Page 1903 of 2158
AW-4 VALVE BODY CHECK BALL DIMENSIONS
AW-4 CLUTCH AND BRAKE PACK REQUIREMENTS
JTRANSMISSION/TRANSFER CASE SPECIFICATIONS 21 - 341
Page 1904 of 2158
AW-4 ACCUMULATOR COMPONENT
IDENTIFICATION
21 - 342 TRANSMISSION/TRANSFER CASE SPECIFICATIONSJ
Page 1905 of 2158
AW-4 VALVE AND SPRING IDENTIFICATION
JTRANSMISSION/TRANSFER CASE SPECIFICATIONS 21 - 343
Page 1906 of 2158
AW-4 TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
NP231/NP242 TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
21 - 344 TRANSMISSION/TRANSFER CASE SPECIFICATIONSJ
Page 1916 of 2158

VEHICLE VIBRATION
Vehicle vibration can be caused by:
²Tire/wheel unbalance or excessive runout
²Defective tires with extreme tread wear
²Nylon overlay flat spots (performance tires only)
²Incorrect wheel bearing adjustment (if applicable)
²Loose or worn suspension/steering components
²Certain tire tread patterns
²Incorrect drive shaft angles or excessive drive
shaft/yoke runout
²Defective or worn U-joints
²Excessive brake rotor or drum runout
²Loose engine or transmission supports/mounts
²And by engine operated accessories
Refer to the appropriate Groups in this man-
ual for additional information.
VIBRATION TYPES
There are two types of vehicle vibration:
²Mechanical
²Audible.
Mechanical vehicle vibration can be felt through
the seats, floor pan and/or steering wheel.
Audible vehicle vibration is heard above normal
background noise. The sound can be a droning or
drumming noise.
Vibrations are sensitive to change in engine torque,
vehicle speed or engine speed.
ENGINE TORQUE SENSITIVE VIBRATION
This vibration can be increased or decreased by:
²Accelerating
²Decelerating
²Coasting
²Maintaining a constant vehicle speed
VEHICLE SPEED SENSITIVE VIBRATION
This vibration condition always occurs at the same
vehicle speed regardless of the engine torque or en-
gine speed.
ENGINE SPEED (RPM) SENSITIVE VIBRATION
This vibration occurs at varying engine speeds. It
can be isolated by increasing or decreasing the en-
gine speed with the transmission in NEUTRAL posi-
tion.
VIBRATION DIAGNOSIS
A vibration diagnosis should always begin with a
10 mile (16 km) trip (to warm the vehicle and tires).
Then a road test to identify the vibration. Corrective
action should not be attempted until the vibration
type has been identified via a road test.
During the road test, drive the vehicle on a smooth
surface. If vibration exists, note and record the fol-
lowing information:²Identify the vehicle speed range when the vibra-
tion occurs
²Identify the type of vibration
²Identify the vibration sensitivity
²Determine if the vibration is affected by changes
in vehicle speed, engine speed and engine torque.
When the vibration has been identified, refer to the
Vibration Diagnosis chart for causes. Consider cor-
recting only those causes coded in the chart that are
related to the vibration condition.
Refer to the following cause codes and descriptions
for explanations when referring to the chart.
TRRÐTire and Wheel Radial Runout:Vehicle
speed sensitive, mechanical vibration. The runout
will not cause vibration below 20 mph (32 km/h).
WHÐWheel Hop:Vehicle speed sensitive, me-
chanical vibration. The wheel hop generates rapid
up-down movement in the steering wheel. The vibra-
tion is most noticeable in the 20 - 40 mph (32 - 64
km/h) range. The wheel hop will not cause vibration
below 20 mph (32 km/h). Wheel hop is caused by a
tire/wheel that has a radial runout of more than
0.045 of-an-inch (1.14 mm). If wheel runout is accept-
able and combined runout cannot be reduced by re-
positioning the tire on wheel, replace tire.
TBÐTire/Wheel Balance:Vehicle speed sensitive,
mechanical vibration. Static tire/wheel unbalance
will not cause vibration below 30 mph (46 km/h). Dy-
namic tire/wheel unbalance will not cause vibration
below 40 mph (64 km/h).
TLRÐTire/Wheel Lateral runout:Vehicle speed
sensitive, mechanical vibration. The runout will not
cause vibration below 50 - 55 mph (80 - 88 km/h). Ex-
cessive lateral runout will also cause front-end
shimmy.
TWÐTire Wear:Vehicle speed sensitive, audible
vibration. Abnormal tire wear causes small vibration
in the 30 - 55 mph (88 km/h) range. This will pro-
duce a whine noise at high speed. The whine will
change to a growl noise when the speed is reduced.
WÐTire Waddle:Vehicle speed sensitive, mechan-
ical vibration. Irregular tire uniformity can cause
side-to-side motion during speeds up to 15 mph (24
km/h). If the motion is excessive, identify the defec-
tive tire and replace it.
UAJÐUniversal Joint (Drive Shaft) Angles:
Torque/vehicle speed sensitive, mechanical/audible vi-
bration. Incorrect drive shaft angles cause mechani-
cal vibration below 20 mph (32 km/h) and in the 70
mph (112 km/h) range. The incorrect angles can also
produce an audible vibration in the 20 - 50 mph (32 -
80 km/h) range. Caster adjustment could be required
to correct the angles.
UJÐUniversal Joints:Engine torque/vehicle
speed sensitive, mechanical/audible vibration. If the
22 - 10 WHEELS AND TIRESJ
Page 1917 of 2158

U-joint is worn it will cause vibration with almost
any vehicle speed/engine torque condition.
DSYÐDrive Shaft and Yokes:Vehicle speed sen-
sitive, mechanical/audible vibration. The condition
will not cause vibration below 35 mph (56 km/h). Ex-
cessive runout, unbalance or dents and bends in the
shaft will cause the vibration. Identify the actual
cause and repair/replace as necessary.
WBÐWheel Bearings:Vehicle speed sensitive,
mechanical/audible vibration. Loose wheel bearings
cause shimmy-like vibration at 35 mph (56 km/h)
and above. Worn bearings will also produce a growl
noise at low vehicle speed and a whine noise at high
vehicle speed. The wheel bearings must be adjusted
or replaced, as applicable.
ANÐAxle Noise:Engine torque/vehicle speed sen-
sitive, mechanical/audible vibration. The axle will not
cause mechanical vibration unless the axle shaft is
bent. Worn or damaged axle pinion shaft or differen-
tial gears and bearings will cause noise. Replace the
defective component(s) as necessary.
SSCÐSuspension and Steering Components:
Vehicle speed sensitive, mechanical vibration. Worn
suspension/steering components can cause mechani-
cal vibration at speeds above 20 mph (32 km/h).
Identify and repair or replace the defective compo-
nent(s).EAÐEngine Driven Accessories:Engine speed
sensitive, mechanical/audible vibration. Vibration can
be caused by loose or broken A/C compressor, PS
pump, water pump, generator or brackets, etc. Usu-
ally more noticeable when the transmission is shifted
into the NEUTRAL position and the engine speed
(rpm) increased. Inspect the engine driven accesso-
ries in the engine compartment. Repair/replace as
necessary.
ADBÐAccessory Drive Belts:Engine speed sen-
sitive, audible vibration. Worn drive belts can cause a
vibration that produces either a droning, fluttering or
rumbling noise. Inspect the drive belt(s) and tighten/
replace as necessary.
DEMÐDamaged Engine or Transmission Sup-
port Mounts:Engine speed sensitive, mechanical/
audible vibration. If a support mount is worn, noise
or vibration will occur. Inspect the support mounts
and repair/replace as necessary.
ESÐExhaust System:Engine speed sensitive,
mechanical/audible vibration. If loose exhaust compo-
nents contact the vehicle body they will cause noise
and vibration. Inspect the exhaust system for loose,
broken and mis-aligned components and repair/re-
place as necessary.
VIBRATION DIAGNOSIS
JWHEELS AND TIRES 22 - 11
Page 1995 of 2158
TRAILER HITCH
TRAILER HITCHÐXJ
CLASS III HITCH
A class III weight-distributing/equalizer type hitch
can be used to tow a trailer:
²Having a maximum gross weight of 5,000 lbs/2250
kg.
²Having a maximum tongue weight of 750 lbs/332
kg).
The following vehicle basic equipment is required
for class III trailer towing:
²P205/75R15 or larger tires.
²Full size spare tire.
²Trailer sway control.
²Trailer tow wire harness and connector.
²Heavy duty turn signal flasher element.
²Heavy duty axle (with synthetic lubricant).
²Heavy duty cooling system.
²Heavy duty generator/battery.
²Auxiliary automatic transmission fluid cooler.
²I-6, 4.0L engine.
Wide-angle type door mirrors are recommended but
not required.
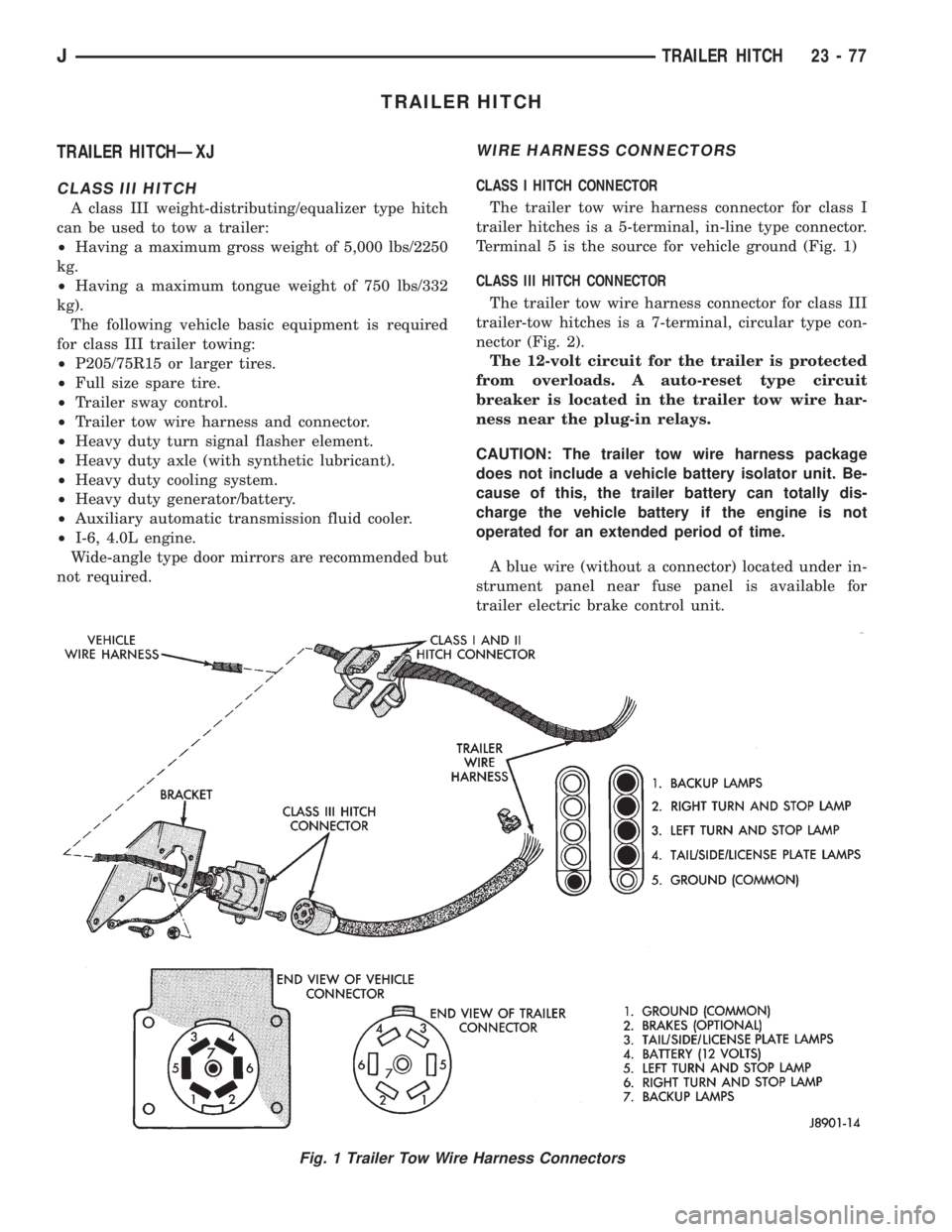
WIRE HARNESS CONNECTORS
CLASS I HITCH CONNECTOR
The trailer tow wire harness connector for class I
trailer hitches is a 5-terminal, in-line type connector.
Terminal 5 is the source for vehicle ground (Fig. 1)
CLASS III HITCH CONNECTOR
The trailer tow wire harness connector for class III
trailer-tow hitches is a 7-terminal, circular type con-
nector (Fig. 2).
The 12-volt circuit for the trailer is protected
from overloads. A auto-reset type circuit
breaker is located in the trailer tow wire har-
ness near the plug-in relays.
CAUTION: The trailer tow wire harness package
does not include a vehicle battery isolator unit. Be-
cause of this, the trailer battery can totally dis-
charge the vehicle battery if the engine is not
operated for an extended period of time.
A blue wire (without a connector) located under in-
strument panel near fuse panel is available for
trailer electric brake control unit.
Fig. 1 Trailer Tow Wire Harness Connectors
JTRAILER HITCH 23 - 77
Page 2008 of 2158

(3) Remove the assist handle from the trim mold-
ing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the handle on the trim molding and in-
stall the retaining screws. Tighten the retaining
screws to 3 Nzm (22 in-lbs) torque.
(2) Install the covers over the retaining screws.
FRONT SHOULDER BELT/BUCKLEÐXJ
REMOVAL
(1) Slide the front seats all the way forward for ac-
cess to the belt anchor bolt.
(2) Disconnect the belt wire harness connector
(Fig. 1).
(3) Remove the anchor bolt cover.
(4) Remove the shoulder belt buckle anchor bolt
with a Torx bit.
(5) Remove the shoulder belt buckle from the
transmission tunnel.
(6) Remove the cap concealing the shoulder belt
upper anchor bolt (Fig. 2 and 3).
(7) Use a Torx bit to remove the upper anchor bolt.
Remove the support/guide washer.
(8) Remove the inner scuff plate/trim panel from
the door sill and remove the shoulder belt lower an-
chor bolt(s) with a Torx bit.
(9) Remove the shoulder belt and the retractor.
INSPECTION
Inspect the front shoulder belts and buckles. Re-
place any belt that is either cut, frayed, torn or dam-
aged in any way. Replace the shoulder belt if the
retractor is damaged or inoperative.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the shoulder belt retractor in the
shield and install the lower anchor bolt with a Torx
bit.
Fig. 17 Outer Scuff PlatesÐ4-Door Vehicles
Fig. 18 Liftgate and Door Sill Outer Scuff Plate
Fig. 19 Assist HandlesÐXJ Vehicles
Fig. 1 Front Shoulder Belt Buckles
23 - 90 INTERIOR COMPONENTSÐXJJ