1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 1169 of 1938
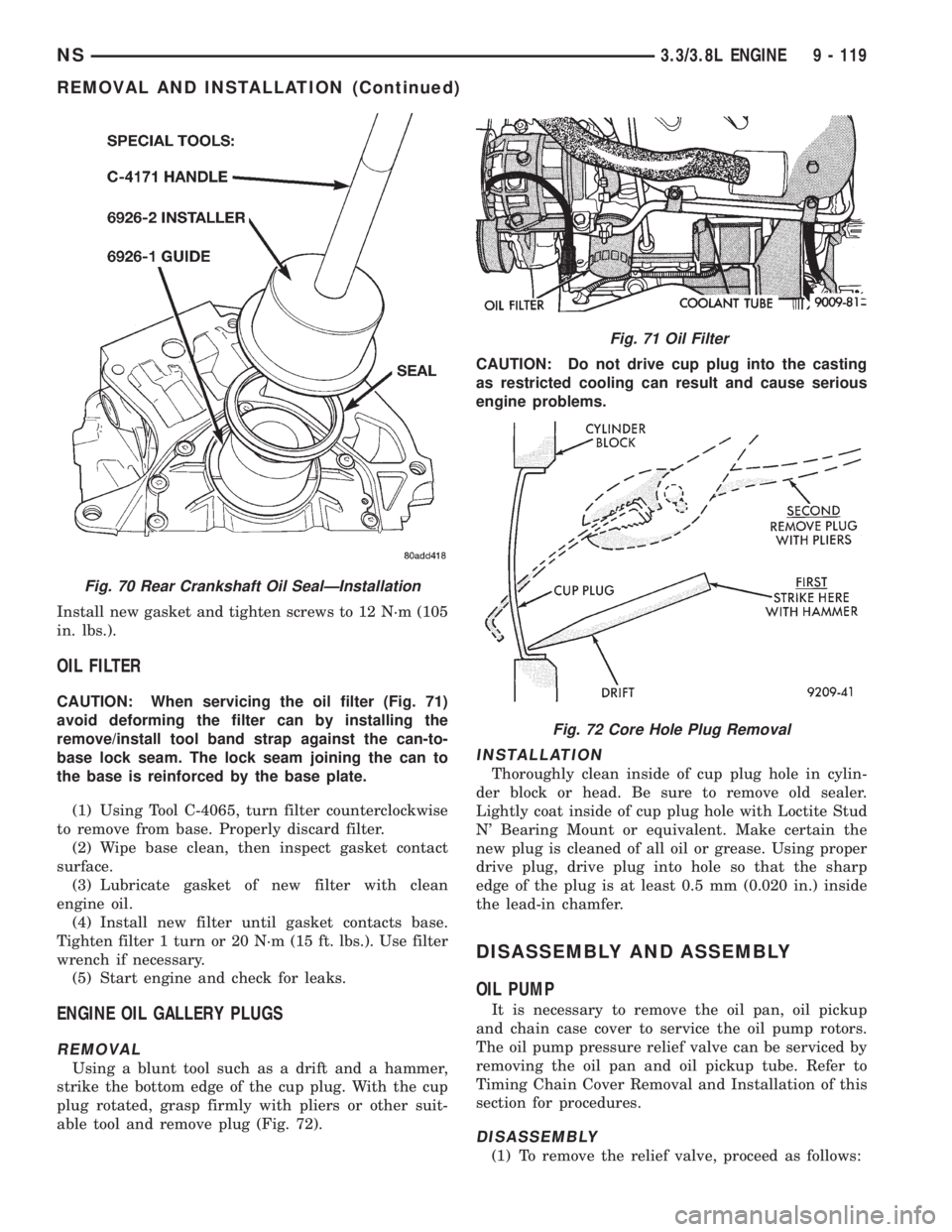
Install new gasket and tighten screws to 12 N´m (105
in. lbs.).
OIL FILTER
CAUTION: When servicing the oil filter (Fig. 71)
avoid deforming the filter can by installing the
remove/install tool band strap against the can-to-
base lock seam. The lock seam joining the can to
the base is reinforced by the base plate.
(1) Using Tool C-4065, turn filter counterclockwise
to remove from base. Properly discard filter.
(2) Wipe base clean, then inspect gasket contact
surface.
(3) Lubricate gasket of new filter with clean
engine oil.
(4) Install new filter until gasket contacts base.
Tighten filter 1 turn or 20 N´m (15 ft. lbs.). Use filter
wrench if necessary.
(5) Start engine and check for leaks.
ENGINE OIL GALLERY PLUGS
REMOVAL
Using a blunt tool such as a drift and a hammer,
strike the bottom edge of the cup plug. With the cup
plug rotated, grasp firmly with pliers or other suit-
able tool and remove plug (Fig. 72).CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting
as restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.
INSTALLATION
Thoroughly clean inside of cup plug hole in cylin-
der block or head. Be sure to remove old sealer.
Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole with Loctite Stud
N' Bearing Mount or equivalent. Make certain the
new plug is cleaned of all oil or grease. Using proper
drive plug, drive plug into hole so that the sharp
edge of the plug is at least 0.5 mm (0.020 in.) inside
the lead-in chamfer.
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
OIL PUMP
It is necessary to remove the oil pan, oil pickup
and chain case cover to service the oil pump rotors.
The oil pump pressure relief valve can be serviced by
removing the oil pan and oil pickup tube. Refer to
Timing Chain Cover Removal and Installation of this
section for procedures.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) To remove the relief valve, proceed as follows:
Fig. 70 Rear Crankshaft Oil SealÐInstallation
Fig. 71 Oil Filter
Fig. 72 Core Hole Plug Removal
NS3.3/3.8L ENGINE 9 - 119
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1170 of 1938

(2) Drill a 3.175 mm (1/8 inch) hole into the relief
valve retainer cap and insert a self-threading sheet
metal screw into cap.
(3) Clamp screw into a vise and while supporting
chain case cover, remove cap by tapping chain case
cover using a soft hammer. Discard retainer cap and
remove spring and relief valve (Fig. 73).
(4) Remove oil pump cover screws, and lift off
cover.
(5) Remove pump rotors.
(6) Wash all parts in a suitable solvent and inspect
carefully for damage or wear (Fig. 76).
OIL PUMP ASSEMBLY
(1) Assemble pump, using new parts as required.
Install the inner rotor with chamfer facing the
cast iron oil pump cover.
(2) Tighten cover screws to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(3) Prime oil pump before installation by filling
rotor cavity with engine oil.
(4) Install chain case cover. Refer to Timing Chain
Cover Installation of this section.
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Pry out plunger retainer spring clip (Fig. 74).
(2) Clean varnish deposits from inside of tappet
body above plunger cap.
(3) Invert tappet body and remove plunger cap,
plunger, flat or ball check valve, check valve spring,
check valve retainer and plunger spring. Check valve
could be flat or ball.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Clean all tappet parts in a solvent that will
remove all varnish and carbon.
(2) Replace tappets that are unfit for further ser-
vice with new assemblies.(3) If plunger shows signs of scoring or wear, valve
is pitted, or valve seat on end of plunger indicates
any condition that would prevent valve from seating,
install a new tappet assembly.
(4) Assemble tappets (Fig. 74).
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CYLINDER HEAD
(1) Before cleaning, check for leaks, damage and
cracks.
(2) Clean cylinder head and oil passages.
(3) Check cylinder head for flatness (Fig. 75).
(4) Inspect all surfaces with a straightedge if there
is any reason to suspect leakage. If out of flatness
exceeds 0.019 mm (0.00075 in.) times the span length
in inches, in any direction, either replace head or
lightly machine the head surface. As an example, if a
12 inch span is 0.1 mm (.004 in.) out of flat, allow-
able is 12 x .019 mm (.00075 in.) equals .22 mm (.009
in.) This amount of out of flat is acceptable. Maxi-
mum of 0.2 mm (.008 in.) for grinding is permitted.
CAUTION: This is a combined total dimension of
stock removal from cylinder head and block top
surface.
Fig. 73 Oil Pressure Relief Valve
Fig. 74 Hydraulic Roller Tappet Assembly
Fig. 75 Check Cylinder Head
9 - 120 3.3/3.8L ENGINENS
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1171 of 1938

OIL PAN
(1) Clean oil pan in solvent and wipe dry with a
clean cloth. Clean all gasket material from mounting
surfaces of pan and block.
(2) Inspect oil drain plug and plug hole for
stripped or damaged threads and repair as necessary.
Install a new drain plug gasket. Tighten to 27 N´m
(20 ft. lbs.).
(3) Inspect oil pan mounting flange for bends or
distortion. Straighten flange if necessary.
(4) Clean oil screen and pipe in clean solvent.
Inspect condition of screen.
OIL PUMP
INSPECTION AND REPAIR
(1) Clean all parts thoroughly. Mating surface of
the chain case cover should be smooth. Replace pump
cover if scratched or grooved.
(2) Lay a straightedge across the pump cover sur-
face (Fig. 77). If a 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) feeler gauge
can be inserted between cover and straight edge,
cover should be replaced.
(3) Measure thickness and diameter of outer rotor.
If outer rotor thickness measures 7.64 mm (0.301 in.)
or less (Fig. 78), or if the diameter is 79.95 mm
(3.148 inches.) or less, replace outer rotor.
(4) If inner rotor measures 7.64 mm (0.301 in.) or
less replace inner rotor (Fig. 79).
(5) Slide outer rotor into chain case cover, press to
one side with fingers and measure clearance between
rotor and chain case cover (Fig. 80). If measurement
is 0.39 mm (0.015 in.) or more, replace CCC only if
outer rotor is in specification.
(6) Install inner rotor into chain case cover. If
clearance between inner and outer rotors (Fig. 81) is
0.203 mm (0.008 in.) or more, replace both rotors.
(7) Place a straightedge across the face of the
chain case cover, between bolt holes. If a feeler gaugeof 0.10 mm (0.004 in.) or more can be inserted
between rotors and the straightedge, replace pump
assembly (Fig. 82).ONLYif rotors are in specs.
(8) Inspect oil pressure relief valve plunger for
scoring and free operation in its bore. Small marks
may be removed with 400-grit wet or dry sandpaper.
(9) The relief valve spring has a free length of
approximately 49.5 mm (1.95 inches) it should test
between 19.5 and 20.5 pounds when compressed to
34 mm (1-11/32 inches). Replace spring that fails to
meet specifications (Fig. 73).
(10) If oil pressure is low and pump is within spec-
ifications, inspect for worn engine bearings or other
reasons for oil pressure loss.
ENGINE BLOCK AND BORE
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
(1) Clean cylinder block thoroughly and check all
core hole plugs for evidence of leaking.
Fig. 76 Oil Pump
Fig. 77 Checking Oil Pump Cover Flatness
Fig. 78 Measuring Outer Rotor Thickness
NS3.3/3.8L ENGINE 9 - 121
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)
Page 1172 of 1938
(2) If new core plugs are installed, see Engine Core
Oil and Cam Plugs.
(3) Examine block for cracks or fractures.
CYLINDER BORE INSPECTION
The cylinder walls should be checked for out-of-
round and taper with Tool C-119 (Fig. 83). If the cyl-
inder walls are badly scuffed or scored, the cylinder
block should be replaced.
Measure the cylinder bore at three levels in direc-
tions A and B (Fig. 83). Top measurement should be
12 mm (0.50 in.) down and bottom measurement
should be 12 mm (0.50 in.) up from bottom of bore.
Refer to Cylinder Bore and Piston Specification
Chart.
Fig. 79 Measuring Inner Rotor Thickness
Fig. 80 Measuring Outer Rotor Clearance in
Housing
Fig. 81 Measuring Clearance Between Rotors
Fig. 82 Measuring Clearance Over Rotors
Fig. 83 Checking Cylinder Bore Size
9 - 122 3.3/3.8L ENGINENS
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)
Page 1173 of 1938

ADJUSTMENTS
ENGINE MOUNTS
ENGINE MOUNT INSULATOR ADJUSTMENT
(1) Remove the load on the engine motor mounts
by carefully supporting the engine and transmission
assembly with a floor jack.
(2) Loosen the right engine mount insulator verti-
cal fastener and the fore and aft fasteners, and the
front engine mount bracket to front crossmember
screws.
(3) Pry the engine right or left as required to
achieve the proper drive shaft assembly length. Refer
to Group 2, Suspension and Driveshafts for drive-
shaft identification and related assembly length mea-
suring.
(4) Tighten engine mounts and fasteners in the
following order:
(a) Right engine mount insulator vertical bolts
to 102 N´m (75 ft. lbs.) and the fore and aft bolts to
150 N´m (110 ft. lbs.).
(b) Front engine mount screws to 54 N´m (40 ft.
lbs.) the clearance between the snubbers and the
engine should be 2 mm (0.078 inch.) each side.
(c) Left engine mount through bolt to 75 N´m (55
ft. lbs.).
(5) Recheck driveshaft length.
SPECIFICATIONS
3.3/3.8L ENGINE
Type.........................60É V-6 Engine
Bore±3.3L..................93.0 mm (3.66 in.)
Bore±3.8L.................96.0 mm (3.779 in.)
Stroke±3.3L...............81.0 mm (3.188 in.)
Stroke±3.8L...............87.0 mm (3.425 in.)
Compression Ratio±3.3L.................8.9:1
Compression Ratio±3.8L.................9.6:1
Displacement±3.3L..........3.3L (201 Cubic in.)
Displacement±3.8L..........3.8L (231 Cubic in.)
Brake Horsepower±3.3L........158 @ 4850 RPM
Brake Horsepower±3.8L........180 @ 4400 RPM
Torque±3.3L............203 lb. ft. @ 3600 RPM
Torque±3.8L............240 lb. ft. @ 3600 RPM
Firing Order....................1±2±3±4±5±6
Compression Pressure.Refer to Engine Performance
in Standard Service Procedures.
Cylinder Number (Front to Rear)
Front Bank...........................2,4,6
Rear Bank............................1,3,6
Cylinder Block
Cylinder Bore (Standard)±3.3L.........93.0 mm
(3.66 in.)
Cylinder Bore (Standard)±3.8L.........96.0 mm
(3.779 in.)
Out-of-Round (Max.)........0.076 mm (0.003 in.)
Taper (Max.)..............0.051 mm (0.002 in.)
Cylinder Bore Oversize (Max.).........0.508 mm
(0.020 in.)
Tappet Bore Diameter.....22.9896 - 23.0099 mm
(0.9051 - 0.9059 in.)
Pistons
Type Material.......Aluminum Alloy Tin Coated
Clearance at Size Location......0.025 - 0.057 mm
(0.001 - 0.0022 in.)
Weight (Standard Only)±3.3L......38165 grams
(13.439460.1764 oz.)
Weight (Standard Only)±3.8L......43865 grams
(15.450160.1764 oz.)
Pistons for Service..............Standard Only
Piston Pins
Type .......................Press Fit in Rod
(Serviced as an Assembly)
Diameter.........................22.88 mm
(0.9009 - 0.9007 in.)
Length±3.3L................67.25 - 67.75 mm
(2.648 - 2.667 in.)
Lenth±3.8L.................71.25 - 71.75 mm
(2.805 - 2.824 in.)
Clearance in Piston @ 70É......0.006 - 0.019 mm
(0.0002 - 0.0007 in.)
Clearance in Rod................(Interference)
CYLINDER BORE AND PISTON
SPECIFICATION CHART
EngineStandard
BoreMaximum
Out-Of-
RoundMaximum
Taper
3.3L 92.993 -
93.007 mm0.076 mm 0.51 mm
(3.661 -
3.6617 in.)(0.003 in.) (0.002 in.)
3.8L 95.993 -
96.007 mmSame Same
3.7792 -
3.780 in.
Standard Piston Size
3.3L 92.950 - 92.968 mm
(3.6594 - 3.6602 in.)
3.8L 95.950 - 95.968 mm
(3.7776 - 3.7783 in.)
Piston to Bore Clearance: 0.025 - 0.057 mm
(0.0009 - 0.0022 in.)
Measurements taken at Piston Size Location.
NS3.3/3.8L ENGINE 9 - 123
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)
Page 1179 of 1938

ENGINE
CONTENTS
page page
2.0L SOHC ENGINE...................... 12.5L VM DIESEL....................... 40
2.0L SOHC ENGINE
INDEX
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ENGINE COMPONENTS.................. 3
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION................. 1
ENGINE LUBRICATION SYSTEM............ 2
GENERAL SPECIFICATION................ 2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE........ 3
SERVICE PROCEDURES
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY................. 6
CYLINDER BORE AND PISTON SIZING....... 4
FITTING CONNECTING RODS.............. 5
FITTING CRANKSHAFT BEARINGS.......... 6
FITTING PISTON RINGS.................. 4
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL................... 12
CAMSHAFT............................ 7
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEALÐREAR........... 20
CRANKSHAFT......................... 21
CYLINDER HEAD COVER................. 6
CYLINDER HEAD....................... 10
FRONT CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL........... 18
OILFILTER ........................... 24
OIL FILTER ADAPTER................... 24OILPAN .............................. 17
OIL PUMP............................ 25
PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD.......... 25
ROCKER ARM/HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTER . . 8
SPARK PLUG TUBE...................... 7
TIMING BELT COVER................... 11
TIMING BELT SYSTEM.................. 13
VALVE SEALS AND SPRINGS IN VEHICLE . . . 10
VIBRATION DAMPER.................... 28
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
OIL PUMP............................ 29
VALVE SERVICE WITH THE CYLINDER HEAD
REMOVED.......................... 29
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CYLINDER BLOCK AND BORE............ 34
CYLINDER HEAD AND CAMSHAFT
JOURNALS.......................... 32
OIL PUMP............................ 32
SPECIFICATIONS
ENGINE 2.0L SOHC..................... 34
TORQUE CHART 2.0L SOHC.............. 36
SPECIAL TOOLS
ENGINE 2.0L SOHC..................... 36
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION
The engine identification number is located on the
left rear of the cylinder block behind starter (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 Engine Identification SOHC
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 1
Page 1181 of 1938

SPLASH LUBRICATION
Oil returning to the pan from pressurized compo-
nents supplies lubrication to the valve stems. Cylin-
der bores and wrist pins are splash lubricated from
directed slots on the connecting rod thrust collars.
ENGINE COMPONENTS
CYLINDER BLOCK AND BEDPLATE ASSEM-
B LY:A partial open deck is used for cooling and
weight reduction with water pump molded into the
block. Nominal wall thickness is 4 mm. The bedplate
incorporates main bearing caps. Rear seal retainer is
integral with the block.
CRANKSHAFT:A nodular cast iron crankshaft is
used. The engine has 5 main bearings, with number
3 flanged to control thrust. The 52 mm diameter
main and 48 mm diameter crank pin journals (all)
have undercut fillet radiuses that are deep rolled for
added strength. To optimize bearing loading 8 coun-
terweights are used. Hydrodynamic seals provide end
sealing, where the crankshaft exits the block.
Anaerobic gasket material is used for parting line
sealing. A sintered iron timing belt sprocket is
mounted on the crankshaft nose. This sprocket trans-
mits crankshaft movement, via timing belt to the
camshaft sprocket providing timed valve actuation.
PISTONS:The SOHC EngineDOES NOThave
provision for a free wheeling valve train. Non free
wheeling valve train means, in the event of a broken
timing belt Pistons will contact the Valves. All
engines use pressed-in piston pins to attach forged
powdered metal connecting rods. The connecting rods
are a cracked cap design and are not repairable. Hexhead cap screw are used to provide alignment and
durability in the assembly. Pistons And Connecting
rods are serviced as an assembly.
PISTON RINGS:The piston rings include a
molybdenum faced top ring for reliable compression
sealing and a taper faced intermediate ring for addi-
tional cylinder pressure control. Oil Control Ring
Package consist of 2 steel rails and a expander
spacer.
CYLINDER HEADÐSOHC:It features a Single
Over Head Camshaft, four-valves per cylinder cross
flow design. The valves are arranged in two inline
banks, with the two intake per cylinder facing
toward the radiator. The exhaust valves facing
toward the dash panel. Rocker arm shafts mount
directly to the cylinder head. It incorporates powder
metal valve guides and seats. The hollow rocker arm
shafts supplies oil to the hydraulic lash adjusters,
camshaft and valve mechanisms.
CAMSHAFTÐSOHC:The nodular iron camshaft
has five bearing journals and 3 cam lobes per cylin-
der. Provision for cam position sensor on the cam at
the rear of cylinder head which also acts as thrust
plate. A hydrodynamic oil seal is used for oil control
at the front of the camshaft.
VALVESÐSOHC:Four valves per cylinder are
actuated by roller rocker arms/hydraulic lash adjust-
ers assemblies which pivot on rocker arm shafts. All
valves have 6 mm diameter chrome plated valve
stems. The valve train has 33 mm (1.299 inch) diam-
eter intake valves and 28 mm (1.10 inch) diameter
exhaust valves. Viton rubber valve stem seals are
integral with spring seats. Valve springs, spring
retainers, and locks are conventional design.
INTAKE MANIFOLD:The intake manifold is a
molded plastic composition, attached to the cylinder
head with ten fasteners. This long branch design
enhances low and mid-range torque.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD:The exhaust manifold is
made of nodular cast iron for strength and high tem-
peratures. Exhaust gasses exit through a machined,
articulated joint connection to the exhaust pipe.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure switch and install gauge
assembly C-3292 with adaptor.
(2) Run engine until thermostat opens.
CAUTION: If oil pressure is 0 at idle, Do Not per-
form the 3000 RPM test in the next step.
(3) Oil Pressure:Curb Idle25 kPa (4 psi) mini-
mum3000 RPM170-550 kPa (25-80 psi).
Fig. 2 Engine Lubrication SystemÐ SOHC
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1182 of 1938

(4) If oil pressure is 0 at idle. Shut off engine,
check for pressure relief valve stuck open, a clogged
oil pick-up screen or a damaged oil pick-up tube
O-ring.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
CYLINDER BORE AND PISTON SIZING
The cylinder walls should be checked for out-of-
round and taper with Tool C-119 (Fig. 3). The cylin-
der bore out-of-round is 0.050 mm (.002 inch)
maximum and cylinder bore taper is 0.051 mm (0.002
inch) maximum. If the cylinder walls are badly
scuffed or scored, the cylinder block should be
rebored and honed, and new pistons and rings fitted.
Whatever type of boring equipment is used, boring
and honing operation should be closely coordinated
with the fitting of pistons and rings in order that
specified clearances may be maintained.Refer to
Honing Cylinder Bores outlined in the Stan-
dard Service Procedures for specification and
procedures.
Measure the cylinder bore at three levels in direc-
tions A and B (Fig. 3). Top measurement should be
10 mm (3/8 inch) down and bottom measurement
should be 10 mm (3/8 inch.) up from bottom of bore.
Refer to Cylinder Bore and Piston Specifications
Chart.
SIZING PISTONS
Piston and cylinder wall must be clean and dry.
Piston diameter should be measured 90 degrees to
piston pin about 17.5 mm (11/16 inch) from the bot-tom of the skirt as shown in (Fig. 4). Cylinder bores
should be measured halfway down the cylinder bore
and transverse to the engine crankshaft center line
shown in (Fig. 3). Refer to Cylinder Bore and Speci-
fications Table. Correct piston to bore clearance must
be established in order to assure quiet and economi-
cal operation.
Chrysler engines use pistons designed specifically
for each engine model. Clearance and sizing locations
vary with respect to engine model.
NOTE: Pistons and cylinder bores should be mea-
sured at normal room temperature, 21ÉC (70ÉF).
FITTING PISTON RINGS
(1) Wipe cylinder bore clean. Insert ring and push
down with piston to ensure it is square in bore. The
ring gap measurement must be made with the ring
positioning at least 12 mm (0.50 inch) from bottom of
cylinder bore. Check gap with feeler gauge (Fig. 5).
Refer to Piston Ring Specification Chart.
Fig. 3 Checking Cylinder Bore Size
CYLINDER BORE AND PISTON
SPECIFICATION CHART
Standard Bore Maximum
Out-of-RoundMaximum
Taper
87.5 mm
(3.445 in.)0.051 mm
(0.002 in.)0.051 mm
(0.002 in.)
Standard Piston Size
Federal
Emission:87.463 - 87.481 mm
(3.4434 - 3.4441 in.)
Low Emission
Vehicle (LEV):87.456 - 87.474 mm
(3.4432 - 3.4439 in.)
Piston to Bore Clearance
Federal
Emission:0.012 - 0.044 mm
(0.0004 - 0.0017 in.)
Low Emission
Vehicle (LEV):0.18 - 0.050 mm
(0.0008 - 0.0020 in.)
Measurements Taken at Piston Size Location
Fig. 4 Piston Measurements
9 - 4 ENGINENS/GS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)