1995 JEEP YJ recommended oil
[x] Cancel search: recommended oilPage 1398 of 2158

The frame is constructed of high-strength channel
steel siderails and crossmembers. The crossmembers
join the siderails and retain them in alignment in re-
lation to each other. This provides resistance to
frame twists and strains.
FRAME STRAIGHTENING
When necessary, a conventional frame that is bent
or twisted can be straightened by application of heat.
The temperature must not exceed 566ÉC (1050ÉF).
The use of a specially designed heat crayon can de-
termine the desired temperature. Excessive heat will
decrease the strength of the metal and result in a
weakened frame.
Welding the joints around riveted cross members
and frame side rails is not recommended.
A straightening repair process should be limited to
frame members that are not severely damaged.
FRAME REPAIRS
DRILLING HOLES
Do not drill holes in frame side rail top and bottom
flanges, metal fatigue can result causing frame fail-
ure. Holes drilled in the side of the frame rail must
be at least 38 mm (1.5 in.) from the top and bottom
flanges.
Additional drill holes should be located away from
existing holes.
WELDING
Use MIG, TIG or arc welding equipment to repair
welded frame components.
Frame components that have been damaged should
be inspected for cracks before returning the vehicle
to use. If cracks are found in accessible frame com-
ponents perform the following procedures.
(1) Drill a hole at each end of the crack with a 3
mm (O.125 in.) diameter drill bit.
(2) Using a suitable die grinder with 3 inch cut off
wheel, V-groove the crack to allow 100% weld pene-
tration.
(3) Weld the crack.
(4) If necessary when a side rail is repaired, grind
the weld smooth and install a reinforcement channel
(Fig. 4) over the repaired area.
If a reinforcement channel is required, the
top and bottom flanges should be 0.250 inches
narrower than the side rail flanges. Weld only
in the areas indicated (Fig. 4).
FRAME FASTENERS
Bolts, nuts and rivets can be used to repair frames
or to install a reinforcement section on the frame.
Bolts can be used in place of rivets. When replacing
rivets with bolts, install the next larger size diameter
bolt to assure proper fit. If necessary, drill the hole
out just enough to receive the bolt.Conical-type washers are preferred over the split-
ring type lock washers. Normally, grade-5 bolts are
adequate for frame repair.Grade-3 bolts or softer
should not be used.Tightening bolts/nuts with the
correct torque, refer to the Introduction Group at the
front of this manual for tightening information.
FRAME DIMENSIONS
Frame dimensions are listed in millimeter scale.
All dimensions are from center to center of Principal
Locating Point (PLP), or from center to center of PLP
and fastener location (Fig. 5).
TOW HOOKS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the two bolts that attach the tow hook
to the bumper rail and to the frame rail.
(2) Remove the tow hook.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the tow hook on the bumper rail and
frame rail.
(2) Install the attaching bolts. Tighten the bolts to
102 Nzm (75 ft. lbs.) torque.
GENERATOR SPLASH SHIELD
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the shield retaining nut and washer
(Fig. 6) from the engine oil pan stud (2.5L engines
only).
(2) Pry the serrated retainers from the frame rail
holes at each side of the vehicle.
(3) Pry the serrated retainers from the fan shroud
holes (Fig. 6).
(4) Remove the shield from the vehicle.
Fig. 4 Frame Reinforcement
JYJÐFRAME 13 - 13
Page 1564 of 2158
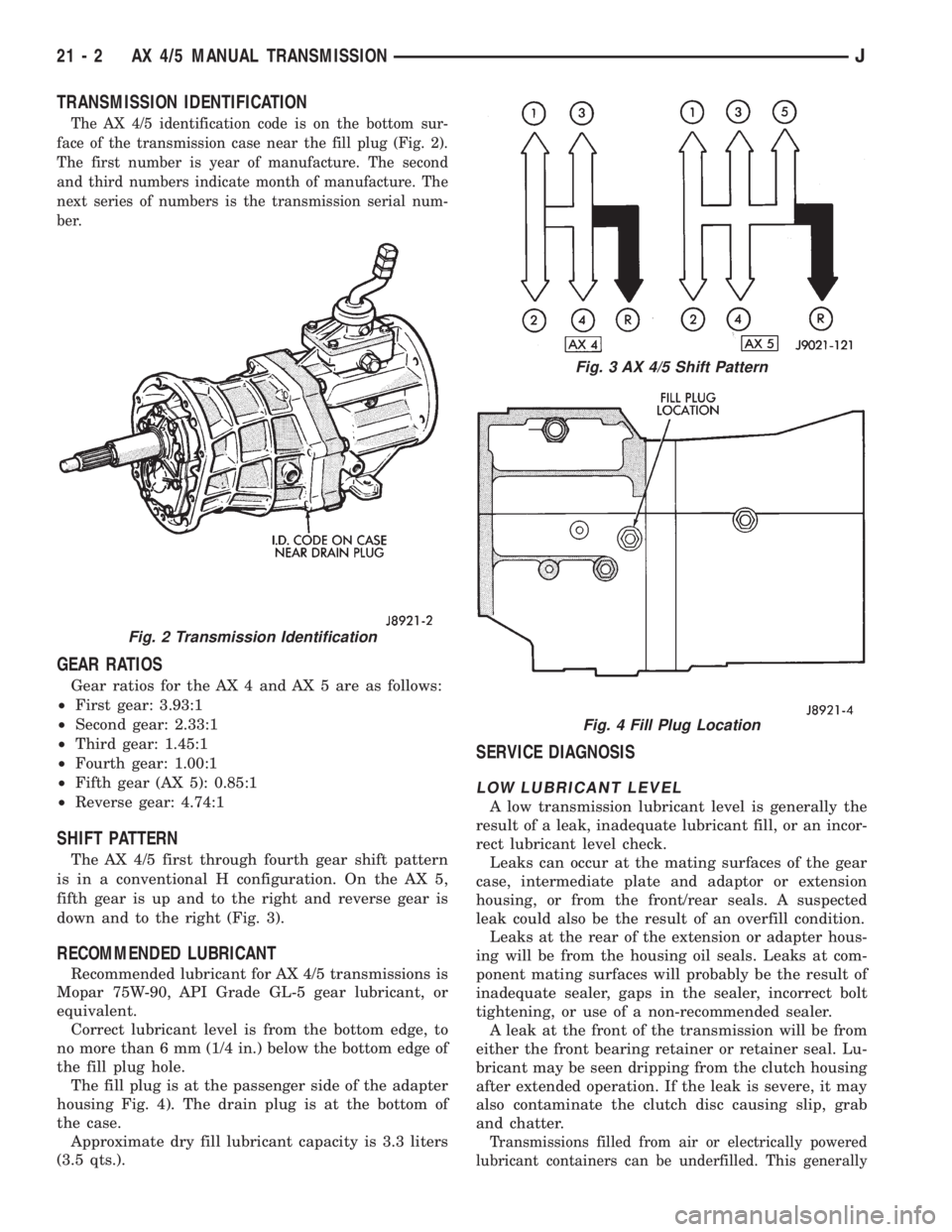
TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION
The AX 4/5 identification code is on the bottom sur-
face of the transmission case near the fill plug (Fig. 2).
The first number is year of manufacture. The second
and third numbers indicate month of manufacture. The
next series of numbers is the transmission serial num-
ber.
GEAR RATIOS
Gear ratios for the AX 4 and AX 5 are as follows:
²First gear: 3.93:1
²Second gear: 2.33:1
²Third gear: 1.45:1
²Fourth gear: 1.00:1
²Fifth gear (AX 5): 0.85:1
²Reverse gear: 4.74:1
SHIFT PATTERN
The AX 4/5 first through fourth gear shift pattern
is in a conventional H configuration. On the AX 5,
fifth gear is up and to the right and reverse gear is
down and to the right (Fig. 3).
RECOMMENDED LUBRICANT
Recommended lubricant for AX 4/5 transmissions is
Mopar 75W-90, API Grade GL-5 gear lubricant, or
equivalent.
Correct lubricant level is from the bottom edge, to
no more than 6 mm (1/4 in.) below the bottom edge of
the fill plug hole.
The fill plug is at the passenger side of the adapter
housing Fig. 4). The drain plug is at the bottom of
the case.
Approximate dry fill lubricant capacity is 3.3 liters
(3.5 qts.).
SERVICE DIAGNOSIS
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
A low transmission lubricant level is generally the
result of a leak, inadequate lubricant fill, or an incor-
rect lubricant level check.
Leaks can occur at the mating surfaces of the gear
case, intermediate plate and adaptor or extension
housing, or from the front/rear seals. A suspected
leak could also be the result of an overfill condition.
Leaks at the rear of the extension or adapter hous-
ing will be from the housing oil seals. Leaks at com-
ponent mating surfaces will probably be the result of
inadequate sealer, gaps in the sealer, incorrect bolt
tightening, or use of a non-recommended sealer.
A leak at the front of the transmission will be from
either the front bearing retainer or retainer seal. Lu-
bricant may be seen dripping from the clutch housing
after extended operation. If the leak is severe, it may
also contaminate the clutch disc causing slip, grab
and chatter.
Transmissions filled from air or electrically powered
lubricant containers can be underfilled. This generally
Fig. 2 Transmission Identification
Fig. 3 AX 4/5 Shift Pattern
Fig. 4 Fill Plug Location
21 - 2 AX 4/5 MANUAL TRANSMISSIONJ
Page 1565 of 2158

happens when the container delivery mechanism is im-
properly calibrated. Always check the lubricant level af-
ter filling to avoid an under fill condition.
A correct lubricant level check can only be made
when the vehicle is level; use a drive-on hoist to en-
sure this. Also allow the lubricant to settle for a
minute or so before checking. These recommenda-
tions will ensure an accurate check and avoid an un-
der-or-overfill condition.
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting is usually caused by a low lubricant
level, improper or contaminated lubricants, compo-
nent damage, incorrect clutch adjustment, or by a
damaged clutch pressure plate or disc.
Substantial lubricant leaks can result in gear, shift
rail, synchro and bearing damage. If a leak goes un-
detected for an extended period, the first indications
of a problem are usually hard shifting and noise.
Incorrect or contaminated lubricants can also con-
tribute to hard shifting. The consequence of using
non-recommended lubricants is noise, excessive wear,
internal bind and hard shifting.
Improper clutch release is a frequent cause of hard
shifting. Incorrect adjustment or a worn, damaged
pressure plate or disc can cause incorrect release. If
the clutch problem is advanced, gear clash during
shifts can result.
Worn or damaged synchro rings can cause gear clash
when shifting into any forward gear. In some new or re-
built transmissions, new synchro rings may tend to
stick slightly causing hard or noisy shifts. In most
cases, this condition will decline as the rings wear-in.
TRANSMISSION NOISE
Most manual transmissions make some noise dur-
ing normal operation. Rotating gears generate a mild
whine that is audible but only at extreme speeds.
Severe, highly audible transmission noise is gener-
ally the result of a lubricant problem. Insufficient,
improper, or contaminated lubricant will promote
rapid wear of gears, synchros, shift rails, forks and
bearings. The overheating caused by a lubricant
problem, can also lead to gear breakage.
TRANSMISSION REMOVAL
(1) Shift transmission into first or third gear. Then
raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Support engine with adjustable jack stand. Po-
sition wood block between jack and oil pan to avoid
damaging pan.
(3) Disconnect necessary exhaust system components.
(4) Remove skid plate.
(5) Disconnect rear cushion and bracket from
transmission (Fig. 5).
(6) Remove rear crossmember.
Fig. 5 Rear Mount Components (YJ Shown)
JAX 4/5 MANUAL TRANSMISSION 21 - 3
Page 1596 of 2158

The first number is year of manufacture. The sec-
ond and third numbers indicate month of manufac-
ture. The next series of numbers is the transmission
serial number.
TRANSMISSION SHIFT PATTERN
The AX 15 shift pattern is shown in Figure 3. First
and second and third and fourth gear ranges are in
line for improved shifting. Fifth and reverse gear
ranges are also in line at the extreme right of the
pattern (Fig. 3).
The AX 15 is equipped with a reverse lockout
mechanism. The shift lever must be moved through
the Neutral detent before making a shift to reverse.
TRANSMISSION LUBRICANT
Recommended lubricant for AX 15 transmissions is
Mopar 75W-90, API Grade GL-5 gear lubricant, or
equivalent.
Correct lubricant level is from the bottom edge, to
no more than 6 mm (1/4 in.) below the bottom edge of
the fill plug hole.
Approximate dry fill lubricant capacity is:
²3.10 liters (3.27 qts.) in 4-wheel drive models
²3.15 liters (3.32 qts.) in 2-wheel drive models
TRANSMISSION SWITCH AND PLUG LOCATIONS
The fill plug is at the driver side of the gear case
(Fig. 4).
The drain plug and backup light switch are on the
passenger side of the gear case (Fig. 5).
TRANSMISSION GEAR RATIOS
AX 15 gear ratios are:
First gear - 3.83:1
Second gear - 2.33:1
Third gear - 1.44:1
Fourth gear - 1.00:1
Fifth gear - 0.79:1
Reverse - 4.22:1
SERVICE DIAGNOSIS
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
A low transmission lubricant level is generally the
result of a leak, inadequate lubricant fill, or an incor-
rect lubricant level check.
Leaks can occur at the mating surfaces of the gear
case, intermediate plate and adapter or extension
housing, or from the front/rear seals. A suspected
leak could also be the result of an overfill condition.
Leaks at the rear of the extension or adapter hous-
ing will be from the housing oil seals. Leaks at com-
ponent mating surfaces will usually be the result of
inadequate sealer, gaps in the sealer, incorrect bolt
tightening, or use of a non-recommended sealer.
A leak at the front of the transmission will be from
either the front bearing retainer or retainer seal. Lu-
bricant may be seen dripping from the clutch housing
after extended operation. If the leak is severe, it may
also contaminate the clutch disc causing slip, grab
and chatter.
Transmissions filled from air or electrically pow-
ered lubricant containers can be underfilled. This
Fig. 3 AX 15 Shift Pattern
Fig. 4 Fill Plug Location
Fig. 5 Drain Plug/Backup Light Switch Location
21 - 34 AX 15 MANUAL TRANSMISSIONJ
Page 1629 of 2158

30RH/32RH AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
GENERAL INFORMATION
INDEX
page page
Recommended Fluid....................... 67
Torque Converter......................... 67
Transmission Application.................... 67
Transmission Changes and Parts Interchangeability.. 67
Transmission Controls and Components........ 67
Transmission Identification.................. 67
TRANSMISSION APPLICATION
Chrysler 30RH and 32RH automatic transmissions
are used in XJ/YJ models. Both are 3-speed auto-
matic transmissions with a gear-type oil pump, two
clutches and bands and a planetary gear system (Fig.
1).
The 30RH is used in XJ/YJ models with a 2.5L en-
gine. The 32RH is used in YJ models with a 4.0L en-
gine.
TORQUE CONVERTER
A three element, torque converter is used for all
applications. The converter consists of an impeller,
stator, and turbine.
The converter used with 30RH/32RH transmissions
has a converter clutch. The clutch is engaged by an
electrical solenoid and mechanical module on the
valve body. The solenoid is operated by the power-
train control module.
The torque converter is a welded assembly and is
not a repairable component. The converter is serviced
as an assembly.
RECOMMENDED FLUID
The recommended and preferred fluid for 30RH/
32RH transmissions is Mopar ATF Plus, Type 7176.
Dexron II is not really recommended and should
only be used when ATF Plus is not available.
TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION
The transmission identification numbers are
stamped on the left side of the case just above the oil
pan gasket surface (Fig. 2). The first set of numbers
is the transmission part number. The next set of code
numbers set is the date of build. The final set of code
numbers represents the transmission serial number.
TRANSMISSION CHANGES AND PARTS
INTERCHANGEABILITY
1995 transmissions are similar to previous models
but only in appearance. Current transmissions are
dimensionally different. Do not interchange new/oldparts. Different dimensions, fluid passages, input/
output shafts, cases, bands, valve bodies and gover-
nor assemblies are just a few of the changed items.
CAUTION: Special bolts are used to attach the
driveplate to the crankshaft on models with a 2.5L
engine and 30RH transmission,. These bolts have a
smaller hex head for torque converter clearance.
DO NOT interchange these bolts with similar size
bolts for any reason.
Different governor weight assemblies are used in
30RH/32RH transmissions. The 30RH weight assem-
bly is much the same as in previous years. However,
the 32RH has a three stage governor weight assem-
bly consisting of the outer weight, a smaller weight
spring, and a new intermediate weight. Refer to the
overhaul and in-vehicle service sections for more de-
tailed information.
Plastic check balls are now used in many 30RH/
32RH valve bodies. The new check balls entered pro-
duction as a running change. Plastic and steel check
balls are not interchangeable.
A converter drainback check valve has been added
to the fluid cooler system. The one-way valve is lo-
cated in the transmission outlet (pressure) line. The
valve prevents fluid drainback when the vehicle is
parked for lengthy periods.
TRANSMISSION CONTROLS AND COMPONENTS
The transmission hydraulic control system per-
forms five basic functions, which are:
²pressure supply
²pressure regulation
²flow control
²clutch/band apply and release
²lubrication
Pressure Supply And Regulation
The oil pump generates the fluid working pressure
needed for operation and lubrication. The pump is
J30RH/32RH AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 21 - 67
Page 1639 of 2158

(4) Apply thick soapy water solution to suspected
leak areas.
CAUTION: The recommended test pressure is 8 psi.
The maximum allowable test pressure is 10 psi. Do
not exceed specified test pressure.
(5) Pressurize transmission to 8 psi with air pump.
(6) Observe suspected leak areas. Air bubbles ap-
pearing in soapy water solution indicate leak points.
(7) Remove test tools and plugs after test comple-
tion and make necessary repairs as described in Leak
Correction procedure.
CONVERTER HOUSING AREA LEAK
CORRECTION
(1) Remove converter.
(2) Tighten front band adjusting screw until band
is tight around clutch retainer. This prevents
clutches from coming out when oil pump is removed.
(3) Remove oil pump and seal. Inspect pump hous-
ing drainback and vent holes for obstructions. Clear
holes with solvent and wire.(4) Inspect pump bushing and converter hub. If
bushing is scored, replace it. If converter hub is
scored, either polish it with crocus cloth or replace
converter if scoring is severe.
(5) Install new pump seal, O-ring, gasket, bushing.
Replace oil pump if cracked, porous or damaged in
any way.
(6) Loosen kickdown lever pin plug two turns. Ap-
ply Permatex No. 2 or equivalent to plug threads and
tighten plug to 17 Nzm (150 in-lbs) torque.
(7) Adjust front band.
(8) Lubricate pump seal and converter hub with
transmission fluid or petroleum jelly and install con-
verter.
(9) Install transmission.
(10) Install converter housing dust shield and
lower vehicle.
DIAGNOSIS GUIDES AND CHARTS
The diagnosis charts provide additional reference
for transmission and converter clutch diagnosis.
The hydraulic flow charts outline fluid flow and hy-
draulic circuitry. Circuit operation is provided for all
gear ranges. Normal working pressures are also sup-
plied for each of the various gear ranges.
Fig. 15 Vent Plug And Hub Seal Cup Installation
Fig. 16 Pressurizing Transmission
J30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS 21 - 77
Page 1661 of 2158

30RH/32RH IN-VEHICLE SERVICE
INDEX
page page
Converter Drainback Check Valve Service...... 113
Fluid and Filter Replacement................. 99
Fluid Level Check......................... 99
Front Band Adjustment.................... 102
Governor and Park Gear Service............. 105
Oil Filter Replacement..................... 103
Park Interlock Cable Adjustment (XJ).......... 101
Park Lock Component Replacement.......... 108
Park/Neutral Position Switch Service.......... 109
Rear Band Adjustment.................... 103
Recommended Fluid....................... 99Refilling After Overhaul or Fluid/Filter Change . . . 100
Shift Cable Adjustment (XJ)................. 100
Shift Linkage Adjustment (YJ)............... 100
Speedometer Service..................... 109
Throttle Valve Cable Adjustment (XJ/YJ)....... 101
Transmission Cooler Flow Testing............ 113
Transmission Cooler Line and Fitting Service.... 111
Transmission Cooler Reverse Flushing......... 114
Valve Body Installation.................... 104
Valve Body Removal...................... 104
Valve Body Service....................... 104
RECOMMENDED FLUID
Recommended (and preferred) fluid for 30RH/32RH
transmissions is Mopar ATF Plus, type 7176.
Dexron II is not really recommended and should
only be used when ATF Plus is not available.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK
Transmission fluid level should be checked monthly
under normal operation. If the vehicle is used for
trailer towing or similar heavy load hauling, check
fluid level and condition weekly.
Fluid level is checked with the engine running at
curb idle speed, the transmission in Neutral and the
transmission fluid at normal operating temperature.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK PROCEDURE
(1) Transmission fluid must be at normal operating
temperature for accurate fluid level check. Drive ve-
hicle if necessary to bring fluid temperature up to
normal hot operating temperature of 82ÉC (180ÉF).
(2) Position vehicle on level surface. This is ex-
tremely important for accurate fluid level check.
(3) Start and run engine at curb idle speed.
(4) Apply parking brakes.
(5) Shift transmission momentarily into all gear
ranges. Then shift transmission back to Neutral.
(6) Clean top of filler tube and dipstick to keep dirt
from entering tube.
(7) Remove dipstick and check fluid level as fol-
lows:
(a) Dipstick has three fluid level indicator levels
(Fig. 1) which are a MIN dot, an OK crosshatch
area, and a MAX fill arrow.
(b) Correct maximum level is to MAX arrow
mark. Correct acceptable level is to OK mark in
crosshatch area.
(c) Incorrect level is at or below MIN dot.
(d) If fluid is low, add only enough Mopar ATF
Plus restore correct level. Do not overfill.CAUTION: Do not overfill the transmission. Overfill-
ing may cause leakage out the pump vent which
can be mistaken for a pump seal leak. Overfilling
will also cause fluid aeration and foaming as the ex-
cess fluid is picked up and churned by the gear
train. This will reduce fluid life significantly.
FLUID AND FILTER REPLACEMENT
NORMAL CHANGE INTERVAL
The fluid and filter should be changed (and the
bands adjusted) at recommended maintenance inter-
vals, or whenever the transmission has been disas-
sembled for any reason.
Refer to the Driveline section in Group O, Lubrica-
tion and Maintenance for recommended change inter-
vals. Refer to the fluid/filter replacement and band
adjustment procedures in this section.
SEVERE USAGE CHANGE INTERVAL
Under severe usage, the fluid and filter should be
changed and the bands adjusted at 12,000 mile (19
000 Km) intervals.
Severe usage is defined as:
(a) More than half of vehicle operation occurs in
heavy city traffic during hot weather (above 90É F).
(b) Vehicle is used for taxi, police, limousine, or
similar commercial operation.
Fig. 1 Fluid Level Marks On Transmission Dipstick
J30RH/32RH IN-VEHICLE SERVICE 21 - 99
Page 1687 of 2158

(47) Remove rear servo spring retainer snap ring.
Then remove compressor tools and remove rear servo
spring and piston.
OVERHAUL SERVICE INFORMATION
Inspect the transmission bushings during overhaul.
Bushing condition is important as severely worn, or
scored bushings contribute to low pressures, clutch
slip and accelerated wear of other components.How-
ever, do not replace bushings as a matter of
course. Replace bushings only when they are
actually worn, or scored.
Use recommended tools to replace bushings. The
tools are sized and designed to remove, install and
seat bushings correctly. The bushing replacement
tools are included in Bushing Tool Set C-3887-B or
C-3887-J. The bushing tools are manufactured by
Miller Tool Co. and is available through the dealer
tool program.
Pre-sized service bushings are available for replace-
ment purposes. Only the sun gear bushings are not
serviced. Replace the gear as an assembly if the
bushings are worn, or scored.
Heli-Coil inserts are recommended for repairing
damaged, stripped or worn threads in aluminum
parts. These inserts are available from most automo-
tive jobbers. Stainless steel inserts are preferred.
The use of crocus cloth is permissible where neces-
sary. When used on valves, use care to avoid round-
ing off sharp edges. Sharp edges are vital as they
prevent foreign matter from getting between the
valve and valve bore.
Do not reuse oil seals, gaskets, seal rings, or
O-rings during overhaul. Replace these parts as a
matter of course. Also do not reuse snap rings or E-
clips that are bent or distorted. Replace these parts
as well.Lubricate transmission parts with Mopar ATF
Plus, Type 7176 transmission fluid during overhaul
and assembly.
Use petroleum jelly to hold parts like thrust wash-
ers in place during assembly. Use Mopar Door Ease,
Ru-Glyde, or similar products to lubricate piston
seals and O-rings to ease installation. Petroleum jelly
can also be used to prelubricate parts during reas-
sembly if desired.
TRANSMISSION CASE CLEANING AND
INSPECTION
Clean the case in a solvent tank. Flush the case
bores and fluid passages thoroughly with solvent.
Use compressed air to dry the case and clear the
fluid passages. Be sure all solvent is removed from
the case as well.
Do not use shop towels or rags to dry the case
(or any other transmission component) unless
they are made from lint-free materials. Lint
will readily adhere to case surfaces and trans-
mission components and will circulate through-
out the transmission after assembly. A sufficient
quantity of lint can block fluid passages and in-
terfere with valve body operation.
Inspect the case for cracks, porous spots, worn
bores, or damaged threads. Damaged threads can be
repaired with Helicoil thread inserts. However, the
case will have to be replaced if it exhibits any type of
damage or wear.
Lubricate the front band adjusting screw threads
with petroleum jelly and thread the screw part-way
into the case. Be sure the screw turns freely.
Remount the case in a repair stand after cleaning
and inspection.
OVERRUNNING CLUTCHÐLOW-REVERSE
DRUMÐREAR SUPPORT OVERHAUL
DISASSEMBLING OVERRUNNING CLUTCH/
LOW-REVERSE DRUM
If the clutch assembly came out with the low-re-
verse drum, thread two clutch cam bolts into the
cam. Then lift the cam out of the drum with the bolts
(Fig. 30). Rotate the cam back and forth to ease re-
moval if necessary. Remove the clutch roller and
spring assembly from the race afterward.
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
Clean the overrunning clutch assembly, clutch cam,
low-reverse drum and rear support in solvent. Dry
them with compressed air after cleaning.
Inspect condition of each clutch part after cleaning.
Replace the overrunning clutch roller and spring as-
sembly if any rollers or springs are worn or damaged,
or if the roller cage is distorted, or damaged. Replace
the cam if worn, cracked or damaged.
Fig. 29 Compressing Rear Servo Spring
J30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION OVERHAUL 21 - 125