Page 186 of 2053
M162 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F1 -- 23
D AEW OO M Y_2000
KAB1F150
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
17
Crankshaft position
sensor signal failure (no
engine revolution signal)Even through cam position
recognition is normal, no
crankshaft position signal
recognition
DMonitoring the actual rpm through or
scan tool
18
Crankshaft position
sensor signal failure
(rpm > max. value)When more than applicable
revolution values or
implausibleto60–2teeth
scantool
DInspection the ECM pin 100, 99 about
short circuit with bad contact
DInspection the CKP sensor
20
Crankshaft position
sensor signal failure
(gap recognition failure)
When implausible recognition
of cam and crank angle signal
or intermittent sensing the
signal or error count of
undetected gap.
p
DInspection the air gap between sensor
and drive plate
DInspection the drive plate (teeth
condition)
DInspection the ECM
67Crankshaft position
sensor adaptation failureWhen faulty crank angle
sensor adaption
p
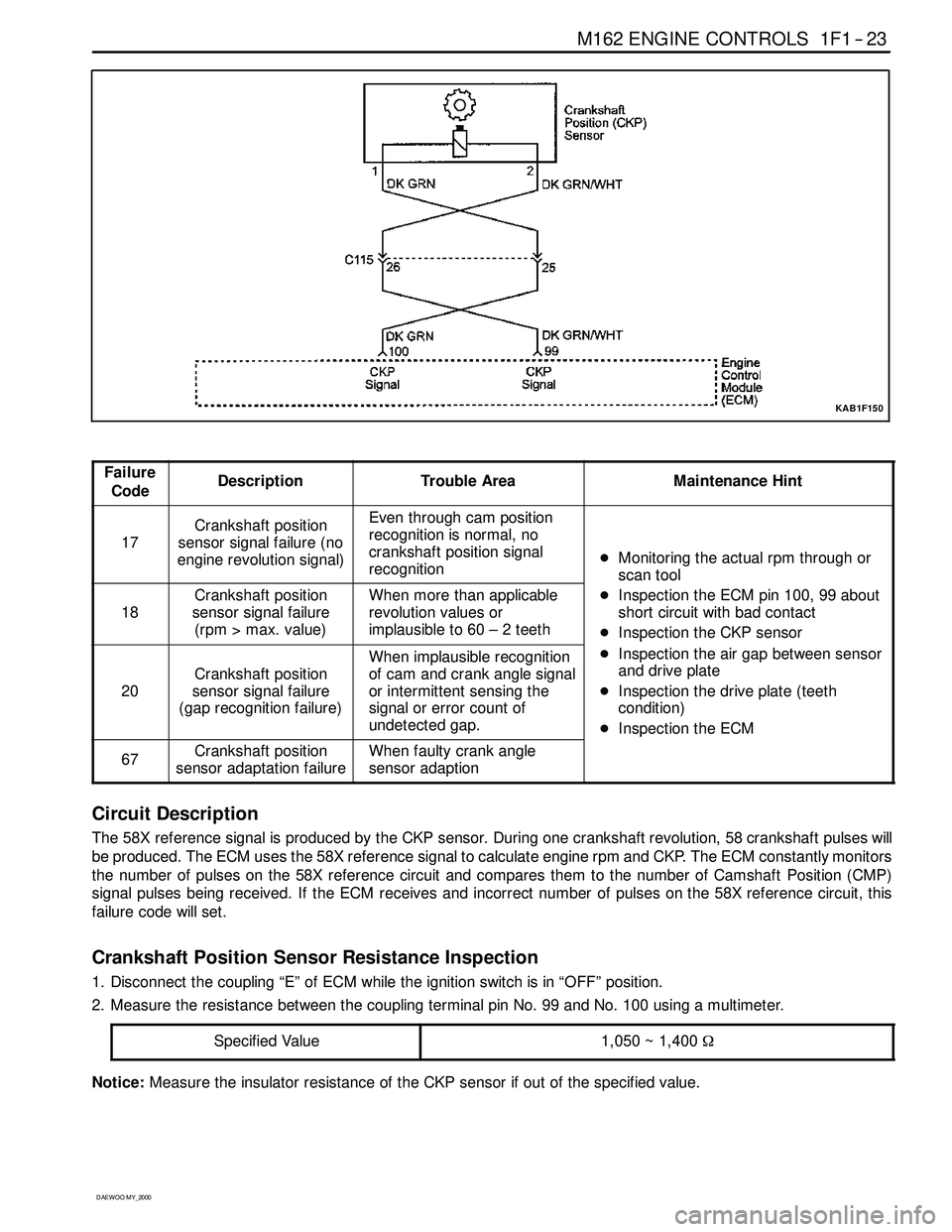
Circuit Description
The 58X reference signal is produced by the CKP sensor. During one crankshaft revolution, 58 crankshaft pulseswill
be produced. The ECM uses the 58X reference signal to calculate engine rpm and CKP. The ECM constantly monitors
the number of pulses on the 58X reference circuit and compares them to the number of Camshaft Position (CMP)
signal pulses being received. If the ECM receives and incorrect number of pulses on the 58X reference circuit, this
failure code will set.
Crankshaft Position Sensor Resistance Inspection
1. Disconnect the coupling “E” of ECM while the ignition switch is in “OFF” position.
2. Measure the resistance between the coupling terminal pin No. 99 and No. 100 using a multimeter.
Specified Value
1,050 ~ 1,400Ω
Notice:Measure the insulator resistance of the CKP sensor if out of the specified value.
Page 187 of 2053
1F1 -- 24 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Crankshaft Position Sensor Output Wave Inspection
1. Measure the output wave between the ECM termi-
nals No. 99 and No. 100 using the scan tool or the os-
cilloscope whileengine cranking (start motor
activated).
Notice:Check the segment or crankshaft position sen-
sor and air gap if cannot get the output wave as shown in
the figure.
YAA1F270
Crankshaft Position Sensor Insulator Resistance Inspection
1. Disconnect the coupling from ECM while the ignition switch is in “OFF” position.
2. Measure the resistance between the coupling terminal pin No. 100 and No. 69 using a multimeter.
Specified Value
>20 kΩ
Notice:Measure the check and ground terminal of the CKP sensor if out of the specified value.
Page 189 of 2053
1F1 -- 26 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
CAMSHAFT POSITION (CMP) SENSOR
YAA1F280
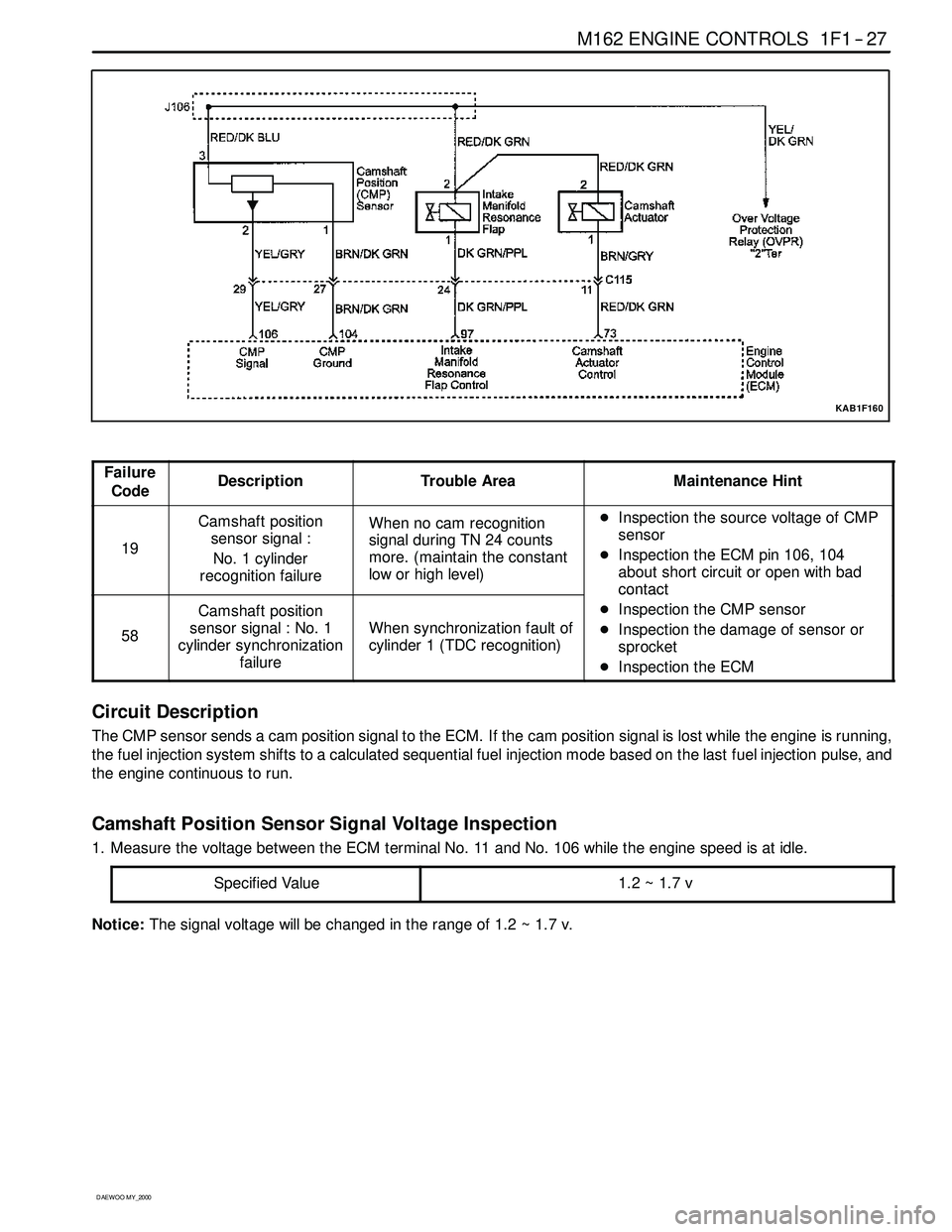
The Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor sends a CMP signal to the Engine Control Module (ECM). The ECM uses this
signal as a “synchronized pulse” to trigger the injectors in the proper sequence. The ECM uses the CMP signal to
indicate the position of the #1 piston during its power stroke. This allows the ECM to calculate true sequential fuel
injection mode of operation.
Page 190 of 2053
M162 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F1 -- 27
D AEW OO M Y_2000
KAB1F160
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
19
Camshaft position
sensor signal :
No. 1 cylinder
recognition failureWhen no cam recognition
signal during TN 24 counts
more. (maintain the constant
low or high level)DInspection the source voltage of CMP
sensor
DInspection the ECM pin 106, 104
about short circuit or open with bad
contact
58
Camshaft position
sensor signal : No. 1
cylinder synchronization
failure
When synchronization fault of
cylinder 1 (TDC recognition)
contact
DInspection the CMP sensor
DInspection the damage of sensor or
sprocket
DInspection the ECM
Circuit Description
The CMP sensor sends a cam position signal to the ECM. If the cam position signal is lost while the engine is running,
the fuel injection system shifts to a calculated sequential fuel injection mode based on the last fuel injection pulse, and
the engine continuous to run.
Camshaft Position Sensor Signal Voltage Inspection
1. Measure the voltage between the ECM terminal No. 11 and No. 106 while the engine speed is at idle.
Specified Value
1.2~1.7v
Notice:The signal voltagewill be changed in the range of 1.2 ~ 1.7 v.
Page 191 of 2053
1F1 -- 28 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Camshaft Position Sensor Output Wave Inspection
1. Measure the output wave between the ECM termi-
nals No. 104 and No. 106 using the scan tool or the
oscilloscope whileengine speed is at idle.
Notice:Replace the CAM sensor if cannot get the out-
put wave as shown in the figure.
KAA1F0O0
Camkshaft Position Sensor Power Supply Inspection
1. Disconnect the CMP sensor Connector.
2. Measure the resistance between the No. 1 and No. 3 pin of the CMP sensor connector while the ignition switch is in
“ON” position.
Specified Value
11 ~ 14 v
Notice:If the measured value is not within the specified value, check the cable.
Page 193 of 2053
1F1 -- 30 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
CAMSHAFT ACTUATOR
YAA1F300
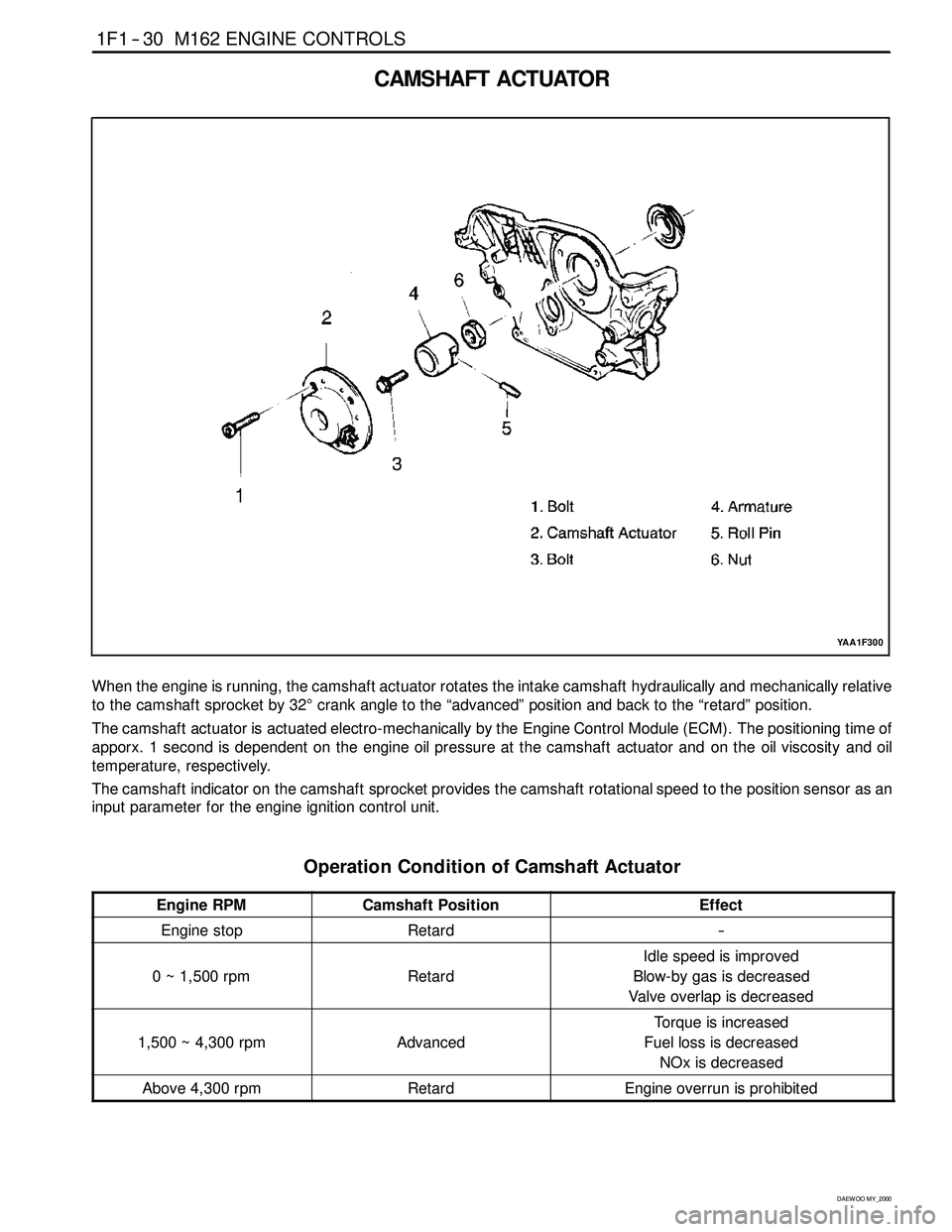
When the engine is running, the camshaft actuator rotates the intake camshaft hydraulically and mechanically relative
to the camshaft sprocket by 32°crank angle to the “advanced” position and back to the “retard” position.
The camshaft actuator is actuated electro-mechanically by the Engine Control Module (ECM). The positioning time of
apporx. 1 second is dependent on the engine oil pressure at the camshaft actuator and on the oil viscosity and oil
temperature, respectively.
The camshaft indicator on the camshaft sprocket provides the camshaft rotational speed to the position sensor as an
input parameter for the engine ignition control unit.
Operation Condition of Camshaft Actuator
Engine RPMCamshaft PositionEffect
Engine stopRetard--
0 ~ 1,500 rpmRetard
Idle speed is improved
Blow-by gas is decreased
Valve overlap is decreased
1,500 ~ 4,300 rpmAdvanced
Torque is increased
Fuel loss is decreased
NOx is decreased
Above 4,300 rpmRetardEngine overrun is prohibited
Page 195 of 2053
1F1 -- 32 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
KNOCK SENSOR (KS)
YAA1F320
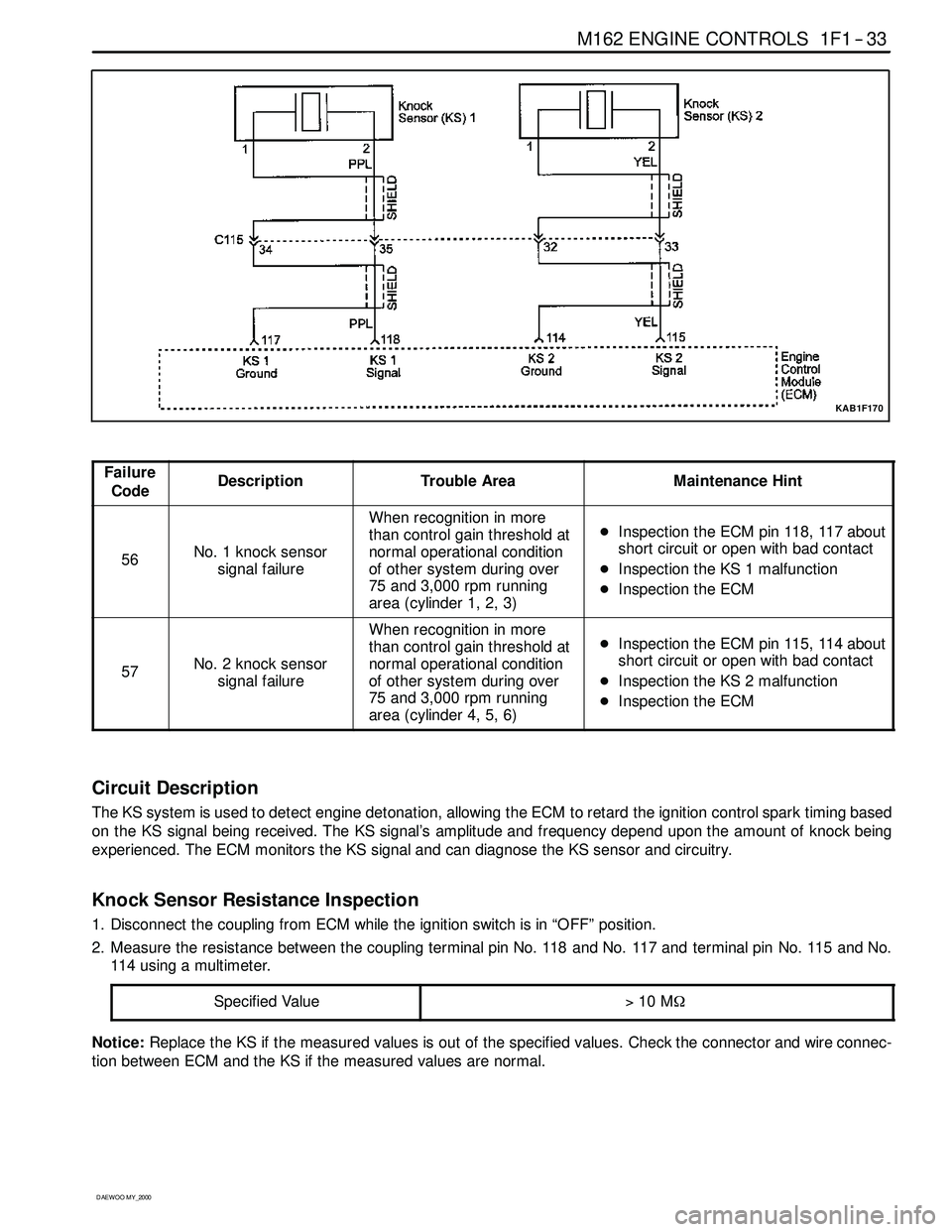
The Knock Sensor (KS) detects abnormal knocking in the engine. The two KS are mounted in the engine block near
the cylinders. The sensors produce an output voltage which increases with the severity of the knock. This signal is sent
to the Engine Control Module (ECM) via a shielded cable. The ECM then adjusts the ignition timing to reduce the spark
knock.
Page 196 of 2053
M162 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F1 -- 33
D AEW OO M Y_2000
KAB1F170
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
56No. 1 knock sensor
signal failure
When recognition in more
than control gain threshold at
normal operational condition
of other system during over
75 and 3,000 rpm running
area (cylinder 1, 2, 3)DInspection the ECM pin 118, 117 about
short circuit or open with bad contact
DInspection the KS 1 malfunction
DInspection the ECM
57No. 2 knock sensor
signal failure
When recognition in more
than control gain threshold at
normal operational condition
of other system during over
75 and 3,000 rpm running
area (cylinder 4, 5, 6)DInspection the ECM pin 115, 114 about
short circuit or open with bad contact
DInspection the KS 2 malfunction
DInspection the ECM
Circuit Description
The KS system is used to detect engine detonation, allowing the ECM to retard the ignition control spark timing based
on the KS signal being received. The KS signal’s amplitude and frequency depend upon the amount of knock being
experienced. The ECM monitors the KS signal and can diagnose the KS sensor and circuitry.
Knock Sensor Resistance Inspection
1. Disconnect the coupling from ECM while the ignition switch is in “OFF” position.
2. Measure the resistance between the coupling terminal pin No. 118 and No. 117 and terminal pin No. 115 and No.
114usingamultimeter.
Specified Value
>10 MΩ
Notice:Replace the KS if the measured values is out of the specified values. Check the connector and wire connec-
tion between ECM and the KS if the measured values are normal.