Page 363 of 1600
BRAKES 5-35
INSPECTION AND REPAIR
Make necessary correction or parts replacement if wear damage or any other abnormal conditions are found
through inspection.
Rotor
Caliper body
Cylinder bore
Piston
Support bracket
Lock bolt
Guide pin
Visual Check
Inspect the following parts for wear, bending, distortion,
cracking, corrosion, or other abnormal conditions.
Rotor
Thickness (t) mm(in)
Standard Minimum
thickness after
refinishingReplacement
thickness
(Discard)
22.0(0.866) 20.97(0.826) 20.6(0.811)
Run out
Limit mm(in)
0.13 (0.005)
Before inspection, adjust the wheel bearing correctly.
Using a dial gauge, measure the run out at the center of disc
pad contact surface.
Parallelism (Total circumferential thickness variation)
Limit mm(in)
0.15 (0.0006)
Contact surface must be within 0.015 mm at the circumference
of 203 mm dia. Circle.
Page 367 of 1600
BRAKES 5-39
REAR DRUM BRAKE ASSEMBLY
DISASSEMBLY
First, disassemble the brake drum. Then disassemble the rear brake assembly.
Refer to the “REAR AXLE” section for the brake drum disassembly procedure.
MAJOR COMPONENTS
Disassembly Steps
1. Brake line
2. Holding spring and cups
3. Return spring ; lower
4. Return Spring ; upper
(shoe to adjust lever)
5. Return spring ; upper
(shoe to shoe)
6. Shoe assembly (primary)7. Shoe assembly with lever
8. Retainer with pin
9. Washer ; wave
10. Lever ; auto adjust
11. Shoe assembly (secondary)
12. Adjuster assembly
13. Wheel cylinder assembly
MINOR COMPONENTS
Disassembly Steps
Wheel Cylinder Assembly (13)
14. Boot ; wheel cylinder
15. Piston assembly
16. Cup ; piston17. Return spring ; piston
18. Bleeder ; wheel cylinder
Page 369 of 1600
BRAKES 5-41
Free length
mm(in.)Set length
mm(in.)Set load
kg(lbs.)
Return spring :
upper
(adjust lever)124.9
(4.917)134.9
(5.311)70.7
(15.4
1.6)
Shoe return
spring : upper112.4
(4.425)121.5
(4.783)20.2
(4.4
0.4)
Shoe return
spring : lower167.2
(6.583)190.2
(7.488)28.02.8
(61.7
6.4)
Clean wheel Cylinder Parts
Always use clean brake fluid to clean wheel cylinder parts.
Note:
Do not use mineral-vase cleaning solvents such as
gasoline, kerosene, acetone, paint thinner, or carbon
tetrachloride.
Clearance Between the Wheel Cylinder
and the Piston
mm(in)
Standard Limit
0.02 - 0.1(0.001 - 0.004) 0.15(0.006)
Piston Cups
Inspect the piston cups for wear, distortion, fatigue, fatigue or
other abnormal conditions.
Measuring the Brake Drum
mm(in)
Standard Limit
Inside diameter 254(10.000) 255.5(10.059)
Run out 0.05(0.002) 0.15(0.006)
Inside diameter 295(11.614) 296.5(11.673)
Run out 0.05(0.02) 0.15(0.006)TFS
TFR
Page 370 of 1600
5-42 BRAKES
REASSEMBLY
MINOR COMPONENTS
Reassembly Steps
Wheel cylinder Assembly (7)
1. Bode ; wheel cylinder
2. Return spring ; piston
3. Cup ; piston4. Piston assembly
5. Boot ; wheel cylinder
6. Bleeder ; wheel cylinder
MAJOR COMPONENTS
Reassembly Steps
7. Wheel cylinder assembly
8. Adjuster assembly
9. Shoe assembly (secondary)
10. Lever ; auto adjuster
11. Washer ; wave
12. Retainer with pin
13. Shoe assembly (primary)14. Return spring ; upper
(shoe to shoe)
15. Return spring ; upper
(shoe to adjust lever)
16. Return spring ; lower
17. Holding spring and cups
18. Brake line
Page 371 of 1600
BRAKES 5-43
Important Operations
1. Bode ; Wheel Cylinder
Lubricate the cylinder bore with clean rubber grease.
4. Piston Assembly
Install new piston cups on each piston so that the flared end of
the cups are turned to the inboard side of the pistons.
Attach the return spring and the boot to the piston.
Apply DELCO silicone lube No.5459912 (or equivalent) to the
piston and the inner face of the boots.
6. Bleeder ; Wheel Cylinder
Torque N
m(kgfm/Ibft)
6.9 - 11.8 (0.7 - 1.2 / 5.1 - 8.7)
7. Wheel Cylinder Assembly
Torque N
m(kgfm/Ibft)
11 - 15 (1.1 - 1.5 / 8 - 11)
Page 394 of 1600

5-66 BRAKES
Important Operations - Removal
Preparation
Raise vehicle to the working level.
Support the axle assembly with the proper jack and chassis
stands.
Remove the tire and wheel.
Remove the brake drum.
1. Lock Nut
2. Adjusting Nut
3. Bolt
4. Retainer
Loosen lock nut and adjusting nut, then disconnect rear
cable from the equalizer.
Remove bolt and retainer.
Important Operations - Installation
10.Hand Brake Rear Cable
Apply grease (BESCO L-2 or equivalent) to the
circumference of the pin and joint.
Apply grease (BESCO L-2 or equivalent) to the equalizer
joint portion.
9. Clip and Bolt; Leaf Spring
8. Clip and Bolt; Spring Eye
7. Clip and Bolt; Side Member
6. Clip and Bolt; Side Member
5. Clip and Bolt; Crossmember
Torque N
m (kgfm/lbft)
6 (0.6 / 4.3)
4. Retainer
3. Bolt
Torque N
m(kgfm/lbft)
16 (0.6 / 4.3)
2. Adjusting Nut
1. Lock Nut
Apply grease (BESCO L-2 or equivalent) to the front cable
contact portion.
Connect rear cable to the equalizer, then adjust the parking
brake. Refer to "SERVICING".
Tighten lock nut to the specified torque.
Torque N
m(kgfm/lbft)
16 (0.6 / 4.3)
Page 395 of 1600
BRAKES 5-67
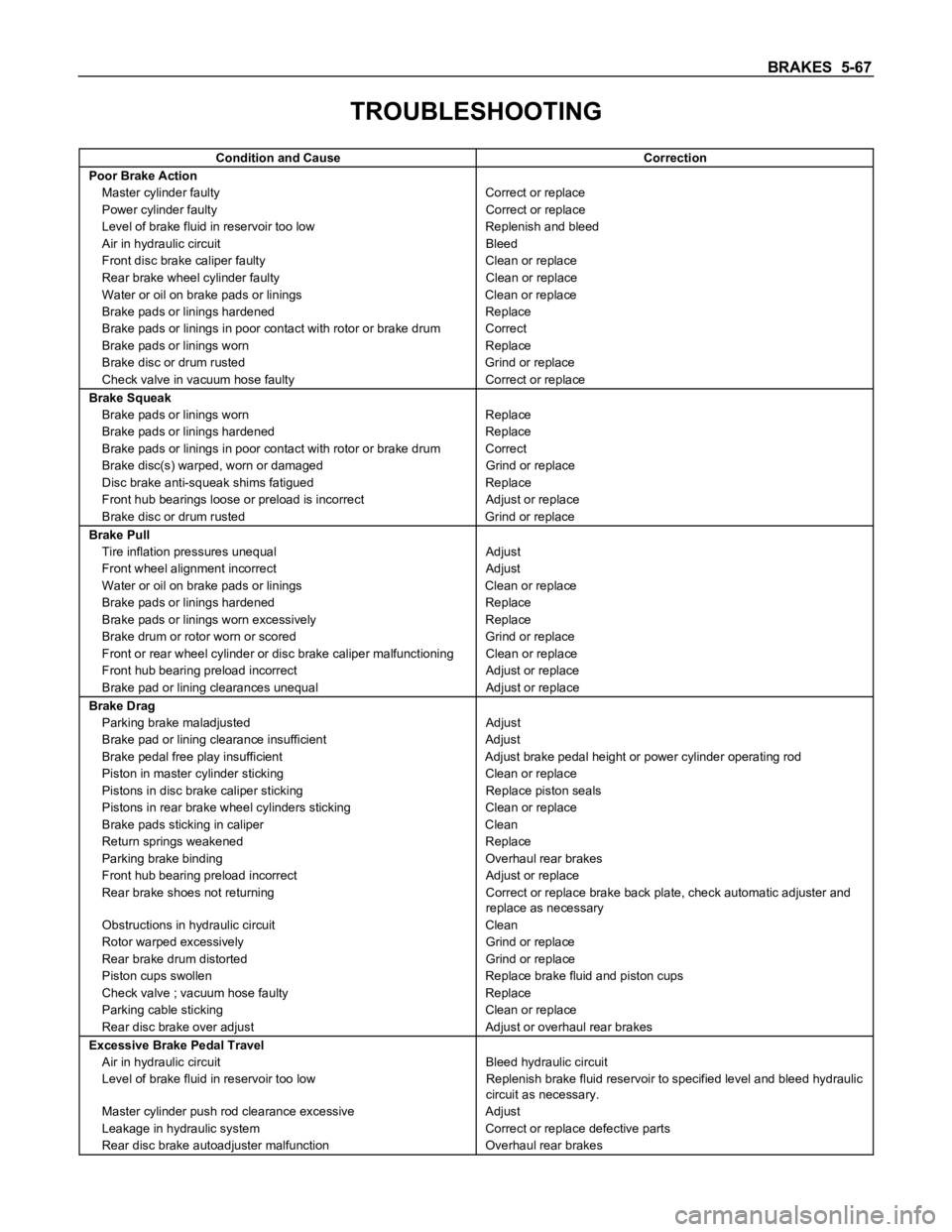
TROUBLESHOOTING
Condition and Cause Correction
Poor Brake Action
Master cylinder faulty Correct or replace
Power cylinder faulty Correct or replace
Level of brake fluid in reservoir too low Replenish and bleed
Air in hydraulic circuit Bleed
Front disc brake caliper faulty Clean or replace
Rear brake wheel cylinder faulty Clean or replace
Water or oil on brake pads or linings Clean or replace
Brake pads or linings hardened Replace
Brake pads or linings in poor contact with rotor or brake drum Correct
Brake pads or linings worn Replace
Brake disc or drum rusted Grind or replace
Check valve in vacuum hose faulty Correct or replace
Brake Squeak
Brake pads or linings worn Replace
Brake pads or linings hardened Replace
Brake pads or linings in poor contact with rotor or brake drum Correct
Brake disc(s) warped, worn or damaged Grind or replace
Disc brake anti-squeak shims fatigued Replace
Front hub bearings loose or preload is incorrect Adjust or replace
Brake disc or drum rusted Grind or replace
Brake Pull
Tire inflation pressures unequal Adjust
Front wheel alignment incorrect Adjust
Water or oil on brake pads or linings Clean or replace
Brake pads or linings hardened Replace
Brake pads or linings worn excessively Replace
Brake drum or rotor worn or scored Grind or replace
Front or rear wheel cylinder or disc brake caliper malfunctioning Clean or replace
Front hub bearing preload incorrect Adjust or replace
Brake pad or lining clearances unequal Adjust or replace
Brake Drag
Parking brake maladjusted Adjust
Brake pad or lining clearance insufficient Adjust
Brake pedal free play insufficient Adjust brake pedal height or power cylinder operating rod
Piston in master cylinder sticking Clean or replace
Pistons in disc brake caliper sticking Replace piston seals
Pistons in rear brake wheel cylinders sticking Clean or replace
Brake pads sticking in caliper Clean
Return springs weakened Replace
Parking brake binding Overhaul rear brakes
Front hub bearing preload incorrect Adjust or replace
Rear brake shoes not returning Correct or replace brake back plate, check automatic adjuster and
replace as necessary
Obstructions in hydraulic circuit Clean
Rotor warped excessively Grind or replace
Rear brake drum distorted Grind or replace
Piston cups swollen Replace brake fluid and piston cups
Check valve ; vacuum hose faulty Replace
Parking cable sticking Clean or replace
Rear disc brake over adjust Adjust or overhaul rear brakes
Excessive Brake Pedal Travel
Air in hydraulic circuit Bleed hydraulic circuit
Level of brake fluid in reservoir too low Replenish brake fluid reservoir to specified level and bleed hydraulic
circuit as necessary.
Master cylinder push rod clearance excessive Adjust
Leakage in hydraulic system Correct or replace defective parts
Rear disc brake autoadjuster malfunction Overhaul rear brakes
Page 543 of 1600

CLUTCH 7C-3
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
HYDRAULIC CONTROL TYPE
HEC Engine Series4J Engine Series
6VD1
The clutch assembly consists of the pressure plate, the clutch cover, the diaphragm spring pivot pin and the driven
plate assembly.
The clutch pedal is connected to the shift block through the clutch shaft and the shift fork.
The driven plate assembly is installed between the flywheel and the pressure plate.
Diaphragm spring pressure holds the driven plate against flywheel and the pressure plate to provide the friction
necessary to engage the clutch.
Depressing the clutch pedal moves the shift fork against the shift block.
The shift block forces the release bearing against the diaphragm to overcome the force of the diaphragm spring and
separate the driven plate from the flywheel and pressure plate to disengage the clutch.
Except 6VD1 (3.2L) engine model, the conventional push-type clutch is used.
For 6VD1 (3.2L) engine model, the pull-type clutch is employed. The pull-type clutch is disengaged by pulling the
release lever (release bearing) to disengage the pressure plate.