1995 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY air filter
[x] Cancel search: air filterPage 303 of 976

19FUEL SYSTEM
20
REPAIRADD: 09/95 FUEL SYSTEM - DEPRESSURISE - ADVANCED
EVAPS
Service repair no - 19.50.02
WARNING: Fuel pressure of up to 2.5 bar
will be present in the system, even if the
engine has not been run for some time.
Always depressurise the system before
disconnecting any components in the fuel feed
line (between fuel pump and pressure regulator).
The spilling of fuel is unavoidable during this
operation. Ensure that all necessary precautions
are taken to prevent fire and explosion.
NOTE: Fuel pressure can be relieved at
fuel filter unions.
1.Position cloth around relevant union to protect
against fuel spray.
2.Carefully loosen union.
CAUTION: Use two spanners when
loosening or tightening unions.
3.Tighten union once fuel pressure is relieved.
4.Remove cloth.FUEL TANK - ADVANCED EVAPS
Service repair no - 19.55.01
WARNING: Ensure fuel handling
precautions given in section 01
Introduction are strictly adhered to when
carrying out following instructions.
CAUTION: Before disconnecting any part
of fuel system, it imperative that all dust,
dirt and debris is removed from around
components to prevent ingress of foreign matter
into fuel system.
Remove
1.Disconnect battery negative lead.
2.Drain fuel tank completely.
See fuel tank -
draining - advanced evaps
3.Remove 6 screws securing tail door tread strip
and remove tread strip.
4.Remove RH luggage compartment side panel.
See CHASSIS AND BODY, Repair, rear
compartment lower trim panels
Page 380 of 976
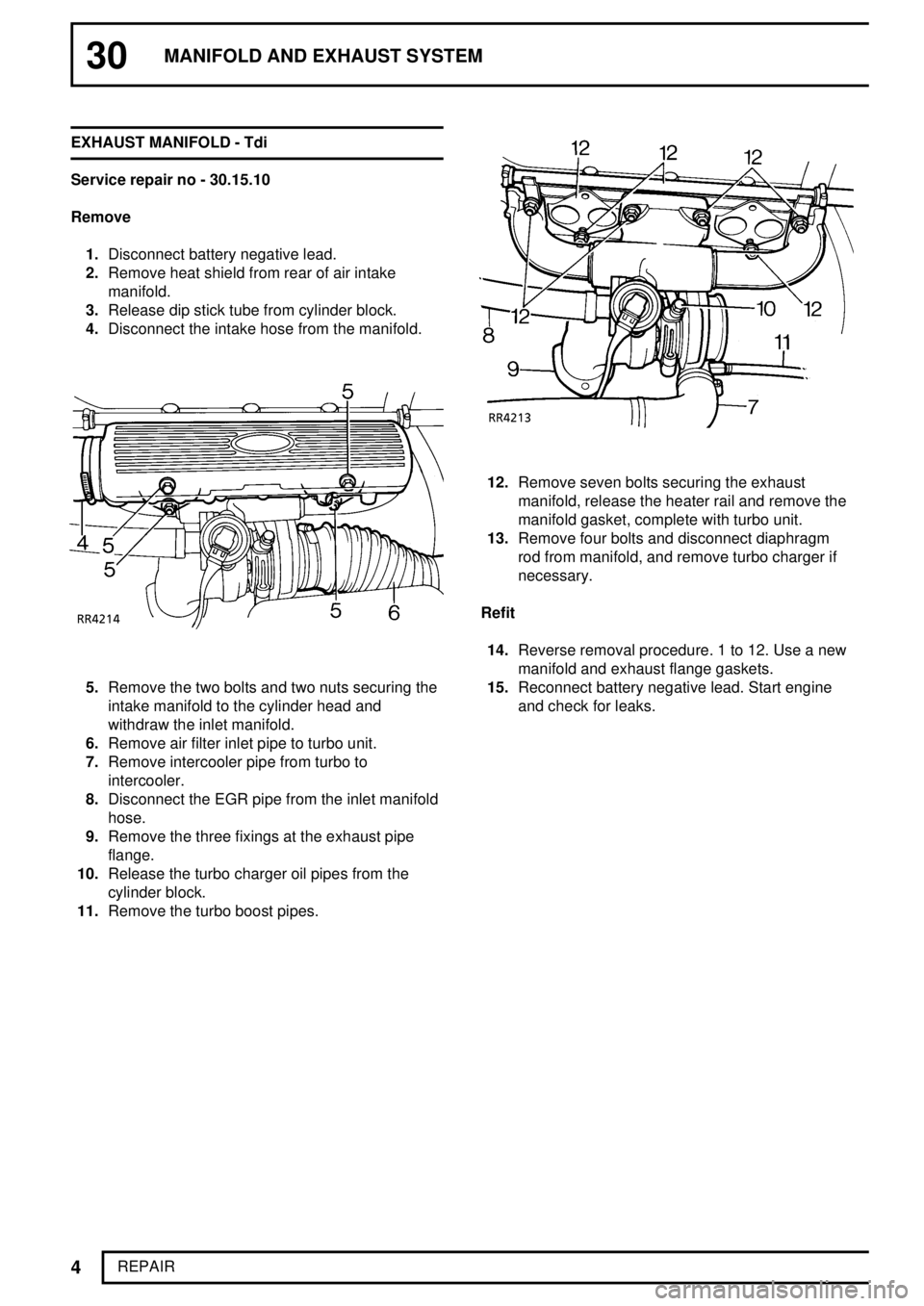
30MANIFOLD AND EXHAUST SYSTEM
4
REPAIR EXHAUST MANIFOLD - Tdi
Service repair no - 30.15.10
Remove
1.Disconnect battery negative lead.
2.Remove heat shield from rear of air intake
manifold.
3.Release dip stick tube from cylinder block.
4.Disconnect the intake hose from the manifold.
5.Remove the two bolts and two nuts securing the
intake manifold to the cylinder head and
withdraw the inlet manifold.
6.Remove air filter inlet pipe to turbo unit.
7.Remove intercooler pipe from turbo to
intercooler.
8.Disconnect the EGR pipe from the inlet manifold
hose.
9.Remove the three fixings at the exhaust pipe
flange.
10.Release the turbo charger oil pipes from the
cylinder block.
11.Remove the turbo boost pipes.
12.Remove seven bolts securing the exhaust
manifold, release the heater rail and remove the
manifold gasket, complete with turbo unit.
13.Remove four bolts and disconnect diaphragm
rod from manifold, and remove turbo charger if
necessary.
Refit
14.Reverse removal procedure. 1 to 12. Use a new
manifold and exhaust flange gaskets.
15.Reconnect battery negative lead. Start engine
and check for leaks.
Page 599 of 976
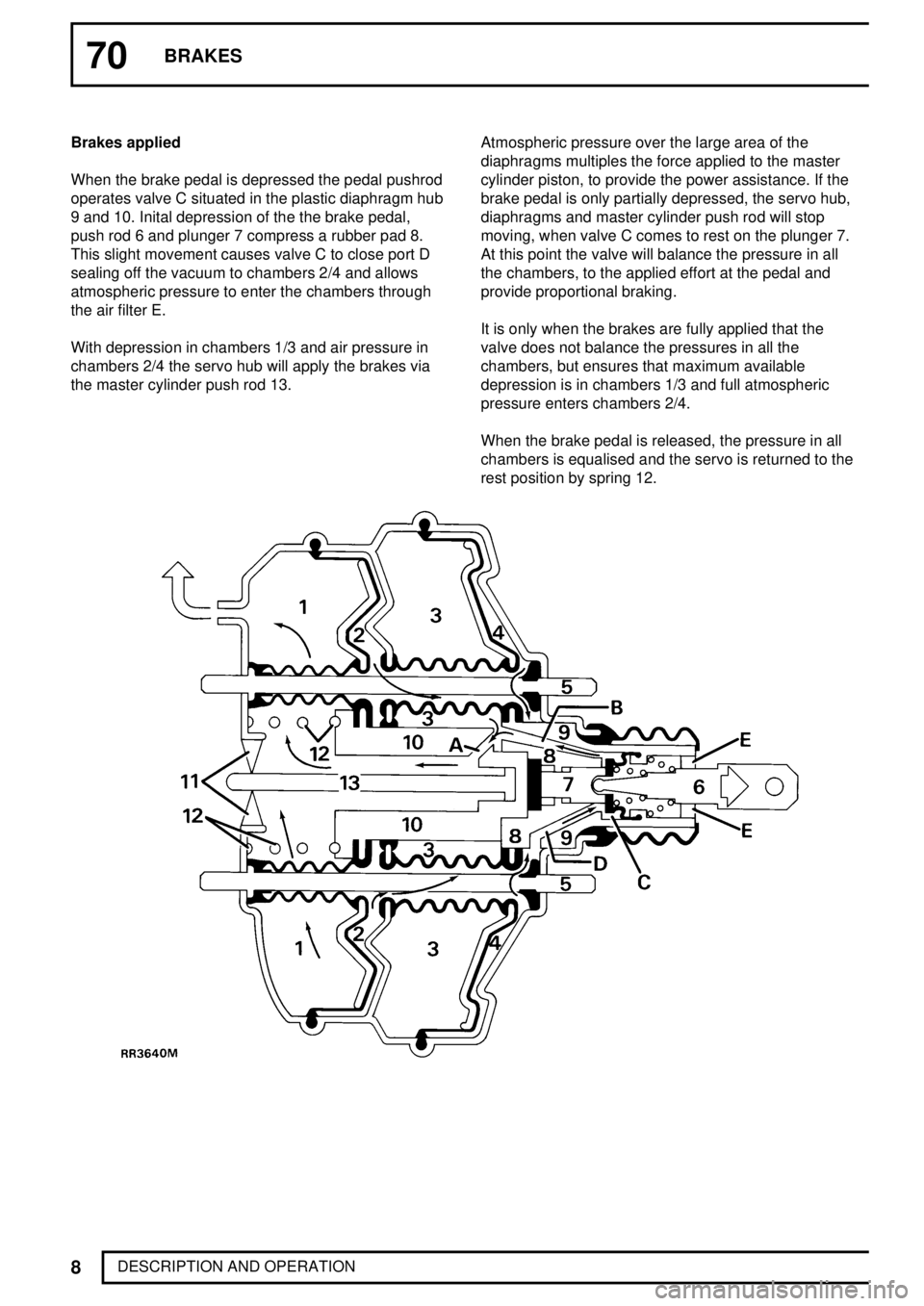
70BRAKES
8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Brakes applied
When the brake pedal is depressed the pedal pushrod
operates valve C situated in the plastic diaphragm hub
9 and 10. Inital depression of the the brake pedal,
push rod 6 and plunger 7 compress a rubber pad 8.
This slight movement causes valve C to close port D
sealing off the vacuum to chambers 2/4 and allows
atmospheric pressure to enter the chambers through
the air filter E.
With depression in chambers 1/3 and air pressure in
chambers 2/4 the servo hub will apply the brakes via
the master cylinder push rod 13.Atmospheric pressure over the large area of the
diaphragms multiples the force applied to the master
cylinder piston, to provide the power assistance. If the
brake pedal is only partially depressed, the servo hub,
diaphragms and master cylinder push rod will stop
moving, when valve C comes to rest on the plunger 7.
At this point the valve will balance the pressure in all
the chambers, to the applied effort at the pedal and
provide proportional braking.
It is only when the brakes are fully applied that the
valve does not balance the pressures in all the
chambers, but ensures that maximum available
depression is in chambers 1/3 and full atmospheric
pressure enters chambers 2/4.
When the brake pedal is released, the pressure in all
chambers is equalised and the servo is returned to the
rest position by spring 12.
Page 611 of 976
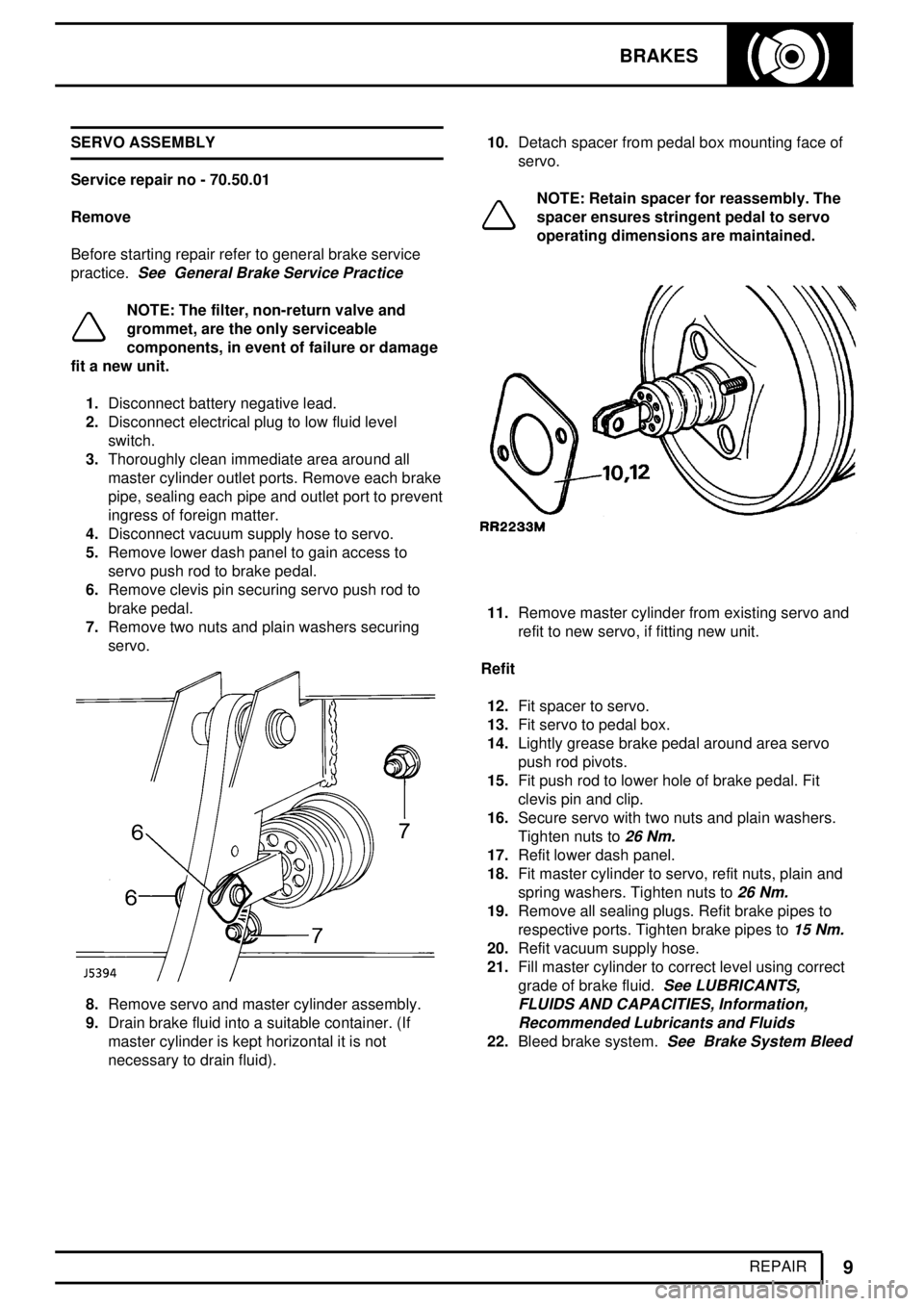
BRAKES
9
REPAIR SERVO ASSEMBLY
Service repair no - 70.50.01
Remove
Before starting repair refer to general brake service
practice.
See General Brake Service Practice
NOTE: The filter, non-return valve and
grommet, are the only serviceable
components, in event of failure or damage
fit a new unit.
1.Disconnect battery negative lead.
2.Disconnect electrical plug to low fluid level
switch.
3.Thoroughly clean immediate area around all
master cylinder outlet ports. Remove each brake
pipe, sealing each pipe and outlet port to prevent
ingress of foreign matter.
4.Disconnect vacuum supply hose to servo.
5.Remove lower dash panel to gain access to
servo push rod to brake pedal.
6.Remove clevis pin securing servo push rod to
brake pedal.
7.Remove two nuts and plain washers securing
servo.
8.Remove servo and master cylinder assembly.
9.Drain brake fluid into a suitable container. (If
master cylinder is kept horizontal it is not
necessary to drain fluid).10.Detach spacer from pedal box mounting face of
servo.
NOTE: Retain spacer for reassembly. The
spacer ensures stringent pedal to servo
operating dimensions are maintained.
11.Remove master cylinder from existing servo and
refit to new servo, if fitting new unit.
Refit
12.Fit spacer to servo.
13.Fit servo to pedal box.
14.Lightly grease brake pedal around area servo
push rod pivots.
15.Fit push rod to lower hole of brake pedal. Fit
clevis pin and clip.
16.Secure servo with two nuts and plain washers.
Tighten nuts to
26 Nm.
17.Refit lower dash panel.
18.Fit master cylinder to servo, refit nuts, plain and
spring washers. Tighten nuts to
26 Nm.
19.Remove all sealing plugs. Refit brake pipes to
respective ports. Tighten brake pipes to
15 Nm.
20.Refit vacuum supply hose.
21.Fill master cylinder to correct level using correct
grade of brake fluid.
See LUBRICANTS,
FLUIDS AND CAPACITIES, Information,
Recommended Lubricants and Fluids
22.Bleed brake system.See Brake System Bleed
Page 759 of 976
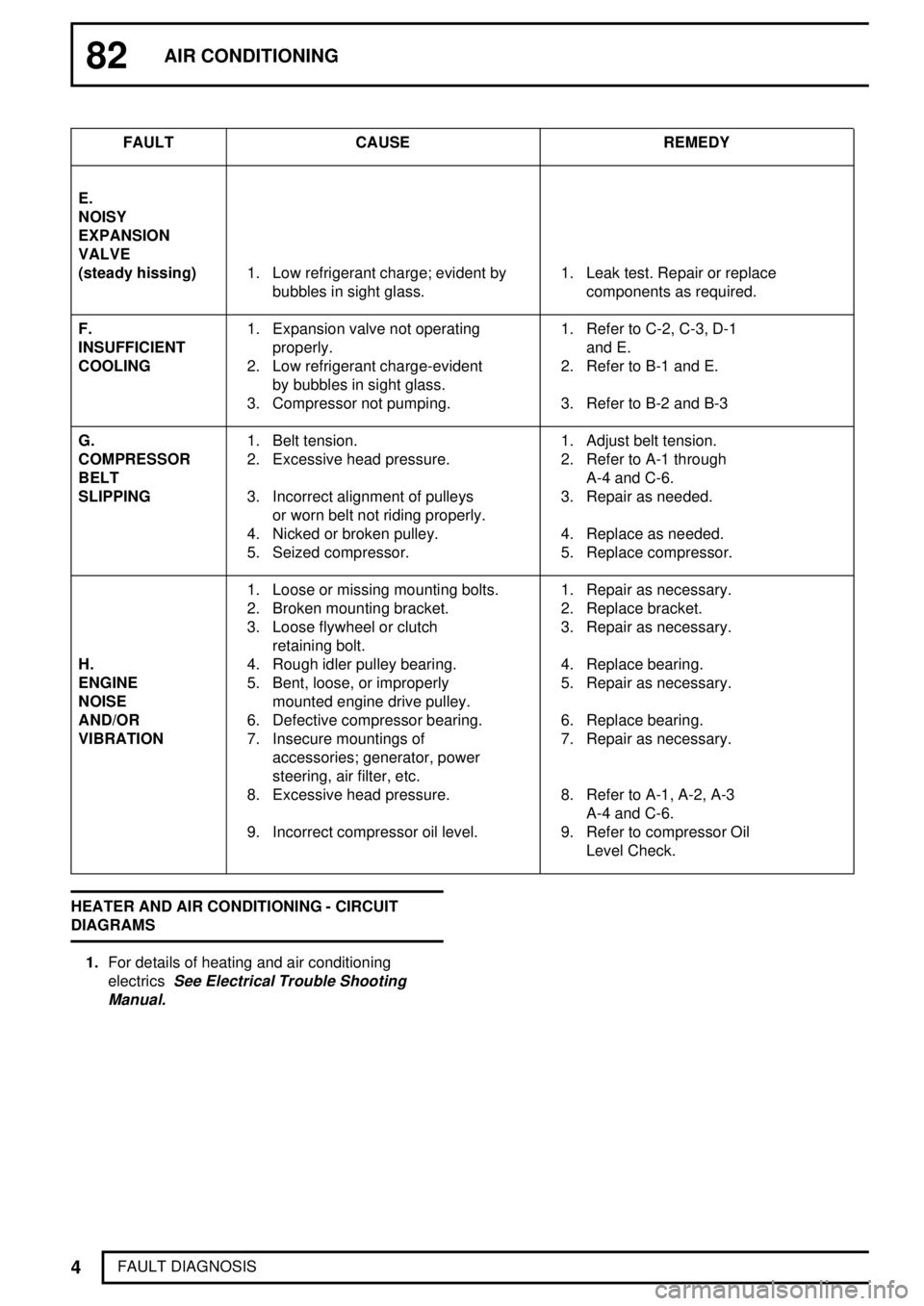
82AIR CONDITIONING
4
FAULT DIAGNOSISFAULT CAUSE REMEDY
E.
NOISY
EXPANSION
VALVE
(steady hissing)1. Low refrigerant charge; evident by
bubbles in sight glass.1. Leak test. Repair or replace
components as required.
F.1. Expansion valve not operating 1. Refer to C-2, C-3, D-1
INSUFFICIENTproperly. and E.
COOLING2. Low refrigerant charge-evident 2. Refer to B-1 and E.
by bubbles in sight glass.
3. Compressor not pumping. 3. Refer to B-2 and B-3
G.1. Belt tension. 1. Adjust belt tension.
COMPRESSOR2. Excessive head pressure. 2. Refer to A-1 through
BELTA-4 and C-6.
SLIPPING3. Incorrect alignment of pulleys 3. Repair as needed.
or worn belt not riding properly.
4. Nicked or broken pulley. 4. Replace as needed.
5. Seized compressor. 5. Replace compressor.
1. Loose or missing mounting bolts. 1. Repair as necessary.
2. Broken mounting bracket. 2. Replace bracket.
3. Loose flywheel or clutch 3. Repair as necessary.
retaining bolt.
H.4. Rough idler pulley bearing. 4. Replace bearing.
ENGINE5. Bent, loose, or improperly 5. Repair as necessary.
NOISEmounted engine drive pulley.
AND/OR6. Defective compressor bearing. 6. Replace bearing.
VIBRATION7. Insecure mountings of 7. Repair as necessary.
accessories; generator, power
steering, air filter, etc.
8. Excessive head pressure. 8. Refer to A-1, A-2, A-3
A-4 and C-6.
9. Incorrect compressor oil level. 9. Refer to compressor Oil
Level Check.
HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONING - CIRCUIT
DIAGRAMS
1.For details of heating and air conditioning
electrics
See Electrical Trouble Shooting
Manual.
Page 762 of 976

AIR CONDITIONING
3
ADJUSTMENT SERVICING EQUIPMENT
The following equipment is required for full servicing
of the air conditioning system.
Recovery, recycling and charging station
Leak detector
Thermometer +20°C to -60°C
Safety goggles and gloves
REFRIGERANT RECOVERY RECYCLING
RECHARGING
WARNING: The air conditioning system is
charged with a high pressure, potentially
toxic refrigerant. Repairs or servicing must
only be carried out by an operator familiar with
both the vehicle system and the charging and
testing equipment.
All operations must be carried out in a
well-ventilated area away from open flame and
heat sources.
Always wear safety goggles and gloves when
opening refrigerant connections.
WARNING: Wear eye and hand safety
protection. Open connections slowly in
case liquid or pressure is present. Allow to
bleed off slowly.
CAUTION: Overcharging air conditioning
system will cause excessive head
pressure.
An air conditioning portable Refrigerant Recovery
Recycling Recharging Station for use with R134a
refrigerant incorporates all the features necessary to
recover refrigerant R134a from the air conditioning
system, to filter and remove moisture, to evacuate and
recharge with the reclaimed refrigerant. The unit can
also be used for performance testing and air
conditioning system analysis.
The operator must adhere to the equipment
manufacturer's instructions.Recovery and recycling
1. High pressure servicing connection
2. Low pressure servicing connection
1.Connect a Refrigerant Station to the high and
low pressure servicing connections.
2.Operate the refrigerant recovery system
according to the manufacturer's instructions.
3.Measure the amount of oil discharged from the
system. Add an equal amount of new refrigerant
oil to compressor before evacuation sequence.
WARNING: Refrigerant must always be
recycled before reuse, to ensure that the
purity of the refrigerant is high enough for
safe use in the air conditioning system.
Recycling should always be carried out with
equipment which is design certified by
Underwriter Laboratory Inc. for compliance with
SAE-J1991. Other equipment may not recycle
refrigerant to the required level of purity.
A R134a Refrigerant Recovery Recycling
Recharging Station must not be used with any
other type of refrigerant.
Refrigerant R134a from domestic and commercial
sources must not be used in motor vehicle air
conditioning systems.