1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 1923 of 1938

the amount of EGR supplied to the engine. This pro-
vides the correct amount of exhaust gas recirculation
for different operating conditions.
This system does not allow EGR at idle. The EGR
systems can operate at all coolant temperatures
above 60ÉF as long as the battery ambient tempera-
ture is above 7ÉF.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
EGR SYSTEM ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
The PCM performs an on-board diagnostic check of
the EGR system. The diagnostic system uses the
electronic EGR transducer for the system tests.
The diagnostic check activates only during selected
engine/driving conditions. When the conditions are
met, the PCM energizes the transducer solenoid to
disable the EGR. The PCM checks for a change in
the heated oxygen sensor signal. If the air-fuel mix-
ture goes lean, the PCM will attempt to enrichen the
mixture. The PCM registers a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) if the EGR system is not operating cor-
rectly. After registering a DTC, the PCM turns on the
malfunction indicator (Check Engine) lamp after 2
consecutive trips. There are 2 types of failures sensed
by the PCM. The first is a short or open in the elec-
trical solenoid circuit. The second is a mechanical
failure or loss of vacuum. The Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) indicates the need for service.
If a problem is indicated by the MIL and a DTC for
the EGR system is set, check for proper operation of
the EGR system. Use the System Test, EGR Gas
Flow Test. If the EGR system tests properly, check
the system using the DRB scan tool. Refer to
On-Board Diagnosis sections in this Group. Also,
refer to the DRB scan tool and the appropriate Pow-
ertrain Diagnostics Procedure manual.
EGR SYSTEM TEST
WARNING: APPLY PARKING BRAKE AND/OR
BLOCK WHEELS BEFORE TESTING THE EGR SYS-
TEM.
(1) Check the condition of all EGR system hoses
and tubes for leaks, cracks, kinks and hardening of
rubber hoses. Repair and correct these conditions
before performing any tests.
(2) Be sure the hoses at both the EGR valve and
EGR valve control are connected to the proper fit-
tings (Fig. 4).
(3) Be sure the electrical connector is firmly con-
nected at the valve control.
(4) To check EGR system operation, connect the
DRB scan tool to the 16±way data link connector.
The data link connector is located on the lower edge
of the instrument panel near the steering column.
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Pro-
cedures service manual for operation of the DRB
scan tool when diagnosing the EGR system.
(5) After checking the system with the DRB scan
tool, proceed to the following EGR Valve Leakage and
EGR Valve Control Tests and repair as necessary.
Fig. 3 Electric EGR Transducer Assembly
Fig. 4 EGR Value and EGR Value ÐTypical
NSEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 19
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1929 of 1938

EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
CONTENTS
page page
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMÐ
2.0L ENGINE.......................... 9
EXHAUST EMISSION CONTROLSÐ
2.5L DIESEL ENGINE................... 5ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICSÐ
2.5L DIESEL ENGINE................... 1
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICSÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE
INDEX
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONÐ
2.5L DIESEL ENGINE................... 1DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES............ 2
GENERAL INFORMATION
SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE
The 2.5L diesel Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
monitors and controls many different circuits in the
fuel injection pump and engine systems. If the PCM
senses a problem with a monitored circuit that indi-
cates an actual problem, a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) will be stored in the PCM's memory, and even-
tually will illuminate the Diesel Glow Plug lamp con-
stantly while the key is on. If the problem is
repaired, or is intermittent, the PCM will erase the
DTC after 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle con-
sists of starting the vehicle when the engine is cold,
then the engine to warms up to a certain tempera-
ture, and finally, the engine temperature falls to a
normal operating temperature, then the key is
turned off.
Certain criteria must be met for a DTC to be
entered into PCM memory. The criteria may be a
specific range of engine rpm, engine or fuel tempera-
ture and/or input voltage to the PCM. A DTC indi-
cates that the PCM has identified an abnormal
signal in a circuit or the system. A DTC may indicate
the result of a failure, but never identify the failed
component directly.
There are several operating conditions that the
PCM does not monitor and set a DTC for. Refer to
the following Monitored Circuits and Non±Monitored
Circuits in this section.
MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM can detect certain problems in the elec-
trical system.
Open or Shorted Circuit± The PCM can deter-
mine if sensor output (which is the input to PCM) is
within proper range. It also determines if the circuit
is open or shorted.
Output Device Current Flow± The PCM senses
whether the output devices are electrically connected.
If there is a problem with the circuit, the PCM
senses whether the circuit is open, shorted to ground
(±), or shorted to (+) voltage.
NON±MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM does not monitor the following circuits,
systems or conditions that could have malfunctions
that result in driveability problems. A DTC will not
be displayed for these conditions.
Fuel Pressure:Fuel pressure is controlled by the
fuel injection pump. The PCM cannot detect prob-
lems in this component.
Cylinder Compression:The PCM cannot detect
uneven, low, or high engine cylinder compression.
Exhaust System:The PCM cannot detect a
plugged, restricted or leaking exhaust system.
Fuel Injector Malfunctions:The PCM cannot
determine if the fuel injector is clogged, or the wrong
injector is installed. The fuel injectors on the diesel
engine arenot controlledby the PCM, although a
NS/GSEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM 25 - 1
Page 1930 of 1938

defective fuel injector sensoris monitoredby the
PCM.
Vacuum Assist:Leaks or restrictions in the vac-
uum circuits of vacuum assisted engine control sys-
tem devices are not monitored by the PCM.
PCM System Ground:The PCM cannot deter-
mine a poor system ground. However, a DTC may be
generated as a result of this condition.
PCM Connector Engagement:The PCM cannot
determine spread or damaged connector pins. How-
ever, a DTC may be generated as a result of this con-
dition.
HIGH AND LOW LIMITS
The PCM compares input signal voltages from each
input device. It will establish high and low limits
that are programmed into it for that device. If the
input voltage is not within specifications and other
DTC criteria are met, a DTC will be stored in mem-
ory. Other DTC criteria might include engine rpm
limits or input voltages from other sensors or
switches. The other inputs might have to be sensed
by the PCM when it senses a high or low input volt-
age from the control system device in question.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
On the following pages, a list of DTC's is provided
for the 2.5L diesel engine. A DTC indicates that the
PCM has recognized an abnormal signal in a circuitor the system. A DTC may indicate the result of a
failure, but most likely will not identify the failed
component directly.
ACCESSING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A stored DTC can be displayed through the use of
the DRB III scan tool. The DRB III connects to the
data link connector. The data link connector is
located under the instrument panel near bottom of
the steering column (Fig. 1).
ERASING TROUBLE CODES
After the problem has been repaired, use the DRB
III scan tool to erase a DTC.
Generic Scan
Tool CodeDRB III Scan Tool Display
P1112 Boost Pressure Sensor Signal High
Boost Pressure Sensor Signal Low
Boost Pressure Sensor Supply High
Boost Pressure Sensor Supply Low
Boost Pressure Sensor Plausibility
P0110 Intake Air Temperature Sensor Signal High
Intake Air Temperature Sensor Signal Low
P1685 Immobilizer Signal Lost
Invalid SKIM Message
P0115 Temperature of Engine Coolant SRC High Exceeded
Temperature of Engine Coolant SRC Low Exceeded
P0180 Fuel Temperature Sensor SRC High Exceeded
Fuel Temperature Sensor SRC Low Exceeded
P0400 EGR Open Circuit
EGR Short Circuit
P0500 Vehicle Speed Sensor PEC Frequency Too High
Vehicle Speed Sensor Signal SRC High Exceeded
Fig. 1 Data Link Connector LocationÐTypical
25 - 2 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMNS/GS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 1931 of 1938

Generic Scan
Tool CodeDRB III Scan Tool Display
P0725 Engine Speed Sensor Dynamic Plausibility
Engine Speed Sensor Over Speed Recognition
Engine Speed Sensor Static Plausibilty
P1105 Atmospheric Pressure Sensor SRC High Exceeded
Atmospheric Pressure Sensor SRC Low Exceeded
P1201 Needle Movement Sensor SRC High Exceeded
Needle Movement Sensor SRC Low Exceeded
P1220 Fuel Quantity Actuator Neg. Gov. Deviation Cold
Fuel Quantity Actuator Neg. Gov. Deviation Warm
Fuel Quantity Actuator Pos. Gov. Deviation Cold
Fuel Quantity Actuator Pos. Gov. Deviation Warm
P1225 Control Sleeve Sensor Signal High Exceeded
Control Sleeve Sensor Start End Pos. Not Attained
Control Sleeve Sensor Stop End Pos. Not Attained
P1230 Timing Governing Negative Governor Deviation
Timing Governing Positive Governor Deviation
P1515 Accelerator Pedal Sensor Signal High Exceeded
Accelerator Pedal Sensor Signal Low Exceeded
Accelerator Pedal Sensor Signal PWG Plaus With Low Idle Switch
Accelerator Pedal Sensor Signal PWG Plaus With Potentiometer
P1600 Battery Voltage SRC High Exceeded
P1605 Terminal #15 Plausibility After Startup
P1610 Regulator Lower Regulator Limit
Regulator Upper Regulator Limit
P1615 Microcontroller Gate-Array Monitoring
Microcontroller Gate-Array Watchdog
Microcontroller Prepare Fuel Quantity Stop
Microcontroller Recovery Was Occurred
Microcontrller Redundant Overrun Monitoring
P1630 Timing Solenoid Valve Controller Open Circuit
Timing Solenoid Valve Controller Short Circuit
P1635 Glow Relay Controller Open Circuit
Glow Relay Controller Short Circuit
P1650 Diagnostic Lamp Open Circuit
Diagnostic Lamp Short Circuit
P1655 A/C Control Short Circuit
A/C Control Open Circuit
P1660 Redundant Emer. Stop Plausibility In After-Run
Redundant Emer Stop Powerstage Defective
P1665 Cruise Status Indicator Lamp Short Circuit
P1680 EEPROM Plausibility Checksum Error for Adj.
EEPROM Plausibility Checksum Error in CC212
EEPROM Plausibility Communication With EEPROM
EEPROM Plausibility Func. Switch Wrong or Missing
NS/GSEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM 25 - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1932 of 1938
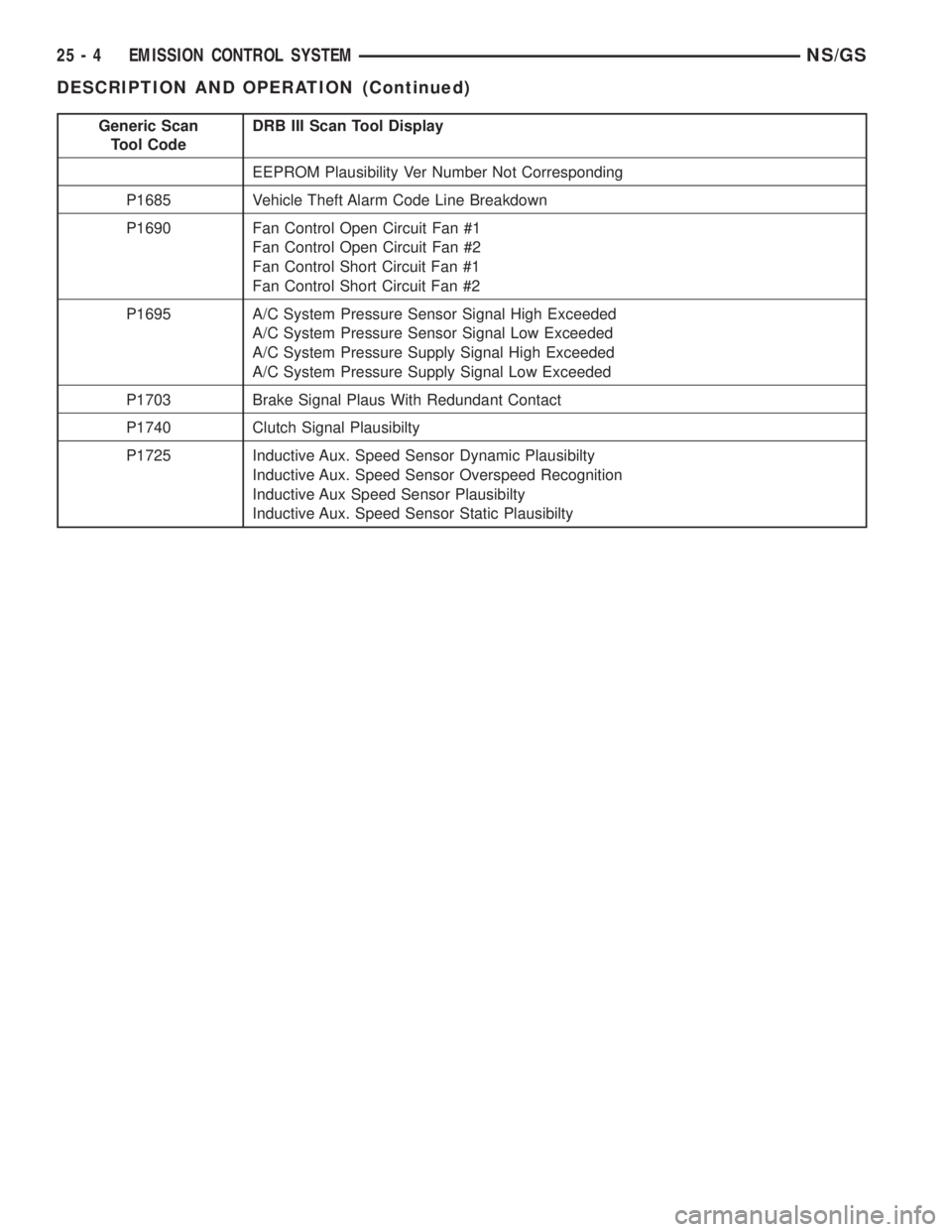
Generic Scan
Tool CodeDRB III Scan Tool Display
EEPROM Plausibility Ver Number Not Corresponding
P1685 Vehicle Theft Alarm Code Line Breakdown
P1690 Fan Control Open Circuit Fan #1
Fan Control Open Circuit Fan #2
Fan Control Short Circuit Fan #1
Fan Control Short Circuit Fan #2
P1695 A/C System Pressure Sensor Signal High Exceeded
A/C System Pressure Sensor Signal Low Exceeded
A/C System Pressure Supply Signal High Exceeded
A/C System Pressure Supply Signal Low Exceeded
P1703 Brake Signal Plaus With Redundant Contact
P1740 Clutch Signal Plausibilty
P1725 Inductive Aux. Speed Sensor Dynamic Plausibilty
Inductive Aux. Speed Sensor Overspeed Recognition
Inductive Aux Speed Sensor Plausibilty
Inductive Aux. Speed Sensor Static Plausibilty
25 - 4 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMNS/GS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)