1998 DODGE RAM 1500 transfer output shaft bushing
[x] Cancel search: transfer output shaft bushingPage 1704 of 2627

TRANSMISSION AND TRANSFER CASE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500..........1
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500..........43
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600..........88
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE........130
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE.311
TRANSFER CASE - NV241 GENII...........415TRANSFER CASE - NV271................447
TRANSFER CASE - NV243................482
TRANSFER CASE - NV244 GENII...........512
TRANSFER CASE - NV273................542
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................3
REMOVAL.............................3
DISASSEMBLY..........................4CLEANING............................15
INSPECTION..........................16
ASSEMBLY............................17
INSTALLATION.........................39
SPECIFICATIONS.......................40
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................40
MANUAL TRANSMISSION -
NV3500
DESCRIPTION
The transmission is a medium-duty 5-speed, con-
stant mesh fully synchronized manual transmission
with fifth gear overdrive range. The transmission is
available in two and four-wheel drive configurations.
The transmission gear case consists of two aluminum
housings (Fig. 1). The clutch housing is an integral
part of the transmission front housing.
A combination of roller and ball bearings are used
to support the transmission shafts in the two hous-
ings. The transmission gears all rotate on caged type
needle bearings. A roller bearing is used between the
input and output shaft.
The transmission has a single shaft shift mecha-
nism with three shift forks all mounted on the shaft.
The shaft is supported in the front and rear housings
by bushings and one linear ball bearing. Internal
shift components consist of the forks, shaft, shift
lever socket and detent components
OPERATION
The manual transmission receives power through the
clutch assembly from the engine. The clutch disc issplined to the transmission input shaft and is turned at
engine speed at all times that the clutch is engaged.
The input shaft is connected to the transmission coun-
tershaft through the mesh of fourth speed gear on the
input shaft and the fourth countershaft gear. At this
point, all the transmission gears are spinning.
The driver selects a particular gear by moving the
shift lever to the desired gear position. This movement
moves the internal transmission shift components to
begin the shift sequence. As the shift lever moves the
selected shift rail, the shift fork attached to that rail
begins to move. The fork is positioned in a groove in the
outer circumference of the synchronizer sleeve. As the
shift fork moves the synchronizer sleeve, the synchro-
nizer begins to speed-up or slow down the selected gear
(depending on whether we are up-shifting or down-shift-
ing). The synchronizer does this by having the synchro-
nizer hub splined to the mainshaft and moving the
blocker ring into contact with the gear's friction cone. As
the blocker ring and friction cone come together, the
gear speed is brought up or down to the speed of the
synchronizer. As the two speeds match, the splines on
the inside of the synchronizer sleeve become aligned
with the teeth on the blocker ring and the friction cone
and eventually will slide over the teeth, locking the gear
to the mainshaft, or countershaft, through the synchro-
nizer.
DRTRANSMISSION AND TRANSFER CASE 21 - 1
Page 1951 of 2627

OPERATION
To apply the clutch, pressure is applied between
the clutch retainer and piston. The fluid pressure is
provided by the oil pump, transferred through the
control valves and passageways, and enters the
clutch through the hub of the reaction shaft support.
With pressure applied between the clutch retainer
and piston, the piston moves away from the clutch
retainer and compresses the clutch pack. This action
applies the clutch pack, allowing torque to flow
through the input shaft into the driving discs, and
into the clutch plates and pressure plate that are
lugged to the clutch retainer. The waved spring is
used to cushion the application of the clutch pack.
The snap-ring is selective and used to adjust clutch
pack clearance.
When pressure is released from the piston, the
spring returns the piston to its fully released position
and disengages the clutch. The release spring also
helps to cushion the application of the clutch assem-
bly. When the clutch is in the process of being
released by the release spring, fluid flows through a
vent and one-way ball-check-valve located in the pis-
ton. The check-valve is needed to eliminate the pos-
sibility of plate drag caused by centrifugal force
acting on the residual fluid trapped in the clutch pis-
ton retainer.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove fiber thrust washer from forward side
of clutch retainer.
(2) Remove input shaft front and rear seal rings.
(3) Remove selective clutch pack snap-ring (Fig.
214).
(4) Remove the reaction plate, clutch discs, steel
plates, pressure plate, wave spring, spacer ring, and
piston spring (Fig. 214).
(5) Remove clutch piston with rotating motion.
(6) Remove and discard piston seals.
(7) Remove input shaft retaining ring. It may be
necessary to press the input shaft in slightly to
relieve tension on the retaining ring
(8) Press input shaft out of retainer with shop
press and suitable size press tool. Use a suitably
sized press tool to support the retainer as close to the
input shaft as possible.
CLEANING
Clean the clutch components with solvent and dry
them with compressed air. Do not use rags or shop
towels to dry any of the clutch parts. Lint from such
materials will adhere to component surfaces and
could restrict or block fluid passages after assembly.
INSPECTION
Replace the clutch discs if warped, worn, scored,
burned/charred, the lugs are damaged, or if the fac-
ing is flaking off. Replace the top and bottom pres-
sure plates if scored, warped, or cracked. Be sure the
driving lugs on the pressure and clutch plates are
also in good condition. The lugs must not be bent,
cracked or damaged in any way.
Replace the piston spring and wave spring if either
part is distorted, warped or broken.
Check the lug grooves in the clutch retainer. The
clutch and pressure plates should slide freely in the
slots. Replace the retainer if the grooves are worn or
damaged. Also check action of the check balls in the
retainer and piston. Each check ball must move
freely and not stick.
Replace the retainer bushing if worn, scored, or
doubt exists about bushing condition.
Inspect the piston and retainer seal surfaces for
nicks or scratches. Minor scratches can be removed
with crocus cloth. However, replace the piston and/or
retainer if the seal surfaces are seriously scored.
Check condition of the fiber thrust washer and
metal output shaft thrust washer. Replace either
washer if worn or damaged.
Check condition of the seal rings on the input shaft
and clutch retainer hub. Replace the seal rings only
if worn, distorted, or damaged. The input shaft front
seal ring is teflon with chamfered ends. The rear ring
is metal with interlocking ends.
Check the input shaft for wear, or damage. Replace
the shaft if worn, scored or damaged in any way.
21 - 248 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
REAR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 2118 of 2627

TRANSFER CASE - NV241 GENII
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TRANSFER CASE - NV241 GENII
DESCRIPTION........................415
OPERATION..........................415
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER
CASE - NV241 GENII..................416
REMOVAL............................417
DISASSEMBLY........................417
CLEANING...........................426
INSPECTION.........................426
ASSEMBLY...........................428
INSTALLATION........................438
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSFER CASE - NV241 GENII........438
SPECIAL TOOLS
TRANSFER CASE - NV241/NV243........439
EXTENSION HOUSING BUSHING AND SEAL
REMOVAL............................440INSTALLATION........................440
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID DRAIN AND
REFILL............................441
FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL............................441
INSTALLATION........................442
POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................442
OPERATION..........................442
REMOVAL............................443
INSTALLATION........................443
SHIFT LEVER
REMOVAL............................444
INSTALLATION........................445
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - SHIFT LEVER..........446
TRANSFER CASE - NV241
GENII
DESCRIPTION
The NV241 GENII transfer case is a part-time
transfer case with a low-range gear system. It pro-
vides three operating ranges plus a NEUTRAL posi-
tion. The low range position provides a gear
reduction ratio of 2.72:1 for increased low speed
torque capability.
The gear cases and extension are all of aluminum
(Fig. 1). Drive sprockets and an interconnecting drive
chain are used to transmit engine torque to the front/
rear propeller shafts. The mainshaft, input gear and
front output shaft are supported by ball and needle
bearings.
IDENTIFICATION
An identification tag (Fig. 2) is attached to the rear
case of every transfer case. The tag provides the
transfer case model number, assembly number, serial
number, and low range ratio.
The transfer case serial number also represents
the date of build.
OPERATION
OPERATING RANGE
Transfer case operating ranges are:
²2H (2-wheel drive)²4H (4-wheel drive)
²4LO (4-wheel drive low range)
The 2H range is for use on any road surface at any
time.
The 4H and 4LO ranges are for off road use only.
They are not for use on hard surface roads. The only
exception being when the road surface is covered by
ice and snow.
The low range reduction gear system is operative
in 4LO range only. This range is for extra pulling
Fig. 1 Transfer Case - Front View
1 - TRANSFER CASE
2 - MANUAL LEVER
3 - POSITION SENSOR
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV241 GENII 21 - 415
Page 2152 of 2627
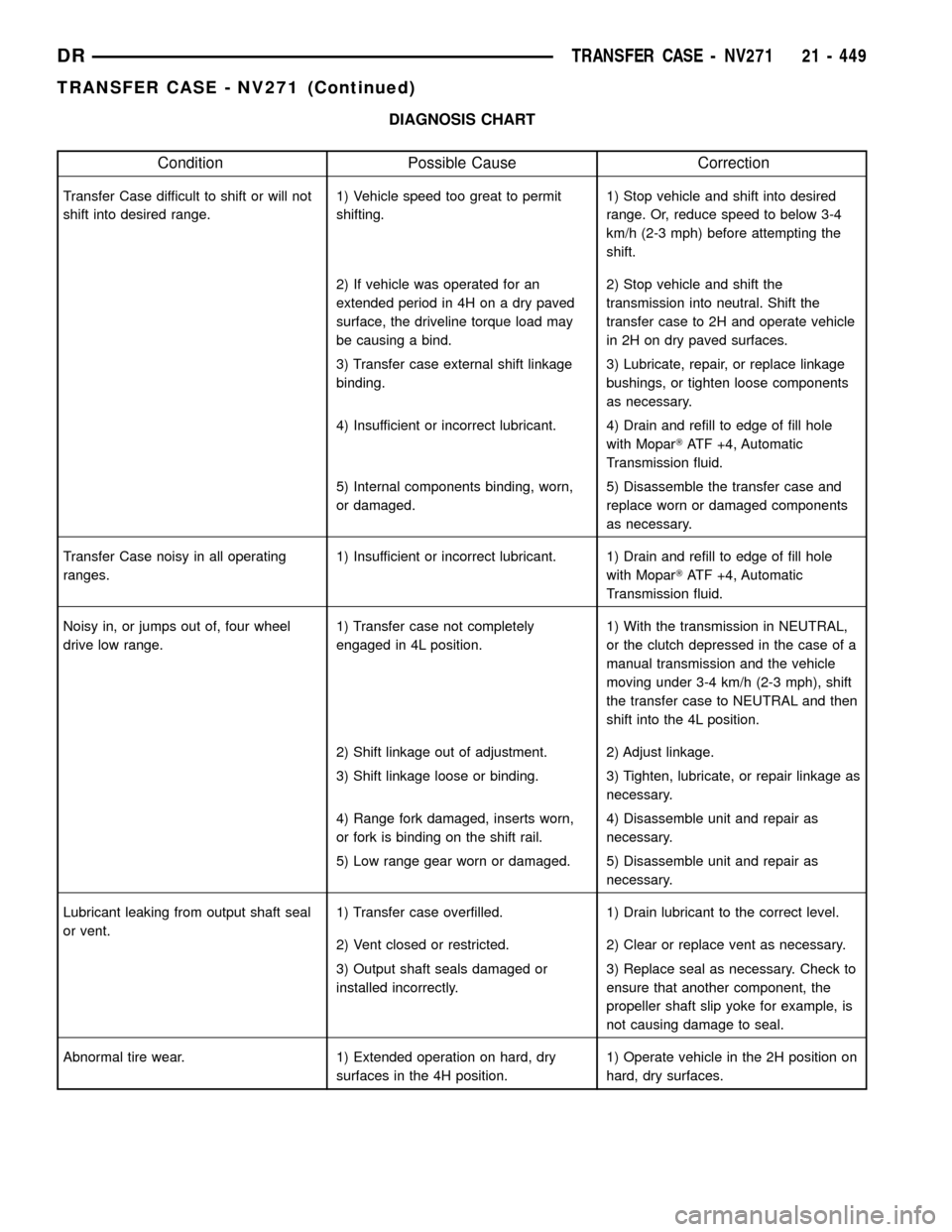
DIAGNOSIS CHART
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Transfer Case difficult to shift or will not
shift into desired range.1) Vehicle speed too great to permit
shifting.1) Stop vehicle and shift into desired
range. Or, reduce speed to below 3-4
km/h (2-3 mph) before attempting the
shift.
2) If vehicle was operated for an
extended period in 4H on a dry paved
surface, the driveline torque load may
be causing a bind.2) Stop vehicle and shift the
transmission into neutral. Shift the
transfer case to 2H and operate vehicle
in 2H on dry paved surfaces.
3) Transfer case external shift linkage
binding.3) Lubricate, repair, or replace linkage
bushings, or tighten loose components
as necessary.
4) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 4) Drain and refill to edge of fill hole
with MoparTATF +4, Automatic
Transmission fluid.
5) Internal components binding, worn,
or damaged.5) Disassemble the transfer case and
replace worn or damaged components
as necessary.
Transfer Case noisy in all operating
ranges.1) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 1) Drain and refill to edge of fill hole
with MoparTATF +4, Automatic
Transmission fluid.
Noisy in, or jumps out of, four wheel
drive low range.1) Transfer case not completely
engaged in 4L position.1) With the transmission in NEUTRAL,
or the clutch depressed in the case of a
manual transmission and the vehicle
moving under 3-4 km/h (2-3 mph), shift
the transfer case to NEUTRAL and then
shift into the 4L position.
2) Shift linkage out of adjustment. 2) Adjust linkage.
3) Shift linkage loose or binding. 3) Tighten, lubricate, or repair linkage as
necessary.
4) Range fork damaged, inserts worn,
or fork is binding on the shift rail.4) Disassemble unit and repair as
necessary.
5) Low range gear worn or damaged. 5) Disassemble unit and repair as
necessary.
Lubricant leaking from output shaft seal
or vent.1) Transfer case overfilled. 1) Drain lubricant to the correct level.
2) Vent closed or restricted. 2) Clear or replace vent as necessary.
3) Output shaft seals damaged or
installed incorrectly.3) Replace seal as necessary. Check to
ensure that another component, the
propeller shaft slip yoke for example, is
not causing damage to seal.
Abnormal tire wear. 1) Extended operation on hard, dry
surfaces in the 4H position.1) Operate vehicle in the 2H position on
hard, dry surfaces.
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV271 21 - 449
TRANSFER CASE - NV271 (Continued)
Page 2198 of 2627

Inspect the shift fork wear pads (Fig. 41). The
mode and range fork pads are serviceable and can be
replaced if necessary.
Check both of the sleeves for wear or damage,
especially on the interior teeth. Replace the sleeves if
wear or damage is evident.
REAR EXTENSION HOUSING
Inspect the extension housing seal and bushing.
Replace both components if either show any sign of
wear or damage.
FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT AND DRIVE CHAIN
Inspect the shaft threads, sprocket teeth, and bear-
ing surfaces. Minor nicks on the teeth can be
smoothed with an oilstone. Use 320-400 grit emery to
smooth minor scratches on the shaft bearing sur-
faces. Rough threads on the shaft can be chased if
necessary. Replace the shaft if the threads are dam-
aged, bearing surfaces are scored, or if any sprocket
teeth are cracked or broken.
Examine the drive chain and shaft bearings.
Replace the chain and both sprockets if the chain is
stretched, distorted, or if any of the links bind.
Replace the bearings if rough, or noisy.
LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
Inspect annulus gear condition carefully. The gear
is only serviced as part of the front case. If the gear
is damaged, it will be necessary to replace the gear
and front case as an assembly. Do not attempt to
remove the gear (Fig. 42)
FRONT AND REAR CASES
Inspect the cases for wear and damage.
Check case condition. If leaks were a problem, look
for gouges and severe scoring of case sealing sur-
faces. Also make sure the front case mounting studs
are in good condition.
Check the front case mounting studs and vent
tube. The tube can be secured with LoctiteŸ 271 or
680 if loose. The stud threads can be cleaned up with
a die if necessary. Also check condition of the fill/
drain plug threads in the rear case. The threads can
be repaired with a thread chaser or tap if necessary.
Or the threads can be repaired with Helicoiltstain-
less steel inserts if required.
OIL PUMP/OIL PICKUP
Examine the oil pump pickup parts. Replace the
pump if any part appears to be worn or damaged. Do
not disassemble the pump as individual parts are not
available. The pump is only available as a complete
assembly. The pickup screen, hose, and tube are the
only serviceable parts and are available separately.
Fig. 41 Shift Fork And Wear Pad Locations
1 - RANGE FORK
2 - MODE FORK
3 - WEAR PADS (SERVICEABLE)
4 - WEAR PADS (SERVICEABLE)
Fig. 42 Low Range Annulus Gear
1 - FRONT CASE
2 - LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV243 21 - 495
TRANSFER CASE - NV243 (Continued)
Page 2227 of 2627

REAR EXTENSION HOUSING
Inspect the extension housing seal and bushing.
Replace both components if either show any sign of
wear or damage.
FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT AND DRIVE CHAIN
Inspect the shaft splines and bearing surfaces.
Minor nicks on the splines can be smoothed with an
oilstone. Use 320-400 grit emery to smooth minor
scratches on the shaft bearing surfaces. Replace the
shaft if the bearing surfaces are scored or if any of
the splines are cracked or broken.Examine the drive chain and shaft bearings.
Replace the chain and both sprockets if the chain is
stretched, distorted, or if any of the links bind.
Replace the bearings if rough, or noisy.
LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
Inspect annulus gear condition carefully. The gear
is only serviced as part of the front case. If the gear
is damaged, it will be necessary to replace the gear
and front case as an assembly. Do not attempt to
remove the gear (Fig. 41)
Fig. 39 Input Gear and Carrier Components
1 - PLANETARY CARRIER 4 - CARRIER LOCK RING
2 - REAR THRUST WASHER 5 - CARRIER LOCK RETAINING RING
3 - FRONT THRUST WASHER 6 - INPUT GEAR
Fig. 40 Shift Fork and Wear Pad Locations
1 - RANGE FORK
2 - MODE FORK
3 - WEAR PADS (SERVICEABLE)
4 - WEAR PADS (SERVICEABLE)
Fig. 41 Low Range Annulus Gear
1 - FRONT CASE
2 - LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
21 - 524 TRANSFER CASE - NV244 GENIIDR
TRANSFER CASE - NV244 GENII (Continued)
Page 2258 of 2627

SHIFT FORKS/HUBS/SLEEVES
Check condition of the shift forks and mode fork
shift rail (Fig. 40). Minor nicks on the shift rail can
be smoothed with 320-400 grit emery cloth.
Inspect the shift fork wear pads (Fig. 41). The
mode and range fork pads are serviceable and can be
replaced if necessary.
Check both of the sleeves for wear or damage,
especially on the interior teeth. Replace the sleeves if
wear or damage is evident.
REAR EXTENSION HOUSING
Inspect the extension housing seal and bushing.
Replace both components if either show any sign of
wear or damage.
FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT AND DRIVE CHAIN
Inspect the shaft threads, sprocket teeth, and bear-
ing surfaces. Minor nicks on the teeth can be
smoothed with an oilstone. Use 320-400 grit emery to
smooth minor scratches on the shaft bearing sur-
faces. Rough threads on the shaft can be chased if
necessary. Replace the shaft if the threads are dam-
aged, bearing surfaces are scored, or if any sprocket
teeth are cracked or broken.
Examine the drive chain and shaft bearings.
Replace the chain and both sprockets if the chain is
stretched, distorted, or if any of the links bind.
Replace the bearings if rough, or noisy.
LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
Inspect annulus gear condition carefully. The gear
is only serviced as part of the front case. If the gear
is damaged, it will be necessary to replace the gear
and front case as an assembly. Do not attempt to
remove the gear (Fig. 42)
FRONT AND REAR CASES
Inspect the cases for wear and damage.
Check case condition. If leaks were a problem, look
for gouges and severe scoring of case sealing sur-
faces. Also make sure the front case mounting studs
are in good condition.
Fig. 40 Shift Forks
1 - RANGE FORK
2 - MODE FORK AND RAIL
3 - MODE SPRING
Fig. 41 Shift Fork And Wear Pad Locations
1 - RANGE FORK
2 - MODE FORK
3 - WEAR PADS (SERVICEABLE)
4 - WEAR PADS (SERVICEABLE)
Fig. 42 Low Range Annulus Gear
1 - FRONT CASE
2 - LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV273 21 - 555
TRANSFER CASE - NV273 (Continued)