1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER bulb
[x] Cancel search: bulbPage 491 of 1938

LAMP SERVICE
INDEX
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
HEADLAMP DIMMER SWITCH............. 13
HEADLAMP SWITCH.................... 13
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP
(CHMSL)............................ 16FOG LAMP............................ 14
HEADLAMP LEVELING MOTOR............ 14
HEADLAMP MODULE................... 13
LICENSE PLATE LAMP.................. 15
SIDE REPEATER LAMP.................. 14
TAIL LAMP............................ 15
GENERAL INFORMATION
HEADLAMP SWITCH
Service procedures for the headlamp switch can be
found in Group 8E, Instrument Panel and Gauges.
More information can be found in Group 8W, Wiring
Diagrams.
HEADLAMP DIMMER SWITCH
The headlamp dimmer switch is incorporated into
the multi-function (turn signal) switch. Proper proce-
dures can be found in Group 8J, Turn Signal and
Flashers. More information can be found in Group
8W, Wiring Diagrams.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
HEADLAMP MODULE
REMOVAL
(1) Release hood latch and open hood.
(2) Remove bolt holding headlamp module to radi-
ator closure panel (Fig. 1).
(3) From behind the radiator closure panel, remove
the nuts holding the headlamp module to the radia-
tor closure panel.
(4) Separate headlamp module from radiator clo-
sure panel.
(5) Disengage wire connector from headlamp bulb.
(6) Disengage wire connector from headlamp level-
ing motor.
(7) Disengage wire connector for front turn signal
and citylight lamps.(8) Separate headlamp module from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position headlamp module to vehicle.
(2) Engage wire connector for front turn signal and
citylight lamps.
(3) Engage wire connector to headlamp leveling
motor.
(4) Engage wire connector to headlamp bulb.
(5) Position headlamp module to radiator closure
panel.
(6) Press headlamp module rearward until module
is fully seated onto mounting studs.
(7) Install nuts to hold headlamp module to radia-
tor closure panel.
(8) Verify lamp operation.
Fig. 1 Headlamp Module
NS/GSLAMPS 8L - 13
Page 492 of 1938

HEADLAMP LEVELING MOTOR
REMOVAL
(1) Remove headlamp module from vehicle.
(2) Rotate leveling motor one quarter turn counter-
clockwise.
(3) Pull leveling motor from headlamp housing
(Fig. 2).
NOTE: The headlamp leveling motor arm is
snapped into the lens reflector mechanism very
securely. Use a firm, steady pull to disengage motor
arm from reflector mechanism.
(4) Separate leveling motor from headlamp hous-
ing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position headlamp leveling motor to headlamp
housing.
(2) Insert leveling motor arm into hole in backside
of headlamp housing.
(3) Push headlamp bulb toward top of headlamp
housing (Fig. 3).
(4) Push leveling motor firmly into headlamp
housing until leveling motor arm is fully seated into
reflector mechanism.
(5) Rotate leveling motor one quarter turn clock-
wise.
(6) Install headlamp module to vehicle.
FOG LAMP
REMOVAL
(1) Remove screws holding fog lamp to front
bumper fascia (Fig. 4).
(2) Separate fog lamp from fascia.
(3) Disengage wire connector from body wire har-
ness.
(4) Separate fog lamp from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position fog lamp on vehicle.
(2) Engage wire connector to body wire harness.
(3) Insert fog lamp into bumper fascia.
(4) Install screws to hold fog lamp to front bumper
fascia.
SIDE REPEATER LAMP
REMOVAL
(1) Push side repeater lamp to one side and
release retaining tab (Fig. 5).
(2) Pull side repeater lamp out and disengage bulb
socket from lamp (Fig. 6).
(3) Separate side repeater lamp from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Push side repeater lamp socket into side
repeater lamp.
(2) Position side repeater lamp to hole in fender.
(3) Push side repeater lamp to one side and seat
retaining tab into fender.
Fig. 2 Headlamp Leveling Motor
Fig. 3 Headlamp Leveling Motor Installation
Fig. 4 Fog Lamp
8L - 14 LAMPSNS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 493 of 1938
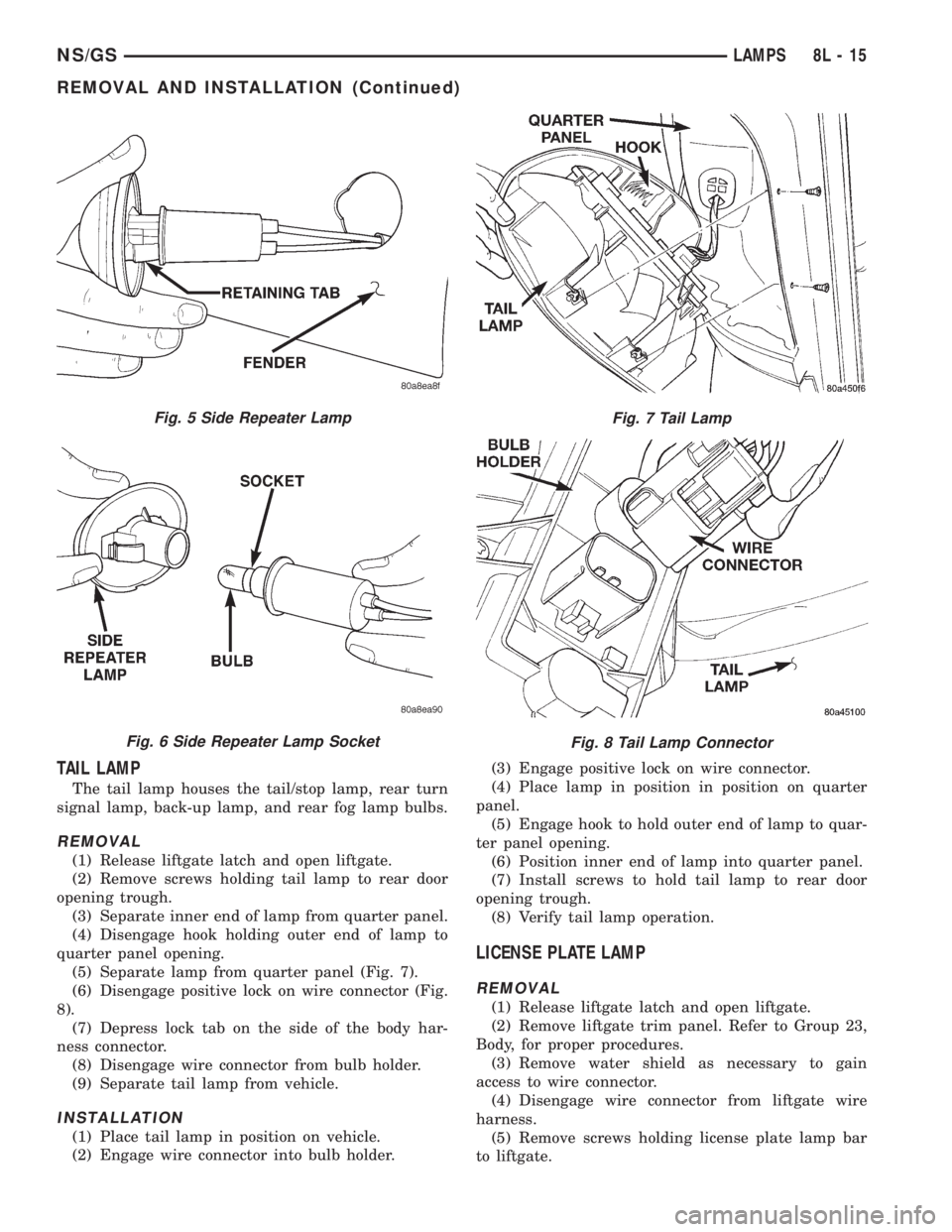
TAIL LAMP
The tail lamp houses the tail/stop lamp, rear turn
signal lamp, back-up lamp, and rear fog lamp bulbs.
REMOVAL
(1) Release liftgate latch and open liftgate.
(2) Remove screws holding tail lamp to rear door
opening trough.
(3) Separate inner end of lamp from quarter panel.
(4) Disengage hook holding outer end of lamp to
quarter panel opening.
(5) Separate lamp from quarter panel (Fig. 7).
(6) Disengage positive lock on wire connector (Fig.
8).
(7) Depress lock tab on the side of the body har-
ness connector.
(8) Disengage wire connector from bulb holder.
(9) Separate tail lamp from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place tail lamp in position on vehicle.
(2) Engage wire connector into bulb holder.(3) Engage positive lock on wire connector.
(4) Place lamp in position in position on quarter
panel.
(5) Engage hook to hold outer end of lamp to quar-
ter panel opening.
(6) Position inner end of lamp into quarter panel.
(7) Install screws to hold tail lamp to rear door
opening trough.
(8) Verify tail lamp operation.
LICENSE PLATE LAMP
REMOVAL
(1) Release liftgate latch and open liftgate.
(2) Remove liftgate trim panel. Refer to Group 23,
Body, for proper procedures.
(3) Remove water shield as necessary to gain
access to wire connector.
(4) Disengage wire connector from liftgate wire
harness.
(5) Remove screws holding license plate lamp bar
to liftgate.
Fig. 5 Side Repeater Lamp
Fig. 6 Side Repeater Lamp Socket
Fig. 7 Tail Lamp
Fig. 8 Tail Lamp Connector
NS/GSLAMPS 8L - 15
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 494 of 1938

(6) Separate license plate lamp bar from liftgate
(Fig. 9).
(7) Separate license plate lamp bar grommet from
vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Route wire connector through hole in liftgate.
(2) Install grommet to wiring harness hole in lift-
gate.
(3) Place license plate lamp bar in position on lift-
gate.
(4) Install screws to hold license plate lamp bar to
liftgate.
(5) Engage wire connector into liftgate wire har-
ness.
(6) Install water shield.
(7) Install liftgate trim panel.(8) Verify license plate lamp operation.
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP (CHMSL)
REMOVAL
(1) Release liftgate latch and open liftgate.
(2) Disengage clip holding CHMSL access cover to
liftgate.
(3) Separate cover from liftgate.
(4) Depress plastic tab holding bulb holder to lamp
housing (Fig. 10).
(5) Separate bulb holder from lamp housing.
(6) Remove screws holding CHMSL to liftgate.
(7) Separate CHMSL from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place CHMSL in position on vehicle.
(2) Install screws to hold CHMSL to liftgate.
(3) Position bulb holder to CHMSL housing.
(4) Snap bulb holder into CHMSL housing.
(5) Place CHMSL access cover in position on lift-
gate.
(6) Engage clip to hold access cover to liftgate.
(7) Verify CHMSL operation.
Fig. 9 License Plate Lamp
Fig. 10 CHMSL Bulb Holder
8L - 16 LAMPSNS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 495 of 1938

BULB APPLICATION
INDEX
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION....................... 17
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
HEADLAMP CLEANING.................. 17SPECIFICATIONS
EXTERIOR LAMP BULBS................. 17
INTERIOR LAMP BULBS................. 17
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
The following Bulb Application Tables list the lamp
title on the left side of the column and trade number
or part number on the right.
CAUTION: Do not use bulbs that have a higher
candle power than the bulb listed in the Bulb Appli-
cation Table. Damage to lamp can result.
Do not touch halogen bulbs with fingers or other
possibly oily surfaces. Bulb life will be reduced.
If a halogen bulb is contaminated with oil, clean
bulb with denatured alcohol or ammonia based sol-
vent.
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
HEADLAMP CLEANING
This vehicle is equipped with plastic headlights
that are lighter and less susceptible to stone break-
age than glass headlights.
This plastic is not as scratch resistant as glass and
therefore a different lens cleaning procedures must
be followed.
To minimize the possibility of scratching the lenses
and reducing light output, avoid wiping with a dry
cloth. To remove road dirt, wash with a mild soap
solution followed by rinsing with water.
Do not use abrasive cleaning components, solvents,
steel wool or other aggressive material to clean the
lenses.
SPECIFICATIONS
EXTERIOR LAMP BULBS
LAMP BULB
Back-up.............................P21W
CHMSL (Non-Solar Tint)................P21W
CHMSL (Solar Tint)....................R10WLAMP BULB
Fog Lamp..............................H3
Headlamp..............................H4
License Plate..........................C5W
Front Turn Signal....................PY21W
Citylight..............................T4W
Front Side Repeater.....................T4W
Tail, Stop...........................P21/5W
Rear Turn Signal......................P21W
Rear Fog Lamp........................P21W
INTERIOR LAMP BULBS
LAMP BULB
ABS ................................PC194
AirBag .............................PC194
Alarm Set (Security/Immobilzer)..........PC194
Brake Warning.......................PC194
Center/Rear Reading Lamps...............578
Center/Rear Dome Lamps.................579
Cruise Indicator.......................PC194
Door Ajar Indicator....................PC194
Engine Compartment Lamps...............579
Engine Temp Indicator.................PC194
Front Door Courtesy......................567
Glove Box Lamp.........................194
Glow Plug Indicator (Diesel Engine Only) . . . PC194
High Beam Indicator...................PC194
Instrument Cluster....................PC194
IP/Ash Tray (Left Hand Drive Only).........161
Liftgate Flood Lamps.....................567
Liftgate Ajar Indicator...................PC74
Low Coolant Level (Diesel Engine Only).....PC74
Low Fuel Indicator....................PC194
Low Volts Warning.....................PC74
Low Washer Fluid......................PC74
Oil Pressure Indicator..................PC194
O/H Console Reading Lamps...............579
Seat Belt Indicator (Except Diesel).........PC74
Service Engine Soon...................PC194
Turn Signal..........................PC194
Visor Vanity Lamp...................6501966
NS/GSLAMPS 8L - 17
Page 520 of 1938

access the SKIS for initialization, or by the dealer
technician to access the system for service. The
SKIM also stores in its memory the Vehicle Identifi-
cation Number (VIN), which it learns through a CCD
data bus message from the PCM during initializa-
tion.
The SKIM and the PCM both use software that
includes a rolling code algorithm strategy, which
helps to reduce the possibility of unauthorized SKIS
disarming. The rolling code algorithm ensures secu-
rity by preventing an override of the SKIS through
the unauthorized substitution of the SKIM or the
PCM. However, the use of this strategy also means
that replacement of either the SKIM or the PCM
units will require a system initialization procedure to
restore system operation.
When the ignition switch is turned to the On or
Start positions, the SKIM transmits an RF signal to
excite the Smart Key transponder. The SKIM then
listens for a return RF signal from the transponder
of the Smart Key that is inserted in the ignition lock
cylinder. If the SKIM receives an RF signal with
valid ªSecret Keyº and transponder identification
codes, the SKIM sends a ªvalid keyº message to the
PCM over the CCD data bus. If the SKIM receives
an invalid RF signal or no response, it sends ªinvalid
keyº messages to the PCM. The PCM will enable or
disable engine operation based upon the status of the
SKIM messages.
The SKIM also sends messages to the instrument
cluster over the CCD data bus network to control the
SKIS indicator lamp. The SKIM sends messages to
the instrument cluster to turn the lamp on for about
three seconds when the ignition switch is turned to
the On position as a bulb test. After completion of
the bulb test, the SKIM sends bus messages to keep
the lamp off for a duration of about one second. Then
the SKIM sends messages to turn the lamp on or off
based upon the results of the SKIS self-tests. If the
SKIS indicator lamp comes on and stays on after the
bulb test, it indicates that the SKIM has detected a
system malfunction and/or that the SKIS has become
inoperative.
If the SKIM detects an invalid key when the igni-
tion switch is turned to the On position, it sends
messages to the instrument cluster to flash the SKIS
indicator lamp. The SKIM can also send messages to
the instrument cluster to flash the lamp and to gen-
erate a single audible chime tone.
For diagnosis or initialization of the SKIM and the
PCM, a DRB scan tool and the proper Diagnostic
Procedures manual are required. The SKIM cannot
be repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the unit must
be replaced.SMART KEY IMMOBILIZER TRANSPONDER
The Smart Key Immobilizer System (SKIS) uses a
transponder that is integral to each of the two igni-
tion keys that are supplied with the vehicle when it
is shipped from the factory. The transponder chip is
insulated within a nylon mount inserted in the head
of the key, and invisible beneath a molded rubber cap
(Fig. 1).
Each Smart Key transponder has a unique tran-
sponder identification code programmed into it by the
manufacturer. The Smart Key Immobilizer Module
(SKIM) has a unique ªSecret Keyº code programmed
into it by the manufacturer. When a Smart Key tran-
sponder is programmed into the memory of the
SKIM, the SKIM learns the transponder identifica-
tion code from the transponder, and the transponder
learns the ªSecret Keyº code from the SKIM. Each of
these codes is stored within the transponder and in
the nonvolatile memory of the SKIM. Therefore,
blank keys for the SKIS must be programmed by and
into the SKIM, in addition to being cut to match the
mechanical coding of the ignition lock cylinder. See
Smart Key Immobilizer System Transponder Pro-
gramming in this group for more information.
The Smart Key transponder is within the range of
the SKIM transceiver antenna ring when it is
inserted in the ignition lock cylinder. When the igni-
tion switch is turned to the Start or On positions, the
SKIM transceiver issues a Radio Frequency (RF) sig-
nal that excites the transponder chip. The transpon-
der chip responds by issuing an RF signal containing
its transponder identification code and the ªSecret
Keyº code. The SKIM transceiver compares the tran-
sponder codes with the codes stored in its memory to
Fig. 1 Smart Key Immobilizer Transponder
8Q - 2 VEHICLE THEFT/SECURITY SYSTEMSNS/GS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 521 of 1938

determine whether a valid key is in the ignition lock
cylinder.
The Smart Key transponder cannot be repaired
and, if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
SMART KEY IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM INDICATOR
LAMP
The Smart Key Immobilizer System (SKIS) indica-
tor lamp gives an indication when the SKIS is faulty
or when the vehicle has been immobilized due to the
use of an invalid ignition key. The lamp is controlled
by the instrument cluster circuitry based upon mes-
sages received from the Smart Key Immobilizer Mod-
ule (SKIM) on the Chrysler Collision Detection (CCD)
data bus.
The SKIM sends messages to the instrument clus-
ter to turn the lamp on for about three seconds when
the ignition switch is turned to the On position as a
bulb test. After completion of the bulb test, the SKIM
sends bus messages to keep the lamp off for a dura-
tion of about one second. Then the SKIM sends mes-
sages to the instrument cluster circuitry to turn the
lamp on or off based upon the results of the SKIS
self-tests. If the SKIS indicator lamp comes on and
stays on after the bulb test, it indicates that the
SKIM has detected a system malfunction and/or that
the SKIS has become inoperative. If the SKIM
detects an invalid key when the ignition switch is
turned to the On position, it sends messages to the
instrument cluster to flash the SKIS indicator lamp.
The SKIM can also send messages to the instru-
ment cluster to flash the lamp and to generate a sin-
gle audible chime tone. These functions serve as an
indication to the customer that the SKIS has been
placed in its ªCustomer Learnº programming mode.
See Smart Key Immobilizer System Transponder Pro-
gramming in this group for more information on the
ªCustomer Learnº programming mode.
The SKIS indicator lamp uses a replaceable incan-
descent bulb and bulb holder on the instrument clus-
ter electronic circuit board. Refer to Group 8E -
Instrument Panel Systems for diagnosis and service
of a faulty SKIS indicator lamp. If the SKIS indicator
lamp comes on and stays on after the bulb test func-
tion, diagnosis of the SKIS should be performed with
a DRB scan tool and the proper Diagnostic Proce-
dures manual.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
SMART KEY IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, REFER TO GROUP 8M - PASSIVE
RESTRAINT SYSTEMS BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY
STEERING WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, OR
INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
NOTE: The following tests may not prove conclu-
sive in the diagnosis of this system. The most reli-
able, efficient, and accurate means to diagnose the
Smart Key Immobilizer System involves the use of a
DRB scan tool. Refer to the proper Diagnostic Pro-
cedures manual for the procedures.
The Smart Key Immobilizer System (SKIS) and the
Chrysler Collision Detection (CCD) data bus network
should be diagnosed using a DRB scan tool. The DRB
will allow confirmation that the CCD data bus is
functional, that the Smart Key Immobilizer Module
(SKIM) is placing the proper messages on the CCD
data bus, and that the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) and the instrument cluster are receiving the
CCD data bus messages. Refer to the proper Diag-
nostic Procedures manual for the procedures. Refer
to 8W-30 - Fuel/Ignition System in Group 8W - Wir-
ing Diagrams for complete circuit descriptions and
diagrams.
(1) Check the fuses in the fuseblock module. If OK,
go to Step 2. If not OK, repair the shorted circuit or
component as required and replace the faulty fuse.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Unplug the wire harness connector at the
SKIM. Check for continuity between the ground cir-
cuit cavity of the SKIM wire harness connector and a
good ground. There should be continuity. If OK, go to
Step 3. If not OK, repair the open circuit to ground
as required.
(3) Connect the battery negative cable. Check for
battery voltage at the fused B(+) circuit cavity of the
SKIM wire harness connector. If OK, go to Step 4. If
not OK, repair the open circuit to the fuse in the
fuseblock module as required.
NS/GSVEHICLE THEFT/SECURITY SYSTEMS 8Q - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 551 of 1938

OVERHEAD CONSOLE
CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
COMPASS MINI-TRIP COMPUTER (CMTC).... 1
COMPASS/TEMPERATURE MINI TRIP
COMPUTER SELF-DIAGNOSTIC TEST....... 1
THERMOMETER AND COMPASS............ 2
UNIVERSAL TRANSMITTER................ 2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
READING/DOME LAMP DIAGNOSIS......... 3
TRAVELER MESSAGES.................... 3
UNIVERSAL TRANSMITTER................ 3
SERVICE PROCEDURES
COMPASS CALIBRATION PROCEDURE (FAST
METHOD)............................. 4
COMPASS CALIBRATION PROCEDURE....... 4
DEMAGNETIZING PROCEDURE............. 4UNIVERSAL TRANSMITTER................ 5
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE SENSOR.......... 5
COMPASS MINI-TRIP COMPUTER (CMTC)
LAMP BULBS......................... 6
COMPASS MINI-TRIP COMPUTER (CMTC)
MODULE............................. 6
FRONT HEADER READING/COURTESY LAMP . . 6
OVERHEAD CONSOLE.................... 6
READING/COURTESY LAMP ASSEMBLY...... 7
READING/COURTESY LAMP............... 6
UNIVERSAL TRANSMITTER................ 7
SPECIAL TOOLS
SPECIAL TOOL.......................... 9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
COMPASS/TEMPERATURE MINI TRIP COMPUTER
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC TEST
The CMTC is capable of performing a diagnostic
self check on many of its internal functions. CMTC
diagnostics may be performed using a scan tool
(DRB) and the proper Body Diagnostic Procedures
manual or by the following procedure.
(1) With the ignition switch in the OFF position,
press both the US/M and STEP button.
(2) Turn ignition switch to the ON position.
The CMTC will perform internal checks while
lighting all segments of the vacuum florescent dis-
play. Upon completion of the internal check, the
CMTC will display.
²PASS
²FAIL
²CCd
If any segment of the CMTC fails to light replace
the module.
If FAIL is displayed, replace the module.
If CCd is displayed, check the CCD and Body Con-
trol Module (BCM) for proper operation, refer to the
appropriate diagnostic test procedures manual If the
CCD and the BCM are OK, replace the CMTC mod-
ule.
For additional diagnostic information on the CMTC
and for identifying CMTC problems, refer to the
proper Body Diagnostic Procedures manual.
COMPASS MINI-TRIP COMPUTER (CMTC)
The Compass Mini-Trip Computer (CMTC) system
is located in the overhead console. CMTC consists of
a electronic control module with a vacuum fluores-
cent display (VFD) and function switches. The CMTC
consists of a electronic module that displays compass,
trip computer, and temperature features. Actuating
the STEP switch will cause the CMTC to change
mode of operation when ignition is ON. Example:
²Compass/Temperature
²Trip odometer (ODO)
²Average miles per gallon (ECO)
²Instant miles per gallon (ECO)
²Distance to empty (DTE)
²Elapsed time (ET)
²Off
The CMTC module in the overhead console has
three buttons used to select various functions. The
CMTC selector buttons will not operate until the
ignition is in the RUN position (Fig. 1).
When the ignition switch is first turned to the
RUN position the CMTC display;
²Blanks momentarily
²All segments of the VFD will light for one sec-
ond
²Blanks momentarily
²Returns to the last mode setting selected before
the ignition was last switched OFF.
NSOVERHEAD CONSOLE 8V - 1