1995 JEEP YJ checking oil
[x] Cancel search: checking oilPage 35 of 2158

CONTAINER IDENTIFICATION
Standard engine oil identification notations have
been adopted to aid in the proper selection of engine
oil. The identifying notations are located on the label
of engine oil plastic bottles and the top of engine oil
cans (Fig. 2).
ENGINE OIL ADDITIVES
In some instances, such as infrequent operation,
short trip driving, and during break-in after a major
overhaul, addition of special materials containing an-
ti-rust and anti-scuff additives are beneficial. A suit-
able product for this purpose is MOPAR Engine Oil
Supplement.
OIL LEVEL INDICATOR (DIPSTICK)
The engine oil level indicator (Dipstick) is located
at the right rear of both 2.5L engines and 4.0L en-
gines (Fig. 3).
CRANKCASE OIL LEVEL INSPECTION
CAUTION: Do not overfill crankcase with engine oil,
oil foaming and oil pressure loss can result.
Inspect engine oil level approximately every 800 ki-
lometers (500 miles). Unless the engine has exhibited
loss of oil pressure, run the engine for about five
minutes before checking oil level. Checking engine oil
level on a cold engine is not accurate.
To ensure proper lubrication of an engine, the en-
gine oil must be maintained at an acceptable level.
The acceptable levels are indicated between the ADD
and SAFE marks on the engine oil dipstick (Fig. 4
and 5).
(1) Position vehicle on level surface.
(2) With engine OFF, allow approximately ten min-
utes for oil to settle to bottom of crankcase, remove
engine oil dipstick.
(3) Wipe dipstick clean.
(4) Install dipstick and verify it is seated in the
tube.
(5) Remove dipstick, with handle held above the
tip, take oil level reading (Figs.4 and 5).
(6) Add oil only if level is below the ADD mark on
dipstick.
ENGINE OIL CHANGE AND FILTER REPLACEMENT
ENGINE OIL CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in Maintenance Schedules.
TO CHANGE ENGINE OIL
Run engine until achieving normal operating tem-
perature.
(1) Position the vehicle on a level surface and turn
engine off.
(2) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands. Re-
fer to Hoisting and Jacking Recommendations in this
group.
Fig. 2 API Certification Mark
Fig. 3 Engine Oil Dipstick LocationÐTypical
Fig. 4 Engine Oil DipstickÐ2.5L Engine
0 - 16 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEJ
Page 91 of 2158
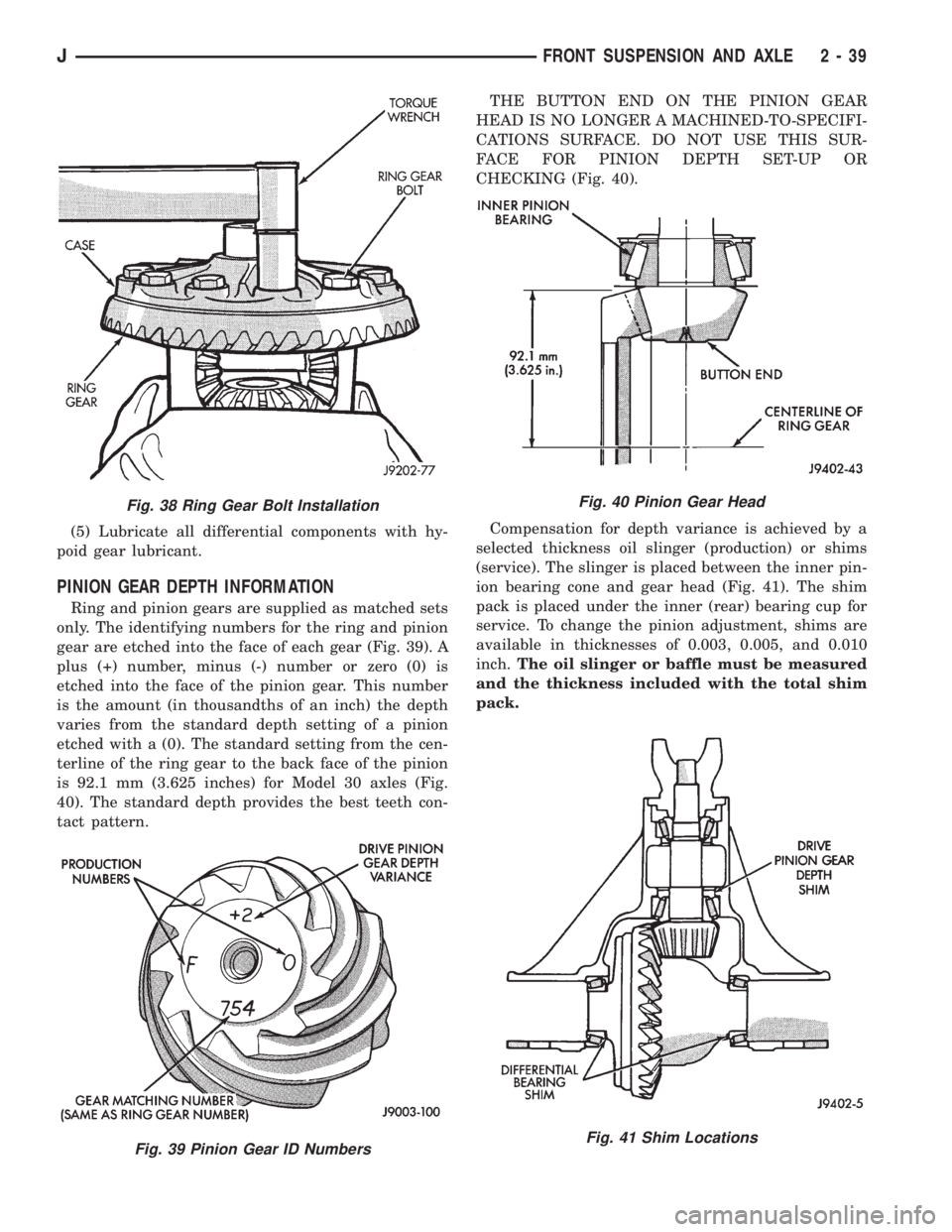
(5) Lubricate all differential components with hy-
poid gear lubricant.
PINION GEAR DEPTH INFORMATION
Ring and pinion gears are supplied as matched sets
only. The identifying numbers for the ring and pinion
gear are etched into the face of each gear (Fig. 39). A
plus (+) number, minus (-) number or zero (0) is
etched into the face of the pinion gear. This number
is the amount (in thousandths of an inch) the depth
varies from the standard depth setting of a pinion
etched with a (0). The standard setting from the cen-
terline of the ring gear to the back face of the pinion
is 92.1 mm (3.625 inches) for Model 30 axles (Fig.
40). The standard depth provides the best teeth con-
tact pattern.THE BUTTON END ON THE PINION GEAR
HEAD IS NO LONGER A MACHINED-TO-SPECIFI-
CATIONS SURFACE. DO NOT USE THIS SUR-
FACE FOR PINION DEPTH SET-UP OR
CHECKING (Fig. 40).
Compensation for depth variance is achieved by a
selected thickness oil slinger (production) or shims
(service). The slinger is placed between the inner pin-
ion bearing cone and gear head (Fig. 41). The shim
pack is placed under the inner (rear) bearing cup for
service. To change the pinion adjustment, shims are
available in thicknesses of 0.003, 0.005, and 0.010
inch.The oil slinger or baffle must be measured
and the thickness included with the total shim
pack.
Fig. 38 Ring Gear Bolt Installation
Fig. 39 Pinion Gear ID Numbers
Fig. 40 Pinion Gear Head
Fig. 41 Shim Locations
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 39
Page 156 of 2158

SERVICE BRAKE DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
Brake Drag............................... 6
Brake Fade.............................. 6
Brake Fluid Contamination................... 7
Brake Noise.............................. 7
Brake Pull............................... 6
Brake Warning Light Operation................ 5
Brakes Do Not Hold After Driving Through Deep
Water Puddles........................... 7
Component Inspection...................... 5
Contaminated Brakelining.................... 7
Diagnosing Parking Brake Malfunctions.......... 8
Diagnosis Procedures....................... 4
General Information........................ 4Hard Pedal or High Pedal Effort............... 6
Low Pedal............................... 5
Master Cylinder/Power Booster Test............ 8
Pedal Falls Away.......................... 5
Pedal Pulsation (Non-ABS Brakes Only)......... 6
Power Booster Check Valve Test............... 9
Power Booster Vacuum Test.................. 9
Preliminary Brake Check..................... 4
Rear Brake Grab.......................... 7
Road Testing............................. 5
Spongy Pedal............................. 5
Wheel and Tire Problems.................... 7
GENERAL INFORMATION
The diagnosis information in this section covers
service brake components which include:
²disc brake calipers
²disc brakeshoes
²drum brake wheel cylinders
²drum brakeshoes and brake drums
²drum brake support plates
²parking brake mechanism
²master cylinder/combination valve
²vacuum power brake booster
²brake pedal and brakelight switch
²brake warning light
DIAGNOSIS PROCEDURES
Service brake diagnosis involves determining if a
problem is related to a mechanical, hydraulic or vac-
uum operated component. A preliminary brake check,
followed by road testing and component inspection
are needed to determine a problem cause.
Road testing will either verify proper brake opera-
tion or confirm the existence of a problem. Compo-
nent inspection will, in most cases, identify the
actual part responsible for a problem.
The first diagnosis step is the preliminary brake
check. This involves inspecting fluid level, parking
brake action, wheel and tire condition, checking for
obvious leaks or component damage and testing
brake pedal response. A road test will confirm or
deny the existence of a problem. The final diagnosis
procedure involves road test analysis and a visual in-
spection of brake components.
PRELIMINARY BRAKE CHECK
(1) If amber ABS light is illuminated, refer to ABS
Brake System Diagnosis. If red warning light is illu-
minated, or if neither warning light is illuminated,
continue with brake check.(2) Inspect condition of tires and wheels. Damaged
wheels and worn, damaged, or underinflated tires
can cause pull, shudder, tramp and a condition simi-
lar to grab.
(3) If complaint was based on noise when braking,
check suspension components. Jounce front and rear
of vehicle and listen for noise that might be caused
by loose, worn, or damaged suspension or steering
components.
(4) Inspect brake fluid level:
(a) If vehicle has one-piece master cylinder, fluid
level should be within 6 mm (1/4 in.) of reservoir
rim.
(b) If vehicle has nylon reservoir with single
filler cap, correct level is to FULL mark on side of
reservoir. Acceptable level is between FULL and
ADD marks.
(c) Remember that fluid level in the reservoir
compartments will decrease in proportion to nor-
mal lining wear. However, if fluid level is abnor-
mally low, look for leaks at calipers, wheel
cylinders, brakelines and master cylinder.
(5) Inspect brake fluid condition:
(a) Fluid should be free of foreign material.Note
that brake fluid tends to darken over time.
This is normal and should not be mistaken for
contamination. If fluid is clear of foreign ma-
terial, it is OK.
(b) If fluid is highly discolored, or appears to con-
tain foreign material, drain out a sample with a
clean suction gun. Pour sample in a glass container
and note condition described in step (c).
(c) If fluid separates into layers, obviously con-
tains oil, or a substance other than brake fluid,
system seals and cups will have to be replaced and
hydraulic system flushed.
(6) Check parking brake operation. Verify free
movement and full release of cables and foot pedal or
5 - 4 SERVICE BRAKE DIAGNOSISJ
Page 263 of 2158

CAUTION: Do not operate the engine with a spark
plug shorted for more than a minute. The catalytic
converter may be damaged.
Isolate the compression leak by shorting each
spark plug to the cylinder block. The gauge pointer
should stop or decrease vibration when spark plug
for leaking cylinder is shorted. This happens because
of the absence of combustion pressure.
COMBUSTION LEAKAGE TEST (WITHOUT
PRESSURE TESTER)
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If the solution
is clean, drain the coolant into a clean container for
reuse.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
Drain sufficient coolant to allow for thermostat re-
moval. Refer to Thermostat Replacement. Disconnect
the water pump drive belt.
Disconnect the upper radiator hose from the ther-
mostat housing. Remove the housing and thermostat.
Install the thermostat housing.
Add coolant to the radiator to bring the level to
within 6.3 mm (1/4 in) of the top of the thermostat
housing.
CAUTION: Avoid overheating. Do not operate the
engine for an excessive period of time. Open the
draincock immediately after the test to eliminate
boil over of coolant.
Start the engine and accelerate rapidly three times
(to approximately 3000 rpm) while observing the
coolant. If internal engine combustion gases are leak-
ing into the cooling system, bubbles will appear in
the coolant. If bubbles do not appear, there is no in-
ternal combustion gas leakage.
COOLANT RESERVE/OVERFLOW SYSTEM
The system works along with the radiator pressure
cap. This is done by using thermal expansion and
contraction of the coolant to keep the coolant free of
trapped air. It provides:
²A volume for coolant expansion and contraction.
²A convenient and safe method for checking/adjust-
ing coolant level at atmospheric pressure. This is
done without removing the radiator pressure cap.
²Some reserve coolant to the radiator to cover mi-
nor leaks and evaporation or boiling losses.
As the engine cools, a vacuum is formed in the
cooling system of both the radiator and engine. Cool-ant will then be drawn from the coolant tank and re-
turned to a proper level in the radiator.
The coolant reserve/overflow system consists of a
radiator mounted pressurized cap, a plastic reserve/
overflow tank (Figs. 22, 23 or 24), a tube (hose) con-
necting the radiator and tank, and an overflow tube
on the side of the tank.
Fig. 22 Reserve/Overflow TankÐYJ Models
Fig. 23 Reserve/Overflow TankÐXJ ModelsÐExcept
Right Hand Drive
7 - 24 COOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURESJ
Page 334 of 2158

IGNITION SECONDARY CIRCUIT DIAGNOSIS
CHECKING FOR SPARK
CAUTION: When disconnecting a high voltage cable
from a spark plug or from the distributor cap, twist
the rubber boot slightly (1/2 turn) to break it loose
(Fig. 12). Grasp the boot (not the cable) and pull it
off with a steady, even force.
(1) Disconnect the ignition coil secondary cable
from center tower of the distributor cap. Hold the ca-
ble terminal approximately 12 mm (1/2 in.) from a
good engine ground (Fig. 13).
WARNING: BE VERY CAREFUL WHEN THE ENGINE
IS CRANKING. DO NOT PUT YOUR HANDS NEAR
THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR THE FAN. DO NOT WEAR
LOOSE FITTING CLOTHING.
(2) Rotate (crank) the engine with the starter mo-
tor and observe the cable terminal for a steady arc. If
steady arcing does not occur, inspect the secondary
coil cable. Refer to Spark Plug Cables in this group.
Also inspect the distributor cap and rotor for cracksor burn marks. Repair as necessary. If steady arcing
occurs, connect ignition coil cable to the distributor
cap.
(3) Remove a cable from one spark plug.
(4) Using insulated pliers, hold the cable terminal
approximately 12 mm (1/2 in.) from the engine cylin-
der head or block while rotating the engine with the
starter motor. Observe the spark plug cable terminal
for an arc. If steady arcing occurs, it can be expected
that the ignition secondary system is operating cor-
rectly.(note that if the ignition coil cable is re-
moved for this test, instead of a spark plug
cable, the spark intensity will be much higher.)
If steady arcing occurs at the spark plug cables, but
the engine will not start, connect the DRB scan tool.
Refer to the Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures ser-
vice manual.
FAILURE TO START TEST
To prevent unnecessary diagnostic time and wrong
test results, the previous Checking For Spark test
should be performed prior to this test.
WARNING: SET PARKING BRAKE OR BLOCK THE
DRIVE WHEELS BEFORE PROCEEDING WITH THIS
TEST.
(1) Unplug the ignition coil harness connector at
the coil (Fig. 14).
(2) Connect a set of small jumper wires (18 gauge
or smaller) between the disconnected harness termi-
nals and the ignition coil terminals. To determine po-
larity at connector and coil, refer to the Wiring
Diagrams section.
(3) Attach one lead of a voltmeter to the positive
(12 volt) jumper wire. Attach the negative side of
voltmeter to a good ground. Determine that sufficient
battery voltage (12.4 volts) is present for the starting
and ignition systems.
Fig. 12 Cable Removal
Fig. 13 Checking for SparkÐTypical
Fig. 14 Coil Harness ConnectorÐTypical (4.0L
Shown)
8D - 10 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 1282 of 2158

CAUTION: DO NOT use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits or kerosene.
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a crosshatch pattern.
The hone marks should INTERSECT at 50É to 60É
for proper seating of rings (Fig. 1).
(4) A controlled hone motor speed between 200 and
300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 50É to 60É
angle. Faster up and down strokes increase the cross-
hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned to remove all traces of abrasive. Use a brush
to wash parts with a solution of hot water and deter-
gent. Dry parts thoroughly. Use a clean, white, lint-
free cloth to check that the bore is clean. Oil the
bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
MEASURING WITH PLASTIGAGE
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING CLEARANCE
Engine crankshaft bearing clearances can be deter-
mined by use of Plastigage, or equivalent. The follow-
ing is the recommended procedures for the use of
Plastigage:
(1) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(2) The total clearance of the main bearings can
only be determined by removing the weight of the
crankshaft. This can be accomplished by either of two
methods:
METHOD - 1 (PREFERRED)ÐShim the bear-
ings adjacent to the bearing to be checked. This will
remove the clearance between upper bearing shell
and the crankshaft. Place a minimum of 0.254 mm
(0.010 inch) shim between the bearing shell and the
adjacent bearing cap. Tighten the bolts to 18 Nzm (13
ft. lbs.) torque.²ALL ENGINESÐWhen checking No.1 main bear-
ing; shim No.2 main bearing.
²ALL ENGINESÐWhen checking No.2 main bear-
ing; shim No.1 and No.3 main bearing.
²ALL ENGINESÐWhen checking No.3 main bear-
ing; shim No.2 and No.4 main bearing.
²ALL ENGINESÐWhen checking No.4 main bear-
ing; shim No.3 and No.5 main bearing.
²2.5L ENGINEÐWhen checking No.5 main bear-
ing; shim No.4 main bearing.
²4.0L ENGINEÐWhen checking No.5 main bear-
ing; shim No.4 and No.6 main bearing.
²4.0L ENGINEÐWhen checking No.6 main bear-
ing; shim No.5 and No.7 main bearing.
²4.0L ENGINEÐWhen checking No.7 main bear-
ing; shim No.6 main bearing.
Remove all shims before assembling engine.
METHOD - 2 (ALTERNATIVE)ÐThe weight of
the crankshaft is supported by a jack under the coun-
terweight adjacent to the bearing being checked.
(3) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing cap shell (Fig. 2). Position the
Plastigage approximately 6.35 mm (1/4 inch) off cen-
ter and away from the oil holes. In addition, suspect
areas can be checked by placing the Plastigage in
that area. Tighten the bearing cap bolts of the bear-
ing being checked to 108 Nzm (80 ft. lbs.) torque.DO
NOT rotate the crankshaft or the Plastigage
may be smeared, giving inaccurate results.
(4) Remove the bearing cap and compare the width
of the flattened Plastigage with the scale provided on
the package (Fig. 3). Plastigage generally comes in 2
scales (one scale is in inches and the other is a met-
ric scale). Locate the band closest to the same width.
This band shows the amount of clearance. Differ-
ences in readings between the ends indicate the
amount of taper present. Record all readings taken
(refer to Engine Specifications).
(5) Plastigage is available in a variety of clearance
ranges. The 0.025-0.076 mm (0.001-0.003 inch) range
is usually the most appropriate for checking engine
bearing clearances.
Fig. 1 Cylinder Bore Crosshatch Pattern
Fig. 2 Placement of Plastigage in Bearing Shell
JENGINES 9 - 3
Page 1283 of 2158

CONNECTING ROD BEARING CLEARANCE
Engine connecting rod bearing clearances can be
determined by use of Plastigage, or equivalent. The
following is the recommended procedures for the use
of Plastigage:
(1) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(2) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire width
of the bearing cap shell (Fig. 2). Position the Plastigage
approximately 6.35 mm (1/4 inch) off center and away
from the oil holes. In addition, suspect areas can be
checked by placing the Plastigage in the suspect area.
(3) The crankshaft must be turned until the connect-
ing rod to be checked starts moving toward the top of
the engine. Only then should the rod cap with Plasti-
gage in place be assembled. Tighten the rod cap nut to
45 Nzm (33 ft. lbs.) torque.DO NOT rotate the crank-
shaft or the Plastigage may be smeared, giving in-
accurate results.
(4) Remove the bearing cap and compare the width
of the flattened Plastigage with the scale provided on
the package (Fig. 3). Plastigage generally comes in 2
scales (one scale is in inches and the other is a met-
ric scale). Locate the band closest to the same width.
This band shows the amount of clearance. Differ-
ences in readings between the ends indicate the
amount of taper present. Record all readings taken
(refer to Engine Specifications).
(5) Plastigage is available in a variety of clearance
ranges. The 0.025-0.076 mm (0.001-0.003 inch) range
is usually the most appropriate for checking engine
bearing clearances.
REPAIR DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS
Damaged or worn threads can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of:
²Drilling out worn or damaged threads.
²Tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil Tap, or
equivalent.
²Installing an insert into the tapped hole.
This brings the hole back to its original thread
size.
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.Heli-Coil tools and inserts are readily available
from automotive parts jobbers.
SERVICE ENGINE ASSEMBLY (SHORT BLOCK)
A service replacement engine assembly (short
block) may be installed whenever the original cylin-
der block is defective or damaged beyond repair. It
consists of the cylinder block, crankshaft, piston and
rod assemblies. If needed, the camshaft must be pro-
cured separately and installed before the engine is
installed in the vehicle.
A short block is identified with the letter ``S'' stamped
on the same machined surface where the build date
code is stamped for complete engine assemblies.
Installation includes the transfer of components
from the defective or damaged original engine. Fol-
low the appropriate procedures for cleaning, inspec-
tion and torque tightening.
HYDROSTATIC LOCK
When an engine is suspected of hydrostatic lock
(regardless of what caused the problem), follow the
steps below.
(1) Perform the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure
(refer to Group 14, Fuel System).
(2) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(3) Inspect air cleaner, induction system and in-
take manifold to ensure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(4) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs to
catch any fluid that may possibly be under pressure in
the cylinder head. Remove the plugs from the engine.
CAUTION: DO NOT use the starter motor to rotate
the crankshaft. Severe damage could occur.
(5) With all spark plugs removed, rotate the crank-
shaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(6) Identify the fluid in the cylinders (i.e. coolant,
fuel, oil, etc.).
(7) Make sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders.
(8) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from occurring again.
(9) Squirt engine oil into the cylinders to lubricate
the walls. This will prevent damage on restart.
(10) Install new spark plugs. Tighten the spark
plugs to 37 Nzm (27 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Drain engine oil. Remove and discard the oil
filter.
(12) Install the drain plug. Tighten the plug to 34
Nzm (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install a new oil filter.
(14) Fill engine crankcase with the specified
amount and grade of oil (refer to Group 0, Lubrica-
tion and Maintenance).
(15) Connect the negative cable to the battery.
(16) Start the engine and check for any leaks.
Fig. 3 Clearance Measurement
9 - 4 ENGINESJ
Page 1565 of 2158

happens when the container delivery mechanism is im-
properly calibrated. Always check the lubricant level af-
ter filling to avoid an under fill condition.
A correct lubricant level check can only be made
when the vehicle is level; use a drive-on hoist to en-
sure this. Also allow the lubricant to settle for a
minute or so before checking. These recommenda-
tions will ensure an accurate check and avoid an un-
der-or-overfill condition.
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting is usually caused by a low lubricant
level, improper or contaminated lubricants, compo-
nent damage, incorrect clutch adjustment, or by a
damaged clutch pressure plate or disc.
Substantial lubricant leaks can result in gear, shift
rail, synchro and bearing damage. If a leak goes un-
detected for an extended period, the first indications
of a problem are usually hard shifting and noise.
Incorrect or contaminated lubricants can also con-
tribute to hard shifting. The consequence of using
non-recommended lubricants is noise, excessive wear,
internal bind and hard shifting.
Improper clutch release is a frequent cause of hard
shifting. Incorrect adjustment or a worn, damaged
pressure plate or disc can cause incorrect release. If
the clutch problem is advanced, gear clash during
shifts can result.
Worn or damaged synchro rings can cause gear clash
when shifting into any forward gear. In some new or re-
built transmissions, new synchro rings may tend to
stick slightly causing hard or noisy shifts. In most
cases, this condition will decline as the rings wear-in.
TRANSMISSION NOISE
Most manual transmissions make some noise dur-
ing normal operation. Rotating gears generate a mild
whine that is audible but only at extreme speeds.
Severe, highly audible transmission noise is gener-
ally the result of a lubricant problem. Insufficient,
improper, or contaminated lubricant will promote
rapid wear of gears, synchros, shift rails, forks and
bearings. The overheating caused by a lubricant
problem, can also lead to gear breakage.
TRANSMISSION REMOVAL
(1) Shift transmission into first or third gear. Then
raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Support engine with adjustable jack stand. Po-
sition wood block between jack and oil pan to avoid
damaging pan.
(3) Disconnect necessary exhaust system components.
(4) Remove skid plate.
(5) Disconnect rear cushion and bracket from
transmission (Fig. 5).
(6) Remove rear crossmember.
Fig. 5 Rear Mount Components (YJ Shown)
JAX 4/5 MANUAL TRANSMISSION 21 - 3