1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER service
[x] Cancel search: servicePage 1185 of 1938

SPARK PLUG TUBE
(1) Remove valve cover. Refer to procedure out-
lined in this section.
(2) Using locking pliers remove the tube from the
cylinder head (Fig. 11). Discard old tube.
(3) Clean area around spark plug with Mopart
parts cleaner or equivalent.
(4) Apply MopartStud and Bearing Mount or
equivalent to a new tube approximately 1 mm from
theendina3mmwide area.
(5) Install sealer end of tube into the cylinder
head. Then carefully install the tube using a hard-
wood block and mallet until the tube is seated into
the bottom of the bore.
(6) Install valve cover. Refer to procedure outlined
in this section.
SPARK PLUG TUBE SEALS
The spark plug tube seals are located in the cylin-
der head cover (Fig. 12). These seals are pressed into
the cylinder head cover to seal the outside perimeterof the spark plug tubes. If these seals show signs of
hardness and/or cracking they should be replaced.
CAMSHAFT
NOTE: TO REMOVE CAMSHAFT THE CYLINDER
HEAD MUST BE REMOVED.
REMOVAL
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before attempting any repairs.Refer to Group 14,
Fuel System
(2) Remove the cylinder head cover. Refer to proce-
dure outlined in this section.
(3) Mark rocker arm shaft assemblies so that they
are installed in their original positions.
(4) Remove rocker arm shaft bolts. Refer to proce-
dure outlined in this section.
(5) Remove timing belt, timing belt tensioner, and
camshaft sprocket. Refer to timing belt service out-
lined in this section.
(6) Remove inner timing belt cover.
(7) Remove cylinder head. Refer to procedure out-
lined in this section.
(8) Remove camshaft sensor and camshaft target
magnet.
(9) Remove camshaft from the rear of cylinder
head.
INSPECT CYLINDER HEAD FOR THE FOLLOWING:
NOTE:
²Check oil feed holes for blockage.
²Inspect cylinder head camshaft bearings for
wear, Refer to Cylinder Head, Inspection and Clean-
ing.
²Check camshaft bearing journals for scratches
and worn areas. If light scratches are present, they
may be removed with 400 grit sand paper. If deep
Fig. 10 Ingition Coil Pack
Fig. 11 Servicing Spark Plug Tubes
Fig. 12 Spark Plug Tube Seals
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 7
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1187 of 1938

NOTE: Inspect the rocker arm for scoring, wear on
the roller or damage to the rocker arm (Fig. 16)
Replace if necessary. Check the location where the
rocker arms mount to the shafts for wear or dam-
age. Replace if damaged or worn. The rocker arm
shaft is hollow and is used as a lubrication oil duct.
Check oil holes for clogging with small wire, clean
as required. Lubricate the rocker arms and spacers.
Install onto shafts in their original position (Fig. 15).
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Set crankshaft to 3 notches before TDC
before installing rocker arm shafts. Refer to Timing
Belt System and Camshaft Seal Service of this sec-
tion for procedure.
(1) Install rocker arm/hydraulic lash adjuster
assembly making sure that adjusters are at leastpartially full of oil. This is indicated by little or no
plunger travel when the lash adjuster is depressed. If
there is excessive plunger travel. Place the rocker
arm assembly into clean engine oil and pump the
plunger until the lash adjuster travel is taken up. If
travel is not reduced, replace the assembly. Hydraulic
lash adjuster and rocker arm are serviced as an
assembly.
(2) Install rocker arm and shaft assemblies with
NOTCH in the rocker arm shafts pointing up and
toward the timing belt side of the engine (Fig. 17).
Install the retainers in their original positions on the
exhaust and intake shafts (Fig. 15).
CAUTION: When installing the intake rocker arm
shaft assembly be sure that the plastic spacers do
not interfere with the spark plug tubes. If the spac-
ers do interfere rotate until they are at the proper
angle. To avoid damaging the spark plug tubes, do
not attempt rotating the spacers by forcing down
the shaft assembly.
(3) Tighten bolts to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.) in
sequence shown in (Fig. 18).
Fig. 15 Rocker Arm Shaft Assemblies
Fig. 16 Rocker Arm Assemblies
Fig. 17 Rocker Arm Shaft Notches
Fig. 18 Rocker Arm Shaft Tightening Sequence
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 9
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1188 of 1938
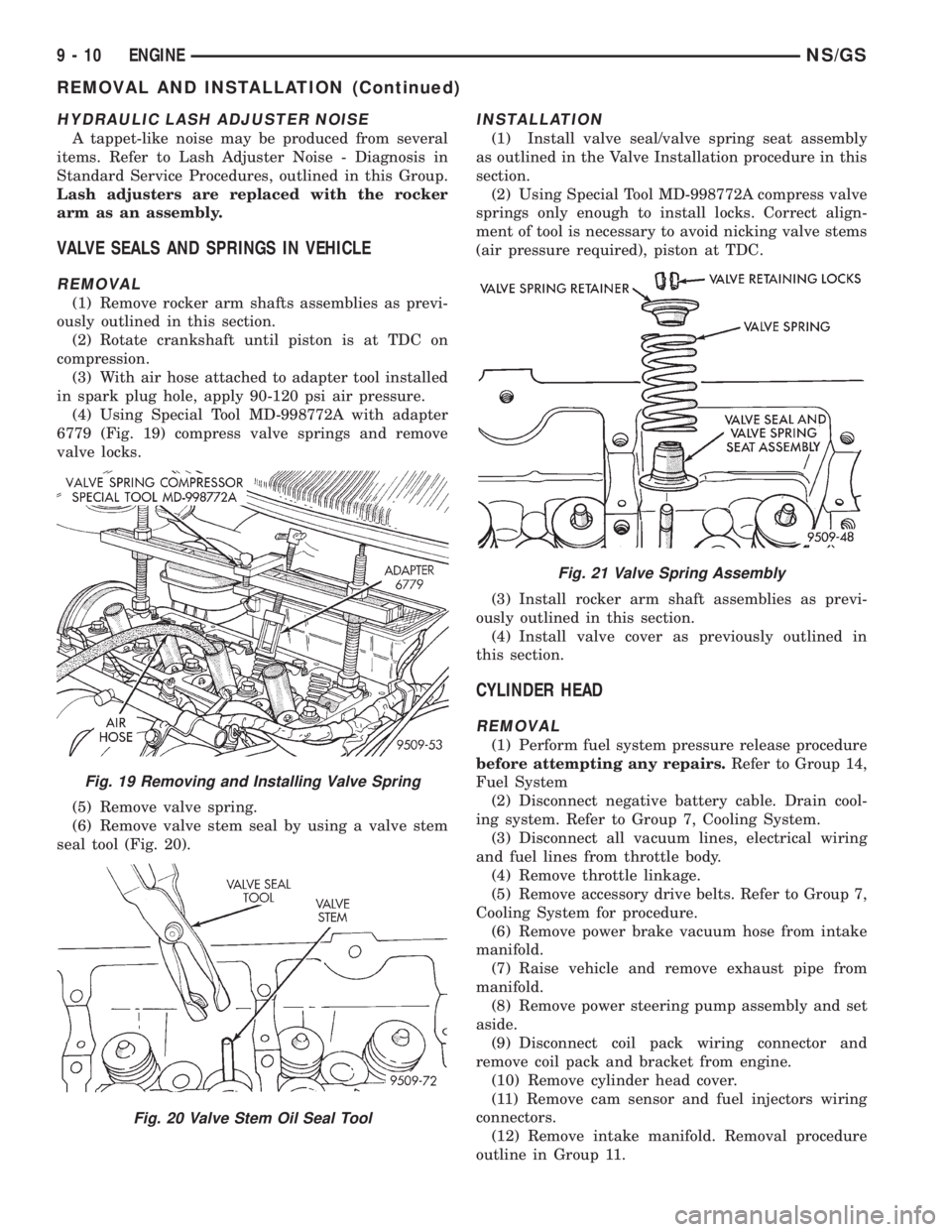
HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTER NOISE
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Refer to Lash Adjuster Noise - Diagnosis in
Standard Service Procedures, outlined in this Group.
Lash adjusters are replaced with the rocker
arm as an assembly.
VALVE SEALS AND SPRINGS IN VEHICLE
REMOVAL
(1) Remove rocker arm shafts assemblies as previ-
ously outlined in this section.
(2) Rotate crankshaft until piston is at TDC on
compression.
(3) With air hose attached to adapter tool installed
in spark plug hole, apply 90-120 psi air pressure.
(4) Using Special Tool MD-998772A with adapter
6779 (Fig. 19) compress valve springs and remove
valve locks.
(5) Remove valve spring.
(6) Remove valve stem seal by using a valve stem
seal tool (Fig. 20).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install valve seal/valve spring seat assembly
as outlined in the Valve Installation procedure in this
section.
(2) Using Special Tool MD-998772A compress valve
springs only enough to install locks. Correct align-
ment of tool is necessary to avoid nicking valve stems
(air pressure required), piston at TDC.
(3) Install rocker arm shaft assemblies as previ-
ously outlined in this section.
(4) Install valve cover as previously outlined in
this section.
CYLINDER HEAD
REMOVAL
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before attempting any repairs.Refer to Group 14,
Fuel System
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable. Drain cool-
ing system. Refer to Group 7, Cooling System.
(3) Disconnect all vacuum lines, electrical wiring
and fuel lines from throttle body.
(4) Remove throttle linkage.
(5) Remove accessory drive belts. Refer to Group 7,
Cooling System for procedure.
(6) Remove power brake vacuum hose from intake
manifold.
(7) Raise vehicle and remove exhaust pipe from
manifold.
(8) Remove power steering pump assembly and set
aside.
(9) Disconnect coil pack wiring connector and
remove coil pack and bracket from engine.
(10) Remove cylinder head cover.
(11) Remove cam sensor and fuel injectors wiring
connectors.
(12) Remove intake manifold. Removal procedure
outline in Group 11.
Fig. 19 Removing and Installing Valve Spring
Fig. 20 Valve Stem Oil Seal Tool
Fig. 21 Valve Spring Assembly
9 - 10 ENGINENS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1200 of 1938

CAUTION: Do not pry up on one side of the bed-
plate. Damage may occur to cylinder block and bed-
plate alignment.(7) Bedplate should be removed evenly from the
cylinder block dowel pins.
(8) Lift out crankshaft from cylinder block. Be sure
not to damage the main bearings or journals when
removing the crankshaft.
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS LOCATION
The crankshaft is supported in five main bearings.
All upper bearing shells in the crankcase have oil
grooves. All lower bearing shells installed in the (bed-
plate) main bearing cap are plain. Crankshaft end
play is controlled by a flanged bearing on the number
three main bearing journal (Fig. 64).
NOTE: The upper and lower main Bearing shells
are Not interchangeable. The lower shells have a
revised tab to prevent improper installation.
CRANKSHAFT MAIN JOURNALS INSPECTION
The crankshaft journals should be checked for
excessive wear, taper and scoring. Limits of taper or
out-of-round on any crankshaft journals should be
held to .025 mm (.001 inch). Journal grinding should
not exceed .305 mm (.012 inch) under the standard
journal diameter. DO NOT grind thrust faces of
Number 3 main bearing. DO NOT nick crank pin or
bearing fillets. After grinding, remove rough edges
from crankshaft oil holes and clean out all passages.
CAUTION: With the nodular cast iron crankshafts
used it is important that the final paper or cloth pol-
ish after any journal regrind be in the same direc-
tion as normal rotation in the engine.
Upper and lower Number 3 bearing halves are
flanged to carry the crankshaft thrust loads and are
NOT interchangeable with any other bearing halves
in the engine (Fig. 64). All bearing cap bolts removed
during service procedures are to be cleaned and oiled
before installation. Bearing shells are available in
standard and the following undersized: 0.016 mm
(.0006 inch), .032 mm (.0012 inch), .250 mm (.010
inch). Never install an undersize bearing that will
reduce clearance below specifications.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the main bearing shells with the lubri-
cation groove in the cylinder block. Install O-ring
into recess in the block (Fig. 65).
(2) Make certain oil holes in block line up with oil
hole in bearings and bearing tabs seat in the block
tab slots.
CAUTION: Do Not get oil on the bedplate mating
surface. It will affect the sealer ability to seal the
bedplate to cylinder block.
Fig. 61 Crankshaft Seal Special Tool 6926-2
Fig. 62 Rear Crankshaft SealÐInstallation
9 - 22 ENGINENS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1202 of 1938
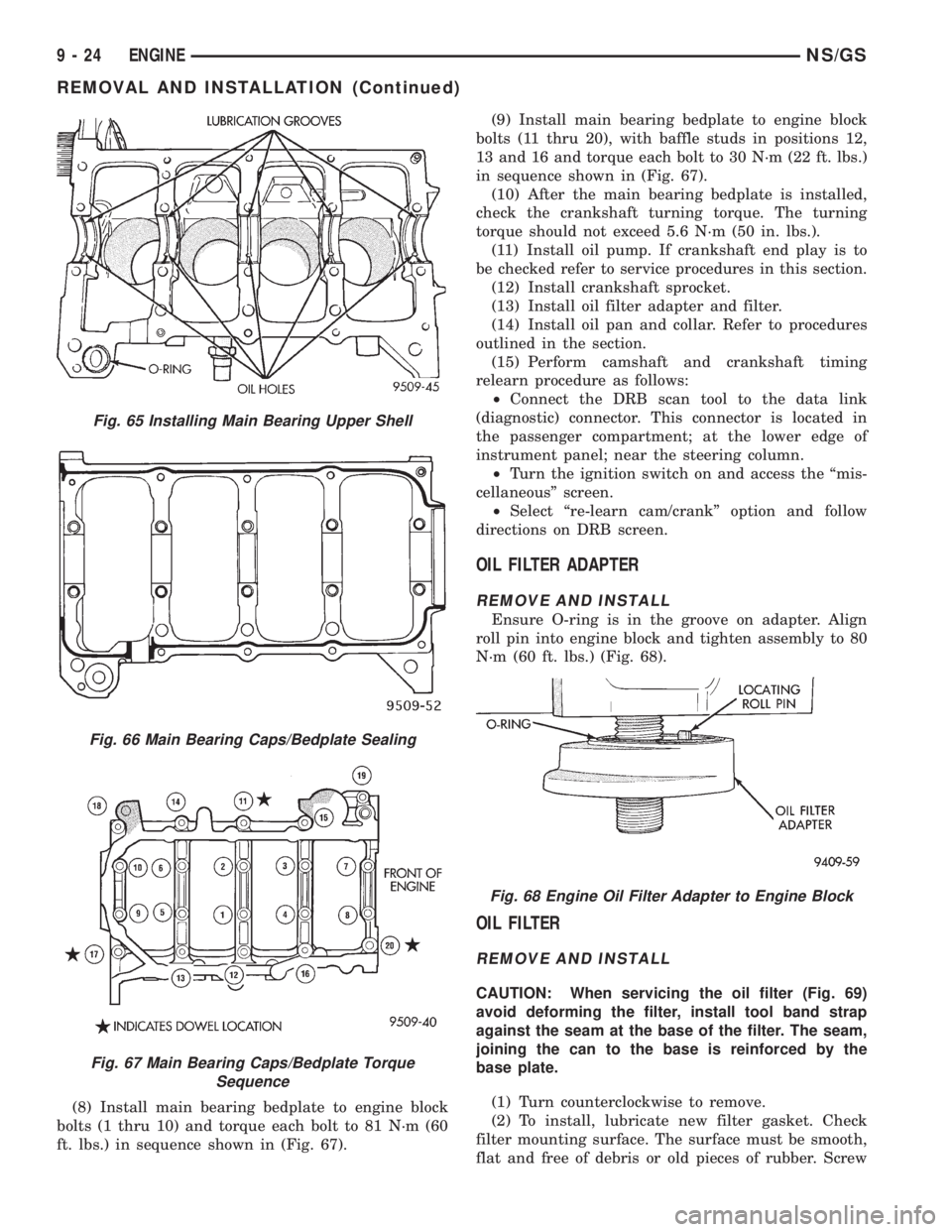
(8) Install main bearing bedplate to engine block
bolts (1 thru 10) and torque each bolt to 81 N´m (60
ft. lbs.) in sequence shown in (Fig. 67).(9) Install main bearing bedplate to engine block
bolts (11 thru 20), with baffle studs in positions 12,
13 and 16 and torque each bolt to 30 N´m (22 ft. lbs.)
in sequence shown in (Fig. 67).
(10) After the main bearing bedplate is installed,
check the crankshaft turning torque. The turning
torque should not exceed 5.6 N´m (50 in. lbs.).
(11) Install oil pump. If crankshaft end play is to
be checked refer to service procedures in this section.
(12) Install crankshaft sprocket.
(13) Install oil filter adapter and filter.
(14) Install oil pan and collar. Refer to procedures
outlined in the section.
(15) Perform camshaft and crankshaft timing
relearn procedure as follows:
²Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
²Turn the ignition switch on and access the ªmis-
cellaneousº screen.
²Select ªre-learn cam/crankº option and follow
directions on DRB screen.
OIL FILTER ADAPTER
REMOVE AND INSTALL
Ensure O-ring is in the groove on adapter. Align
roll pin into engine block and tighten assembly to 80
N´m (60 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 68).
OIL FILTER
REMOVE AND INSTALL
CAUTION: When servicing the oil filter (Fig. 69)
avoid deforming the filter, install tool band strap
against the seam at the base of the filter. The seam,
joining the can to the base is reinforced by the
base plate.
(1) Turn counterclockwise to remove.
(2) To install, lubricate new filter gasket. Check
filter mounting surface. The surface must be smooth,
flat and free of debris or old pieces of rubber. Screw
Fig. 65 Installing Main Bearing Upper Shell
Fig. 66 Main Bearing Caps/Bedplate Sealing
Fig. 67 Main Bearing Caps/Bedplate Torque
Sequence
Fig. 68 Engine Oil Filter Adapter to Engine Block
9 - 24 ENGINENS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1203 of 1938

filter on until gasket contacts base. Tighten to 21
N´m (15 ft. lbs.).
OIL PUMP
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove Timing Belt. Refer to Timing Belt Sys-
tem, in this section.
(3) Remove Oil Pan. Refer to Oil Pan Removal in
this section.
(4) Remove Crankshaft Sprocket using Special Tool
6793 and insert C-4685-C2 (Fig. 70).
(5) Remove oil pick-up tube.
(6) Remove oil pump (Fig. 71) and front crankshaft
seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Make sure all surfaces are clean and free of oil
and dirt.(2) Apply MopartGasket Maker to oil pump as
shown in (Fig. 72). Install o±ring into oil pump body
discharge passage.
(3) Prime oil pump before installation.
(4) Align oil pump rotor flats with flats on crank-
shaft as you install the oil pump to the block.
NOTE: Front crankshaft seal MUST be out of pump
to align, or damage may result.
(5) Torque all oil pump attaching bolts to 28 N´m
(250 in. lbs.)
(6) Install new front crankshaft seal using Special
Tool 6780 (Fig. 73).
(7) Install crankshaft sprocket, using Special Tool
6792 (Fig. 74).
(8) Install oil pump pick-up tube and oil pan.
(9) Install Timing Belt. Refer to procedure outlined
in this section.
(10) Connect negative cable to battery.
PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD
REMOVAL
(1) Remove top ridge of cylinder bores with a reli-
able ridge reamer before removing pistons from cyl-
inder block.Be sure to keep tops of pistons
covered during this operation. Mark piston with
matching cylinder number (Fig. 75).
(2) Remove oil pan. Scribe the cylinder number on
the side of the rod and cap (Fig. 76) for identification.
(3) Pistons will have a stamping in the approxi-
mate location shown in (Fig. 75). These stamps will
be either a directional arrow or a weight identifica-
tion for the assembly. L is for light and H is for
heavy. These assemblies should all be the same
weight class. Service piston assemblies are marked
with a S and can be used with either L or H produc-
tion assemblies. The weight designation stamps
should face toward the timing belt side of the engine.
(4) Pistons and connecting rods must be removed
from top of cylinder block. Rotate crankshaft so that
each connecting rod is centered in cylinder bore.
(5) Remove connecting rod cap boltsDo not use
old bolts if reinstalling connecting rod.Push
each piston and rod assembly out of cylinder bore.
NOTE: Be careful not to nick crankshaft journals.
(6) After removal, install bearing cap on the mat-
ing rod.
(7) Piston and Rods are serviced as an assembly.
PISTON RINGÐREMOVAL
(1) ID mark on face of upper and intermediate pis-
ton rings must point toward piston crown.
Fig. 69 Engine Oil Filter
Fig. 70 Crankshaft SprocketÐRemoval
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 25
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1207 of 1938

INSTALLATION
(1) Install crankshaft damper using M12-1.75 x
150 mm bolt, washer, thrust bearing and nut from
Special Tool 6792. Install crankshaft damper bolt and
tighten to 142 N´m (105 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 84).
(2) Install accessory drive belts. Refer to Group 7,
Cooling System Accessory Drive section for proce-
dure.
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
OIL PUMP
(1) To remove the relief valve, proceed as follows:
(2) Remove the threaded plug and gasket from the
oil pump (Fig. 85).
CAUTION: Oil pump pressure relief valve must be
installed as shown in (Fig. 85) or serious damage
may occur.
(3) Remove spring and relief valve (Fig. 85).(4) Remove oil pump cover screws, and lift off
cover.
(5) Remove pump rotors.
(6) Wash all parts in a suitable solvent and inspect
carefully for damage or wear (Fig. 86).
VALVE SERVICE WITH THE CYLINDER HEAD
REMOVED
REMOVAL
(1) With cylinder head removed, compress valve
springs using Special Tool C-3422-B or equivalent.
(2) Remove valve retaining locks, valve spring
retainers, valve stem seals and valve springs.
(3) Before removing valves,remove any burrs
from valve stem lock grooves to prevent dam-
age to the valve guides.Identify valves to insure
installation in original location.
VALVE INSPECTION
(1) Clean valves thoroughly and discard burned,
warped and cracked valves.
(2) Measure valve stems for wear. Measure stem
about 60 mm beneath the valve lock grooves.
(3) If valve stems are worn more than 0.05 mm
(.002 in.), replace valve.
VALVE GUIDES
(1) Remove carbon and varnish deposits from
inside of valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner.
(2) Using a small hole gauge and a micrometer,
measure valve guides in 3 places top, middle and bot-
tom (Fig. 87). Refer to Valve Guide Specification
Chart for specifications. Replace guides if they are
not within specification.
(3) Check valve guide height (Fig. 88).
TESTING VALVE SPRINGS
(1) Whenever valves have been removed for inspec-
tion, reconditioning or replacement, valve springs
Fig. 84 Crankshaft DamperÐInstallation
Fig. 85 Oil Pressure Relief Valve
Fig. 86 Oil Pump
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 29
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1208 of 1938
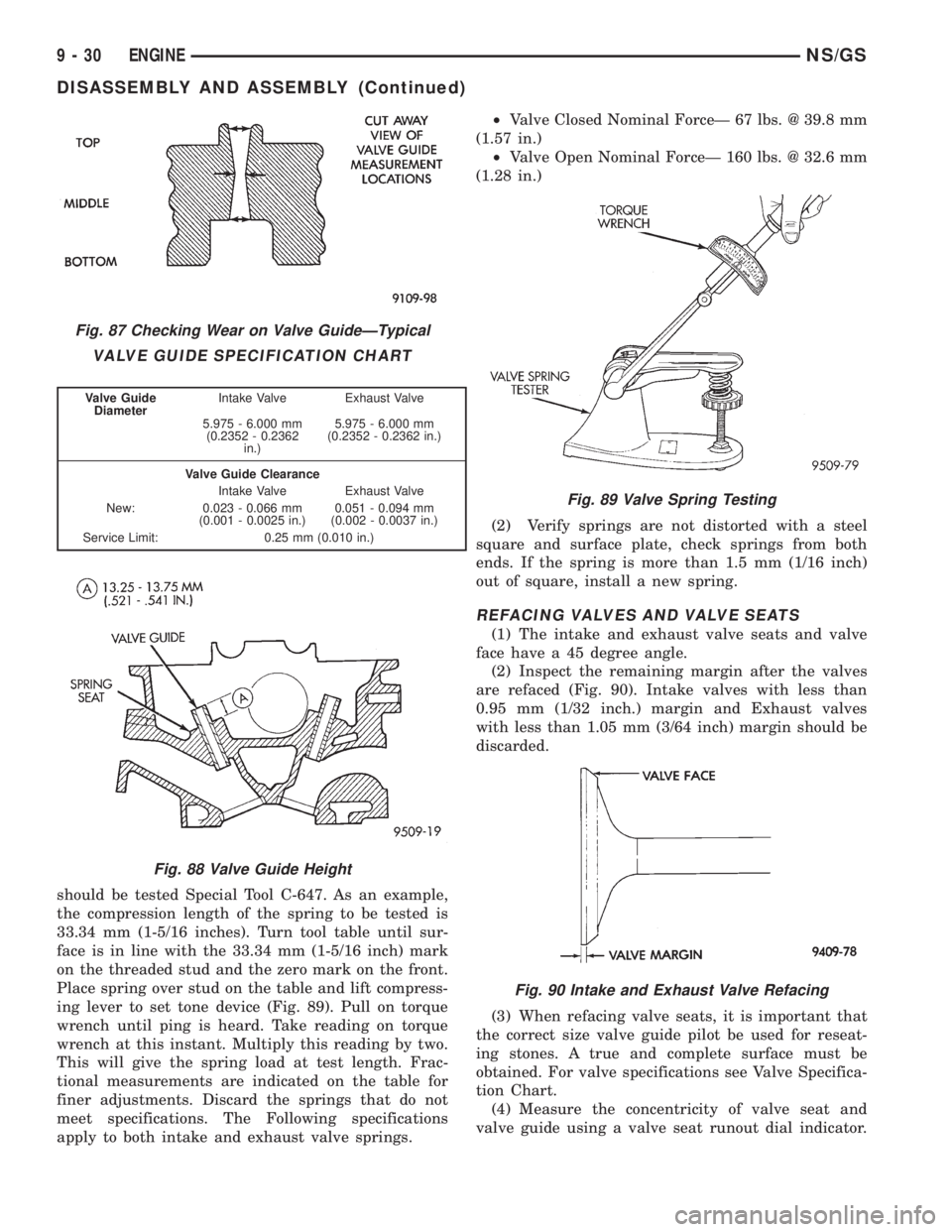
should be tested Special Tool C-647. As an example,
the compression length of the spring to be tested is
33.34 mm (1-5/16 inches). Turn tool table until sur-
face is in line with the 33.34 mm (1-5/16 inch) mark
on the threaded stud and the zero mark on the front.
Place spring over stud on the table and lift compress-
ing lever to set tone device (Fig. 89). Pull on torque
wrench until ping is heard. Take reading on torque
wrench at this instant. Multiply this reading by two.
This will give the spring load at test length. Frac-
tional measurements are indicated on the table for
finer adjustments. Discard the springs that do not
meet specifications. The Following specifications
apply to both intake and exhaust valve springs.²Valve Closed Nominal ForceÐ 67 lbs. @ 39.8 mm
(1.57 in.)
²Valve Open Nominal ForceÐ 160 lbs. @ 32.6 mm
(1.28 in.)
(2) Verify springs are not distorted with a steel
square and surface plate, check springs from both
ends. If the spring is more than 1.5 mm (1/16 inch)
out of square, install a new spring.
REFACING VALVES AND VALVE SEATS
(1) The intake and exhaust valve seats and valve
face have a 45 degree angle.
(2) Inspect the remaining margin after the valves
are refaced (Fig. 90). Intake valves with less than
0.95 mm (1/32 inch.) margin and Exhaust valves
with less than 1.05 mm (3/64 inch) margin should be
discarded.
(3) When refacing valve seats, it is important that
the correct size valve guide pilot be used for reseat-
ing stones. A true and complete surface must be
obtained. For valve specifications see Valve Specifica-
tion Chart.
(4) Measure the concentricity of valve seat and
valve guide using a valve seat runout dial indicator.
Fig. 87 Checking Wear on Valve GuideÐTypical
VALVE GUIDE SPECIFICATION CHART
Valve Guide
DiameterIntake Valve Exhaust Valve
5.975 - 6.000 mm
(0.2352 - 0.2362
in.)5.975 - 6.000 mm
(0.2352 - 0.2362 in.)
Valve Guide Clearance
Intake Valve Exhaust Valve
New: 0.023 - 0.066 mm
(0.001 - 0.0025 in.)0.051 - 0.094 mm
(0.002 - 0.0037 in.)
Service Limit: 0.25 mm (0.010 in.)
Fig. 88 Valve Guide Height
Fig. 89 Valve Spring Testing
Fig. 90 Intake and Exhaust Valve Refacing
9 - 30 ENGINENS/GS
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)