1997 MERCEDES-BENZ ML320 air condition
[x] Cancel search: air conditionPage 3148 of 4133

of repairs or for service fills.
2.6 Transmission oils, sheet 235.11
The fully synthetic gear oils are approved for all MB commercial vehicle manual transmissions installed
in MB vehicles with steel/molybdenum synchronization with and without oil coolers, in MB transfer
cases with and without oil coolers as well as in ZF manual transmissions with steel/molybdenum
synchronization.
Due to the favorable viscosity/temperature characteristics, a good cold-shifting response and, due to the
composition of the transmission oil, a good thermal/oxidative stability of the oil at high transmission oil
temperatures as well as a fuel savings potential depending on the operating conditions can be expected.
2.7 Engine oils, sheet 235.12
The engine oils must be used with a common oil system for transmissions used in tropical countries, and
for manual transmissions with a torque converter and clutch unit. These engine oils display the very high
seizure resistance required for use in transmissions. The oils need not comply with the engine oil pour
point specifications in these Specifications for Operating Fluids.
2.8 Engine oils, sheet 235.27
Commercial vehicle retarder oils: the products listed in the tables apply to commercial vehicle
transmissions: see MB Specifications for Operating Fluids 231.2. The engine oils are suitable for retarder
use. The oils need not comply with the engine Specifications for Operating Fluids 231.2. The engine oils
are suitable for retarder use. The oils need not comply with the engine oil pour point specifications in
these Specifications for Operating Fluids.
3. Automatic transmission fluids (ATF), sheet 236.1/.2/.3/.5/.6/.7/.8/.81/.9/.10/.11/.12/.13/.20
ATFs are comparatively low-viscosity gear oils which, due to their universal use potential as a gear oil or
a hydraulic fluid, can cover a wide spectrum of applications. The ATFs in the individual their universal
use potential as a gear oil or a hydraulic fluid, can cover a wide spectrum of applications. The ATFs in the
individual sheets differ essentially due to their inherent friction coefficients in tribological contact. This
property predestines these oils as function fluids for automatic transmissions whose ease of shifting,
among other things, is considerably affected by the friction coefficient of the ATF. Therefore, to achieve
optimum performance of the vehicles, only the ATF quality (sheet no.) assigned to the major assembly is
to be used. The individual ATF qualities will be described in greater detail below.
3.1 Automatic transmission fluids (ATF), sheet 236.1
The approved ATF correspond to the currently no longer valid GM specification Dexron II-D or the
currently valid GM specification Dexron III.
The field of application of these ATF includes MB automatic transmissions without controlled torque
converter lockup clutch in passenger cars, ZF Ecomat transmissions, Allison automatic transmissions,
Voith-Diwa transmissions and MB automatic transmissions in commercial vehicles and busses except
2004 Mercedes-Benz ML350
1998-2005 GENINFO Overall vehicle - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:47:56 PMPage 503 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3149 of 4133

W4B035.
3.2 Automatic transmission fluids (ATF), sheet 236.2 , for MB passenger car and commercial vehicle
transmissions with non-ferrous metal synchronization except front-wheel drive manual transmissions of
the A-Class (see Section 2.5, Sheet 235.10), Allison transmission, commercial vehicle power steering,
hydraulic fan drive.
The ATF must meet all the requirements of the transmissions with nonferrous metal synchronization.
These include, in particular, wear protection against pitting and seizure as well as a defined friction
coefficient of the synchronizer components that is as constant as possible over the entire service life. As a
hydraulic fluid, the ATF is used for hydraulic power transmission and for protecting the hydraulic
assemblies from wear. The seal compatibility must be ensured with all elastomer materials used.
If the approved ATF are not available, engine oils according to sheet 227.0, SAE 10W or, depending on
the outside temperature, 20W-20 can be used in the above-mentioned synchronized manual transmissions
as a makeshift measure (queries should be directed to the Abt. Betriebstoffe EP/QWB (EP/QWB
Operating Fluids Dept.).
The approved ATF according to Sheet 236.2 correspond to the currently no longer valid GM specification
Type A Suffix A. The kinematic fresh oil viscosity at 100°C must be at least 7.0 mm
2 /s, after shearing
(as per CEC- TLPG 7) at least 6.0 mm
2 s.
3.3 Steering gear oil, sheet 236.3 , for all commercial vehicle steering systems, except vans T0 and T1N,
power steering systems for passenger cars, except
S-Class W220, power pack of the A-Class, and cross-country vehicles, manual steering L 075 Z for
passenger cars and manual steering in cross-country vehicle.
In the S class W220, in the Power-Pack of the A class as well as in the Transporters T0 and T1N as
of/below outside temperatures of 25°C the hydraulic fluids according to sheet 345.0 must be used.
3.4 Automatic transmission fluids (ATF) and/or engine oils, sheet 236.5 , for Allison transmission HAT
700
The oils listed here correspond to the Allison-C4 specification. Allison automatic transmissions in makes
AT 500, MT 600, S1000, S2000, World Transmission MD 3000, HD 4000 must only be filled with the
oils specified in Sheet 236.9 or TES 295.
If prior to starting the vehicle the gear oil temperature is below the critical temperature for the oil used,
then either the gear oil should be prewarmed or the transmission should be warmed up while in neutral.
Automatic transmissions in the model series CLBT 750 must only ever be filled with oils according to
Sheet 236.5. Under extreme operating conditions or for off-road use and/or with outside temperatures
higher than 30°C an engine oil of SAE grade 30 and/or 15W-40 from Sheet 236.5 should be used.
Depending on the outside temperature during vehicle operation, the oils used must be selected from the
followin
g diagram according to their SAE viscosity class and/or Dexron specification:
2004 Mercedes-Benz ML350
1998-2005 GENINFO Overall vehicle - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:47:56 PMPage 504 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3169 of 4133

provide reliable cooling system protection. In special cases (commercial-vehicle engines, no antifreeze
specification) coolant additives can be used that are primarily corrosion protection additives. In this case
item 2.3 is valid.
As an exception, if neither anticorrosion/antifreeze agent conforming to Sheet 325.0 nor coolant additives
without addition of antifreeze conforming to Sheet 312.0 are available, proceed according to point 2.4
(exception: OM 500 and OM 900). The systems described under items 2.2/2.3/2.4 are not compatible
with each other. It is recommended to mix the entire coolant quantity outside the engine.
2.1 Anticorrosion/antifreeze agent for passenger-car engines
Alongside the correct constitution of the cooling water (point 1.2.2), care must be taken to ensure that
only anticorrosion/antifreeze agents as approved for all engines in accordance with Sheet 325.0 are used.
These products serve to guarantee that, in particular, an effective protection against corrosion is provided
for all light-alloy parts in the cooling system and they are also specified for all passenger-car engines.
In order to ensure that the protection against corrosion is effective, the anticorrosion/antifreeze agent must
remain in the cooling system throughout the year - including when in tropical climates - and regardless of
the operating conditions. In countries with high outside temperatures this is also important in terms of
raising the boiling point.
In the event that these regulations are not observed the cooling system may suffer from damage by
corrosion. As a consequence of corrosion deposits there is a danger that ducts in the radiators (engine
overheating) and heat exchangers (poor heat output) get plugged up thus causing damage to the engine.
As a result of the optimizations we have carried out on the system of engine/coolant/cooling system, in
the majority of our newer passenger cars, a replacement of coolant is not necessary until reaching 15
operating years or 250,000 km (whichever comes first). This may not apply to some models; in these
cases the maintenance booklet will stipulate another regulation.
2.2 Anticorrosion/antifreeze agent for commercial-vehicle engines (normal case)
(not: BR 600, BR 100 and BR 200)
The coolant in commercial-vehicle engines is made up of both water and anticorrosion/antifreeze agent
(refer to item 1.1.1) and as such offers ideal protection against corrosion and cavitation.
All the approved products on the Sheets 325.2, 325.3 or 325.0 which are part of the Specifications for
Operating Fluids can be used to select an anticorrosion/antifreeze agent. However, it should be noted that
passenger vehicle engines built into commercial vehicles must be filled like passenger vehicles (e.g. OM
601 in T1), i.e. a product conforming to Sheet 325.0 and 326.0 must be used.
Products that are not listed in Sheets 325.0 and 326.0, or 325.2 and 326.2, or 325.3 and 326.3 are not
approved and are therefore not to be used under any circumstances.
Anticorrosion/antifreeze agents or coolants conforming to Sheet 325.3 or 326.3 may be used for
longer than other products due to their composition. The change interval is set at 5 years (refer to
2004 Mercedes-Benz ML350
1998-2005 GENINFO Overall vehicle - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:47:57 PMPage 524 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3171 of 4133

the regulation filling of 50 vol.% (-37°C). When topping up (after coolant loss), an anticorrosion/
antifreeze agent content in the coolant of at least 50 vol. % (antifreeze protection down to -37°C) must be
ensured, or the concentration regulations according to point 2.3/2.4.1 must be observed. In closing an
example is given in Overview Section 5.
Non observance a observance of these regulations or the use of non-approved products will
result in serious damage.
The corrosion inhibitors diminish during operation and lose their protective capability. Coolant that is too
old, and has lost its important inhibitors and anti-aging additives, becomes strongly corrosive. The
coolant additives as under Sheets 311.0 and 312.0 will also age. This causes a deterioration in the level of
protection capability, and with regard to coolant refining agents this will also cause the emulsion to break
down.
For this reason it is important to replace the coolant, in order to ensure that its corrosion protection
capability is retained. If necessary the cooling system should be thoroughly cleansed before refilling with
the new coolant. A sufficient level of heat dissipation will only be given if the cooler surfaces are clean.
The maximum permissible period of usage for coolant is cited in Overview Section 5.
The use of approved operatin
g fluids, which naturally include the anticorrosion/antifreeze agents, is
a well-known constituent of the warranty conditions.
4.Disposal of coolants
The coolants are biologically-degradable material.
All statutory regulations or waste water regulations in each individual country with regard to the disposal
of used coolant must be observed.
It is recommended to have the possibilities available for disposing of materials explained by the local
responsible water authorities.
Currently in Germany methods are being compiled for the purification of used coolant. The separate
collection of all used operating fluids is highly recommended.
However, as a consequence of the complex tasks asked of a modern coolant, it is on no account advisable
to use an improperly "recycled" coolant, which has only undergone a mechanical pre-purification process
5.Overview
Which coolant additive, what change interval for which engines?
Passenger cars engines
Sheet No.Engine seriesChange interval
years/km
M100/M200OM600
2004 Mercedes-Benz ML350
1998-2005 GENINFO Overall vehicle - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:47:57 PMPage 526 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3175 of 4133

GENERAL BRAKE FLUID - BB00.40-P-0330-01A
These specifications are valid for the Mercedes-Benz and smart brands.
General
The brake fluid in the brake system and in the hydraulic clutch operating system fulfills hydraulic tasks. Due to
the high heat build-up during braking, these tasks can only be fulfilled by brake fluids which comply with all of
today's technical requirements in terms of their various properties (viscosity-temperature-characteristic, boiling
point, corrosion protection, oxidation resistance, etc.).
The most important properties which a brake fluid must exhibit are:
High boiling point, to ensure that the brake fluid does not form vapor locks at high temperatures. Vapor
locks reduce the operating pressure and thus the braking effect and may ultimately lead to brake failure.
The boiling point should remain as constant as possible throughout the duration of use of the coolant and
not drop under varying atmospheric influences or operating conditions (pressure, temperature), i.e. the
"wet boiling point" should be as high as possible.
Low compressibility, in particular at high temperatures.
The low-temperature characteristic of the fluid - even when at 40°C - must permit operation, i.e.
primarily, the viscosity must not become too high in the cold.
Compatibility with the materials used in the brake units and clutch operating systems, e.g. the rubber
boots or any other seal materials (elastomers) included in the brake components may only swell to a
controlled extent, any shrinkage must be avoided.
Sufficient corrosion protection for all metals present in the brake system.
The brake fluids released for use in MB vehicle models are listed on Sheet 331.0. These brake fluids not only
comply with our requirements, but also those of the US safety specifications FMVSS 116, DOT 4. The released
"DOT 4 plus" brake fluids (internal designation) are more advanced DOT 4 brake fluids with higher wet boiling
point, standard change interval: 2 years. In order to be able to comply with this useful period without any
problem, we strongly advise the use of released products as per Sheet 331.0, during the warranty phase this is a
precondition for any acceptance of customer claims.
The brake fluid listed on Sheet 331.1 "DOT 4 Type 200" is released for special applications in the UNIMOG
range with more stringent thermal requirements. For this type of use, a brake fluid change interval of 1 year
must be adhered to.
Handling brake fluid
Brake fluid based on polyhydric alcohols in oligomer or polymer form and/or their
Esters are hygroscopic and thus absorbs moisture from the air. Water, however, reduces the boiling point of the
brake fluid, whereby the danger of vapor lock formation is present. Therefore it should be noted that brake fluid
is always stored in sealed vessels. Brake fluid that has been stored unsealed can absorb so much moisture in a
few hours that it is rendered unusable.
2004 Mercedes-Benz ML350
1998-2005 GENINFO Overall vehicle - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:47:57 PMPage 530 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3204 of 4133
3
Remove engine hood hinge on the front
passenger side
AR88.40-P-3060GH
*BR00.45-Z-1004-01A
Danger!
Risk of explosion
from explosive gas.
Risk
of poisoning and caustic burns from
swallowing battery electrolyte.
Risk of injury
through burns to skin and eyes from battery
acid or when handling damaged lead-acid
batteries
No fire, sparks, naked flames or smoking.
Wear protective gloves, acid-resistant
clothing and safety glasses. Pour battery
electrolyte only into suitable and appropriately
marked containers.
AS54.10-Z-0001-01A
4
Remove battery
AR54.10-P-0005GH
5
Remove air conditioning blower motor
AR83.30-P-5560GH
6
Print out template (6) and adapt the size to
the correct dimensions (a, b)Determine ACTUAL dimension (a) from the
drawing.
Divide the SPECIFIED dimension (a) by the
determined ACTUAL dimension (a) and copy
the template to the original size with the
corresponding factor.
Check dimensions for both axles.
7
Cut out template
8
Cut out holes (7, 8) for engine hood hinge
studs
9
Position template in the engine hood hinge
support using the stud holes
The template is drawn for the left side.
Turn over to obtain the right side.
10
Center the engine hood hinge support on the
template using the markings (9, 10, 11)
11
Remove template
12
Drill a hole at each center punch mark (3, 4, 5)
Only drill through the 2 upper panels. Do
not drill through the reinforcement panel (3rd
panel).
*201589005100
13
Cover windshield, paint surface and adjacent
components adequately in order to avoid
damage due to welding work
Cover apertures in the body in order to
prevent flying sparks: the foam in the
instrument panel burns easily.
c
General information on repairs to body
AH60.00-N-0001-01A
Danger!
The high voltage used for arc welding
presents a lethal hazard
.
Explosion hazard
when welding in area of materials easily
inflammable.
Injury hazard
from welding
spatter and UV-light while welding.
Risk of
poisoning
when inhaling welding vapors.
Use insulating mats. Wear protective clothing,
safety glasses, and protective mask.
Remove
highly inflammable materials from the danger
zone. Use air extractor.
AS00.00-Z-0007-01A
14
Plug weld each hole
*WE58.40-Z-1005-02A
15
Plug welds should be flat and ground smooth
16
Remove covers and clean the repair area
17
Prime untreated points in the area of the
engine hood hinge support
18
Prime the underside of the reinforcement
panel of the engine hood hinge
Access to underside of engine hood hinge
support through the recess for the wiper motor.
19
Spray the underside of the reinforcement
panel of the engine hood hinge support with
wax preservative
Access to underside of engine hood hinge
support through the recess for the wiper motor.
20
Install in the reverse order
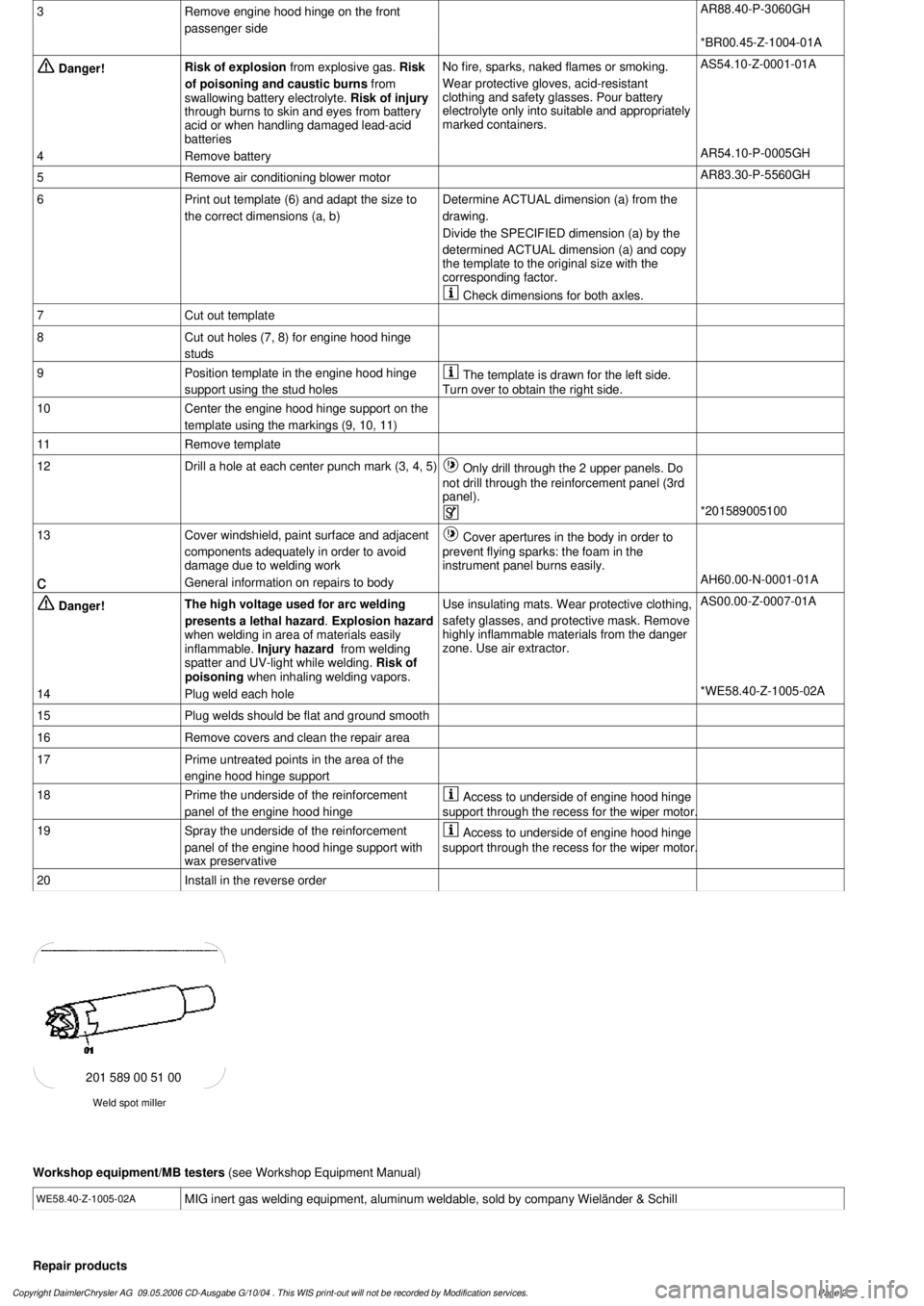
Weld spot miller
201 589 00 51 00
Workshop equipment/MB testers
(see Workshop Equipment Manual)
WE58.40-Z-1005-02A
MIG inert gas welding equipment, aluminum weldable, sold by company Wieländer & Schill
Repair products
Copyright DaimlerChrysler AG 09.05.2006 CD-Ausgabe G/10/04 . This WIS print-out will not be recorde
d by Modification services.
Page 2
Page 3216 of 4133

Fig. 2: Locating Climate Control Components
Courtesy of MERCEDES-BENZ OF NORTH AMERICA
FRESH/RECIRCULATION SWITCH
Fresh/recirculation switch controls voltage signal to fresh air recirculation door motor. See Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 .
With switch indicator light on, air will recirculate. With switch indicator light off, air will enter from outside of
vehicle.
A/C CONTROL MODULE
The A/C control module (A/C amplifier) is the control unit for the A/C system. See Fig. 2 . The module
receives inputs from various sensors and processes the information to control various outputs for the A/C
system for optimal control.
The A/C control module inputs are as follows:
A/C Switch
In-Vehicle Air Temperature Sensor
Temperature Selector Knob
Blower Motor Knob
Evaporator Temperature Sensor
Air Mix Damper Door Position Sensor
The A/C control module output functions are as follows:
Air Mix Damper Door Motor
All Activity Module
Fresh/Recirculation Door Motor
ALL ACTIVITY MODULE
All Activity Module (AAM) receives inputs to determine if specified conditions have been met to allow
operation of A/C-heater system. If conditions are met, the AAM will send signals to the A/C compressor,
condenser fans relay and the blower motor relay to command or enable operation.
IN-VEHICLE TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The in-vehicle temperature sensor is a negative temperature coefficient resistor. Sensor sends signals to the A/C
control module to maintain in-vehicle temperature. Sensor is located on the center panel of the instrument
cluster.
DUST FILTER
A dust filter provides filtering of air entering or recirculating in the passenger's compartment. The dust filter is
mounted between blower motor and evaporator, below passen
ger's side of instrument panel, to left of blower
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
2000-01 MANUAL A/C-HEATER SYSTEMS ML 320, ML 430 & ML 55
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:25:10 PMPage 5 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3220 of 4133

FUNCTIONAL TEST PREPARATION
1. Check condition of fuses F16, F41, F43 and F44. See WIRING DIAGRAMS . Repair and/or replace
fuses and necessary.
2. Turn ignition on. Locate in-vehicle temperature sensor aspirator blower vent grille above anti-theft
indicator light. Place a half-inch square of tissue paper over aspirator blower vent grille. If paper stays on
vent grille, go to next step. If paper does not stay on vent grille, correct insufficient aspirator blower
ventilation.
3. Put shift lever in "P" and engage parking brake. Run engine at idle until it reaches normal operating
temperature, about 176°F (80°C). Ensure ambient (outside) temperature is greater than 58°F (15°C).
4. Manually open center and side air outlets. Ensure recirculation button is not depressed. Set blower speed
knob to position No. 1.
FUNCTION TEST
Defrost Mode
To check operation in defrost mode, set temperature selector knob to White range (vertical). Set mode control
knob to 12-o'clock position (vertical). Ensure A/C button indicator is illuminated. Air will vent from defrost and
center outlets and A/C compressor will engage. If operation is not as specified, perform the following in order:
Check voltage supply circuit Z50/2 between No. 16 fuse (15-amp) and connected components. See
VOLTAGE SUPPLY CIRCUIT Z50/2
under ELECTRICAL TESTS.
Check ground circuit. See GROUND CIRCUIT Z50/4 under ELECTRICAL TESTS.
Check in-vehicle temperature sensor signal voltage. See IN-VEHICLE TEMPERATURE SENSOR
under ELECTRICAL TESTS.
Check in-vehicle temperature sensor signal resistance. See IN-VEHICLE TEMPERATURE SENSOR
under ELECTRICAL TESTS.
Check icing protection temperature sensor signal voltage. See ICING PROTECTION
TEMPERATURE SENSOR under ELECTRICAL TESTS.
Check icing protection temperature sensor resistance. See ICING PROTECTION TEMPERATURE
SENSOR under ELECTRICAL TESTS.
Check activation voltage during temperature reduction. See ACTIVATION VOLTAGE
TEMPERATURE under ELECTRICAL TESTS.
Check activation voltage during temperature increase. See ACTIVATION VOLTAGE
TEMPERATURE under ELECTRICAL TESTS.
Check blend air flap actuator motor operation voltage. See BLEND AIR FLAP ACTUATOR MOTOR
under ELECTRICAL TESTS.
Check blend air flap actuator motor resistance. See BLEND AIR FLAP ACTUATOR MOTOR under
ELECTRICAL TESTS.
Check A/C button activation. See A/C BUTTON under ELECTRICAL TESTS.
Check A/C pressure switch. See A/C REFRIGERANT PRESSURE SWITCH under ELECTRICAL NOTE: Function test steps must be performed in order given.
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
2000-01 MANUAL A/C-HEATER SYSTEMS ML 320, ML 430 & ML 55
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:25:10 PMPage 9 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.