1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER check oil
[x] Cancel search: check oilPage 1137 of 1938

CAUTION: This is a combined total dimension of
stock removal from cylinder head if any and block
top surface.
CYLINDER BORE
INSPECTION
(1) Measure the cylinder bore at three levels in
directions A and B (Fig. 77). Top measurementshould be 12 mm (0.50 in.) down and bottom mea-
surement should be 10 mm (0.38 in.) up.
(2) Standard bore dimension: 91.1 mm (3.587 in.)
(3) Maximum out-of-round or taper: 0.02 mm
(0.0008 in.).
OIL PUMP
(1) Check oil pump case for damage. Remove rear
oil pump cover.
(2) Remove pump rotors and inspect case for exces-
sive wear.
(3) Measure clearance between case and inner
rotor (Fig. 78).
(4) Insert the rotor into the oil pump case and
measure clearance between outer rotor and case with
a feeler gauge (Fig. 79). Replace if out of specifica-
tions.
Fig. 74 Timing Belt Inspection
Fig. 75 Timing Belt Covers
Fig. 76 Check Cylinder Head
Fig. 77 Checking Cylinder Bore Size
NS3.0L ENGINE 9 - 87
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)
Page 1138 of 1938
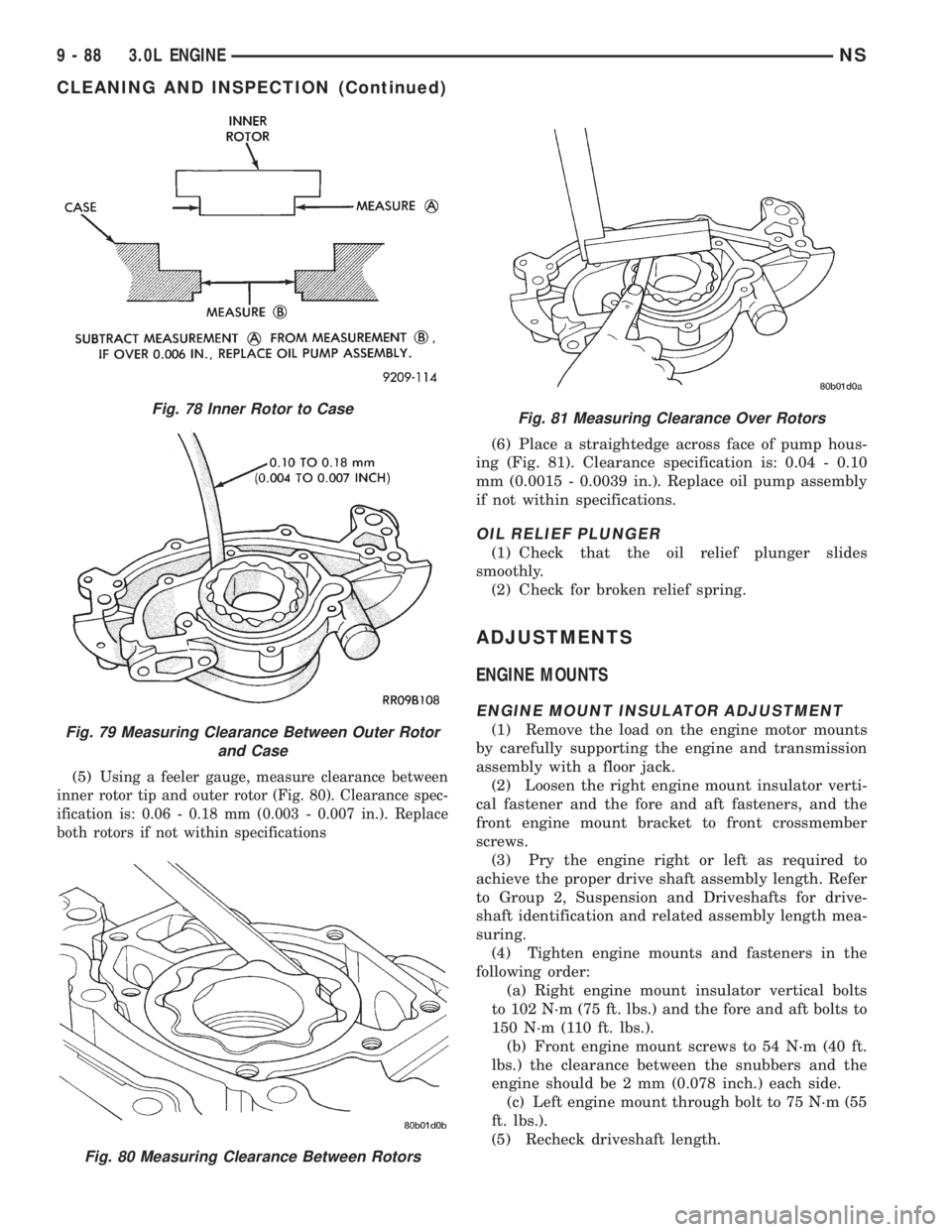
(5)Using a feeler gauge, measure clearance between
inner rotor tip and outer rotor (Fig. 80). Clearance spec-
ification is: 0.06 - 0.18 mm (0.003 - 0.007 in.). Replace
both rotors if not within specifications
(6) Place a straightedge across face of pump hous-
ing (Fig. 81). Clearance specification is: 0.04 - 0.10
mm (0.0015 - 0.0039 in.). Replace oil pump assembly
if not within specifications.
OIL RELIEF PLUNGER
(1) Check that the oil relief plunger slides
smoothly.
(2) Check for broken relief spring.
ADJUSTMENTS
ENGINE MOUNTS
ENGINE MOUNT INSULATOR ADJUSTMENT
(1) Remove the load on the engine motor mounts
by carefully supporting the engine and transmission
assembly with a floor jack.
(2) Loosen the right engine mount insulator verti-
cal fastener and the fore and aft fasteners, and the
front engine mount bracket to front crossmember
screws.
(3) Pry the engine right or left as required to
achieve the proper drive shaft assembly length. Refer
to Group 2, Suspension and Driveshafts for drive-
shaft identification and related assembly length mea-
suring.
(4) Tighten engine mounts and fasteners in the
following order:
(a) Right engine mount insulator vertical bolts
to 102 N´m (75 ft. lbs.) and the fore and aft bolts to
150 N´m (110 ft. lbs.).
(b) Front engine mount screws to 54 N´m (40 ft.
lbs.) the clearance between the snubbers and the
engine should be 2 mm (0.078 inch.) each side.
(c) Left engine mount through bolt to 75 N´m (55
ft. lbs.).
(5) Recheck driveshaft length.
Fig. 78 Inner Rotor to Case
Fig. 79 Measuring Clearance Between Outer Rotor
and Case
Fig. 80 Measuring Clearance Between Rotors
Fig. 81 Measuring Clearance Over Rotors
9 - 88 3.0L ENGINENS
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)
Page 1143 of 1938

3.3/3.8L ENGINE
INDEX
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ENGINE COMPONENTS.................. 93
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION................. 93
ENGINE LUBRICATION SYSTEM............ 93
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE......... 96
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS.................... 94
SERVICE PROCEDURES
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY................. 99
FITTING CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS...... 97
FITTING MAIN BEARINGS................. 98
FITTING PISTONS AND RINGS............. 97
MEASURING TIMING CHAIN FOR STRETCH . . . 96
VALVE SERVICE RECONDITION........... 100
VALVE TIMING.......................... 96
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
CAMSHAFT BEARINGS.................. 114
CAMSHAFT........................... 113
CRANKSHAFT DAMPER................. 106
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEALÐFRONT.......... 117
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEALÐREAR........... 118
CRANKSHAFT......................... 116
CYLINDER HEAD COVER................ 107
CYLINDER HEAD....................... 108
ENGINE ASSEMBLY..................... 104
ENGINE MOUNTS...................... 102
ENGINE OIL GALLERY PLUGS............. 119OILFILTER ............................ 119
OILPAN .............................. 114
PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD.......... 115
ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFT ASSEMBLY..... 106
TAPPET REMOVAL...................... 110
TIMING CHAIN COVER................... 111
TIMING CHAIN......................... 112
VALVE STEM SEALS OR SPRINGS,
CYLINDER HEAD NOT REMOVED........ 106
VALVES AND VALVE SPRINGS............ 109
WIPER UNIT.......................... 102
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS................... 120
OIL PUMP............................ 119
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CYLINDER HEAD....................... 120
ENGINE BLOCK AND BORE............... 121
OILPAN .............................. 121
OIL PUMP............................ 121
ADJUSTMENTS
ENGINE MOUNTS...................... 123
SPECIFICATIONS
3.3/3.8L ENGINE....................... 123
TORQUE CHART....................... 125
SPECIAL TOOLS
3.3/3.8L ENGINE....................... 127
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION
The engine identification number is located on the
rear of the cylinder block just below the cylinder
head (Fig. 1).
ENGINE LUBRICATION SYSTEM
The lubrication system is a full flow filtration pres-
sure feed type. Oil from the oil pan is pumped by a
internal gear type oil pump directly coupled to the
crankshaft. The pressure is regulated by a relief
valve located in the chain case cover. The oil is
pumped through an oil filter and feeds a main oil
galley. This oil gallery feeds oil under pressure to the
main and rod bearings, camshaft bearings. Passages
in the cylinder block feed oil to the hydraulic lifters
and rocker shaft brackets which feeds the rocker arm
pivots (Fig. 2).
ENGINE COMPONENTS
ENGINE:The 3.3L (201 Cubic Inches) and 3.8L
(231 Cubic Inches) displacement engines are 60É V
type six cylinder power plants with cast iron cylinder
blocks and aluminum cylinder heads (Fig. 3). Firing
order for these engines is 1-2-3-4-5-6. High turbu-
lence cylinder heads allow a 8.9-1 compression ratio.
CRANKSHAFT:The nodular iron crankshaft is
supported by four main bearings, with number two
being the thrust bearing. Crankshaft end sealing is
provided by front and rear rubber seals.
PISTONS:The pistons are cast aluminum alloy.
Three rings are used. Piston pins, press fitted into
place, join the pistons to forged steel connecting rods.
CAMSHAFT:The nodular iron camshaft is
mounted in four steel backed babbitt bearings. A
thrust plate located in front of the first bearing, and
bolted to the block, controls end play. Silent timing
chain drives the camshaft. This chain is enclosed by
a cast aluminum cover which also carries a front
NS3.3/3.8L ENGINE 9 - 93
Page 1145 of 1938

aligning yokes. The yokes are secured by an align-
ment yoke retainer (Fig. 4).
PRELIMINARY STEP TO CHECKING THE
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS
Before disassembling any part of the engine to cor-
rect tappet noise, read the oil pressure at the gauge.
Install a reliable gauge at pressure sending unit if
vehicle has no oil pressure gauge and check the oil
level in the oil pan. The pressure should be between
30 and 80 psi (206.8 to 551.6 kPa) at 2000 rpm.
The oil level in the pan should never be above the
MAX mark on dipstick, or below the MIN mark.
Either of these two conditions could be responsible
for noisy tappets.Oil Level Check: stop engineafter reaching normal operating temperature.
Allow 5 minutes to stabilize oil level, check dipstick.
OIL LEVEL TOO HIGH
If oil level is above the MAX mark on dip stick, it
is possible for the connecting rods to dip into the oil
while engine is running and create foam. Foam in oil
pan would be fed to the hydraulic tappets by the oil
pump causing them to become soft and allow valves
to seat noisily.
OIL LEVEL TOO LOW
Low oil level may allow pump to take in air which
when fed to the tappets, causes them to become soft
and allows valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on intake
side of pump through which air can be drawn will
create the same tappet action. Check the lubrication
system from the intake strainer to the pump cover,
including the relief valve retainer cap. When tappet
noise is due to aeration, it may be intermittent or
constant, and usually more than one tappet will be
noisy. When oil level and leaks have been corrected,
engine should be operated at fast idle to allow all of
the air inside of the tappets to be bled out.
VALVE TRAIN NOISE DIAGNOSIS
To determine source of valve train noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed and
listen for source of the noise.
Fig. 3 3.3/3.8L V-6 Engines
Fig. 4 Roller Tappets Aligning Yoke and Retainer
NS3.3/3.8L ENGINE 9 - 95
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1146 of 1938

NOTE: Worn valve guides or cocked springs are
sometimes mistaken for noisy tappets. If such is
the case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not apprecia-
bly reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in the
tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod sockets
and push rod ends for wear.
Valve tappet noise ranges from light noise to a
heavy click. A light noise is usually caused by exces-
sive leak-down around the unit plunger which will
necessitate replacing the tappet, or by the plunger
partially sticking in the tappet body cylinder. A heavy
click is caused either by a tappet check valve not
seating, or by foreign particles becoming wedged
between the plunger and the tappet body causing the
plunger to stick in the down position. This heavy
click will be accompanied by excessive clearance
between the valve stem and rocker arm as valve
closes. In either case, tappet assembly should be
removed for inspection and cleaning.
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
Check oil pressure using gauge at oil pressure
switch location. Oil pressure should be 34.47 kPa (5
psi.) at idle or 205 to 551 kPa (30 to 80 psi.) at 3000
RPM.
(1) Remove pressure sending unit and install oil
pressure gauge (Fig. 5).
CAUTION: If oil pressure is 0 at idle, do not run
engine at 3000 RPM.
(2) Warm engine at high idle until thermostat
opens.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
VALVE TIMING
(1) Remove front cylinder head cover and all 6
spark plugs.
(2) Rotate engine until the #2 piston is at TDC of
the compression stroke.
(3) Install a degree wheel on the crankshaft pulley.
(4) With proper adaptor, install a dial indicator
into #2 spark plug hole. Using the indicator find TDC
on the compression stroke.
(5) Position the degree wheel to zero.
(6) Remove dial indicator from spark plug hole.
(7) Place a 5.08 mm (0.200 in.) spacer between the
valve stem tip of #2 intake valve and rocker arm pad.
Allow tappet to bleed down to give a solid tappet
effect.
(8) Install a dial indicator so plunger contacts the
#2 intake valve spring retainer as nearly perpendic-
ular as possible. Zero the indicator.
(9) Rotate the engine clockwise until the intake
valve has lifted .254 mm (0.010 in.).
CAUTION: Do not turn crankshaft any further
clockwise as intake valve might bottom and result
in serious damage.
(10) Degree wheel should read 6 degrees BTDC to
6 degrees ATDC.
MEASURING TIMING CHAIN FOR STRETCH
(1) Place a scale next to timing chain so that any
movement of chain may be measured.
(2) Place a torque wrench and socket on camshaft
sprocket attaching bolt and apply torque in direction
of crankshaft rotation to take up slack; 41 N´m (30 ft.
lb.) with cylinder head installed or 20 N´m (15 ft. lb.)
with cylinder heads removed.With a torque
applied to the camshaft sprocket bolt, crank-
shaft should not be permitted to move. It may
be necessary to block crankshaft to prevent
rotation.
(3) Holding a scale even, with dimension reading
as shown (Fig. 6), along edge of chain links. Apply
torque in the reverse direction to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.)
with cylinder heads installed, or 20 N´m (15 ft. lbs.)
with cylinder heads removed. Check amount of chain
movement.
(4) Install a new timing chain, if its movement
exceeds 3.175 mm (1/8 inch).
(5) If chain is not satisfactory, refer to Timing
Chain Removal and Installation in this section.
Fig. 5 Checking Oil Pump Pressure
9 - 96 3.3/3.8L ENGINENS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1148 of 1938

with an old bearing half. Do not file the rods or
bearing caps.
(1) Follow procedure specified in the Standard Ser-
vice Procedure Section for Measuring Main Bearing
Clearance and Connecting Rod Bearing Clearance
(Fig. 11).
NOTE: The rod bearing bolts should be examined
before reuse. If the threads are necked down the
bolts should be replaced (Fig. 13). Necking can be
checked by holding a scale or straight edge againstthe threads. If all the threads do not contact the
scale the bolt should be replaced.
(2) Before installing the nuts the threads should
be oiled with engine oil.
(3) Install nuts finger tight on each bolt then alter-
nately torque each nut to assemble the cap properly.
(4) Tighten the nuts to 54 N´m PLUS 1/4 turn (40
ft. lbs. PLUS 1/4 turn).
(5) Using a feeler gauge, check connecting rod side
clearance (Fig. 12). Refer to Connecting Rod Specifi-
cation Chart.
FITTING MAIN BEARINGS
CRANKSHAFT OIL CLEARANCE
Measure the journal outside diameter as shown in
(Fig. 14). Refer to Crankshaft Specification Chart.
PISTON RING SPECIFICATION CHART
Ring Position Ring Gap Wear Limit Groove Clearance Maximum Clearance
Upper Ring 0.30 - 0.55 mm
(0.012 - 0.022 in.)1.0 mm (0.039 in.) 0.030 - 0.085 mm
(0.001 - 0.003 in.)0.10 mm (0.004 in.)
Intermediate Ring 0.30 - 0.55 mm
(0.012 - 0.022 in.)1.0 mm (0.039 in.) 0.030 - 0.095 mm
(0.001 - 0.0037 in.)0.10 mm (0.004 in.)
Oil Control Ring 0.25 - 1.00 mm
(0.010 - 0.039 in.)1.88 mm (0.074 in.) 0.014 - 0.266 mm
(0.0005 - 0.009 in.)0.266 mm (0.009 in.)
Fig. 9 Check Gap on Piston Rings
Fig. 10 Measuring Piston Ring Side Clearance
Fig. 11 Checking Connecting Rod Bearing
Clearance
9 - 98 3.3/3.8L ENGINENS
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1149 of 1938

PLASTIGAGE (OIL CLEARANCE)
MEASUREMENT
(1) Remove oil from journal and bearing shell.
(2) Install crankshaft.
(3) Cut plastigage to same length as width of the
bearing and place it in parallel with the journal axis
(Fig. 15).
(4) Install the main bearing cap carefully and
tighten the bolts to specified torque.
CAUTION: Do not rotate crankshaft or the plasti-
gage will be smeared.(5) Carefully remove the bearing cap and measure
the width of the plastigage at the widest part using
the scale on the plastigage package (Fig. 15). Refer to
Crankshaft Specification Chart for proper clearances.
If the clearance exceeds the specified limits, replace
the main bearing(s) and if necessary, have the crank-
shaft machined to next undersize.
CAUTION: Do not rotate crankshaft or the Plasti-
gage may be smeared.
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY
DIAL INDICATOR METHOD
(1) Mount a dial indicator to front of engine, locat-
ing probe on nose of crankshaft (Fig. 16).
Fig. 12 Checking Connecting Rod Side Clearance
CONNECTING ROD SPECIFICATION CHART
Connecting Rod Bearing Clearance
New Part: 0.019 - 0.073 mm
(0.0008 - 0.0029 in.)
Wear Limit: 0.074 mm
(0.003 in.)
Connecting Rod Side Clearance
New Part: 0.13 - 0.32 mm
(0.005 - 0.013 in.)
Wear Limit: 0.38 mm
(0.015 in.)
Fig. 13 Check for Stretched (Necked) Bolts
CRANKSHAFT SPECIFICATION CHART
Crankshaft End-Play
New Part: 0.09 - 0.24 mm
(0.0036 - 0.0095 in.)
Wear Limit: 0.38 mm
(0.015 in.)
Main Bearing Clearance
New Part: 0.011 - 0.059 mm
(0.0005 - 0.0024 in.)
Wear Limit: 0.076 mm
(0.003 in.)
Crankshaft Main Bearing Journal
Standard Size: 63.992 - 64.013 mm
(2.5194 - 2.5202 in.)
Crankshaft Connecting Rod Journal
Standard Size: 57.989 - 58.005 mm
(2.2831 - 2.2837 in.)
Fig. 14 Measure Crankshaft Journal O.D.
NS3.3/3.8L ENGINE 9 - 99
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1158 of 1938

²Non±isolatedcylinder head cover to 12 N´m
(105 in. lbs.).
²Isolatedcylinder head cover to 10 N´m (90 in.
lbs.) (Fig. 32).
(4) Connect PCV hose from cylinder head cover.
(5) Install intake manifold upper plenum. Refer to
Group 11, Exhaust System and Intake Manifold for
procedure.
(6) Install Wiper Unit. Refer to Group 8K, Wind-
shield Wipers and Washers for procedure.
(7) Connect negative cable to battery.
CYLINDER HEAD
REMOVAL
(1) Drain cooling system. Refer to Group 7, Cooling
System for procedure and disconnect negative cable
from battery.
(2) Remove upper and lower intake manifolds.
Refer to Group 11, Exhaust System and Intake Man-
ifold.
WARNING: INTAKE MANIFOLD GASKET IS MADE
OF VERY THIN METAL AND MAY CAUSE PER-
SONAL INJURY, HANDLE WITH CARE.
(3) Disconnect coil wires, sending unit wire, heater
hoses and bypass hose.
(4) Remove PCV system hoses, evaporation control
system hose and cylinder head covers.
(5) Remove exhaust manifolds.
(6) Remove rocker arm and shaft assemblies.
Remove push rods andmark positions to ensure
installation in original locations.
(7) Remove the 9 head bolts from each cylinder
head and remove cylinder heads (Fig. 33).
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean all sealing surfaces of cylinder block and
cylinder heads.
(2) Install new gaskets on cylinder block (Fig. 34).
(3)The cylinder head bolts are torqued using
the torque yield method, they should be exam-
ined BEFORE reuse. If the threads are necked
down, the bolts should be replaced(Fig. 35).
(4) Necking can be checked by holding a scale or
straight edge against the threads. If all the threads
do not contact the scale the bolt should be replaced.
(5) Tighten the cylinder head bolts1-8inthe
sequence shown in (Fig. 33). Using the 4 step torque
turn method, tighten according to the following val-
ues:
²Step 1: Bolts1±8to61N´m(45ft.lbs.)
²Step 2: Bolts1±8to88N´m(65ft.lbs.)
²Step 3: Bolts1±8(again) to 88 N´m (65 ft. lbs.)
²Step 4: Bolts1±8turn an additional 1/4 Turn.
(Do not use a torque wrench for this step.)
NOTE: Bolt torque after 1/4 turn should be over 122
N´m (90 ft. lbs.). If not, replace the bolt.
(6) Tighten head bolt number 9 (Fig. 33) to 33 N´m
(25 ft. lbs.) after head bolts1±8have been tighten
to specifications.
Fig. 33 Cylinder Head Bolts Location and
Tightening Sequence
Fig. 34 Head Gasket Installation
Fig. 35 Checking Bolts for Stretching (Necking)
9 - 108 3.3/3.8L ENGINENS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)