1998 DODGE RAM 1500 coolant temperature
[x] Cancel search: coolant temperaturePage 2105 of 2627

STATOR
The stator assembly (Fig. 120) is mounted on a sta-
tionary shaft which is an integral part of the oil
pump. The stator is located between the impeller and
turbine within the torque converter case (Fig. 121).
The stator contains an over-running clutch, which
allows the stator to rotate only in a clockwise direc-
tion. When the stator is locked against the over-run-
ning clutch, the torque multiplication feature of the
torque converter is operational.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The TCC (Fig. 122) was installed to improve the
efficiency of the torque converter that is lost to the
slippage of the fluid coupling. Although the fluid cou-
pling provides smooth, shock-free power transfer, it is
natural for all fluid couplings to slip. If the impeller
and turbine were mechanically locked together, a
zero slippage condition could be obtained. A hydraulic
piston with friction material was added to the tur-
bine assembly to provide this mechanical lock-up.
In order to reduce heat build-up in the transmis-
sion and buffer the powertrain against torsional
vibrations, the TCM can duty cycle the L/R-CC Sole-
noid to achieve a smooth application of the torque
converter clutch. This function, referred to as Elec-
tronically Modulated Converter Clutch (EMCC) can
occur at various times depending on the following
variables:
²Shift lever position
²Current gear range
²Transmission fluid temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Input speed
²Throttle angle²Engine speed
Fig. 120 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 121 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 122 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
21 - 402 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2111 of 2627

INSTALLATION
(1) Place TRS selector plate in the PARK position.
(2) Position the transmission solenoid/TRS assem-
bly onto the valve body. Be sure that both alignment
dowels are fully seated in the valve body and that
the TRS switch contacts are properly positioned in
the selector plate
(3) Install the screws to hold the transmission
solenoid/TRS assembly onto the valve body.
(4) Tighten the solenoid assembly screws adjacent
to the arrows cast into the bottom of the valve body
first. Tighten the screws to 5.7 N´m (50 in.lbs.).
(5) Tighten the remainder of the solenoid assembly
screws to 5.7 N´m (50 in.lbs.).
(6) Install the valve body into the transmission.
TRANSMISSION
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The transmission temperature sensor is a ther-
mistor that is integral to the Transmission Range
Sensor (TRS).
OPERATION
The transmission temperature sensor is used by
the TCM to sense the temperature of the fluid in the
sump. Since fluid temperature can affect transmis-
sion shift quality and convertor lock up, the TCM
requires this information to determine which shift
schedule to operate in.
Calculated Temperature
A failure in the temperature sensor or circuit will
result in calculated temperature being substituted for
actual temperature. Calculated temperature is a pre-
dicted fluid temperature which is calculated from a
combination of inputs:
²Battery (ambient) temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²In-gear run time since start-up
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION
The valve body consists of a cast aluminum valve
body, a separator plate, and a transfer plate. The
valve body contains valves and check balls that con-
trol fluid delivery to the torque converter clutch,
bands, and frictional clutches. The valve body con-
tains the following components (Fig. 129) and (Fig.
130):
²Solenoid switch valve
²Manual valve
²Low/reverse switch valve
²5 Accumulators
²7 check balls
OPERATION
NOTE: Refer to the Hydraulic Schematics for a
visual aid in determining valve location, operation
and design.
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
The Solenoid Switch Valve (SSV) controls the direc-
tion of the transmission fluid when the L/R-TCC sole-
noid is energized.
When shifting into 1st gear, a special hydraulic
sequence is performed to ensure SSV movement into
the downshifted position. The L/R pressure switch is
monitored to confirm SSV movement. If the move-
ment is not confirmed (the L/R pressure switch does
not close), 2nd gear is substituted for 1st. A DTC will
be set after three unsuccessful attempts are made to
get into 1st gear in one given key start.
MANUAL VALVE
The manual valve is a relay valve. The purpose of
the manual valve is to direct fluid to the correct cir-
cuit needed for a specific gear or driving range. The
manual valve, as the name implies, is manually oper-
ated by the driver with a lever located on the top of
the valve body. The valve is connected mechanically
by a cable to the gearshift mechanism. The valve is
held in each of its positions by a roller detent spring
(Fig. 131) that engages the ªroostercombº of the TRS
selector plate.
21 - 408 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
TRANSMISSION SOLENOID/TRS ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 2493 of 2627

Condition Possible Causes Correction
The low side pressure is too
low, and the high side
pressure is too high.1. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the refrigerant lines.1. See Liquid, Suction, and Discharge Line in this
group. Inspect the refrigerant lines for kinks, tight
bends or improper routing. Correct the routing or
replace the refrigerant line, if required.
2. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the fixed orifice tube.2. See A/C Orifice Tube in this group. Replace
the liquid line, if required.
3. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the condenser.3. See A/C Condenser in this group. Replace the
restricted condenser, if required.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATER
PERFORMANCE TEST
Review Safety Warnings and Cautions before per-
forming this procedure (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING) and
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - CAUTION).
Check the coolant level, drive belt tension, vacuum
line connections, radiator air flow and fan operation.
Start engine and allow to warm up to normal tem-
perature.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE RADIATOR CAP
WHEN ENGINE IS HOT, PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
If vehicle has been run recently, wait 15 minutes
before removing cap. Place a rag over the cap andturn it to the first safety stop. Allow pressure to
escape through the overflow tube. When the system
stabilizes, remove the cap completely.
MAXIMUM HEATER OUTPUT: TEST AND ACTION
Engine coolant is provided to the heater system by
two heater hoses. With the engine idling at normal
operating temperature, set the temperature control
to maximum heat, the mode control to the floor posi-
tion, and the blower in the highest speed position.
Using a test thermometer, check the temperature of
the air being discharged from the floor outlets. Com-
pare the test thermometer reading to the Tempera-
ture Reference chart.
TEMPERATURE REFERENCE CHART
Ambient Air Temperature15.5É C
(60É F)21.1É C
(70É F)26.6É C
(80É F)32.2É C
(90É F)
Minimum Air Temperature at
Floor Outlet62.2É C
(144É F)63.8É C
(147É F)65.5É C
(150É F)67.2É C
(153É F)
Both of the heater hoses should be HOT to the
touch (coolant return hose should be slightly cooler
than the supply hose). If the coolant return hose is
much cooler than the supply hose, locate and repair
the engine coolant flow obstruction in the heater sys-
tem. If both heater hoses are cool to the touch,
inspect the engine cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
OBSTRUCTED COOLANT FLOW Possible loca-
tions or causes of obstructed coolant flow are as fol-
lows:
²Pinched or kinked heater hoses.
²Improper heater hose routing.
²Plugged heater hoses or supply and return ports
at the cooling system connections.
²Plugged heater core.If proper coolant flow through the cooling system is
verified, and heater outlet air temperature is insuffi-
cient, a mechanical problem may exist.
MECHANICAL PROBLEMS Possible causes of
insufficient heat due to mechanical problems are as
follows:
²Obstructed cowl air intake.
²Obstructed heater system outlets.
²Blend door not functioning properly.
TEMPERATURE CONTROL
If the heater outlet air temperature cannot be
adjusted with the temperature control knob on the
A/C-heater control, the following could require ser-
vice:
²Blend door binding.
²Faulty blend door motor.
24 - 6 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGDR
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2494 of 2627
²Faulty A/C-heater control.
²Faulty related wiring harness or connectors.
²Improper engine coolant temperature.
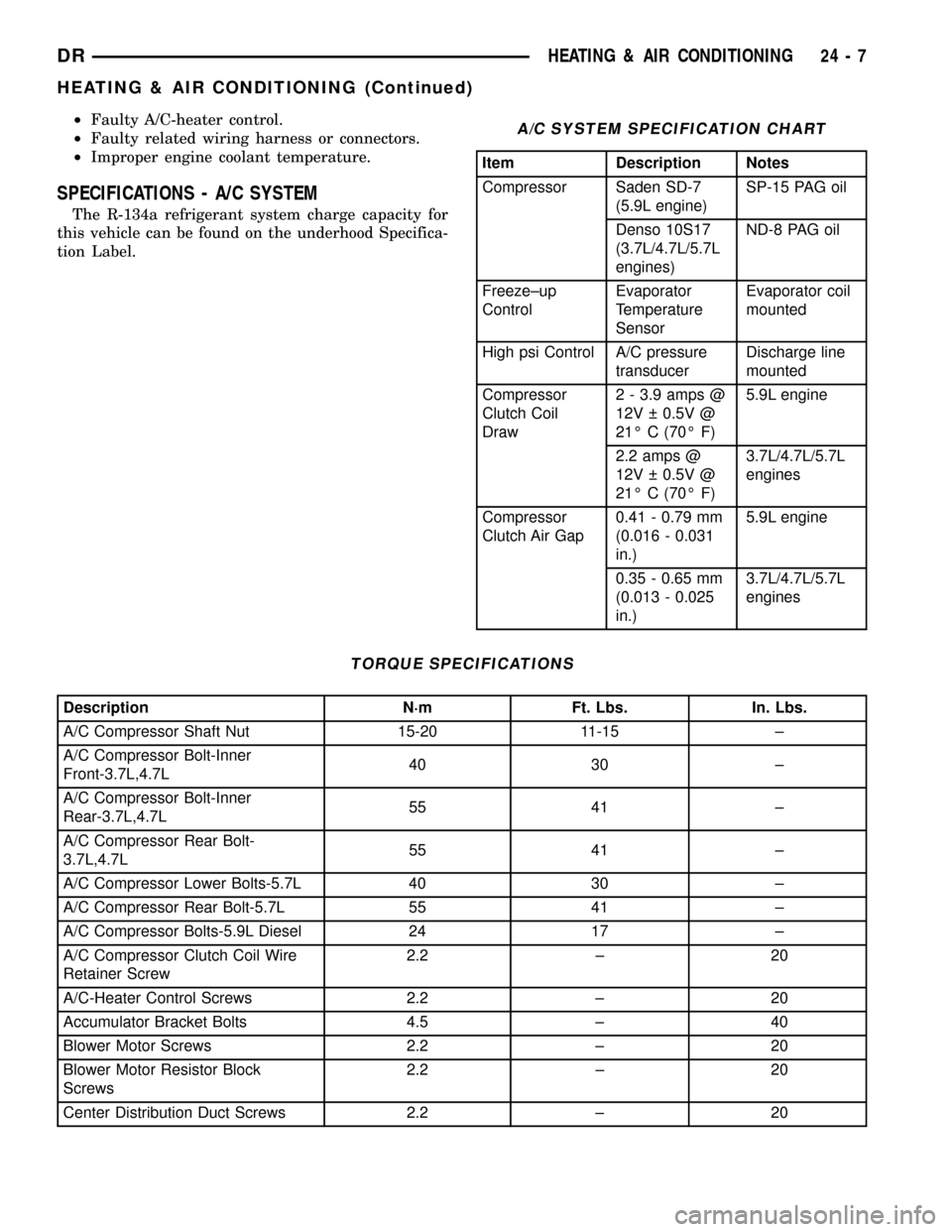
SPECIFICATIONS - A/C SYSTEM
The R-134a refrigerant system charge capacity for
this vehicle can be found on the underhood Specifica-
tion Label.
A/C SYSTEM SPECIFICATION CHART
Item Description Notes
Compressor Saden SD-7
(5.9L engine)SP-15 PAG oil
Denso 10S17
(3.7L/4.7L/5.7L
engines)ND-8 PAG oil
Freeze±up
ControlEvaporator
Temperature
SensorEvaporator coil
mounted
High psi Control A/C pressure
transducerDischarge line
mounted
Compressor
Clutch Coil
Draw2 - 3.9 amps @
12V 0.5V @
21É C (70É F)5.9L engine
2.2 amps @
12V 0.5V @
21É C (70É F)3.7L/4.7L/5.7L
engines
Compressor
Clutch Air Gap0.41 - 0.79 mm
(0.016 - 0.031
in.)5.9L engine
0.35 - 0.65 mm
(0.013 - 0.025
in.)3.7L/4.7L/5.7L
engines
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
Description N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
A/C Compressor Shaft Nut 15-20 11-15 ±
A/C Compressor Bolt-Inner
Front-3.7L,4.7L40 30 ±
A/C Compressor Bolt-Inner
Rear-3.7L,4.7L55 41 ±
A/C Compressor Rear Bolt-
3.7L,4.7L55 41 ±
A/C Compressor Lower Bolts-5.7L 40 30 ±
A/C Compressor Rear Bolt-5.7L 55 41 ±
A/C Compressor Bolts-5.9L Diesel 24 17 ±
A/C Compressor Clutch Coil Wire
Retainer Screw2.2 ± 20
A/C-Heater Control Screws 2.2 ± 20
Accumulator Bracket Bolts 4.5 ± 40
Blower Motor Screws 2.2 ± 20
Blower Motor Resistor Block
Screws2.2 ± 20
Center Distribution Duct Screws 2.2 ± 20
DRHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 7
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2550 of 2627

(12) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
(13) Evacuate the refrigerant system (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM EVACUATE).
(14) Charge the refrigerant system (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE).
HEATER CORE
DESCRIPTION
The heater core is located in the HVAC housing,
behind the instrument panel. It is a heat exchanger
made of rows of tubes and fins.
OPERATION
Engine coolant is circulated through the heater
hoses to the heater core at all times. As the coolant
flows through the heater core, heat is removed from
the engine and is transferred to the heater core fins
and tubes. Air directed through the heater core picks
up the heat from the heater core fins. The blend door
allows control of the heater output air temperature
by regulating the amount of air flowing through the
heater core within the HVAC housing. The blower
motor speed controls the volume of air flowing
through the HVAC housing.
The heater core cannot be repaired and, if faulty or
damaged, it must be replaced.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
NOTE: Disassembly of the HVAC housing is not
required to remove heater core.
(1) Remove the HVAC housing (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/
HVAC HOUSING - REMOVAL).(2) Remove the foam seal from the heater core
tubes.
(3) If equipped with the Dual Zone system, remove
the linkage rod from the actuator levers to gain
access to the heater core (Fig. 23).
(4) Remove the two screws that secure the heater
core tube bracket to the HVAC housing.
(5) Remove the heater core tube bracket.
(6) Pull the heater core out of the HVAC housing.
(7) Inspect all foam seals and repair or replace
them as required.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the heater core into the HVAC housing.
(2) Position the heater core tube bracket onto the
HVAC housing.
(3) Install the two screws that secure the heater
core bracket to the HVAC housing. Tighten the
screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(4) If equipped with the Dual Zone system, install
the linkage rod onto the actuator levers.
(5) Install the foam seal onto the heater core
tubes.
(6) Install the HVAC housing (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC
HOUSING - INSTALLATION).
Fig. 23 Heater Core ± Dual Zone Shown, Single
Zone Typical
1 - SCREWS
2 - TUBE BRACKET
3 - HEATER CORE
4 - LINKAGE ROD (IF EQUIPPED)
DRPLUMBING 24 - 63
ACCUMULATOR (Continued)
Page 2565 of 2627

O2S is used to detect the amount of oxygen in the
exhaust gas before the gas enters the catalytic con-
verter. The PCM calculates the A/F mixture from the
output of the O2S. A low voltage indicates high oxy-
gen content (lean mixture). A high voltage indicates a
low content of oxygen (rich mixture).
When the upstream O2S detects a lean condition,
there is an abundance of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
A functioning converter would store this oxygen so it
can use it for the oxidation of HC and CO. As the
converter absorbs the oxygen, there will be a lack of
oxygen downstream of the converter. The output of
the downstream O2S will indicate limited activity in
this condition.
As the converter loses the ability to store oxygen,
the condition can be detected from the behavior of
the downstream O2S. When the efficiency drops, no
chemical reaction takes place. This means the con-
centration of oxygen will be the same downstream as
upstream. The output voltage of the downstream
O2S copies the voltage of the upstream sensor. The
only difference is a time lag (seen by the PCM)
between the switching of the O2S's.
To monitor the system, the number of lean-to-rich
switches of upstream and downstream O2S's is
counted. The ratio of downstream switches to
upstream switches is used to determine whether the
catalyst is operating properly. An effective catalyst
will have fewer downstream switches than it has
upstream switches i.e., a ratio closer to zero. For a
totally ineffective catalyst, this ratio will be one-to-
one, indicating that no oxidation occurs in the device.
The system must be monitored so that when cata-
lyst efficiency deteriorates and exhaust emissions
increase to over the legal limit, the MIL will be illu-
minated.
DESCRIPTION - TRIP DEFINITION
The term ªTripº has different meanings depending
on what the circumstances are. If the MIL (Malfunc-
tion Indicator Lamp) is OFF, a Trip is defined as
when the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and the Catalyst
Monitor have been completed in the same drive cycle.
When any Emission DTC is set, the MIL on the
dash is turned ON. When the MIL is ON, it takes 3
good trips to turn the MIL OFF. In this case, it
depends on what type of DTC is set to know what a
ªTripº is.
For the Fuel Monitor or Mis-Fire Monitor (contin-
uous monitor), the vehicle must be operated in the
ªSimilar Condition Windowº for a specified amount of
time to be considered a Good Trip.If a Non-Contiuous OBDII Monitor fails twice in a
row and turns ON the MIL, re-running that monitor
which previously failed, on the next start-up and
passing the monitor, is considered to be a Good Trip.
These will include the following:
²Oxygen Sensor
²Catalyst Monitor
²Purge Flow Monitor
²Leak Detection Pump Monitor (if equipped)
²EGR Monitor (if equipped)
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
If any other Emission DTC is set (not an OBDII
Monitor), a Good Trip is considered to be when the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst Monitor have
been completed; or 2 Minutes of engine run time if
the Oxygen Sensor Monitor or Catalyst Monitor have
been stopped from running.
It can take up to 2 Failures in a row to turn on the
MIL. After the MIL is ON, it takes 3 Good Trips to
turn the MIL OFF. After the MIL is OFF, the PCM
will self-erase the DTC after 40 Warm-up cycles. A
Warm-up cycle is counted when the ECT (Engine
Coolant Temperature Sensor) has crossed 160ÉF and
has risen by at least 40ÉF since the engine has been
started.
DESCRIPTION - COMPONENT MONITORS
There are several components that will affect vehi-
cle emissions if they malfunction. If one of these com-
ponents malfunctions the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) will illuminate.
Some of the component monitors are checking for
proper operation of the part. Electrically operated
components now have input (rationality) and output
(functionality) checks. Previously, a component like
the Throttle Position sensor (TPS) was checked by
the PCM for an open or shorted circuit. If one of
these conditions occurred, a DTC was set. Now there
is a check to ensure that the component is working.
This is done by watching for a TPS indication of a
greater or lesser throttle opening than MAP and
engine rpm indicate. In the case of the TPS, if engine
vacuum is high and engine rpm is 1600 or greater,
and the TPS indicates a large throttle opening, a
DTC will be set. The same applies to low vacuum if
the TPS indicates a small throttle opening.
All open/short circuit checks, or any component
that has an associated limp-in, will set a fault after 1
trip with the malfunction present. Components with-
out an associated limp-in will take two trips to illu-
minate the MIL.
25 - 4 EMISSIONS CONTROLDR
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2568 of 2627

Trip Indicator
TheTripis essential for running monitors and
extinguishing the MIL. In OBD II terms, a trip is a
set of vehicle operating conditions that must be met
for a specific monitor to run. All trips begin with a
key cycle.
Good Trip
The Good Trip counters are as follows:
²Specific Good Trip
²Fuel System Good Trip
²Misfire Good Trip
²Alternate Good Trip (appears as a Global Good
Trip on DRB III)
²Comprehensive Components
²Major Monitor
²Warm-Up Cycles
Specific Good Trip
The term Good Trip has different meanings
depending on the circumstances:
²If the MIL is OFF, a trip is defined as when the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor and the Catalyst Monitor
have been completed in the same drive cycle.
²If the MIL is ON and a DTC was set by the Fuel
Monitor or Misfire Monitor (both continuous moni-
tors), the vehicle must be operated in the Similar
Condition Window for a specified amount of time.
²If the MIL is ON and a DTC was set by a Task
Manager commanded once-per-trip monitor (such as
the Oxygen Sensor Monitor, Catalyst Monitor, Purge
Flow Monitor, Leak Detection Pump Monitor, EGR
Monitor or Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor), a good
trip is when the monitor is passed on the next start-
up.
²If the MIL is ON and any other emissions DTC
was set (not an OBD II monitor), a good trip occurs
when the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst Mon-
itor have been completed, or two minutes of engine
run time if the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst
Monitor have been stopped from running.
Fuel System Good Trip
To count a good trip (three required) and turn off
the MIL, the following conditions must occur:
²Engine in closed loop
²Operating in Similar Conditions Window
²Short Term multiplied by Long Term less than
threshold
²Less than threshold for a predetermined time
If all of the previous criteria are met, the PCM will
count a good trip (three required) and turn off the
MIL.
Misfire Good Trip
If the following conditions are met the PCM will
count one good trip (three required) in order to turn
off the MIL:
²Operating in Similar Condition Window
²1000 engine revolutions with no misfireWarm-Up Cycles
Once the MIL has been extinguished by the Good
Trip Counter, the PCM automatically switches to a
Warm-Up Cycle Counter that can be viewed on the
DRB III. Warm-Up Cycles are used to erase DTCs
and Freeze Frames. Forty Warm-Up cycles must
occur in order for the PCM to self-erase a DTC and
Freeze Frame. A Warm-Up Cycle is defined as fol-
lows:
²Engine coolant temperature must start below
and rise above 160É F
²Engine coolant temperature must rise by 40É F
²No further faults occur
Freeze Frame Data Storage
Once a failure occurs, the Task Manager records
several engine operating conditions and stores it in a
Freeze Frame. The Freeze Frame is considered one
frame of information taken by an on-board data
recorder. When a fault occurs, the PCM stores the
input data from various sensors so that technicians
can determine under what vehicle operating condi-
tions the failure occurred.
The data stored in Freeze Frame is usually
recorded when a system fails the first time for two
trip faults. Freeze Frame data will only be overwrit-
ten by a different fault with a higher priority.
CAUTION: Erasing DTCs, either with the DRB III or
by disconnecting the battery, also clears all Freeze
Frame data.
Similar Conditions Window
The Similar Conditions Window displays informa-
tion about engine operation during a monitor. Abso-
lute MAP (engine load) and Engine RPM are stored
in this window when a failure occurs. There are two
different Similar conditions Windows: Fuel System
and Misfire.
FUEL SYSTEM
²Fuel System Similar Conditions WindowÐ
An indicator that 'Absolute MAP When Fuel Sys Fail'
and 'RPM When Fuel Sys Failed' are all in the same
range when the failure occurred. Indicated by switch-
ing from 'NO' to 'YES'.
²Absolute MAP When Fuel Sys FailÐ The
stored MAP reading at the time of failure. Informs
the user at what engine load the failure occurred.
²Absolute MAPÐ A live reading of engine load
to aid the user in accessing the Similar Conditions
Window.
²RPM When Fuel Sys FailÐ The stored RPM
reading at the time of failure. Informs the user at
what engine RPM the failure occurred.
DREMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 7
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2593 of 2627
CASE - NV271 - DESCRIPTION,
TRANSFER.........................21-447
CASE - NV271 - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, TRANSFER.................21-448
CASE - NV271 - DISASSEMBLY,
TRANSFER.........................21-450
CASE - NV271 - INSPECTION, TRANSFER . 21-459
CASE - NV271 - INSTALLATION,
TRANSFER.........................21-473
CASE - NV271 - OPERATION, TRANSFER . 21-448
CASE - NV271 - REMOVAL, TRANSFER . . 21-450
CASE - NV273 - ASSEMBLY, TRANSFER . . 21-556
CASE - NV273 - CLEANING, TRANSFER . . 21-554
CASE - NV273 - DESCRIPTION,
TRANSFER.........................21-542
CASE - NV273 - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, TRANSFER.................21-543
CASE - NV273 - DISASSEMBLY,
TRANSFER.........................21-544
CASE - NV273 - INSPECTION, TRANSFER . 21-554
CASE - NV273 - INSTALLATION,
TRANSFER.........................21-568
CASE - NV273 - OPERATION, TRANSFER . 21-543
CASE - NV273 - REMOVAL, TRANSFER . . 21-544
CASE BEARINGS - INSTALLATION,
DIFFERENTIAL.....3-106,3-134,3-161,3-48,3-75
CASE BEARINGS - REMOVAL,
DIFFERENTIAL.....3-105,3-134,3-161,3-48,3-75
CASE CONTROL MODULE -
DESCRIPTION, TRANSFER.............8E-16
CASE CONTROL MODULE - OPERATION,
TRANSFER..........................8E-16
CASE, NV241 GENII - TRANSFER.......21-438
CASE, NV241/NV243 - TRANSFER......21-439
CASE, NV243 - TRANSFER......21-505,21-506
CASE, NV244 GENII - TRANSFER.......21-535
CASE, NV271 - TRANSFER............21-473
CASE NV271/NV273, SPECIAL TOOLS -
TRANSFER...................21-474,21-569
CASE, NV273 - TRANSFER............21-568
CASE SKID PLATE - INSTALLATION,
TRANSFER..........................13-26
CASE SKID PLATE - REMOVAL,
TRANSFER..........................13-26
CASTER ADJUSTMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, CAMBER..................2-4
CASTER AND TOE ADJUSTMENT -
STANDARD PROCEDURE, CAMBER........2-4
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - DESCRIPTION . . . 11-6
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - OPERATION.....11-6
CATCH - INSTALLATION, LATCH STRIKER
/ SECONDARY.......................23-48
CATCH - REMOVAL, LATCH STRIKER /
SECONDARY........................23-47
CAUTION - A/C SYSTEM...............24-43
CAUTION, HALF SHAFT.................3-20
CAUTION, INTERIOR..................23-62
CENTER - DESCRIPTION, ELECTRONIC
VEHICLE INFO.......................8M-7
CENTER - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
ELECTRONIC VEHICLE INFORMATION.....8M-8
CENTER - INSTALLATION, ELECTRONIC
VEHICLE INFO.......................8M-9
CENTER & LEFT OUTBOARD -
INSTALLATION......................8O-50
CENTER & LEFT OUTBOARD - REMOVAL
. . 8O-48
CENTER - OPERATION, ELECTRONIC
VEHICLE INFO
.......................8M-7
CENTER - REMOVAL, ELECTRONIC
VEHICLE INFO
.......................8M-9
CENTER ANCHOR & RIGHT OUTBOARD -
INSTALLATION
......................8O-50
CENTER ANCHOR & RIGHT OUTBOARD -
REMOVAL
..........................8O-49
CENTER ARMREST / SEAT BACK -
INSTALLATION
.......................23-77
CENTER ARMREST / SEAT BACK -
REMOVAL
..........................23-76
CENTER BEARING - ADJUSTMENTS
........3-9
CENTER BEARING - INSTALLATION
........3-9
CENTER BEARING - REMOVAL
............3-9
CENTER BEZEL - INSTALLATION,
INSTRUMENT PANEL
..................23-57
CENTER BEZEL - REMOVAL,
INSTRUMENT PANEL
..................23-57
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP -
INSTALLATION
.......................8L-11CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP -
REMOVAL..........................8L-11
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP
UNIT - INSTALLATION.................8L-11
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP
UNIT - REMOVAL....................8L-11
CENTER PROGRAMMING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, ELECTRONIC VEHICLE
INFORMATION.......................8M-8
CENTER SEAT - INSTALLATION..........23-76
CENTER SEAT - REMOVAL.............23-75
CENTER SEAT BACK HINGE -
INSTALLATION.......................23-79
CENTER SEAT BACK HINGE - REMOVAL . . . 23-78
CENTER SEAT BACK INERTIA HINGE
COVER - INSTALLATION...............23-77
CENTER SEAT BACK INERTIA HINGE
COVER - REMOVAL...................23-77
CENTER SEAT BACK LID - INSTALLATION . 23-79
CENTER SEAT BACK LID - REMOVAL.....23-79
CENTER SEAT BELT - INSTALLATION,
FRONT.............................8O-31
CENTER SEAT BELT - REMOVAL, FRONT . . 8O-30
CENTER SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR -
INSTALLATION, FRONT................8O-29
CENTER SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR -
INSTALLATION, REAR.................8O-45
CENTER SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR -
REMOVAL, FRONT....................8O-29
CENTER SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR -
REMOVAL, REAR....................8O-44
CENTER SEAT CUSHION - INSTALLATION . . . 23-79
CENTER SEAT CUSHION - REMOVAL.....23-79
CENTER SEAT CUSHION COVER -
INSTALLATION.......................23-79
CENTER SEAT CUSHION COVER -
REMOVAL..........................23-79
CENTERING - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
CLOCKSPRING......................8O-19
CERTIFICATION LABEL - DESCRIPTION,
VEHICLE.........................Intro.-11
CHAIN COVER(S) - INSTALLATION,
TIMING BELT....................9-171,9-81
CHAIN COVER(S) - REMOVAL, TIMING
BELT ..........................9-170,9-81
CHAIN WEAR - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
MEASURING TIMING..................9-167
CHAIN WEAR, STANDARD PROCEDURE -
MEASURING TIMING...................9-77
CHAIN/TENSIONER - DESCRIPTION,
TIMING............................9-229
CHAIN/TENSIONER - OPERATION,
TIMING............................9-229
CHANNEL - INSTALLATION, GLASS RUN . . 23-22,
23-31
CHANNEL - REMOVAL, GLASS RUN . 23-21,23-30
CHARGE - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
REFRIGERANT SYSTEM...............24-47
CHARGE AIR COOLER AND PLUMBING -
CLEANING..........................11-17
CHARGE AIR COOLER AND PLUMBING -
DESCRIPTION.......................11-16
CHARGE AIR COOLER AND PLUMBING -
INSPECTION........................11-17
CHARGE AIR COOLER AND PLUMBING -
INSTALLATION.......................11-17
CHARGE AIR COOLER AND PLUMBING -
OPERATION
.........................11-16
CHARGE AIR COOLER AND PLUMBING -
REMOVAL
..........................11-17
CHARGE AIR COOLER SYSTEM - LEAKS
- DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
............11-16
CHARGING - DESCRIPTION
.............8F-19
CHARGING - OPERATION
..............8F-19
CHARGING - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
BATTERY
............................8F-8
CHARGING SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING
...........................8F-19
CHARGING SYSTEM - SPECIFICATIONS,
TORQUE - GENERATOR
................8F-20
CHART - SPECIFICATIONS, TORQUE
........5-8
CHART, SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE
.......5-46
CHART, SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE
.....19-19,
19-23,19-35,19-42
CHART, SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE
. . 2-10,2-29,
2-42
CHART, SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE
......22-13CHARTS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
DIAGNOSIS........................21-145
CHARTS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
SMOKE DIAGNOSIS...................9-236
CHECK - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
COOLANT LEVEL......................7-17
CHECK - STANDARD PROCEDURE, FLUID
LEVEL......................21-202,21-366
CHECK - STANDARD PROCEDURE, OIL
PUMP VOLUME.....................21-387
CHECK CABLE - INSTALLATION.........23-15
CHECK CABLE - REMOVAL.............23-15
CHECK GAUGES INDICATOR -
DESCRIPTION.......................8J-21
CHECK GAUGES INDICATOR -
OPERATION.........................8J-21
CHECK VALVE - DESCRIPTION...........8R-7
CHECK VALVE - INSTALLATION..........8R-8
CHECK VALVE - OPERATION.............8R-8
CHECK VALVE - REMOVAL..............8R-8
CHILD RESTRAINT ANCHOR -
DESCRIPTION.......................8O-15
CHILD RESTRAINT ANCHOR -
INSTALLATION......................8O-18
CHILD RESTRAINT ANCHOR -
OPERATION.........................8O-17
CHILD RESTRAINT ANCHOR - REMOVAL . . 8O-17
CHIME WARNING SYSTEM -
DESCRIPTION........................8B-1
CHIME WARNING SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING........................8B-3
CHIME WARNING SYSTEM - OPERATION . . . 8B-1
CIGAR LIGHTER OUTLET -
DESCRIPTION.....................8W-97-2
CIGAR LIGHTER OUTLET - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING.....................8W-97-2
CIGAR LIGHTER OUTLET - OPERATION . 8W-97-2
CIRCUIT - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE SENSOR......8M-10
CIRCUIT - OPERATION, FUEL DRAIN.....14-67
CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST MODE -
DESCRIPTION........................25-1
CIRCUIT FUNCTIONS - DESCRIPTION . . 8W-01-6
CIRCUIT INFORMATION - DESCRIPTION . 8W-01-5
CIRCUIT SENSE - DESCRIPTION,
IGNITION...........................8E-10
CIRCUIT SENSE - OPERATION, IGNITION . . 8E-11
CIRCUITS - OPERATION, NON-
MONITORED.........................25-8
CLAMPS - DESCRIPTION, HOSE...........7-3
CLAMPS - OPERATION, HOSE.............7-5
CLEANING/REVERSE FLUSHING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE, COOLING
SYSTEM............................7-17
CLEARANCE - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
CONNECTING ROD BEARING AND
CRANKSHAFT JOURNAL...............9-272
CLEARANCE - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
MAIN BEARING......................9-274
CLEARANCE LAMP - INSTALLATION, CAB . 8L-12
CLEARANCE LAMP - REMOVAL, CAB.....8L-11
CLOCKSPRING - DESCRIPTION.........8O-18
CLOCKSPRING - INSTALLATION.........8O-21
CLOCKSPRING - OPERATION...........8O-19
CLOCKSPRING - REMOVAL............8O-20
CLOCKSPRING CENTERING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE........................8O-19
CLUSTER - ASSEMBLY, INSTRUMENT....8J-15
CLUSTER - DESCRIPTION, INSTRUMENT . . . 8J-2
CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
INSTRUMENT........................8J-10
CLUSTER - DISASSEMBLY, INSTRUMENT . . 8J-14
CLUSTER - INSTALLATION, INSTRUMENT . 8J-16
CLUSTER - OPERATION, INSTRUMENT.....8J-6
CLUSTER - REMOVAL, INSTRUMENT.....8J-14
CLUSTER BEZEL - INSTALLATION........23-49
CLUSTER BEZEL - REMOVAL...........23-49
CLUTCH - 5.9L DIESEL - DESCRIPTION,
FAN DRIVE VISCOUS...................7-52
CLUTCH - 5.9L DIESEL - OPERATION,
FAN DRIVE VISCOUS...................7-52
CLUTCH - ASSEMBLY, FRONT..........21-207
CLUTCH - ASSEMBLY, LOW/REVERSE . . . 21-385
CLUTCH - ASSEMBLY, REAR
...........21-249
CLUTCH - CLEANING, LOW/REVERSE
....21-385
CLUTCH - CLEANING, REAR
...........21-248
CLUTCH - DESCRIPTION, FRONT
.......21-205
CLUTCH - DESCRIPTION, OVERDRIVE
. . . 21-217
6 INDEXDR
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page