1997 MERCEDES-BENZ ML350 check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 3753 of 4133
9
Detach return line (30f) and high-pressure
expansion hose (30i)
Connection fittings or banjo bolts
depending on the version. Seal off line
connections with plugs.
Installation:
Replace sealing rings.
Connection fitting, return line
*BA46.20-P-1001-01D
Connection fitting, high-pressure
expansion hose
*BA46.20-P-1002-01D
Banjo bolt, return line
*BA46.20-P-1004-01D
Banjo bolt, high-pressure expansion hose
*BA46.20-P-1005-01D
Plug
*129589009100
10
Detach nut (25d) and bolt from steering
coupling (25) and pull lower steering shaft
(80a) upwards out of steering coupling (25)
Do not use force as the corrugated tube is
sensitive to lateral forces. Enlarge clamping
groove a little with a screwdriver if necessary.
Installation:
Replace nut (25d).
Installation:
Turn rack-and-pinion
steering to center position and fit steering
coupling.
AR46.20-P-0600-01GH
*BA46.10-P-1001-01D
11
Detach rack-and-pinion steering (23) from
front axle carrier (1) by unscrewing bolts (23a)
The installed position of the shims (23h,
23i) on the right-hand side, between the
rubber mount and the front axle carrier, must
be observed as the shims are of different
thicknesses.
Installation:
Attach rack-and-pinion
steering to front axle carrier.
AR46.20-P-0600-03GH
Assessing condition of steering gear when
repairing accident vehicles
AH46.20-P-9409-01A
12
Check rubber mount (21) of rack-and-pinion
steering mounting for damage
Replace rubber mount if necessary:
#
Removing rubber mounts on rack-and-pinion
steering mounting
AR46.20-P-0600-02GH
13
Install in the reverse order
14
Fill and bleed power steering pump
Engines 112, 113
AR46.30-P-0010B
Engines 111, 612, 628
AR46.30-P-0010P
15
Check steering for function and leaks
There is a grease cushion under the cover
cap. A small amount of escaping grease is to
be regarded as normal and must not be
confused with leakage.
16.1
Check toe on front axle and adjust if necessary
When installing a new rack-and-pinion
steering, see:
#
Performing chassis alignment check
AR40.20-P-0200A
Steering shaft
Number
Designation
Model 163
BA46.10-P-1001-01D
Self-locking nut, steering coupling to steering shaft
and rack-and-pinion steering
Nm
28
Steering gear
Number
Designation
Model 163
BA46.20-P-1001-01D
Screwed connection fitting from return line
to rack-and-pinion steering
Nm
15
BA46.20-P-1002-01D
Screwed connection fitting from high-
pressure expansion hose to rack-and-pinion
steering
Nm
15
BA46.20-P-1003-01D
Bolted connection, rack-and-pinion steering
to front axle carrierNm
50
BA46.20-P-1004-01D
Banjo bolt, return line to rack-and-pinion
steering
Nm
30
BA46.20-P-1005-01D
Banjo bolt, high-pressure expansion hose to
rack-and-pinion steering
Nm
30
Copyright DaimlerChrysler AG 06.07.2006 CD-Ausgabe G/10/04 . This WIS print-out will not be recorde
d by Modification services.
Page 2
Page 3757 of 4133
3.1
Remove viscous fan (1)
Engine 112.942 /970 and 113.942.
Right-hand thread!
AR20.40-P-5660C
3.2
Remove electric fan
Only Engine 113.965 /981.
AR20.40-P-5000GH
4.1
Pull off plate clamps of fan shroud (2)
Only for Engine 112.942, from 5/98.
5.1
Remove fan shroud (3)
Only for Engine 112.942 /970 und
113.942. Unscrew the bolts at bottom of fan
shroud for this step
Installation:
If installing a new radiator
with integral power steering pump oil cooler, a
new fan shroud is required if a radiator
without integral oil cooler was previously
installed.
6
Remove headlamp (7).
AR82.10-P-4730GH
7
Remove radiator crossmember (8)
AR62.30-P-2300GH
8
Detach coolant line (4, 6) and expansion
reservoir coolant line (5) at the radiator
Installation:
Replace the hose clamps on
the radiator fitting for the coolant hose, as
they could cause damage to the screw/thread.
Hose clamp
*BA20.20-P-1004-01A
9
Remove the rubber seal on radiator (9)
10.1
Remove oil line (return line of radiator
!
power steering pump expansion reservoir)
(18) and oil line (feed line of steering gear
!
radiator) (19)
From 5/98 only, seal off the connections.
Set of plugs
*129589009100
11
Unscrew ATF lines (10) at the radiator
Seal off the connections.
*BA20.20-P-1001-01A
*BA20.20-P-1003-01A
Set of plugs
*129589009100
12.1
Detach the connector from the fan and
remove the fan grille (11)
Only for Engine 112.942 /970 and 113.942.
13
Unscrew the condenser from the radiator
Do not disconnect the lines.
14
Remove fasteners (20) and damper rubber
(21)
The damper rubber (21) is designed to
prevent possible vibrations between the
condenser and radiator (15) during off-road
driving.
15
Remove air conditioning system fluid
reservoir (14) from the radiator
Place aside with the lines connected.
Detach the condenser from the radiator.
16
Remove radiator (15)
When installing, the spigots on the
radiator must be inserted in the rubber
grommets in the bottom crossmember.
Installation:
On Model 163.154 with
Engine 112.942 before VIN end number
043553, when installing a new radiator with
integral power steering pump oil cooler,
additional operations are required, if they
have not already been carried out:
#
v
Retrofit the bracket for the oil cooler line of
the power steering pump
SM46.30-P-0002A
k
Radiator with integral oil cooler for the power
steering pump
BT20.20-P-0001-01A
17
Detach air guides (12)
Replace the clamps on air guides (13).
18
Install in the reverse order
19
Pour in coolant
AR20.00-P-1142HA
20
Check the headlamp setting and correct if
necessary
e
Check and adjust the headlamp setting
AP82.10-P-8260GH
Danger!
Risk of accident
caused by vehicle starting
off when engine is running.
Risk of injury
caused by contusions and burns when
working in engine during starting procedure
Secure the vehicle to prevent it from moving.
Wear closed and snug-fitting work clothes.
Do not grasp hot or rotating parts.
AS00.00-Z-0005-01A
21
Check the oil level in the automatic
transmission and correct if necessary
AR27.00-P-0101A
22
Check the cooling system for leaks
AR20.00-P-1010HA
Radiator, coolant hoses
Copyright DaimlerChrysler AG 12.05.2006 CD-Ausgabe G/10/04 . This WIS print-out will not be recorde
d by Modification services.
Page 2
Page 3762 of 4133
13
Disconnect coolant hose to coolant pump (8),
coolant hose from thermostat housing (9) and
coolant hose from coolant expansion tank
(10) at radiator
Hexagon socket wrench
*WH58.30-Z-1001-06A
Hexagon socket wrench
*WH58.30-Z-1002-06A
14
Detach air guides (12)
Installation:
Replace fastening clamps
(13)
15
Unscrew bolts (16) at condenser (17) to
radiator
Avoid deformation of condenser lines.
Do not disconnect lines.
16
Remove attachment parts (20) and rubber
shock absorber (21)
Installation:
Ensure, that the rubber
shock absorbers do not drop when installing
the radiator.
Replace fastening clamps.
17
Take off fluid reservoir of AC (14) at radiator
Place to the side with lines connected.
External torx set
*001589760900
18
Remove bracket of charge air pipe at left
radiator
Installation:
Insert bracket of charge air
pipe into the bracket at the radiator.
19
Remove radiator (15)
Installation:
When installing, the mounting
studs of the radiator must be inserted into the
rubber grommets of the lower crossmember.
20
Install in the reverse order
21
Check headlamp adjustment, correct if
necessary
e
Check and correct headlamp adjustment
AP82.10-P-8260A
22
Inspect cooling system for leaks
AR20.00-P-1010HA
23
Fill power steering pump and bleed
Danger!
Risk of accident
caused by vehicle starting
off by itself when engine is running.
Risk of
injury
caused by contusions and burns when
working in engine during starting procedure
Secure vehicle to prevent it from moving.
Wear closed and snug-fitting work clothes.
Do not grasp hot or rotating parts.
AS00.00-Z-0005-01A
24
Run engine and inspect for leaks
Crankcase ventilation, cylinder head cover
Number
Designation
Engine
612.963
BA01.20-P-1002-01A
Bolt, cylinder head cover trim panel to
cylinder head cover
Nm
10
BA01.20-P-1003-01A
Bolt, cover panel to charge air distribution
pipe
Nm
10
Power steering pump
Number
Designation
Model
163.113
BA46.30-P-1012-01A
Banjo bolt, power steering oil line to radiator
Nm
30
Cooling system
Number
Designation
Engine
612.963
BF20.00-P-1001-02E
Cooling system
Total capacity
Liter
Y
11.0
Copyright DaimlerChrysler AG 12.05.2006 CD-Ausgabe G/10/04 . This WIS print-out will not be recorde
d by Modification services.
Page 3
Page 3832 of 4133
SI47.10-P-0004A
Service Information: Procedure when tank is filled with incorrect fuel
19.12.00
MODEL
202 with ENGINE 611
MODEL
203 with ENGINE 611, 612, 646
MODEL
210 with ENGINE 611, 612, 613
MODEL
220 with ENGINE 613, 628, 648
MODEL
163 with ENGINE 612, 628
MODEL
168 with ENGINE 668
MODEL
209 with ENGINE 612
MODEL
211 with ENGINE 628, 646, 647, 648
MODEL
463 with ENGINE 612, 628
Modification notes
26.7.04
Engines have been added and procedure has been updated
Incorrect refueling of diesel-power vehicles with a common rail
injection system. Please be aware that if the customer fills the fuel
tank with the wrong type of fuel, this is the customer's fault and
cannot be submitted as a warranty claim.
If the diesel-powered vehicle with a common rail injection system has
been refueled with gasoline, follow the steps below:
1.
If the engine was not started after fuel tank is filled with the wrong
type of fuel, then emptying the fuel tank and cleaning the fuel low-
pressure lines should be enough to solve the problem.
2.
If the engine was started after fuel tank was filled with wrong type
of fuel:
On engines 611, 612, 613, 668:
-
On the rail, open the low pressure connection of the high
pressure pump return (plastic connection in area of pressure
regulator valve) and check connecting point in rail for chips.
On engine 646, 647, 648, 628:
-
Disconnect Y-distributor unit (return line HDP/Rail) at the output
and, with ignition ON, collect the fuel in a clean container. Check
fuel for metal shavings.
If the high pressure pump is not damaged and there are no metal
shavings in the injection system:
-
As in step 1, empty fuel as per the guidelines and clean the fuel
low-pressure lines. In addition to this, remove/install/replace the
high-pressure pump and fuel filter.
If metal shavings are found in the fuel
system or the high pressure pump drive is
damaged:
#
b
Engine runs rough, surges or does not start
ENGINE 611 in MODEL 203, 202, 210
ENGINE 612 in MODEL 163, 203, 210, 209
ENGINE 613 in MODEL 210, 220
ENGINE 628 in MODEL 163, 220, 211
ENGINE 646 in MODEL 203, 211
ENGINE 647 in MODEL 211
ENGINE 648 in MODEL 220, 211
ENGINE 668 in MODEL 168
ENGINE 612, 628 in MODEL 463
AF07.00-P-9000B
Copyright DaimlerChrysler AG 28.05.2006 CD-Ausgabe G/10/04 . This WIS print-out will not be recorde
d by Modification services.
Page 1
Page 3835 of 4133

SI18.00-P-0010A
Service Information: oil sludge
26.3.01
ENGINE
111 in MODELS 124, 163, 170, 202, 203, 208, 210
ENGINE
112 in MODELS 129, 163, 170, 202, 203, 208, 210, 220
ENGINE
112, 113 in MODEL 463
ENGINE
113 in MODELS 129, 163, 202, 208, 210, 215, 220
ENGINE
137 in MODEL 215, 220
ENGINE
166 in MODEL 168
Oil sludging in gasoline engines with ASSYST maintenance
system
Recently we have determined that time and time again oil
sludging occurs in gasoline engines with an ASSYST maintenance
system.
Oil sludging can lead to the following complaints:
D
engine oil consumption
D
engine smoke (white/blue)
D
influencing of oil level indicator
D
clogged oil filter, engine oil thickened like jelly
D
Check engine lamp illuminated
D
oil sludge visible during assembly job, e.g. in oil filter, in cylinder
head covers, condensation sludging
(engine 166) etc.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following list of causes may lead individually or as a combination
to engine oil sludging:
D
Crankcase ventilation inoperable, function orifices, bores,
passages in cylinder head cover, cylinder head, crankcase etc.
are mechanically sealed. A nonfunctioning crankcase
ventilation boosts loads on the engine oil through organic
nitrates. The risk of oil sludging increases.
The mechanical condition of the engine is always to be
checked, i.e. all engine oil drain orifices on the cylinder head
and crankcase and all crankcase ventilation ducts must be free
of obstacles. Crankcase breather lines may not be kinked.
Check the ventilation bores in the cylinder head covers.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
D
The engine oil used does not comply with the specifications in
Sheet 229.1 or 229.3 of the Specifications for Service Products.
The additive process, e.g. dirt-carrying capability, neutralization
capability and oxidation resistance as well as the quality of the
base stock influence sludging time.
Use of engine oils with best possible resistance to formation of
sludge, i.e. use only tested and approved engine oils (from
Sheet 229.1 or 229.3). The best protection is afforded by the
engine oils on Sheet 229.3, which fulfill more stringent
specifications with regard to preventing sludge and deposits
(see Sheet 221.0, page 11). These oils have a distinctly better
anti-sludge characteristic than other engine oils.
D
Sludging after adding a fuel or engine oil special additive.
Do not use fuel or engine oil special additives. More information
hereto is available on Sheet 219.0 of the Specifications for
Service products. Reference to customer not to use special
additives.
D
Engine oil change not performed according to ASSYST
specifications. At driven distances
exceeding > approx. 3000 km, engine oil sludging may occur.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Comply with engine oil and filter change as under ASSYST
specifications. Observe remaining distance.
D
Fuel grade lies outside standard (regionally contingent). If
contaminated, deficient fuel is used, then engine oil sludging
may occur even where approved engine oil is used.
Operation with fuel, e.g. as under DIN EN 228. Clarify refueling
behavior of customer. If engine operation regional, is
temporarily possible with deficient oil only, then the startup
distance has to be individually reduced, i.e. the oil change
temporarily performed at an interval of, e.g. 10,000 km.
D
Radiator antifreeze penetration into engine oil, e.g. through an
internal engine leak (cylinder head gasket, casting porosity).
The engine oil sludges within a short period. The crankcase
ventilation clogs up and stops functioning. Condensation
sludging clogs up the oil separator cells
(engine 166).
Rectify coolant leakage. Clean all sludged engine parts, in
particular the crankcase ventilation parts. If the occurrence
repeats, and casting porosity is suspected, e.g. replace
crankcase.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Copyright DaimlerChrysler AG 20.05.2006 CD-Ausgabe G/10/04 . This WIS print-out will not be recorde
d by Modification services.
Page 1
Page 3843 of 4133
The opening angle of the throttle valve will only be determined by the accelerator pedal specification when no
limiting functions are active.
The accelerator pedal position is detected by the set value potentiometer (B37r1) or Hall sensor in the pedal
value sensor (B37) and information is released to the ME control unit (N3/10). In this way, the ME-SFI control
unit determines the position of the throttle valve and actuates the throttle valve motor (M16/1 m1).
The actual value potentiometer in the actuator (M16/1r1) signals the throttle valve position back to the ME-SFI
control unit.
The second potentiometer in the actuator (M16/1 r2) and the second signal from the pedal value sensor
(potentiometer or Hall sensor) supplies a reference value for the plausibility check. In addition, the system
switches over to the second potentiometer or the Hall sensor if the first potentiometer or Hall sensor fails
(emergency mode).
Adaptive accelerator pedal (model 203, 209, 211, 215, 220, 230):
The engine control unit recognizes how the accelerator pedal is being actuated and switches between
characteristic curves. Eighty percent of the engine load is released for a pedal travel of about 50 % for a sporty
driver and about 40 % for a quiet driver. There is no further difference felt above a pedal travel of about 90 %.
If, for example, the characteristic curve for a quiet driver is active after a long drive on the motorway then the
accelerator pedal must be pressed down unusually hard to obtain a higher acceleration level.
Kickdown switch (S16/6)
The kickdown switch was no longer used from 9/01. Recognition of full load is now achieved over the signal
from the pedal value sensor. The pressure point on the accelerator pedal before achieving the full load position
remains.
Motor electronics control unit, location/task/
design/functionexcept M111 EVOGF07.61-P-
5000F
M111 EVOGF07.61-P-
5000GS
Electronic accelerator/cruise control/idle speed
control actuator location/task/design/functionexcept M111 EVOGF30.22-P-
4010F
Throttle valve actuator, location/task/design/
functionM111 EVOGF30.22-P-
4101GS
Pedal value sensor, location/task/design/
function GF30.20-P-
4011L
ME-SFI idle speed control function
Except engine 120 and engine 111 EVOGF30.22-P-
0003E
M111 EVOGF30.22-P-
0003GS
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 ACCESSORIES & BODY CAB Throttle Control, Speed Control Systems - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:36:27 PMPage 3 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3854 of 4133

ENGINE 113.940 /941 /942 /943 /948 /960 /961 /963 /965 /966 /967 /968 /969
ENGINE 119.980 /981 /982 /985
ENGINE 137.970
Task
To allow safe further driving depending on the fault which has arisen in the electronic accelerator pedal system.
Pedal value sensor emergency mode
If the sensor in the pedal value sensor (B37) fails, the system will switch over to the second sensor. The throttle
valve opening is limited to approx. 60%. There is also dynamic limitation of the throttle valve's opening speed
where the throttle valve opening is delayed (the indicator lamp EPC does not light up).
If the plausibility check delivers a negative result or both sensors are defect only the idling speed will be
regulated (the indicator lamp EPC lights up).
Actuator for the throttle valve - emergency running, electrical
If a potentiometer in the actuator for the throttle valve breaks down the system switches-over to the second
intact potentiometer. The air flow mass serves as a second parameter for comparative purposes. Following a
plausibility check, the throttle valve opening is limited to approx. 60% in line with engine speed and load (EPC
indicator lamp does not come on).
If the plausibility check is negative or if both potentiometers are faulty, the throttle valve adopts a mechanical
emergency running position which is fixed by the spring capsule in the actuator (EPC indicator lamp comes on).
Actuator for the throttle valve - emergency running, mechanical emergency running stop
If the actuator motor is defect or there are other faults present the power supply to the actuator will be shut off.
The throttle valve then lies on the mechanical stop (spring box) so the throttle valve opening remains at a
constant 10-12°. At no engine load (idling) engine speed is regulated to about 900 rpm by shutting off or
activating the cylinders at the fuel side.
When driving, engine speed is controlled, in line with the engine load, by switching the cylinders off and on at
the fuel side. The maximum engine speed is about 1800 rpm. which is limited by the mechanical stop (the
indicator lamp EPC lights up).
Safety fuel shutoff
If a mechanical fault exists in the actuator, the safety fuel shutoff is activated.
Here the fuel injection valves are shut off for engine speeds < 1400 rpm and actuated again at speeds < 1200
rpm (the indicator lamp EPC li
ghts up).
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 ACCESSORIES & BODY CAB Throttle Control, Speed Control Systems - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:36:27 PMPage 14 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3861 of 4133
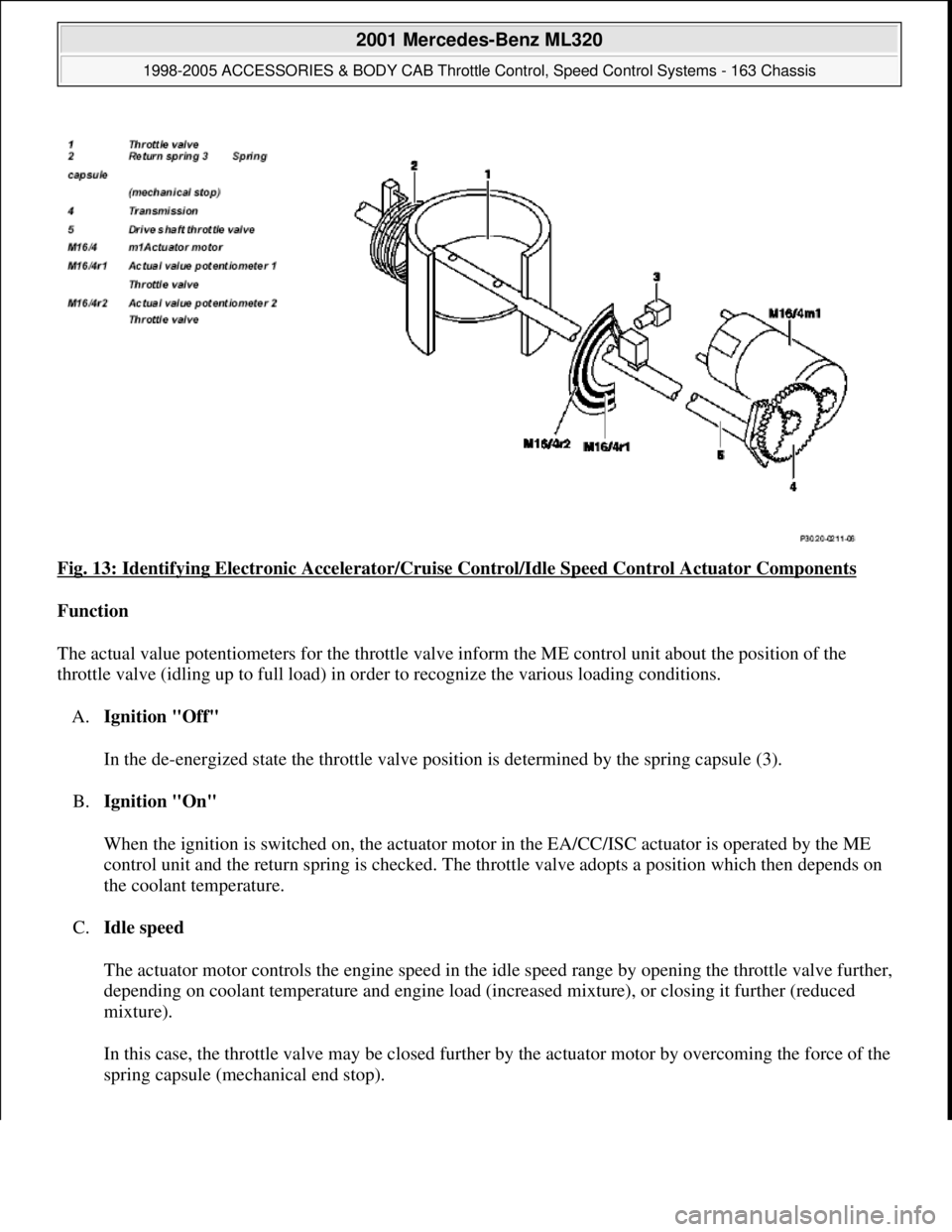
Fig. 13: Identifying Electronic Accelerator/Cruise Control/Idle Speed Control Actuator Components
Function
The actual value potentiometers for the throttle valve inform the ME control unit about the position of the
throttle valve (idling up to full load) in order to recognize the various loading conditions.
A.Ignition "Off"
In the de-energized state the throttle valve position is determined by the spring capsule (3).
B.Ignition "On"
When the ignition is switched on, the actuator motor in the EA/CC/ISC actuator is operated by the ME
control unit and the return spring is checked. The throttle valve adopts a position which then depends on
the coolant temperature.
C.Idle speed
The actuator motor controls the engine speed in the idle speed range by opening the throttle valve further,
depending on coolant temperature and engine load (increased mixture), or closing it further (reduced
mixture).
In this case, the throttle valve may be closed further by the actuator motor by overcoming the force of the
sprin
g capsule (mechanical end stop).
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 ACCESSORIES & BODY CAB Throttle Control, Speed Control Systems - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:36:27 PMPage 21 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.