCK/CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Check the connecting rod for signs of twist or bend-
ing.
Check the piston for taper and elliptical shape
before it is fitted into the cylinder bore (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON & CONNECT-
ING ROD - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Check the piston for scoring, or scraping marks in
the piston skirts. Check the ring lands for cracks
and/or deterioration.
INSTALLATION
(1) Before installing piston and connecting rod
assemblies into the bore, install the piston rings.
(2) Immerse the piston head and rings in clean
engine oil. Position a ring compressor over the piston
and rings. Tighten ring compressor.Ensure posi-
tion of rings do not change during this opera-
tion.
(3) Position bearing onto connecting rod. Ensure
that hole in bearing shell aligns with hole in connect-
ing rod. Lubricate bearing surface with clean engine
oil.
(4) Install Special Tool 8507 Connecting Rod
Guides into connecting rod bolt threads (Fig. 53).
(5) The pistons are marked on the piston pin bore
surface with an raised ªFº indicating installation
position. This mark must be pointing toward the
front of engine on both cylinder banks. The connect-
ing rod oil slinger slot faces the front of the engine
(Fig. 54).
(6) Wipe cylinder bore clean and lubricate with
engine oil.
(7) Rotate crankshaft until connecting rod journal
is on the center of cylinder bore. Insert rod and pis-
ton into cylinder bore and carefully position connect-
ing rod guides over crankshaft journal.
(8) Tap piston down in cylinder bore using a ham-
mer handle. While at the same time, guide connect-
ing rod into position on rod journal.
CAUTION: Connecting Rod Bolts are Torque to
Yield Bolts and Must Not Be Reused. Always
replace the Rod Bolts whenever they are loosened
or removed.
(9) Lubricate rod bolts and bearing surfaces with
engine oil. Install connecting rod cap and bearing.
Tighten bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) plus 90É.
(10) Install the following components:
²Cylinder head(s). (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLIN-
DER HEAD - INSTALLATION).
9 - 52 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)