Page 1341 of 1938
ances the two solenoids to maintain the set speed.
Refer to Group 8H for speed control information.
TACHOMETERÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM supplies engine RPM to the instrument
panel tachometer through the CCD Bus. The CCD
Bus is a communications port. Various modules use
the CCD Bus to exchange information. Refer to
Group 8E for more information.
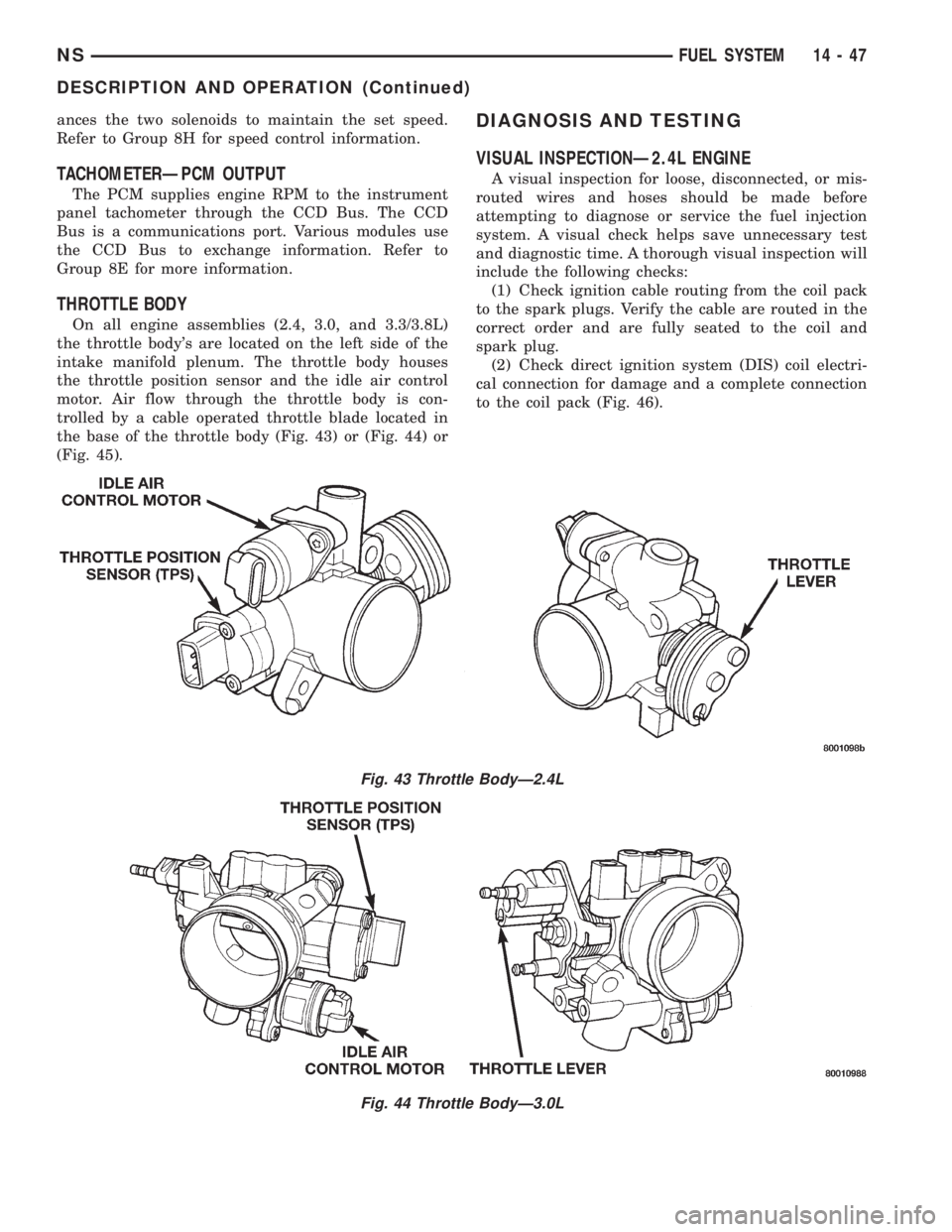
THROTTLE BODY
On all engine assemblies (2.4, 3.0, and 3.3/3.8L)
the throttle body's are located on the left side of the
intake manifold plenum. The throttle body houses
the throttle position sensor and the idle air control
motor. Air flow through the throttle body is con-
trolled by a cable operated throttle blade located in
the base of the throttle body (Fig. 43) or (Fig. 44) or
(Fig. 45).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
VISUAL INSPECTIONÐ2.4L ENGINE
A visual inspection for loose, disconnected, or mis-
routed wires and hoses should be made before
attempting to diagnose or service the fuel injection
system. A visual check helps save unnecessary test
and diagnostic time. A thorough visual inspection will
include the following checks:
(1) Check ignition cable routing from the coil pack
to the spark plugs. Verify the cable are routed in the
correct order and are fully seated to the coil and
spark plug.
(2) Check direct ignition system (DIS) coil electri-
cal connection for damage and a complete connection
to the coil pack (Fig. 46).
Fig. 43 Throttle BodyÐ2.4L
Fig. 44 Throttle BodyÐ3.0L
NSFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 47
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1342 of 1938
(3) Verify the camshaft position sensor electrical
connector is connected to the harness and not dam-
aged (Fig. 47).(4) Ensure the engine temperature sensor electri-
cal connector is connected to the sensor and not dam-
aged (Fig. 48).
(5) Verify the quick connect fuel fitting is fully
inserted on the fuel supply tube.
(6) Check the oil pressure sending unit electrical
connection.
(7) Verify the electrical connector at the knock sen-
sor is fully seated and not damaged (Fig. 49).
Fig. 45 Throttle BodyÐ3.3/3.8L
Fig. 46 Ignition Coil Pack Electrical Connection
Fig. 47 Camshaft Position Sensor
14 - 48 FUEL SYSTEMNS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1343 of 1938
(8) Verify the electrical connector is attached to
the Proportional purge solenoid (Fig. 50) and not
damaged.
(9) Verify the vacuum connection at the Propor-
tional purge solenoid is secure and not leaking.
(10) Verify the hoses are securely attached to the
EVAP canister (Fig. 51).(11) Ensure the harness connectors for the fuel
injectors are attached to the correct injector and not
damaged.
(12) Verify the fuel injector harness and engine
wiring harness connectors are fully inserted into the
main wiring harness.
(13) Check the vacuum connections at the throttle
body and intake plenum.
Fig. 48 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
Fig. 49 Knock Sensor
Fig. 50 Proportional Purge Solenoid
Fig. 51 Evaporative Canister
NSFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 49
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1344 of 1938
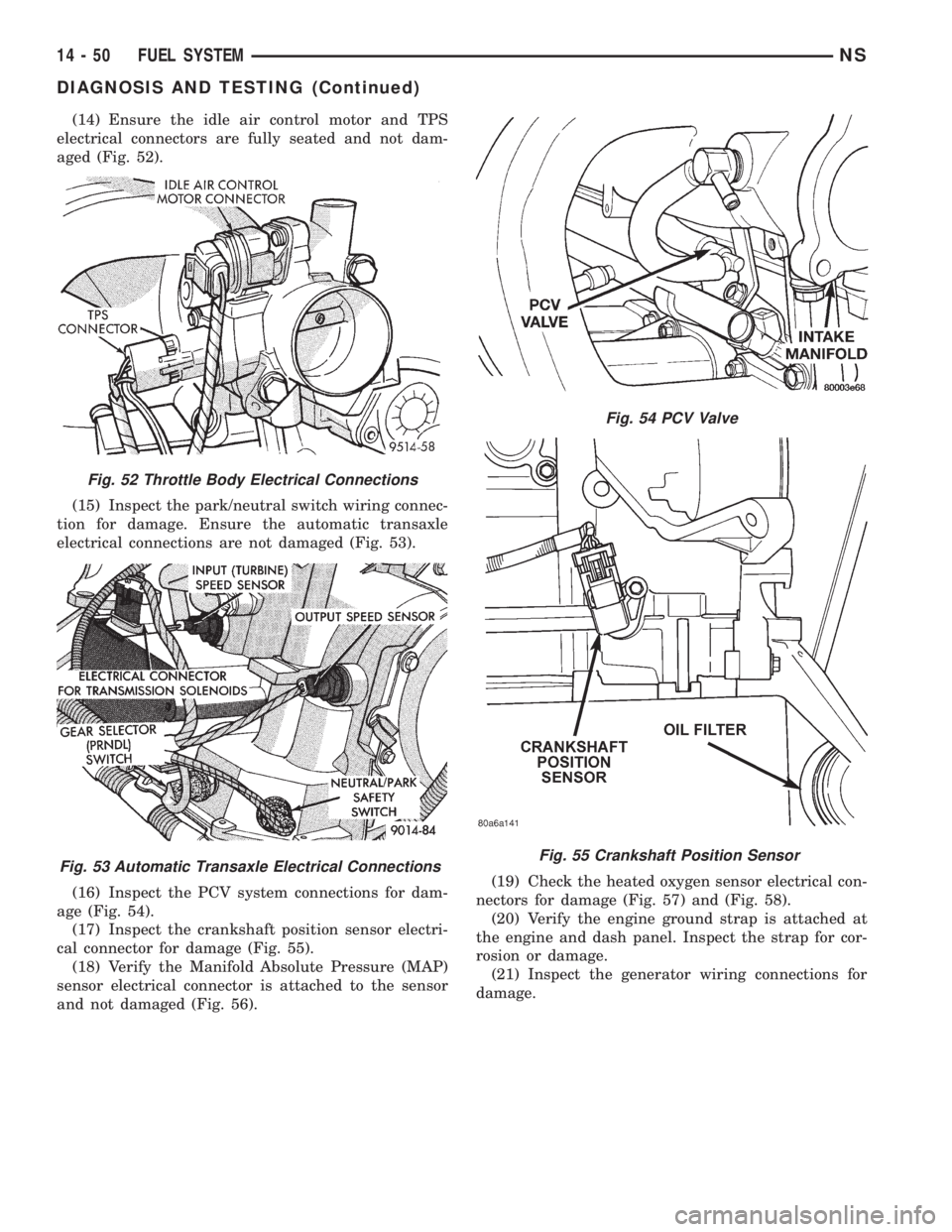
(14) Ensure the idle air control motor and TPS
electrical connectors are fully seated and not dam-
aged (Fig. 52).
(15) Inspect the park/neutral switch wiring connec-
tion for damage. Ensure the automatic transaxle
electrical connections are not damaged (Fig. 53).
(16) Inspect the PCV system connections for dam-
age (Fig. 54).
(17) Inspect the crankshaft position sensor electri-
cal connector for damage (Fig. 55).
(18) Verify the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
sensor electrical connector is attached to the sensor
and not damaged (Fig. 56).(19) Check the heated oxygen sensor electrical con-
nectors for damage (Fig. 57) and (Fig. 58).
(20) Verify the engine ground strap is attached at
the engine and dash panel. Inspect the strap for cor-
rosion or damage.
(21) Inspect the generator wiring connections for
damage.
Fig. 52 Throttle Body Electrical Connections
Fig. 53 Automatic Transaxle Electrical Connections
Fig. 54 PCV Valve
Fig. 55 Crankshaft Position Sensor
14 - 50 FUEL SYSTEMNS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1345 of 1938

(22) Check the accessory drive belt tension.
(23) Check the 40-way electrical connectors at the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) (Fig. 59) for dam-
age or spread terminals. Verify that the connectors
are fully inserted into the PCM sockets. Ensure the
wires are not stretched or pulled out of the connector.
(24) Inspect fuses in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Verify all fuses and relays are fully
inserted into the PDC (Fig. 60). A label affixed to the
underside of the PDC cover identifies the relays and
fuses in the PDC.(25) Inspect battery cable connections for corro-
sion.
(26) Check the power brake booster hose connec-
tion (without anti-lock brake systems) (Fig. 61).
(27) Inspect the speed control vacuum connection.
(28) Inspect hose and wiring connections at fuel
pump module. Check that wiring connector is making
contact with terminals on pump.
Fig. 56 Map Sensor
Fig. 57 Upstream Heated Oxygen Sensor
Fig. 58 Downstream Heated Oxygen Sensor
Fig. 59 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
Connectors
NSFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 51
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1347 of 1938

(5) Verify that the electrical connector is attached
to the MAP sensor (Fig. 64).
(6) Check generator wiring connections. Ensure
the accessory drive belt has proper tension.
(7) Verify that hoses are securely attached to the
evaporative canister (Fig. 65).
(8) Verify the engine ground strap is attached at
the engine and dash panel (Fig. 66).
(9) Ensure the heated oxygen sensor connector is
connected to the harness connector.
(10) Verify the distributor connector is connected
to the harness connector (Fig. 67).
(11) Verify the coolant temperature sensor connec-
tor is connected to the harness connector (Fig. 68).(12) Check vacuum hose connection at fuel pres-
sure regulator and intake plenum connector (Fig. 68).
Fig. 64 Map Sensor Electrical and Vacuum
Connections
Fig. 65 Evaporative Canister
Fig. 66 Engine Ground Strap
Fig. 67 Distributor Connector
Fig. 68 Coolant Temperature Sensor Electrical
Connections and Vacuum Hose Connections at the
Air Intake Plenum
NSFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 53
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1349 of 1938

terminals. Verify the connectors are fully inserted
into the socket of the PCM (Fig. 74). Ensure that
wires are not stretched or pulled out of the connector.
(24) Inspect fuses in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Verify all fuses and relays are fully
inserted into the PDC (Fig. 74). A label affixed to the
underside of the PDC cover identifies the relays and
fuses in the PDC.
(25) Check Battery Cable Connections.
(26) Check hose and wiring connections at fuel
pump module. Check that wiring connector is making
contact with terminals on pump.
VISUAL INSPECTIONÐ3.3/3.8L ENGINES
A visual inspection for loose, disconnected, or mis-
routed wires and hoses should be made before
attempting to diagnose or service the fuel injection
system. A visual check helps save unnecessary test
and diagnostic time. A thorough visual inspection will
include the following checks:
(1) Check ignition cable routing from the coil pack
to the spark plugs. Verify the cable are routed in the
correct order and are fully seated to the coil and
spark plug.(2) Check direct ignition system (DIS) coil electri-
cal connection for damage and a complete connection
to the coil pack (Fig. 75).
(3) Verify the camshaft position sensor electrical
connector is connected to the harness and not dam-
aged (Fig. 76).
(4) Ensure the engine temperature sensor electri-
cal connector is connected to the sensor and not dam-
aged (Fig. 77).
(5) Verify the quick connect fuel fitting is fully
inserted on the fuel supply tube.
(6) Check the oil pressure sending unit electrical
connection (Fig. 78).
Fig. 74 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
Fig. 75 Ignition Coil Pack Electrical Connection
Fig. 76 Camshaft Position Sensor
NSFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 55
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1350 of 1938
(7) Verify the electrical connector at the knock sen-
sor is fully seated and not damaged (Fig. 78).
(8) Verify the electrical connector is attached to
the Proportional purge solenoid (Fig. 79) and not
damaged.
(9) Verify the vacuum connection at the Propor-
tional purge solenoid is secure and not leaking (Fig.
79).(10) Verify the hoses are securely attached to the
EVAP canister (Fig. 80).
(11) Ensure the harness connectors for the fuel
injectors are attached to the correct injector and not
damaged.
(12) Verify the fuel injector harness and engine
wiring harness connectors are fully inserted into the
main wiring harness.
Fig. 77 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
Fig. 78 Knock Sensor and Oil Pressure Sending
Unit Electrical Connection
Fig. 79 Proportional Purge Solenoid
Fig. 80 Evaporative Canister
14 - 56 FUEL SYSTEMNS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)