1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER service
[x] Cancel search: servicePage 1311 of 1938
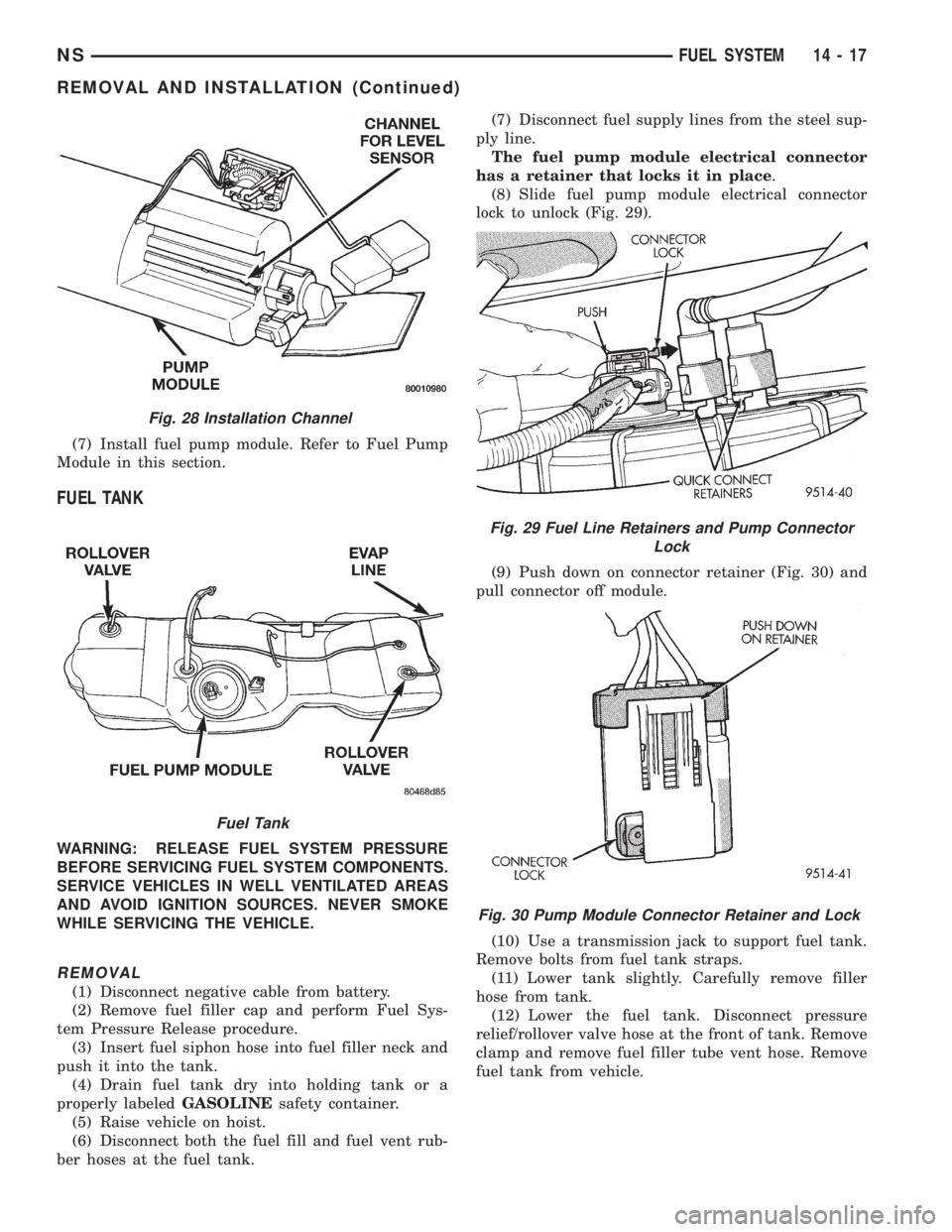
(7) Install fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module in this section.
FUEL TANK
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE SERVICING FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS.
SERVICE VEHICLES IN WELL VENTILATED AREAS
AND AVOID IGNITION SOURCES. NEVER SMOKE
WHILE SERVICING THE VEHICLE.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove fuel filler cap and perform Fuel Sys-
tem Pressure Release procedure.
(3) Insert fuel siphon hose into fuel filler neck and
push it into the tank.
(4) Drain fuel tank dry into holding tank or a
properly labeledGASOLINEsafety container.
(5) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(6) Disconnect both the fuel fill and fuel vent rub-
ber hoses at the fuel tank.(7) Disconnect fuel supply lines from the steel sup-
ply line.
The fuel pump module electrical connector
has a retainer that locks it in place.
(8) Slide fuel pump module electrical connector
lock to unlock (Fig. 29).
(9) Push down on connector retainer (Fig. 30) and
pull connector off module.
(10) Use a transmission jack to support fuel tank.
Remove bolts from fuel tank straps.
(11) Lower tank slightly. Carefully remove filler
hose from tank.
(12) Lower the fuel tank. Disconnect pressure
relief/rollover valve hose at the front of tank. Remove
clamp and remove fuel filler tube vent hose. Remove
fuel tank from vehicle.
Fig. 28 Installation Channel
Fuel Tank
Fig. 29 Fuel Line Retainers and Pump Connector
Lock
Fig. 30 Pump Module Connector Retainer and Lock
NSFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 17
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1319 of 1938

INSTALLATION
(1) Before installing an injector the rubber O-ring
must be lubricated with a drop of clean engine oil to
aid in installation.
(2) Install injector clip by sliding open end into the
top slot of the injector. The edge of the receiver cup
will slide into the side slots of clip.
(3) Install injector top end into fuel rail receiver
cap. Be careful not to damage O-ring during installa-
tion (Fig. 55).
(4) Repeat steps for remaining injectors.
(5) Connect fuel injector wiring.
FUEL INJECTORSÐ3.0L
WARNING: THE 3.0L MPI FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER
A CONSTANT PRESSURE OF APPROXIMATELY 330
KPA (48 PSI). PERFORM FUEL PRESSURE
RELEASE PROCEDURE BEFORE SERVICING THE
FUEL INJECTORS.
REMOVAL
(1) Perform the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure.
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) The fuel rail must be removed first to service
the injectors. Refer to Fuel Injector Rail Assembly
Removal in this section.
(4) Label each injector connector with its cylinder
number. Disconnect electrical connector from injector.
(5) Position fuel rail assembly so that the fuel
injectors are easily accessible.
(6) Remove injector clip from fuel rail and injector
(Fig. 54).
(7) Pull injector straight out of fuel rail receiver
cup (Fig. 55).
(8) Check injector O-ring for damage. If O-ring is
damaged, it must be replaced. If injector is to be
reused, a protective cap must be installed on the
injector tip to prevent damage.
(9) Repeat procedure for remaining injectors.
INSTALLATION
(1) Before installing an injector, the rubber O-ring
must be lubricated with a drop of clean engine oil to
aid in installation.
(2) Being careful not to damage O-ring, install
injector nozzle end into fuel rail receiver cap.
(3) Install injector clip by sliding open end into
top slotof the injector. The edge of the receiver cup
will slide into the side slots of clip (Fig. 55)
(4) Repeat steps for remaining injectors.
(5) Install fuel rail assembly. Refer to Fuel Rail
Assembly Installation in this section.
(6) Connect electrical connectors to injectors in cor-
rect order.
(7) Connect negative battery cable.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the ASD relay and fuel pump relay remain energized
for 7 minutes or until the test is stopped, or until
the ignition switch is turned to the Off position.
(8) With the ignition key in ON position, access
the DRB scan tool ASD Fuel System Test to pressur-
ize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
Fig. 54 Fuel Injector and RailÐTypical
Fig. 55 Servicing Fuel InjectorÐTypical
NSFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 25
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1328 of 1938

When metal aligns with the sensor, voltage goes
low (less than 0.5 volts). When a notch aligns with
the sensor, voltage spikes high (5.0 volts). As a group
of notches pass under the sensor, the voltage
switches from low (metal) to high (notch) then back
to low. The number of notches determine the amount
of pulses. If available, an oscilloscope can display the
square wave patterns of each timing events.
Top dead center (TDC) does not occur when
notches on the camshaft sprocket pass below the cyl-
inder. TDC occurs after the camshaft pulse (or
pulses) and after the 4 crankshaft pulses associated
with the particular cylinder. The arrows and cylinder
call outs on Figure 4 represent which cylinder the
flat spot and notches identify, they do not indicate
TDC position.The camshaft position sensor is mounted to the top
of the timing case cover (Fig. 4). The bottom of the
sensor is positioned above the camshaft sprocket.
The distance between the bottom of sensor and
the camshaft sprocket is critical to the opera-
tion of the system. When servicing the camshaft
position sensor, refer to the 3.3L and 3.8L Multi-
Port Fuel InjectionÐService Procedures sec-
tion in this Group.
2.4L
The camshaft position sensor attaches to the rear
of the cylinder head (Fig. 5). A target magnet
attaches to the rear of the camshaft and indexes to
the correct position (Fig. 6). The target magnet has
four different poles arranged in an asymmetrical pat-
tern. As the target magnet rotates, the camshaft
position sensor senses the change in polarity (Fig. 7).
The sensor output switch switches from high (5.0
volts) to low (0.30 volts) as the target magnet rotates.
When the north pole of the target magnet passes
under the sensor, the output switches high. The sen-
sor output switches low when the south pole of the
target magnet passes underneath.
Fig. 2 Camshaft Position Sensor
Fig. 3 Camshaft Sprocket
Fig. 4 Camshaft Position Sensor Location
14 - 34 FUEL SYSTEMNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1330 of 1938

The crankshaft position sensor is located in the
transaxle housing, above the vehicle speed sensor
(Fig. 10). The bottom of the sensor is positioned next
to the drive plate.The distance between the bot-
tom of sensor and the drive plate is critical to
the operation of the system. When servicing the
crankshaft position sensor, refer to the appro-
priate Multi-Port Fuel Injection Service Proce-
dures section in this Group.
2.4L
The second crankshaft counterweight has
machined into it two sets of four timing reference
notches and a 60 degree signature notch (Fig. 11).
From the crankshaft position sensor input the PCM
determines engine speed and crankshaft angle (posi-
tion).
The notches generate pulses from high to low in
the crankshaft position sensor output voltage. When
a metal portion of the counterweight aligns with the
crankshaft position sensor, the sensor output voltagegoes low (less than 0.3 volts). When a notch aligns
with the sensor, voltage spikes high (5.0 volts). As a
group of notches pass under the sensor, the output
voltage switches from low (metal) to high (notch)
then back to low.
If available, an oscilloscope can display the square
wave patterns of each voltage pulse. From the width
of the output voltage pulses, the PCM calculates
engine speed. The width of the pulses represent the
amount of time the output voltage stays high before
switching back to low. The period of time the sensor
output voltage stays high before switching back to
low is referred to as pulse width. The faster the
engine is operating, the smaller the pulse width on
the oscilloscope.
By counting the pulses and referencing the pulse
from the 60 degree signature notch, the PCM calcu-
lates crankshaft angle (position). In each group of
timing reference notches, the first notch represents
69 degrees before top dead center (BTDC). The sec-
ond notch represents 49 degrees BTDC. The third
notch represents 29 degrees. The last notch in each
set represents 9 degrees before top dead center
(TDC).
The timing reference notches are machined to a
uniform width representing 13.6 degrees of crank-
shaft rotation. From the voltage pulse width the
PCM tells the difference between the timing refer-
ence notches and the 60 degree signature notch. The
60 degree signature notch produces a longer pulse
width than the smaller timing reference notches. If
the camshaft position sensor input switches from
high to low when the 60 degree signature notch
passes under the crankshaft position sensor, the
PCM knows cylinder number one is the next cylinder
at TDC.
The crankshaft position sensor mounts to the
engine block behind the generator, just above the oil
filter (Fig. 12).
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSORÐPCM
INPUT
The engine coolant temperature sensor is a vari-
able resistor with a range of -40ÉC to 129ÉC (-40ÉF to
265ÉF).
The engine coolant temperature sensor provides an
input voltage to the PCM. As coolant temperature
varies, the sensor resistance changes resulting in a
different input voltage to the PCM.
When the engine is cold, the PCM will demand
slightly richer air/fuel mixtures and higher idle
speeds until normal operating temperatures are
reached.
The engine coolant sensor is also used for cooling
fan control.
Fig. 10 Crankshaft Position Sensor LocationÐ3.0/
3.3/3.8L
Fig. 11 Timing Reference Notches
14 - 36 FUEL SYSTEMNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1340 of 1938

Shutdown (ASD) RelayÐPCM Output in this section
for relay operation.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOIDÐPCM
OUTPUT
Three-speed automatic transaxles use a torque con-
verter clutch solenoid. The PCM controls the engage-
ment of the torque converter clutch through the
solenoid. The torque converter clutch is engaged only
in direct drive mode. Refer to Group 21 for transaxle
information.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR (CHECK ENGINE)
LAMPÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM supplies the malfunction indicator (check
engine) lamp on/off signal to the instrument panel
through the CCD Bus. The CCD Bus is a communi-
cations port. Various modules use the CCD Bus to
exchange information.
The Check Engine lamp comes on each time the
ignition key is turned ON and stays on for 3 seconds
as a bulb test.
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) stays on
continuously, when the PCM has entered a Limp-In
mode or identified a failed emission component. Dur-
ing Limp-in Mode, the PCM attempts to keep the
system operational. The MIL signals the need for
immediate service. In limp-in mode, the PCM com-
pensates for the failure of certain components that
send incorrect signals. The PCM substitutes for the
incorrect signals with inputs from other sensors.
If the PCM detects active engine misfire severe
enough to cause catalyst damage, it flashes the MIL.
At the same time the PCM also sets a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC).
For signals that can trigger the MIL (Check
Engine Lamp) refer to Group 25, On-Board
Dianostics.
SOLID STATE FAN RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
The radiator fan runs at a variable speed depend-
ing on coolant temperature and A/C system pressure.
The radiator fan circuit contains a Solid State Fan
Relay (SSFR). Refer to the Group 8W for a circuit
schematic.
A 5 volt signal is supplied to the SSFR. The PCM
provides a pulsed ground for the SSFR. Depending
upon the amount of pulse on time, the SSFR puts out
a proportional voltage to the fan motor at the lower
speed. For instance, if the on time is 30 percent, then
the voltage to the fan motor will be 3.6 volts.
When engine coolant reaches approximately 102ÉC
(215ÉF) the PCM grounds the SSFR relay. If engine
coolant reaches 207ÉC (225ÉF) the PCM grounds the
high speed ground relay and high speed fan relay. If
the fan operates at high speed, the PCM de-energizes
the high speed relay and high speed ground relay
when coolant temperature drops to approximately
101ÉC (214ÉF). When coolant temperature drops to
101ÉC (214ÉF) the fan operates at low speed. The
PCM de-energizes the low speed relay when coolant
temperature drops to approximately 93ÉC (199ÉF).
Also, when the air conditioning pressure switch
closes, the fan operates at high speed. The air condi-
tioning switch closes at 285 psi610 psi. When air
conditioning pressure drops approximately 40 psi, the
pressure switch opens and the fan operates at low
speed.
The SSFR relay is located on the left front inner
frame just behind the radiator (Fig. 42).
SPEED CONTROL SOLENOIDSÐPCM OUTPUT
The speed control vacuum and vent solenoids are
operated by the PCM. When the PCM supplies a
ground to the vacuum and vent solenoids, the speed
control system opens the throttle plate. When the
PCM removes the ground from the vacuum and vent
solenoids, the throttle blade closes. The PCM bal-
Fig. 41 Ignition Coil Ð3.3/3.8L
Fig. 42 Fan Control Module
14 - 46 FUEL SYSTEMNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1341 of 1938
ances the two solenoids to maintain the set speed.
Refer to Group 8H for speed control information.
TACHOMETERÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM supplies engine RPM to the instrument
panel tachometer through the CCD Bus. The CCD
Bus is a communications port. Various modules use
the CCD Bus to exchange information. Refer to
Group 8E for more information.
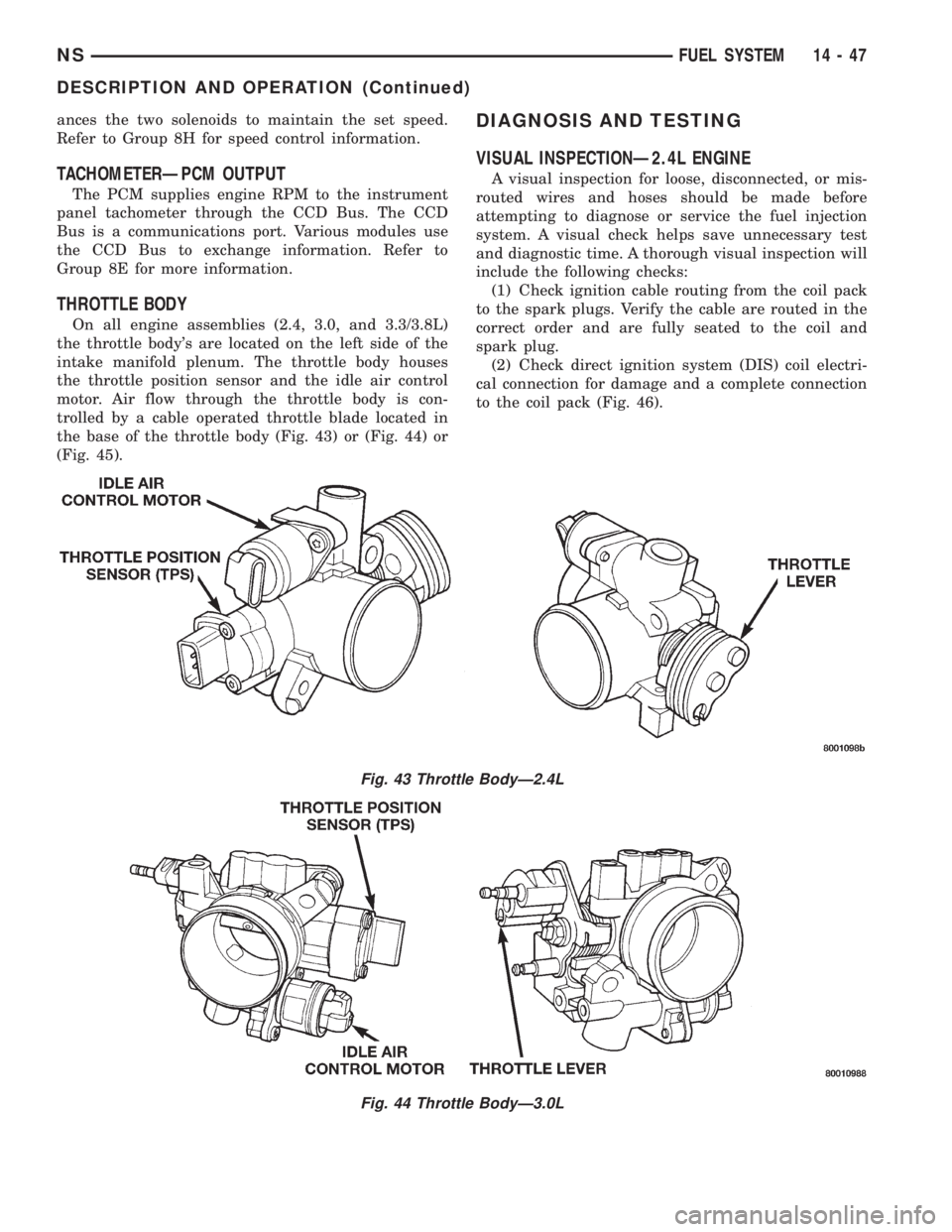
THROTTLE BODY
On all engine assemblies (2.4, 3.0, and 3.3/3.8L)
the throttle body's are located on the left side of the
intake manifold plenum. The throttle body houses
the throttle position sensor and the idle air control
motor. Air flow through the throttle body is con-
trolled by a cable operated throttle blade located in
the base of the throttle body (Fig. 43) or (Fig. 44) or
(Fig. 45).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
VISUAL INSPECTIONÐ2.4L ENGINE
A visual inspection for loose, disconnected, or mis-
routed wires and hoses should be made before
attempting to diagnose or service the fuel injection
system. A visual check helps save unnecessary test
and diagnostic time. A thorough visual inspection will
include the following checks:
(1) Check ignition cable routing from the coil pack
to the spark plugs. Verify the cable are routed in the
correct order and are fully seated to the coil and
spark plug.
(2) Check direct ignition system (DIS) coil electri-
cal connection for damage and a complete connection
to the coil pack (Fig. 46).
Fig. 43 Throttle BodyÐ2.4L
Fig. 44 Throttle BodyÐ3.0L
NSFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 47
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1346 of 1938
VISUAL INSPECTIONÐ3.0L ENGINE
A visual inspection for loose, disconnected, or mis-
routed wires and hoses should be made before
attempting to diagnose or service the fuel injection
system. A visual check helps save unnecessary test
and diagnostic time. A thorough visual inspection will
include the following checks:(1) Check for correct spark plug cable routing.
Ensure that the cables are completely connected to
the spark plugs and distributor.
(2) Check ignition coil electrical connections (Fig.
62).
(3) Verify that the electrical connector is attached
to the Proportional Purge Solenoid (Fig. 63).
(4) Verify that vacuum connection at the duty cycle
Proportional Purge Solenoid valve is secure and not
leaking.
Fig. 60 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
Fig. 61 Power Brake Booster Hose
Fig. 62 Ignition Coil Electrical Connection
Fig. 63 Proportional Purge Solenoid Valve
14 - 52 FUEL SYSTEMNS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1349 of 1938

terminals. Verify the connectors are fully inserted
into the socket of the PCM (Fig. 74). Ensure that
wires are not stretched or pulled out of the connector.
(24) Inspect fuses in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Verify all fuses and relays are fully
inserted into the PDC (Fig. 74). A label affixed to the
underside of the PDC cover identifies the relays and
fuses in the PDC.
(25) Check Battery Cable Connections.
(26) Check hose and wiring connections at fuel
pump module. Check that wiring connector is making
contact with terminals on pump.
VISUAL INSPECTIONÐ3.3/3.8L ENGINES
A visual inspection for loose, disconnected, or mis-
routed wires and hoses should be made before
attempting to diagnose or service the fuel injection
system. A visual check helps save unnecessary test
and diagnostic time. A thorough visual inspection will
include the following checks:
(1) Check ignition cable routing from the coil pack
to the spark plugs. Verify the cable are routed in the
correct order and are fully seated to the coil and
spark plug.(2) Check direct ignition system (DIS) coil electri-
cal connection for damage and a complete connection
to the coil pack (Fig. 75).
(3) Verify the camshaft position sensor electrical
connector is connected to the harness and not dam-
aged (Fig. 76).
(4) Ensure the engine temperature sensor electri-
cal connector is connected to the sensor and not dam-
aged (Fig. 77).
(5) Verify the quick connect fuel fitting is fully
inserted on the fuel supply tube.
(6) Check the oil pressure sending unit electrical
connection (Fig. 78).
Fig. 74 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
Fig. 75 Ignition Coil Pack Electrical Connection
Fig. 76 Camshaft Position Sensor
NSFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 55
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)