1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Reverse
[x] Cancel search: ReversePage 1821 of 2627

(2) Measure mainshaft endplay with Dial Indicator
Set C-3339 and Extension Rod 8161 installed onto
the rear of the transmission gear case (Fig. 84).
(3) Measure countershaft end-play with Dial Indi-
cator Set C-3339 and Extension Rod 8161 installed
onto the rear of the transmission gear case (Fig. 85).
(4) Rotate transmission into a horizontal position
and remove the input shaft retainer.
(5) Install shims necessary to achieve an end-play
of 0-0.10 mm (0-0.004 in.) for the mainshaft and
countershaft.
NOTE: Countershaft shims go between the bearing
race and spacer. Mainshaft shims go into the input
shaft retainer.
(6) Install anewinput shaft seal into the input
shaft retainer with Installer C-4965.
(7) Install input shaft oil guide with C-3972-A and
Handle C-4171.
(8) Apply sealer to the input shaft retainer and
install retainer onto the clutch housing. Install bolts
and tighten to 28 N´m (20 ft.lbs.).
REVERSE GEAR
(1) Install reverse shift fork and synchronizer as
an assembly onto the reverse shift rail and output
shaft (Fig. 86).NOTE: Raised square shoulder and snap-ring on
the synchro face the case.
Fig. 84 MEASURE MAINSHAFT ENDPLAY
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - EXTENSION ROD
3 - MAIN SHAFT
Fig. 85 MEASURE COUNTERSHAFT END-PLAY
1 - EXTENSION ROD
2 - DIAL INDICATOR
3 - COUNTERSHAFT
Fig. 86 REVERSE SHIFT FORK AND SYNCHRO
1 - REVERSE SYNCHRO
2 - REVERSE SHIFT FORK
21 - 118 MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600DR
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 (Continued)
Page 1822 of 2627

(2) Install roll-pin securing the reverse shift fork
to the reverse shift rail with 6 mm (7/32 in.) punch
and a hammer.
(3) Install reverse gear bearing sleeve onto the
output shaft with Installer 6446 if necessary (Fig.
87).
(4) Install reverse gear, reverse gear synchronizer
cone, reverse gear outer blocker ring and reverse
gear bearing (Fig. 88).
(5) Install output shaft ball bearing assembly and
reverse thrust washer onto the output shaft (Fig. 89).
NOTE: Raised shoulder on thrust washer faces
away from the reverse gear.
(6) Install anewoutput shaft nut onto the output
shaft.
(7) With Wrench 8226 on the output shaft nut and
Socket 6993 or 6984 holding the output shaft, tighten
the nut to 339 N´m (250 ft.lbs.).
(8) Stake nut into the slot in the output shaft with
a 9 mm (5/16 in.) punch.
(9) Press countershaft reverse gear into the sleeve
with a shop press.
Fig. 87 REVERSE BEARING SLEEVE
1 - REVERSE GEAR BEARING SLEEVE
Fig. 88 REVERSE GEAR COMPONENTS
1 - REVERSE GEAR
2 - REVERSE BEARING
3 - BLOCKER RING
4 - FRICTION CONE
Fig. 89 OUTPUT SHAFT BEARING AND THRUST
WASHER
1 - OUTPUT SHAFT BALL BEARING
2 - THRUST WASHER
DRMANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 21 - 119
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 (Continued)
Page 1823 of 2627

(10) Install reverse countershaft rear bearing onto
the countershaft reverse gear assembly with Installer
C-4652 and Handle C-4171.
(11) Install reverse idler gear rear bearing, bearing
spacer, front bearing, and front thrust washer onto
the idler gear shaft.
(12) Install idler and reverse countershaft gears
together (Fig. 90).
(13) Install reverse idler thrust washer from the
reverse idler.
(14) Install crossover cam rollers and pin (Fig. 91).EXTENSION/ADAPTER HOUSING
(1) Install extension housing bushing with
Installer 8156 and Handle C-4171, if necessary. The
oil feed hole must be at the 12 o'clock position when
installed.
(2) On 4X2 vehicles, install extension housing seal
with Installer 8154 and Handle C-4171, with the
weep hole at the bottom.
NOTE: Drain hole located in the dust boot portion
of the seal must face downward ( toward the
ground) when installed.
(3) On 4X4 vehicles, install adapter housing seal
with Installer C-3860-A and Handle C-4171.
(4) Install the crossover cam bushing into the
extension/adapter housing with Installer 8239 and
Handle C-4171.
(5) Clean the rear of the transmission case of all
sealer.
(6) Install reverse countershaft gear bearing race
onto the reverse countershaft gear bearing.
(7) Measure the distance from the back of the
bearing race to Gauge Bar 6311 (Fig. 92).
(8) Measure thickness of the gauge bar and record
the total of the two measurements.
(9) Clean all the sealer from the extension/adapter
housing.
Fig. 90 REVERSE IDLER AND COUNTERSHAFT
GEARS
1 - REVERSE IDLER GEAR
2 - COUNTERSHAFT REVERSE GEAR
Fig. 91 CROSSOVER CAM ROLLERS AND PIN
1 - CROSSOVER CAM PIN
2 - CROSSOVER CAM ROLLERS
Fig. 92 Measure Height of Reverse Countershaft
1 - MEASURE DISTANCE FROM RACE TO GAUGE BAR
21 - 120 MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600DR
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 (Continued)
Page 1824 of 2627

(10) Place Gauge Bar 6311 across the housing face.
Measure the distance from the top of the bar to the
bottom of the reverse countershaft bearing race bore
(Fig. 93).
(11) Subtract thickness of the gauge bar from the
measurement and record the result.
(12) The difference between the two measurements
is the end-play for the reverse countershaft gear
assembly.
(13) Install shims to achieve 0.15-0.25 mm (0.006-
0.010 in.) end-play for the reverse countershaft gear
assembly into the reverse countershaft bearing race
bore.
(14) Use Installer to install the reverse counter-
shaft bearing race into the extension/adapter hous-
ing.
(15) Install back-up lamp switch into the exten-
sion/adapter housing and tighten to 28 N´m (20
ft.lbs.).
(16) Install crossover cam into the extension/
adapter housing.
(17) Install bolt to hold the crossover cam to the
extension/adapter housing (Fig. 94).
(18) Install crossover detent plunger, spring and
plug into the extension/adapter housing. Tighten the
plug to 47.5 N´m (35 ft.lbs.) (Fig. 95).
(19) Apply sealer to the surface of the transmis-
sion case.
(20) Install extension/adapter housing onto the
transmission case.(21) Install bolts to hold the extension/adapter
housing onto the transmission gear case. Tighten
bolts to 48 N´m (35 ft.lbs.).
(22) Install shift rail blocker bolt and tighten bolt
to 55 N´m (41 ft.lbs.).
(23) Install primary shift rail detent plunger,
spring and plug into the transmission case. Tighten
detent plug to 47.5 N´m (35 ft.lbs.).
(24) Install shift tower onto the transmission case
and tighten bolts to 9 N´m (7 ft.lbs.).
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If installing a new transmission, use all com-
ponents supplied with the transmission. If a new
shift tower is supplied with the new transmission,
do not re-use the original shift tower.
Fig. 93 MEASURE DEPTH OF REVERSE
COUNTERSHAFT GEAR BEARING RACE BORE
1 - GAUGE BAR TO BEARING RACE BORE MEASUREMENT
Fig. 94 CROSSOVER CAM BOLT
1 - CROSSOVER CAM
2 - BOLT
3 - EXTENSION HOUSING
Fig. 95 CROSSOVER CAM DETENT PLUG
1 - DETENT PLUG
2 - EXTENSION HOUSING
DRMANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 21 - 121
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 (Continued)
Page 1835 of 2627

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION -
48RE
DESCRIPTION
The 48RE (Fig. 1) is a four speed fully automatic
transmissions with an electronic governor. The 48RE
is equipped with a lock-up clutch in the torque con-
verter. First through third gear ranges are provided
by the clutches, bands, overrunning clutch, and plan-
etary gear sets in the transmission. Fourth gear
range is provided by the overdrive unit that contains
an overdrive clutch, direct clutch, planetary gear set,
and overrunning clutch.
The transmission contains a front, rear, and direct
clutch which function as the input driving compo-
nents. It also contains the kickdown (front) and thelow/reverse (rear) bands which, along with the over-
running clutch and overdrive clutch, serve as the
holding components. The driving and holding compo-
nents combine to select the necessary planetary gear
components, in the front, rear, or overdrive planetary
gear set, transfer the engine power from the input
shaft through to the output shaft.
The valve body is mounted to the lower side of the
transmission and contains the valves to control pres-
sure regulation, fluid flow control, and clutch/band
application. The oil pump is mounted at the front of
the transmission and is driven by the torque con-
verter hub. The pump supplies the oil pressure nec-
essary for clutch/band actuation and transmission
lubrication.
21 - 132 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
Page 1839 of 2627

REVERSE POWERFLOW
When the gear selector is moved into the
REVERSE position (Fig. 5), the front clutch and the
rear band are applied. With the application of the
front clutch, engine torque is applied to the sun gear,
turning it in a clockwise direction. The clockwise
rotation of the sun gear causes the rear planet pin-
ions to rotate against engine rotation in a counter-
clockwise direction. The rear band is holding the low
reverse drum, which is splined to the rear carrier.
Since the rear carrier is being held, the torque fromthe planet pinions is transferred to the rear annulus
gear, which is splined to the output shaft. The output
shaft in turn rotates with the annulus gear in a
counterclockwise direction giving a reverse gear out-
put. The entire transmission of torque is applied to
the rear planetary gearset only. Although there is
torque input to the front gearset through the sun
gear, no other member of the gearset is being held.
During the entire reverse stage of operation, the
front planetary gears are in an idling condition.
Fig. 5 Reverse Powerflow
1 - FRONT CLUTCH ENGAGED 5 - OUTPUT SHAFT
2 - OUTPUT SHAFT 6 - INPUT SHAFT
3 - LOW/REVERSE BAND APPLIED 7 - FRONT CLUTCH ENGAGED
4 - INPUT SHAFT 8 - LOW/REVERSE BAND APPLIED
21 - 136 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1840 of 2627

FIRST GEAR POWERFLOW
When the gearshift lever is moved into the DRIVE
position the transmission goes into first gear (Fig. 6).
As soon as the transmission is shifted from PARK or
NEUTRAL to DRIVE, the rear clutch applies, apply-
ing the rear clutch pack to the front annulus gear.
Engine torque is now applied to the front annulus
gear turning it in a clockwise direction. With the
front annulus gear turning in a clockwise direction, it
causes the front planets to turn in a clockwise direc-
tion. The rotation of the front planets cause the sun
to revolve in a counterclockwise direction. The sun
gear now transfers its counterclockwise rotation to
the rear planets which rotate back in a clockwisedirection. With the rear annulus gear stationary, the
rear planet rotation on the annulus gear causes the
rear planet carrier to revolve in a counterclockwise
direction. The rear planet carrier is splined into the
low-reverse drum, and the low reverse drum is
splined to the inner race of the over-running clutch.
With the over-running clutch locked, the planet car-
rier is held, and the resulting torque provided by the
planet pinions is transferred to the rear annulus
gear. The rear annulus gear is splined to the output
shaft and rotated along with it (clockwise) in an
underdrive gear reduction mode.
Fig. 6 First Gear Powerflow
1 - OUTPUT SHAFT 5 - OVER-RUNNING CLUTCH HOLDING
2 - OVER-RUNNING CLUTCH HOLDING 6 - INPUT SHAFT
3 - REAR CLUTCH APPLIED 7 - REAR CLUTCH APPLIED
4 - OUTPUT SHAFT 8 - INPUT SHAFT
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 137
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1842 of 2627
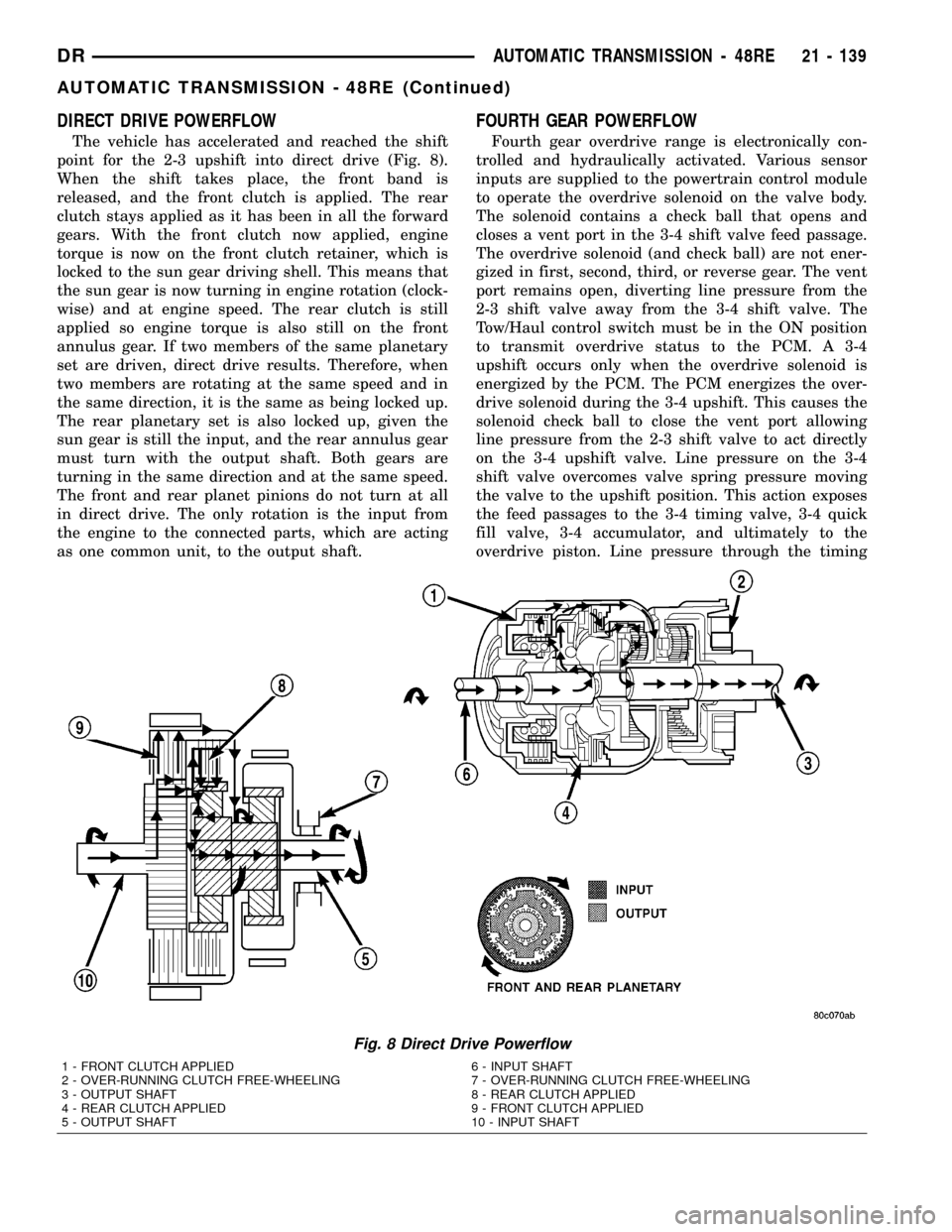
DIRECT DRIVE POWERFLOW
The vehicle has accelerated and reached the shift
point for the 2-3 upshift into direct drive (Fig. 8).
When the shift takes place, the front band is
released, and the front clutch is applied. The rear
clutch stays applied as it has been in all the forward
gears. With the front clutch now applied, engine
torque is now on the front clutch retainer, which is
locked to the sun gear driving shell. This means that
the sun gear is now turning in engine rotation (clock-
wise) and at engine speed. The rear clutch is still
applied so engine torque is also still on the front
annulus gear. If two members of the same planetary
set are driven, direct drive results. Therefore, when
two members are rotating at the same speed and in
the same direction, it is the same as being locked up.
The rear planetary set is also locked up, given the
sun gear is still the input, and the rear annulus gear
must turn with the output shaft. Both gears are
turning in the same direction and at the same speed.
The front and rear planet pinions do not turn at all
in direct drive. The only rotation is the input from
the engine to the connected parts, which are acting
as one common unit, to the output shaft.
FOURTH GEAR POWERFLOW
Fourth gear overdrive range is electronically con-
trolled and hydraulically activated. Various sensor
inputs are supplied to the powertrain control module
to operate the overdrive solenoid on the valve body.
The solenoid contains a check ball that opens and
closes a vent port in the 3-4 shift valve feed passage.
The overdrive solenoid (and check ball) are not ener-
gized in first, second, third, or reverse gear. The vent
port remains open, diverting line pressure from the
2-3 shift valve away from the 3-4 shift valve. The
Tow/Haul control switch must be in the ON position
to transmit overdrive status to the PCM. A 3-4
upshift occurs only when the overdrive solenoid is
energized by the PCM. The PCM energizes the over-
drive solenoid during the 3-4 upshift. This causes the
solenoid check ball to close the vent port allowing
line pressure from the 2-3 shift valve to act directly
on the 3-4 upshift valve. Line pressure on the 3-4
shift valve overcomes valve spring pressure moving
the valve to the upshift position. This action exposes
the feed passages to the 3-4 timing valve, 3-4 quick
fill valve, 3-4 accumulator, and ultimately to the
overdrive piston. Line pressure through the timing
Fig. 8 Direct Drive Powerflow
1 - FRONT CLUTCH APPLIED 6 - INPUT SHAFT
2 - OVER-RUNNING CLUTCH FREE-WHEELING 7 - OVER-RUNNING CLUTCH FREE-WHEELING
3 - OUTPUT SHAFT 8 - REAR CLUTCH APPLIED
4 - REAR CLUTCH APPLIED 9 - FRONT CLUTCH APPLIED
5 - OUTPUT SHAFT 10 - INPUT SHAFT
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 139
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)