Page 194 of 390
Steering in Emergencies
There are times when steering can be more effective than
braking. For example, you come over
a hill and find a
truck stopped in your lane, or a car suddenly pulls out
from nowhere, or a child darts
out from between parked
cars and stops right in front of
you. You can avoid these
problems by braking
-- if you can stop in time. But
sometimes you can’t; there isn’t room. That’s the time
for evasive action
-- steering around the problem.
Your Oldsmobile can perform very well in emergencies
like these. First apply your brakes. (See “Braking in
Emergencies” earlier
in this section.) It is better to
remove as much speed as you can from a possible
collision. Then steer around the problem, to the left or
right depending on the space available.
An emergency like this requires close attention and a
quick decision. If you are holding the steering wheel at
the recommended
9 and 3 o’clock positions, you can
turn it a full
180 degrees very quickly without removing
either hand. But you have to act fast, steer quickly, and
just as quickly straighten the wheel once you have
avoided the object.
The fact that such emergency situations are always
possible is a good reason
to practice defensive driving at
all times and wear safety belts properly.
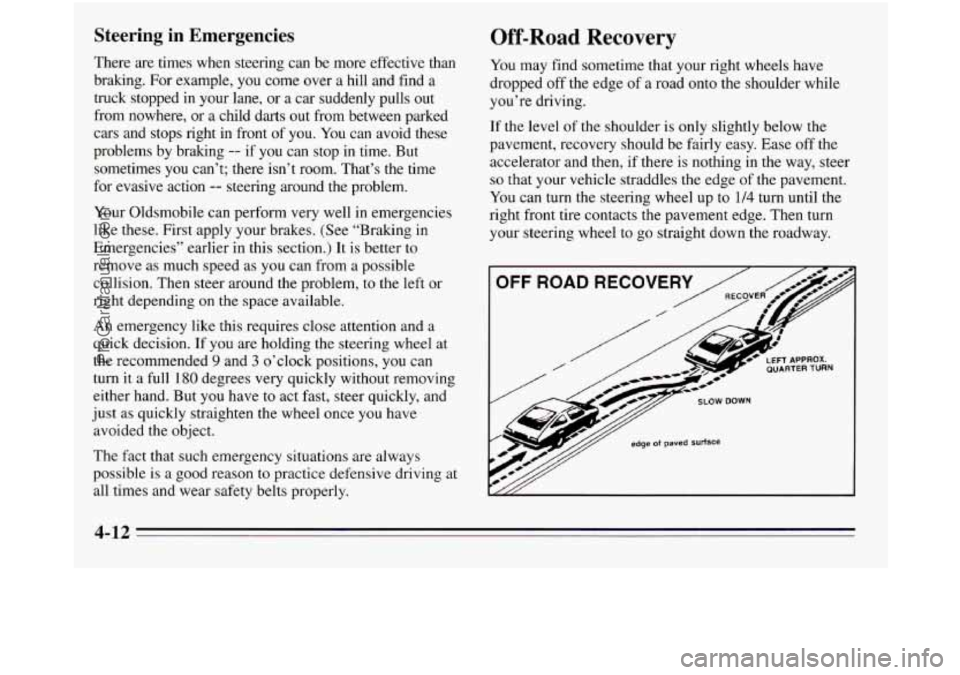
Off-Road Recovery
You may find sometime that your right wheels have
dropped off the edge of a road onto the shoulder while
you’re driving.
If the level of the shoulder is only slightly below the
pavement, recovery should be fairly easy. Ease off the
accelerator and then, if there is nothing in the way, steer
so that your vehicle straddles the edge of the pavement.
You can turn the steering wheel up to
1/4 turn until the
right front tire contacts the pavement edge. Then turn
your steering wheel to go straight down the roadway.
LeT/ SLOW DOWN
p,/y edge of paved surface
4-12
ProCarManuals.com
Page 197 of 390

is off, then an acceleration skid is also best handled by
easing your foot
off the accelerator pedal.
Driving at Night
If your vehicle starts to slide, ease your foot off the
accelerator pedal and quickly steer the way you want the
vehicle to go. If you start steering quickly enough, your
vehicle may straighten out. Always be ready for a
second
skid if it occurs.
Of course, traction is reduced when water, snow, ice,
gravel, or other material
is on the road. For safety, you’ll
want to slow down and adjust your driving
to these
conditions. It is important to slow down on slippery
surfaces because stopping distance
will be longer and
vehicle control more limited.
While driving on
a surface with reduced traction, try
your best
to avoid sudden steering, acceleration, or
braking (including engine braking by shifting
to a lower
gear). Any sudden changes could cause the tires to slide.
You may not realize the surface is slippery until your
vehicle is skidding. Learn to recognize warning clues
--
such as enough water, ice or packed snow on the road to
make
a “mirrored surface” -- and slow down when you
have any doubt.
Remember: Any anti-lock brake system
(ABS) helps
avoid
only the braking skid. Night
driving
is more dangerous than day driving.
One reason is that some drivers are likely to be
impaired
-- by alcohol or drugs, with night vision
problems, or by fatigue.
4-15
ProCarManuals.com
Page 208 of 390

Whatever the condition -- smooth ice, packed, blowing
or loose snow -- drive with caution.
If you have the traction control system, keep the system
on. It will improve your ability to accelerate when
driving on a slippery road. Even though your vehicle has
a traction control system, you’ll want to slow down and
adjust your driving
to the road conditions. See “Traction
Control System”
in the Index.
If you don’t have the traction control system, accelerate
gently. Try not to break the fragile traction.
If you
accelerate too fast, the drive wheels will spin and polish
the surface under the tires even more. Your
anti-lock brakes improve your ability to make a
hard stop on a slippery road. Even though
you have an
anti-lock braking system, you’ll want to begin stopping
sooner than
you would on dry pavement. See
“Anti-Lock’ in the Index.
Allow greater following distance on any slippery
road.
Watch for slippery spots. The road might be fine
until you hit a spot that’s covered with ice. On an
otherwise clear road, ice patches may appear in
shaded areas where the sun can’t reach: around
clumps
of trees, behind buildings, or under bridges.
Sometimes the surface
of a curve or an overpass may
remain icy when the surrounding roads are clear.
If
you see a patch of ice ahead of you, brake before you
are on it. Try not to brake while you’re actually
on
the ice, and avoid sudden steering maneuvers.
4-26
ProCarManuals.com
Page 217 of 390

Safety Chains Driving with a Trauer
You
should always attach chains between your vehicle
and your trailer. Cross the safety chains under the tongue
of the trailer so that the tongue will not drop to the road
if
it becomes separated from the hitch. Instructions
about safety chains may be provided by the hitch
manufacturer or by the trailer manufacturer. Follow the
manufacturer’s recommendation for attaching safety
chains and
do not attach them to the bumper. Always
leave just enough slack
so you can turn with your rig.
And, never allow safety chains to drag
on the ground.
Trailer Brakes
If your trailer weighs more than 1,000 pounds (450 kg)
loaded, then it needs its own brakes
-- and they must be
adequate. Be sure to read and follow the instructions for
the trailer brakes
so you’ll be able to install, adjust and
maintain them properly.
Because
you have anti-lock brakes, do not try to tap into
your vehicle’s brake system.
If you do, both brake
systems won’t work well,
or at all.
4-35
ProCarManuals.com
Page 232 of 390
When your vehicle is being towed, have the key in the
ignition
in the OFF position. The steering wheel should
be clamped in a straight-ahead position, with a clamping
device designed for towing service.
Do not use the
vehicle’s steering column lock for this. The transaxle
should be in
NEUTRAL (N) and the parking brake
released.
Don’t have your vehicle towed on the front wheels,
unless you must.
If the vehicle must be towed on the
front wheels, don’t go more than
35 mph (56 km/h) or
farther than 50 miles (80 km) or your transaxle will be
damaged. If these limits must be exceeded, then the
front wheels have to be supported on a dolly.
5-10
ProCarManuals.com
Page 249 of 390
L
4.
5.
The compact spare tire is located under the vehicle,
behind the rear bumper. Insert the narrow end
of the
shaft into the hole above
the rear bumper. Then
attach the folding wrench to the shaft.
Rotate the folding wrench counterclockwise to lower
the compact spare tire until it can be pulled from
under the vehicle.
6. Slide the cable retainer through the center of the
spare, then place the compact spare tire near the
flat tire.
5-27
ProCarManuals.com
Page 251 of 390
9. Attach the folding wrench to the jack, and rotate the
wrench clockwise to raise the jack head a few inches.
I L L.
Gn J
IO. Near each wheel, there is a notch in the vehicle's
frame. Position the jack and raise the jack head
until
it fits firmly into the notch in the vehicle's frame
(nearest the flat tire).
Do not raise the vehicle yet.
Put the compact spare tire near you.
5-29
ProCarManuals.com
Page 252 of 390
NOTICE:
Raising your vehicle with the jack improperly
positioned will damage the vehicle or may allow the vehicle
to fall off the jack. Be sure to fit the
jack lift head into the proper location before
raising your vehicle.
11. Raise the vehicle by rotating the folding wrench
clockwise in the jack. Raise the vehicle far enough
off the ground so there is enough room for the spare
tire to fit.
12. Remove all the wheel nuts and take off the flat tire.
I
' 5-30
ProCarManuals.com